Today, the editor will talk about selenium. We will talk about these contents
- Introduction and installation of selenium
- Positioning of page elements
- Browser control
- Mouse control
- Keyboard control
- Sets the wait for the element
- Get cookies
- Call JavaScript
- selenium advanced
Introduction and installation of selenium
selenium is one of the most widely used open source Web UI automation test suites. Its supported languages include C + +, Java, Perl, PHP, Python and Ruby. It is also a sharp tool in data capture and can solve the anti crawling measures of most web pages. Of course, it is not omnipotent. One obvious point is that it is relatively slow, If the amount of daily data collection is not very high, you can use this framework.
When it comes to installation, you can directly use pip in installation
pip install selenium
At the same time, we also need to install a browser driver. Different browsers need to install different drivers. The following two are mainly recommended by the Xiaobian here
- Firefox browser driver: geckodriver
- Chrome browser driver: chromedriver
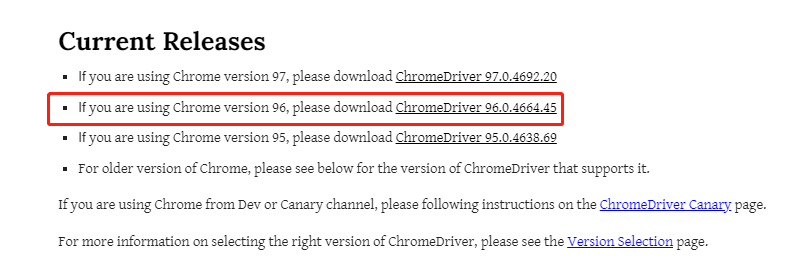
Xiaobian usually uses selenium+chromedriver, so here we take Chrome browser as an example. Since the version of chromedriver needs to be consistent with that of the browser, let's first confirm the version of the browser? Look at the picture below
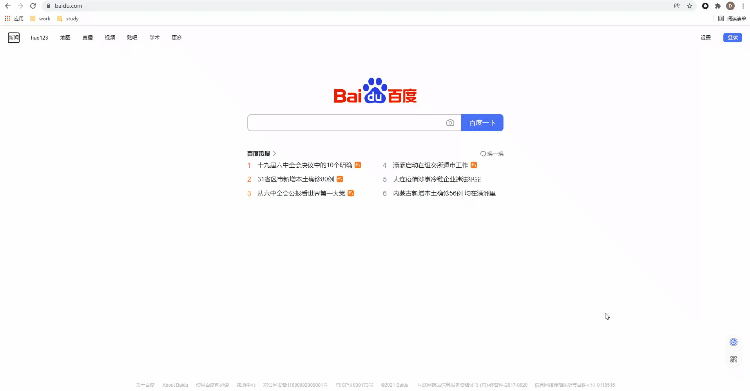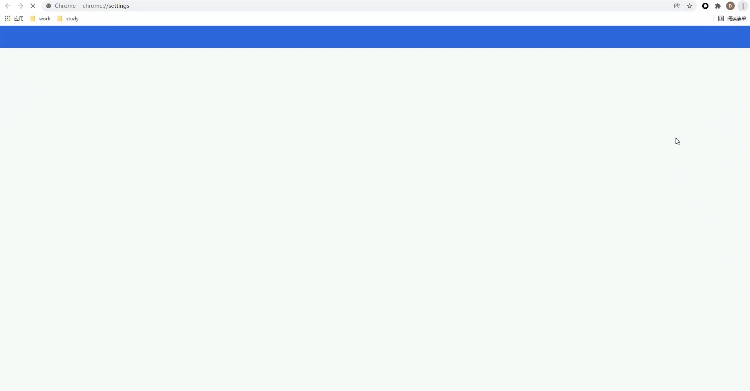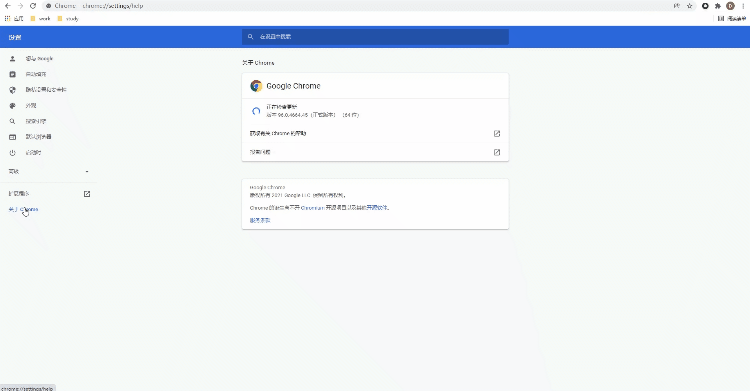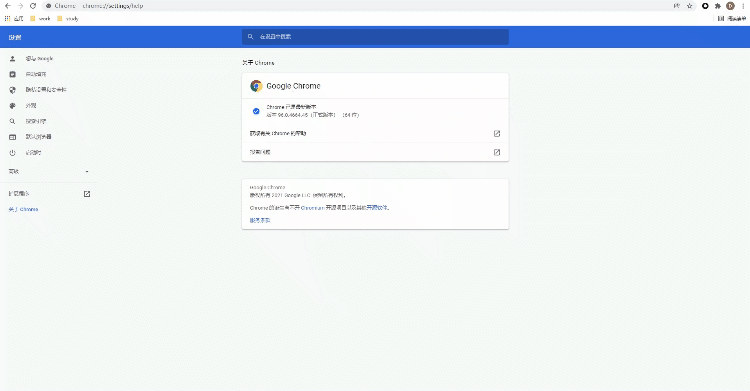
We find the browser version in "about Chrome", and then download the corresponding version of chromedriver. Of course, it also corresponds to the operating system of our computer
Positioning of page elements
When it comes to the positioning of page elements, Xiaobian's default readers have the most basic front-end knowledge, such as HTML, CSS, etc
Positioning of ID tags
In HTML, the ID attribute is the attribute that uniquely identifies an element. Therefore, in selenium, it is also the first choice to locate the element through the ID. we take Baidu home page as an example. The HTML code of the search box is as follows, with the ID of "kw", while the ID of the "Baidu click" button is "su". We use Python script to locate the element through the ID tag
driver.find_element_by_id("kw")
driver.find_element_by_id("su")
Positioning of the NAME tag
In HTML, the functions of Name attribute and ID attribute are basically the same, but the Name attribute is not unique. If there is no ID tag, we can consider locating through the Name tag. The code is as follows
driver.find_element_by_name("wd")
Xpath positioning
Using Xpath to locate almost any element on the page, what is Xpath? Xpath is a language to find information in XML and HTML documents. Of course, when locating elements through Xpath path, it is also divided into absolute path and relative path.
The absolute path is represented by the doc No. / and the relative path is represented by / /, which involves the writing of the Xpath path. The editor is lazy here and directly selects the copy / paste method, for example, for the following HTML code
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Test</title>
</head>
<body>
<form id="loginForm">
<input name="username" type="text" />
<input name="password" type="password" />
<input name="continue" type="submit" value="Login" />
<input name="continue" type="button" value="Clear" />
</form>
</body>
</html>We can do this. Open the developer tool of the browser, move the mouse to the selected element, and then right-click to check. See the following figure for details
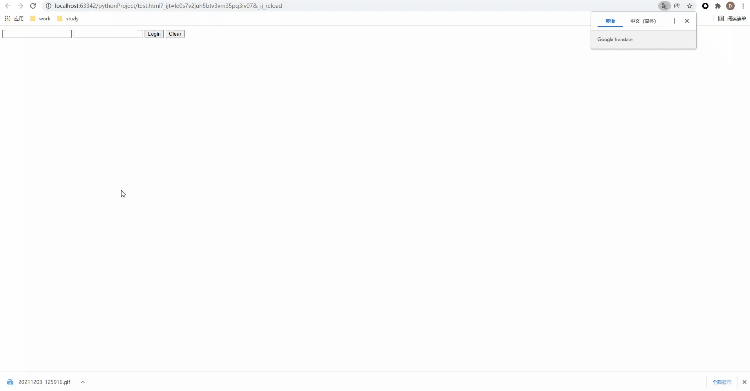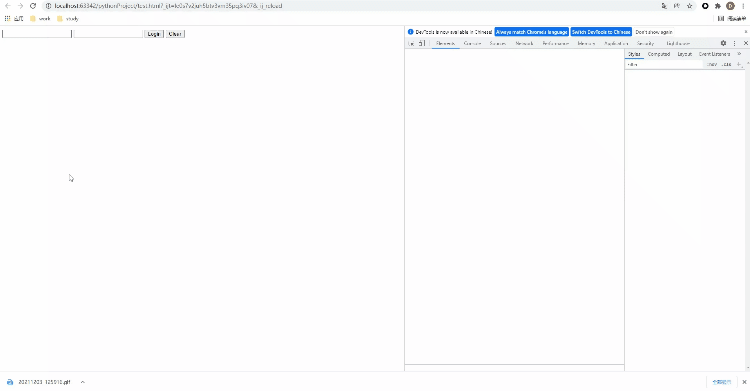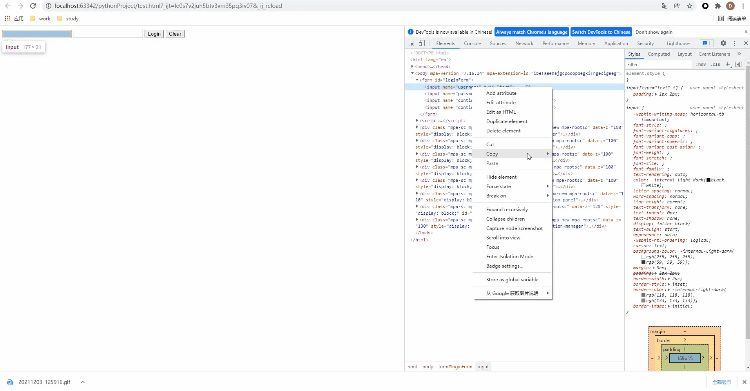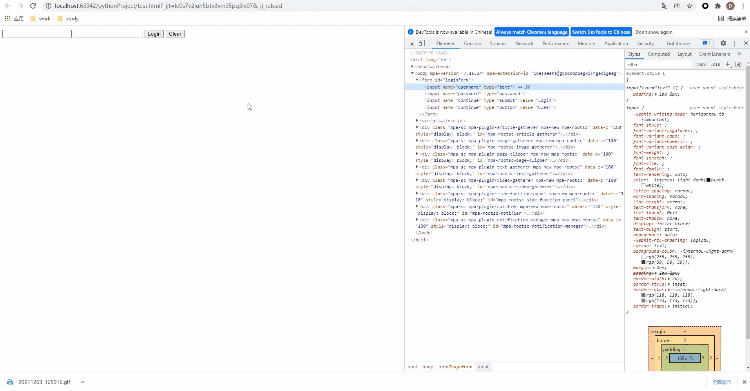
Let's take Baidu home page as an example to see how to locate page elements through Xpath. The code is as follows
driver.find_element_by_xpath('//*[@id="kw"]')
className label positioning
We can also locate elements based on the class attribute, especially when we see that there are multiple parallel elements, such as a list form, and the class uses the same one, such as:
driver.find_element_by_class_name("classname")
At this time, we can locate the element through the class attribute. The method returns a list. When we want to locate the nth element in the list, we can arrange it this way
driver.find_elements_by_class_name("classname")[n]
Note that find is used here_ elements_ by_ class_ Name() method instead of find_element_by_class_name() method. Here we use the example of Baidu home page to locate the element of search box through the className tag
driver.find_element_by_class_name('s_ipt')
CssSelector() method positioning
In fact, the CssSelector() method is more recommended to locate page elements on Selenium's official website. The reason is that compared with Xpath, Css positioning is faster. Css positioning is divided into four categories: ID value, Class attribute, TagName value, etc. Let's look at it in turn
- ID mode to locate
There are probably two ways: one is to add the value of TagName in front of the ID value, and the other is not. The code is as follows
driver.find_element_by_css_selector("#id_value") # Do not add the previous' TagName 'value
driver.find_element_by_css_selector("tag_name.class_value") # Do not add the previous' TagName 'value
Of course, sometimes the value of this TagName is very lengthy, and there may be spaces in the middle, so the spaces in it need to use "." To replace
driver.find_element_by_css_selector("tag_name.class_value1.calss_value2.class_value3") # Do not add the previous' TagName 'value
We still take the search box on baidu home page as an example, and its HTML code is as follows
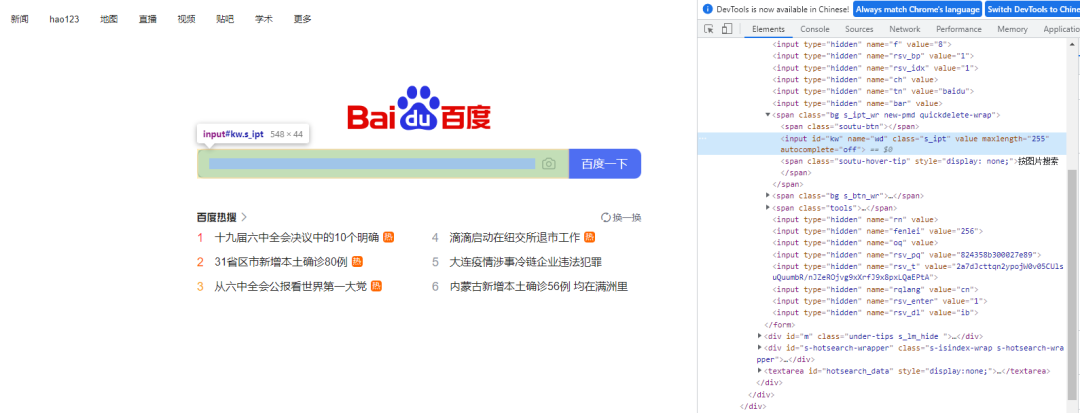
If you use CssSelector If the class() method is used to locate elements, Python code should do so. Like the above Xpath() method, you can be a little lazy and get the location of elements from developer tools by copying / pasting
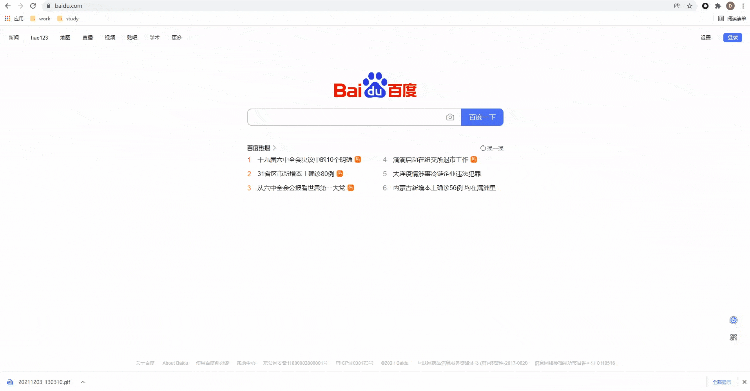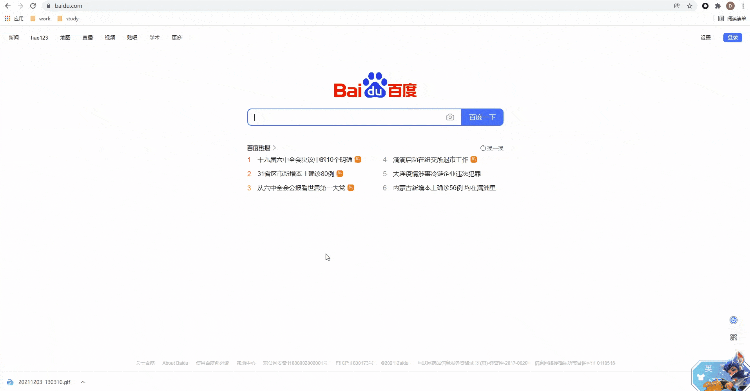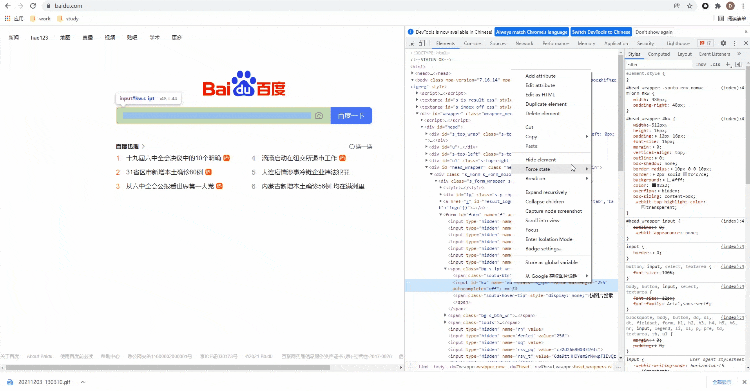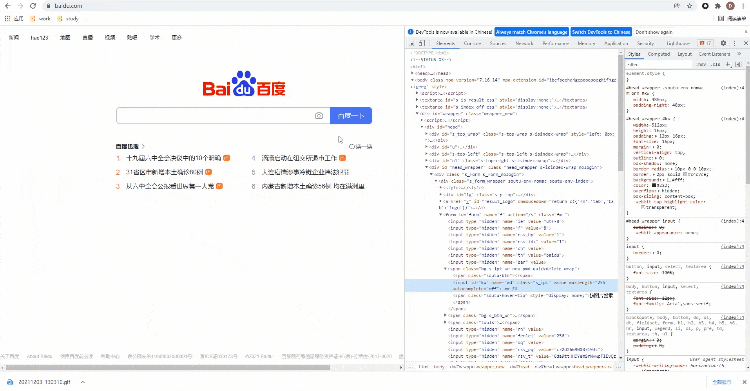
The code is as follows
driver.find_element_by_css_selector('#kw')
linkText()
This method directly links the text above to locate the element. The example is as follows
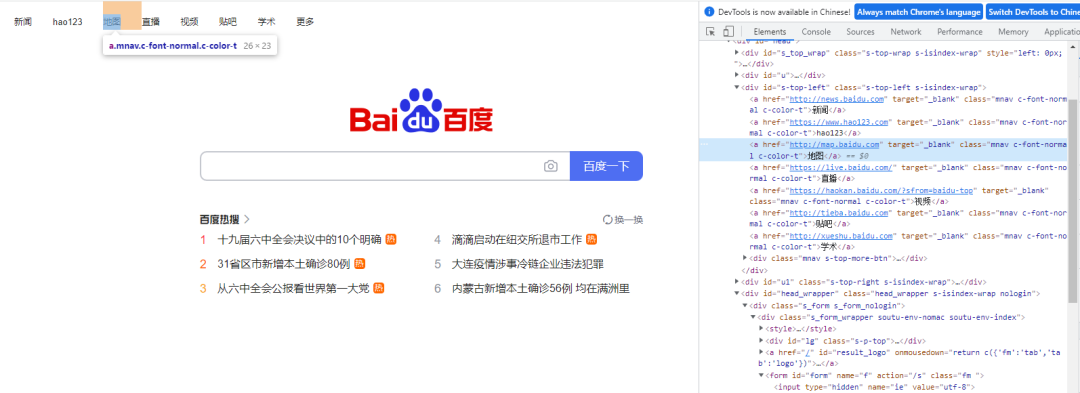
Locate the "map" element through the linkText() method. The code is as follows
driver.find_element_by_link_text("Map").click()Browser control
Modify the size of the browser window
We can use set_ window_ The size () method is used to modify the size of the browser window. The code is as follows
# Modify browser size driver.set_window_size(500, 900)
And maxsize_ The window () method is used to realize the full screen display of the browser. The code is as follows
# Full screen display driver.maximize_window()
Browser forward and backward
The methods used for forward and backward are forward() and back(), respectively. The code is as follows
# Back and Forward driver.forward() driver.back()
Browser refresh
The refresh method is refresh(), and the code is as follows
# Refresh page driver.refresh()
In addition to the above, the common operations of webdriver include
- Close browser: get()
- Clear text: clear()
- Click the element: click()
- Submit form: submit()
- Analog input content: send_keys()
We can try to use some of the methods mentioned above to write a program
from selenium import webdriver
from time import sleep
driver = webdriver.Chrome(executable_path="chromedriver.exe")
driver.get("https://www.baidu.com")
sleep(3)
driver.maximize_window()
sleep(1)
driver.find_element_by_xpath('//*[@id="s-top-loginbtn"]').click()
sleep(3)
driver.find_element_by_xpath('//*[@id="TANGRAM__PSP_11__userName"]').send_keys('12121212')
sleep(1)
driver.find_element_by_xpath('//*[@id="TANGRAM__PSP_11__password"]').send_keys('testtest')
sleep(2)
driver.refresh()
sleep(3)
driver.quit()
output

Mouse control
Mouse controls are encapsulated in ActionChains. The following are common
introduce action_chains class from selenium.webdriver.common.action_chains import ActionChains # Right click ActionChains(driver).context_click(element).perform() # double-click ActionChains(driver).double_click(element).perform() # Drag and drop ActionChains(driver).drag_and_drop(Start, End).perform() # hover ActionChains(driver).move_to_element(Above).perform() # Press ActionChains(driver).click_and_hold(leftclick).perform() # Perform the specified operation
Keyboard control
The Keys() class in webdriver provides methods for almost all keys, commonly used as follows
# Delete key
driver.find_element_by_id('xxx').send_keys(Keys.BACK_SPACE)
# Space bar
driver.find_element_by_id('xxx').send_keys(Keys.SPACE)
# enter key
driver.find_element_by_id('xxx').send_keys(Keys.ENTER)
# Ctrl + A select all
driver.find_element_by_id('xxx').send_keys(Keys.CONTROL, 'a')
# Ctrl + C/V copy / paste content
driver.find_element_by_id('xxx').send_keys(Keys.CONTROL, 'c')
driver.find_element_by_id('xxx').send_keys(Keys.CONTROL, 'v')
Other keyboard operations
- Up arrow: keys ARROW_ UP
- Down arrow: keys ARROW_ DOWN
- Left / right arrow: keys ARROW_ LEFT/Keys. ARROW_ RIGHT
- Shift key: keys SHIFT
- F1 key: keys F1
Element wait
There are two types: display waiting and implicit waiting
Display wait
Display wait refers to setting a timeout time to check whether the element exists at regular intervals. If it exists, execute the following contents. If the maximum waiting time is exceeded, an exception will be thrown (TimeoutException). WebDriverWait() method needs to be used, together with until and not until methods
WebDriverWait(driver, timeout, poll_frequency=0.5, ignored_exceptions=None)
Parameters:
- Timeout: the maximum timeout, in seconds by default
- poll_frequency: the detection interval. The default is 0.5s
- ignored_exceptions: Specifies the exception to be ignored. NoSuchElementException is ignored by default
Let's look at the following case
driver = webdriver.Chrome()
driver.get("http://somedomain/url_that_delays_loading")
try:
element = WebDriverWait(driver, 10).until(
EC.presence_of_element_located((By.ID, "myDynamicElement")))
finally:
driver.quit()
The above code waits up to 10 seconds and throws an exception after timeout. However, assuming that this element is found after waiting for 3 seconds, it will not wait for the remaining 7 seconds, but continue to execute the subsequent code
Implicit waiting
The main use is implicitly_wait()
browser = webdriver.Chrome(path) # Implicit wait for 3 seconds browser.implicitly_wait(3)
Get Cookie
Cookie s are the key to identify users. We usually obtain cookies by simulating login web pages through selenium, and then send requests by carrying cookies through requests.
