Project description
The existing systems are two computers of Windows 10, one of which is used as a server and the other as a client. There is a folder pics in the server, which contains 10 pictures, as shown in the following figure:

This paper aims to use the Socket library in Python to transfer the pictures in the server to the client.
Implementation steps
The server:
- 1. socket object type declaration and connection protocol generation;
- 2. Bind the port to be monitored in the server and start listening;
- 3. After the client uploads the request, establish a connection instance from the server to the client;
- 4. Receiving data, obtaining commands about image names, and specifying pictures to be transmitted;
- 5. Download the picture data to the client in batches according to the number of bytes until the transmission is completed.
client:
- 1. Declare the protocol type and generate the socket connection object at the same time;
- 2. Connect the relevant ports of the server;
- 3. Sending a command about the image name to the server;
- 4. Obtain the data downloaded from the server to the client in batches according to the number of bytes and coexist in a file until the transmission is completed.
code implementation
The code implementation here is only to illustrate the role of some important functions, which is not complete. The complete code is posted at the end of the article.
The server
1. Import required libraries
import socket import os
2. Declare the protocol type and generate the socket connection object at the same time
server = socket.socket()
3. Bind the port in the server that needs to listen and start listening
server.bind(('192.168.43.164', 1200)) # Bind the port to listen on = (server ip address + any port)
server.listen(5) # monitor
The server ip address here can be found by entering ipconfig in the terminal. The port is arbitrarily specified. If it is occupied, it's good to change it to another one.
4. Get the picture information in the server
BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)) # Get current directory PIC_DIR = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'pics') # Path to the picture folder pic_names = sorted(os.listdir(PIC_DIR)) # Get the names of all sorted pictures and put them in a list ['1.jpg','2.jpg',...,'9.jpg'] # Put the picture name into a large string pic_names = " ".join(i for i in pic_names) # '0.jpg 1.jpg 2.jpg 3.jpg 4.jpg 5.jpg 6.jpg 7.jpg 8.jpg 9.jpg'
5. After the client uploads the request, the connection instance from the server to the client is established
conn, addr = server.accept()
print("Received from{}request".format(addr))
The conn generated here is a connection instance that the client connects to and the server generates for it.
6. Receive data and specify the picture name
When receiving data, you can specify the number of bytes received each time to prevent blocking. Here, it is set that up to 1024 bytes can be received each time.
data = conn.recv(1024) # Receive data, obtain the command of image name, and specify the image to be transmitted
print("recv:", data)
7. Upload relevant picture information to the client
The communication between the client and the server is based on the information of bytes type, so after each transmission, the information of bytes type needs to be decoded into the information of string type.
In addition, the size of the image to be downloaded needs to be transmitted to the client, so that the client can specify the number of bytes to be uploaded each time.
img_name = data.decode('utf-8') # Decode the picture name (bytes) transmitted from the client into a string
img_path = os.path.join(PIC_DIR, img_name) # Get the absolute path of the corresponding picture
file_size = os.stat(img_path).st_size # Get the size of the image file in bytes. When calling stat, it is used to return the system status information of relevant files
file_info = '%s|%s' % (img_name, file_size) # Send the image information to the client (used to distinguish two tasks in the document)
conn.sendall(bytes(file_info, 'utf-8'))
8. Open relevant picture files, read bytes in batches and download them to the client
f = open(img_path, 'rb') # Open a file in binary format for read-only has_sent = 0 # Record the number of bytes that have been sent while has_sent != file_size: # If the number of bytes sent is not equal to the size of the image, it is then sent file = f.read(1024) # 1024 bytes read at a time conn.sendall(file) # Send to client has_sent += len(file) # Update bytes sent f.close() # After sending, close the file
client
1. Import required libraries
import socket import os
2. Declare the protocol type and generate the socket connection object at the same time
server = socket.socket()
3. Connect to the relevant port of the server
client.connect(('192.168.43.28', 1200))
The ip address here is the ip address of the server. In other words, the ip address and port number here are the same as those set in the server code.
4. Upload picture name information to the server
msg = input(">>:").strip() # Get the information to be sent to the server in string format
client.send(msg.encode("utf-8")) # Encode the string format into bytes and send
5. Receive the picture information returned by the server
data = client.recv(1024) # Receive the content returned by the server
6. Open a file in binary format to store bytes downloaded by the server
f = open(path, 'ab') # Open a file in binary format for appending. If the file does not exist, create a new file for writing. has_receive = 0 # Count the number of bytes received while has_receive != filesize: data1 = client.recv(1024) # Receive 1024 bytes of data from the server at a time f.write(data1) # write in has_receive += len(data1) # Update bytes received f.close() # Close file
The number of bytes received at one time set here does not need to be the same as that in the server.
Complete code
The server
import socket
import os
server = socket.socket() # 1. Declare the protocol type and generate socket link object at the same time
server.bind(('192.168.43.28', 1200)) # Bind the port to listen on = (server ip address + any port)
server.listen(5) # monitor
BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)) # Get current directory
PIC_DIR = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'pics') # Path to the picture folder
pic_names = sorted(os.listdir(PIC_DIR)) # Get the names of all sorted pictures and put them in a list ['1.jpg','2.jpg',...,'9.jpg']
# Put the picture name into a large string
pic_names = " ".join(i for i in pic_names) # '0.jpg 1.jpg 2.jpg 3.jpg 4.jpg 5.jpg 6.jpg 7.jpg 8.jpg 9.jpg'
print("I'm going to start waiting for the phone")
while True:
conn, addr = server.accept() # Wait for the call
# conn is a connection instance that the client connects to and generates for it on the server
print("Received from{}request".format(addr))
while True:
data = conn.recv(1024) # Receive data, obtain the command of image name, and specify the image to be transmitted
print("recv:", data)
if not data:
print("client has lost...")
break
if data.decode('utf-8') == 'get pics_names': # The command to get the image name is defined as get pics_names
conn.send(pic_names.encode('utf-8'))
elif data.decode('utf-8') == 'break':
break
else:
img_name = data.decode('utf-8') # Decode the picture name (bytes) transmitted from the client into a string
img_path = os.path.join(PIC_DIR, img_name) # Get the absolute path of the corresponding picture
file_size = os.stat(img_path).st_size # Get the size of the image file in bytes. When calling stat, it is used to return the system status information of relevant files
file_info = '%s|%s' % (img_name, file_size) # Send the image information to the client (used to distinguish two tasks in the document)
conn.sendall(bytes(file_info, 'utf-8'))
f = open(img_path, 'rb') # Open a file in binary format for read-only
has_sent = 0 # Record the number of bytes that have been sent
while has_sent != file_size: # If the number of bytes sent is not equal to the size of the image, it is then sent
file = f.read(1024) # 1024 bytes read at a time
conn.sendall(file) # Send to client
has_sent += len(file) # Update bytes sent
f.close() # After sending, close the file
print('Upload successful')
break
server.close()
client
import socket
import os
client = socket.socket() # Declare socket type and generate socket connection object at the same time
client.connect(('192.168.43.28', 1200)) # ip + port of linked server
BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)) # Get current directory
while True:
msg = input(">>:").strip() # Get the information to be sent to the server in string format
if len(msg) == 0:
continue
client.send(msg.encode("utf-8")) # Encode the string format into bytes and send
if msg == 'break':
break
data = client.recv(1024) # Receive the content returned by the server
if len(str(data, 'utf-8').split('|')) == 2: # If the length of the returned string is 2, it indicates that a picture is returned from the server for task 2
filename, filesize = str(data, 'utf8').split('|') # Gets the name and size of the specified image
path = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, filename) # Specifies the path to save the image
filesize = int(filesize) # Convert image size to plastic
f = open(path, 'ab') # Open a file in binary format for appending. If the file does not exist, create a new file for writing.
has_receive = 0 # Count the number of bytes received
while has_receive != filesize:
data1 = client.recv(1024) # Receive 1024 bytes of data from the server at a time
f.write(data1) # write in
has_receive += len(data1) # Update bytes received
f.close() # Close file
print("recv:", data.decode())
client.close()
report errors
The following error messages may appear:
The connection attempt failed because the connecting party did not reply correctly after a period of time or the connecting host did not respond!
At this time, we can go to the terminals of two computers and input:
ping 192.168.43.X
This X refers to the ip address of another computer.
The following prompt should appear
Is Ping 10.16.1.89 Data with 32 bytes: From 192.168.2.135 Reply from: Unable to access the target host. From 192.168.2.135 Reply from: Unable to access the target host. From 192.168.2.135 Reply from: Unable to access the target host. From 192.168.2.135 Reply from: Unable to access the target host.
But the normal prompt should be:
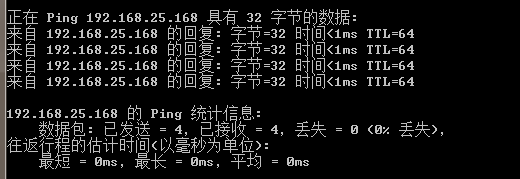
At this time, it is likely to be a network problem. You can try to use the mobile phone hotspot and turn on wifi for these two computers at the same time. The personal test is useful!