list
Use the keyword [] to define the list. Here is a
fruits = ["Apple", "Banana", "Pear"]
The elements in the access list are accessed using subscripts. Like java, subscripts are calculated from 0, but python supports negative indexes, which start from the last bit
print(fruits[0]) print(fruits[-1]) print(fruits[-2])
Apple
Pear
Banana
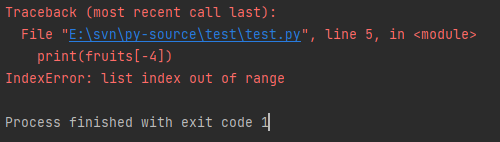
Note that the subscript here cannot exceed the index. The maximum value of the fruits index is 2 and the minimum value is - 3. If it exceeds this range, the subscript will be out of bounds
Modify element
Elements can be modified by direct assignment using subscripts
fruits = ["Apple", "Banana", "Pear"] print(fruits[0]) fruits[0] = "watermelon" print(fruits[0])
Apple
watermelon
Add element
Add append to the tail
fruits = ["Apple", "Banana", "Pear"]
fruits.append("watermelon")
print(fruits)
['Apple', 'Banana', 'pear', 'watermelon']
Add insert in the middle
insert(index,value) receives two values. Index represents the current location to be queried, and value represents the value
fruits = ["Apple", "Banana", "Pear"] fruits.insert(1, "watermelon") print(fruits)
['Apple', 'watermelon', 'Banana', 'pear']
Delete element del
del receives a parameter that specifies the index of the element
fruits = ["Apple", "Banana", "Pear"] del fruits[0] print(fruits)
['Banana', 'pear']
Delete element pop
Pop will delete the last bit of the element and return the deleted element. It is more appropriate to say pop-up
fruits = ["Apple", "Banana", "Pear"] print(fruits.pop()) print(fruits)
Pear
['Apple', 'Banana']
List operation
sort() sort
fruits = ["Apple", "Banana", "Pear"] print(fruits) fruits.sort() print(fruits)
['Apple', 'Banana', 'pear']
['pear', 'Apple', 'Banana']
sorted() temporary sort
sort() will change the original list, but sorted() will not change the original list
fruits = ["Apple", "Banana", "Pear"] print(sorted(fruits)) print(fruits)
['pear', 'Apple', 'Banana']
['Apple', 'Banana', 'pear']
reverse() reverse order
Reverse the list
fruits = ["Apple", "Banana", "Pear"] print(fruits) fruits.reverse() print(fruits)
['Apple', 'Banana', 'pear']
['pear', 'Banana', 'Apple']
List length len
Returns the length of the list
fruits = ["Apple", "Banana", "Pear"] print(len(fruits))
3
Traversal list
fruits = ["Apple", "Banana", "Pear"]
for f in fruits:
print(f)
Apple
Banana
Pear
Create a list of values
range(1,5)
It starts from the specified element, but does not contain the ending number. If you do not specify the starting size, it starts from 0 by default, and you can also specify the interval
nums = list(range(0, 5))
for n in nums:
print(n)
0
1
2
3
4
Make numerical statistics on the list
What are the maximum, minimum, and maximum values in the list
nums = list(range(0, 5)) print(min(nums)) print(max(nums)) print(sum(nums))
0
4
10
section
[1:2] specify two numbers. The first is the start position, and the second parameter is the end position. If you do not specify the default last bit, if you do not specify either, copy the list directly
nums = list(range(0, 5)) print(nums[0:2]) print(nums[0:]) print(nums[:])
[0, 1]
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
tuple
Tuples are very similar to lists, using ()
heros = ("top", "Fight wild")
print(heros[0])
top
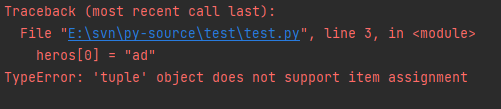
The value of a tuple cannot be changed, but it can be reassigned
heros = ("top", "Fight wild")
heros[0] = "ad"
So you won't report an error
heros = ("top", "Fight wild")
heros = ("ad")
Dictionaries
Here comes the universal key value pair, defined by {}
heros = {"top":"Dema", "Fight wild":"spider"}
print(heros)
print(heros["top"])
{'Shangdan': 'dema', 'beat the wild': 'spider'}
Dema
To access an element, you can also use get() to receive two parameters, the first parameter is the subscript, the key in the key value pair, and the second is the value returned if there is no corresponding key
heros = {"top": "Dema", "Fight wild": "spider"}
print(heros)
print(heros.get("top", "No corresponding element exists"))
print(heros.get("mid", "No corresponding element exists"))
{'Shangdan': 'dema', 'beat the wild': 'spider'}
Dema
No corresponding element exists
Traversal dictionary
Traverse all. items()
heros = {"top": "Dema", "Fight wild": "spider"}
for k,v in heros.items():
print(k + "---" + v)
Shangdan dema
Playing wild - Spider
Traversal keys()
heros = {"top": "Dema", "Fight wild": "spider"}
for k in heros.keys():
print(k)
top
Fight wild
Traversal values()
heros = {"top": "Dema", "Fight wild": "spider"}
for v in heros.values():
print(v)
top
Fight wild