webdriver provides several operations of cookies. We choose several common ones to illustrate
- get_cookies(): returns the cookie information visible in the current session in the form of a dictionary
- get_cookies(name): returns the cookie information specified in the cookie dictionary
- add_cookie(cookie_dict): adds a cookie to the current session
Let's look at a simple example code
driver=webdriver.Chrome(executable_path="chromedriver.exe")
driver.get(url=url)
time.sleep(1)
cookie_list=driver.get_cookies()
cookies =";".join([item["name"] +"=" + item["value"] + "" for item in cookie_list])
session=requests.session()
headers = {
'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/83.0.4103.106 Safari/537.36',
'cookie': cookies
}
response=session.get(url=url,headers=headers)
soup=BeautifulSoup(response.text,'lxml')
Call JavaScript
Execute can be used in webdriver_ Script () method to implement JavaScript execution. Let's take a simple example
from selenium import webdriver
import time
bro=webdriver.Chrome(executable_path='./chromedriver')
bro.get("https://www.baidu.com")
# Execute js code
bro.execute_script('alert(10)')
time.sleep(3)
bro.close()
In addition, we can use selenium to execute JavaScript to scroll up and down the screen
from selenium import webdriver
bro=webdriver.Chrome(executable_path='./chromedriver')
bro.get("https://www.baidu.com")
# Execute js code
bro.execute_script('window.scrollTo(0,document.body.scrollHeight)')
selenium advanced
The browser launched by selenium can be easily detected, usually through window navigator. Check the value of webdriver. If it is true, it indicates that selenium is used to simulate the browser. If it is undefined, it is usually considered as a normal browser.
Then it seems that we can execute the following code to forcibly change the window navigator. The last value returned by webdriver
driver.execute_script(
'Object.defineProperties(navigator,{webdriver:{get:()=>false}})'
)
Of course, this method also has some defects. After all, this code runs after the web page has been loaded. At this time, the JavaScript program of the web page itself has read the window navigator. Webdriver knows you're using an analog browser. So we have two ways to solve this defect.
- Add experimental function parameters in Chrome
The code is as follows
from selenium.webdriver import Chrome
from selenium.webdriver import ChromeOptions
option = ChromeOptions()
option.add_experimental_option('excludeSwitches',['enable-automation'])
driver=Chrome(options=option)
- Call the command of the development tool protocol in chrome
The core idea is to let Chrome browser execute the code given by us before running the JavaScript code of the web page when opening the page_ cdp_ Cmd() method,
driver.execute_cdp_cmd("Page.addScriptToEvaluateOnNewDocument", {
"source": """
Object.defineProperty(navigator, 'webdriver', {
get: () => undefined
})
"""
})
Of course, in order to better hide fingerprint features, we can combine the above two methods
from selenium import webdriver
options = webdriver.ChromeOptions()
options.add_experimental_option("excludeSwitches", ["enable-automation"])
options.add_experimental_option('useAutomationExtension', False)
driver = webdriver.Chrome(options=options, executable_path='./chromedriver')
driver.execute_cdp_cmd("Page.addScriptToEvaluateOnNewDocument", {
"source": """
Object.defineProperty(navigator, 'webdriver', {
get: () => undefined
})
"""
})
driver.get(url)
Finally, we can also run steelth Min.js file to hide the features of selenium simulation browser. This file was previously used by puppeter to hide the fingerprint features of browser. When Python uses it, you need to import this JS file first
import time
from selenium.webdriver import Chrome
option = webdriver.ChromeOptions()
option.add_argument("--headless")
# Headless browsers need to add user agent to hide features
option.add_argument('user-agent=.....')
driver = Chrome(options=option)
driver.implicitly_wait(5)
with open('stealth.min.js') as f:
js = f.read()
driver.execute_cdp_cmd("Page.addScriptToEvaluateOnNewDocument", {
"source": js
})
driver.get(url)