Common ports:
| port | service |
|---|---|
| 21 | The default is ftp port, which mainly depends on whether anonymous is supported or weak password can be used |
| 22 | The default is shh port |
| 23 | The default is telnet port |
| 25 | The default is smtp service |
| 53 | The default is DNS |
| 123 | NTP |
| 161,162,8161 | SNMP service (8161 SNMP opened by IBM) |
| 389 | ldap community |
| 80 | http service |
| 443 | https service |
| 512,513 | rlogin service or exec |
| 873 | rsync mainly depends on whether it supports anonymity or weak passwords |
| 1433 | mssql database |
| 1080 | socks proxy |
| 1521 | oracle Database |
| 1900 | bes default background |
| 2049 | nfs service |
| 2601,2604 | Zebra routing, default password zebra |
| 2028,2083 | cpanel host management system |
| 3128,3312 | squid proxy default port. If no password is set, it is likely to roam the intranet directly |
| 3306 | mysql database |
| 4899 | R-admin connection end |
| 4440 | rundeck reference WooYun: successfully roaming Sina intranet by borrowing a service from Sina |
| 8834 | nessus service |
| 4848 | glashfish |
| 3311,3312 | kangle host management system |
| 3389 | Remote login |
| 5672 | rabbitMQ |
| 5900 | VNC |
| 6082 | Access to the intranet directly by wonivar cli without authorization |
| 6379 | redis generally has no authentication and can be accessed directly |
| 7001 | weblogic |
| 8080 | tomcat |
| 8089 | jboss |
| 8161 | activeMQ |
| 8649 | ganglia cluster system monitoring software |
| 9000 | fastcgi service |
| 9090 | IBM services |
| 9200,9300 | ElasticSearch reference WooYun: play more ElasticSearch Command Execution Vulnerability of a server |
| 9999 | amg encrypted version |
| 10050 | zabbix |
| 11211 | memcache unauthorized access |
| 27017,28017 | mongodb is not authorized to access and logs in without password by default |
| 3777 | Dahua monitoring equipment |
| 50000 | sap netweaver remote command execution vulnerability |
Write your own TCP port scanner, use TCP full connection scanning to identify the host, and first import the socket module:
socket.gethostbyname(hostname): change the host name to the IP address;
socket.gethostbyaddr(ip_address): pass in an IP address and return a tuple, including host name, alias list and IP address list of the same interface;
socket.socket([family[,type[,proto]]]): a new socket will be generated. Given the socket address cluster and socket type, the address cluster can be AF_ INET (default), AF_INET6 or AF_UNIX. In addition, the socket type can be a TCP socket, that is, sock_ Stream (default), or UDP socket, i.e. SOCK_DGRAM, or other socket type. Finally, the agreement number is usually zero, which is omitted in most cases.
socket.connect(address): connect to the socket at address. Generally, the format of address is tuple (hostname,port). If there is a connection error, socket is returned Error error.
socket.connect_ex(adddress): the function is the same as that of connect(address), but 0 is returned for success and error is returned for failure.
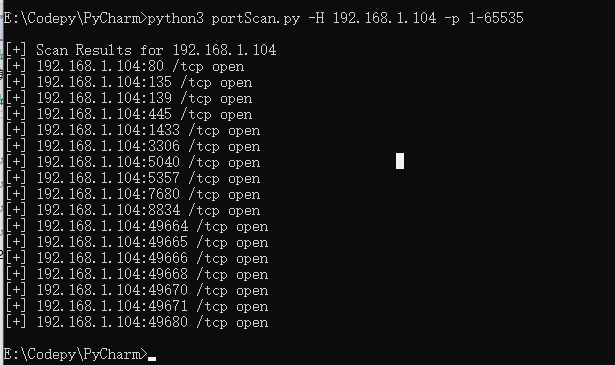
The first step is to enter the target host name and the list of ports to scan. Then get the network IP address of the target through the target host name. Use each port in the list to get the connection target address, and finally determine the special services running on the port. Finally, the specific data will be sent and the identification returned by the specific application will be read. After the help information is determined, you need to socket connect the specific port to the host, and finally check the port connection status. Use multithreading to improve speed.
The source code is as follows
import optparse
import socket
import threading
import re
screenLock = threading.Semaphore(value=1)
def connScan(tgtHost, tgtPort):
try:
connSkt = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
result = connSkt.connect_ex((tgtHost, tgtPort))
# connSkt.send(b'test')
# results = connSkt.recv(100)
screenLock.acquire()
if (result == 0):
print('[+] {0}:{1} /tcp open'.format(tgtHost, tgtPort))
# else:
# print('[-] %d/tcp closed' % tgtPort)
# print('[-] ' + str(results))
# connSkt.close()
except:
screenLock.acquire()
print('[-] error')
finally:
screenLock.release()
connSkt.close()
def portScan(tgtHost, tgtPorts):
try:
tgtIP = socket.gethostbyname(tgtHost)
except Exception as e:
print("[-] Cannot resolve '%s':Unknown host" % tgtHost)
return
# try:
# tgtName = socket.gethostbyaddr(tgtIP)
# print('\n[+]Scan Results for '+tgtName[0])
# except:
print('\n[+] Scan Results for ' + tgtIP)
socket.setdefaulttimeout(1)
for tgtPort in tgtPorts:
# print('[+] Scaningport' + str(tgtPort))
t = threading.Thread(target=connScan, args=(tgtHost, int(tgtPort)))
t.start()
# connScan(tgtHost,int(tgtPort))
def main():
parser = optparse.OptionParser('usage %prog -H <target host> -p <target port>')
parser.add_option('-H', dest='tgtHost', type='string', help='specify target host')
parser.add_option('-p', dest='tgtPort', type='string', help='specify target port')
(options, args) = parser.parse_args()
tgtHost = options.tgtHost
tgtPort = options.tgtPort
if '-' in tgtPort:
Ports = re.findall(r'[0-9]{1,5}', tgtPort)
first = int(Ports[0])
last = int(Ports[1])
for i in range(first, last + 1):
args.append(i)
else:
args.append(int(tgtPort))
if (tgtHost == None) | (tgtPort == None):
print('[-] You must specify a target host and port[s]!')
exit(0)
portScan(tgtHost, args)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
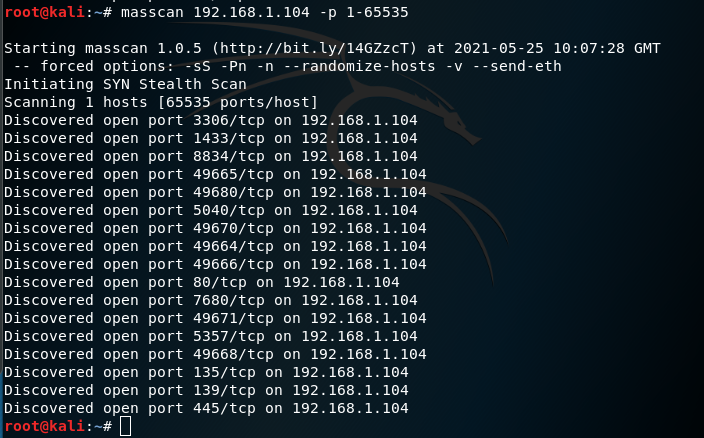
Comparison between operation results and masscan: