1, Subscript output of string
The simulation scenario has such a string: myname = "dujunyan"
1. Take the first element of myname string and output it
2. Take the fifth element of myname string and output it
3. Take the last element of myname string and output it
4. Take the penultimate element of myname string and output it
code:
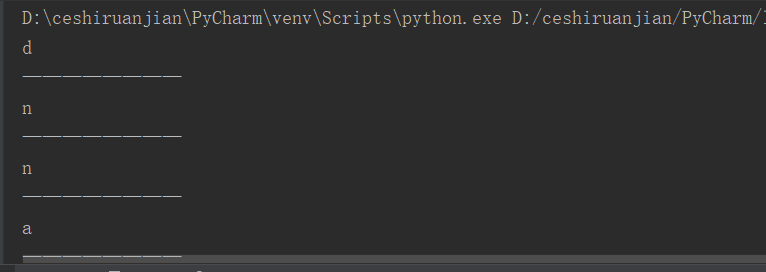
myname = 'dujunyan';
print(myname[0]);
print('--Dividing line————');
print(myname[4]);
print('--Dividing line————');
print(myname[-1]);
print('--Dividing line————');
print(myname[-2]);
print('--Dividing line————');result:
2, String slicing operation
Explanation:
Slicing refers to the operation of intercepting part of the operated object. String, list and tuple all support slicing.
Syntax of slice: [start subscript: end subscript: step size] (colon is in English)
Note: the selected interval starts from the "start subscript" bit and ends at the previous bit of the "end subscript" bit (excluding the end bit itself). The step size represents the selection interval.
Let me do the following for you in the form of string:
code:
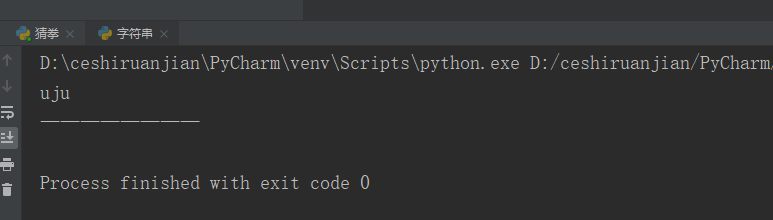
myname = 'dujunyan';
#Slicing operation
print(myname[1:4:1]);#Variable name [start subscript: end subscript: step size]
print('--Dividing line————');result:
Take the above string as an example to perform the operation of "uju" in the string.
3, Common operations in strings
1. Operation method: find()
Operation instructions: check whether "python" is included in my_str string. If it is included, return the starting index value; otherwise, return - 1
code:
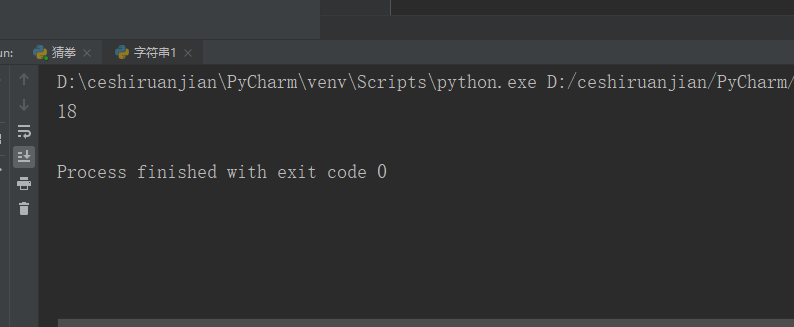
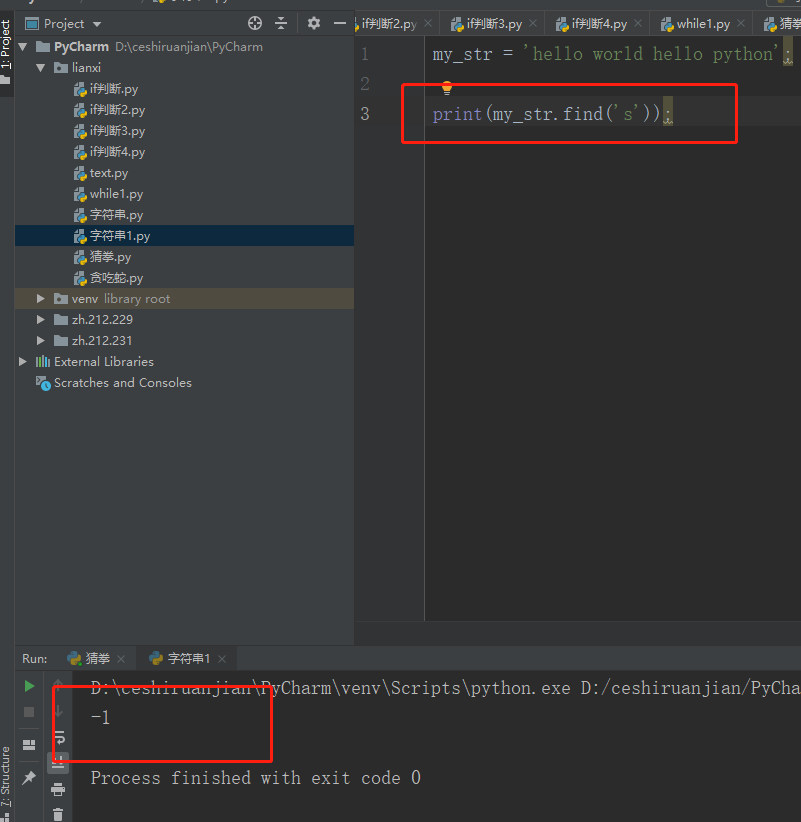
my_str = 'hello world hello python';
print(my_str.find('python'));#Result 1 display
print(my_str.find('s'));#Result 2 showsResult 1:
Result 2:
2. Operation method: index()
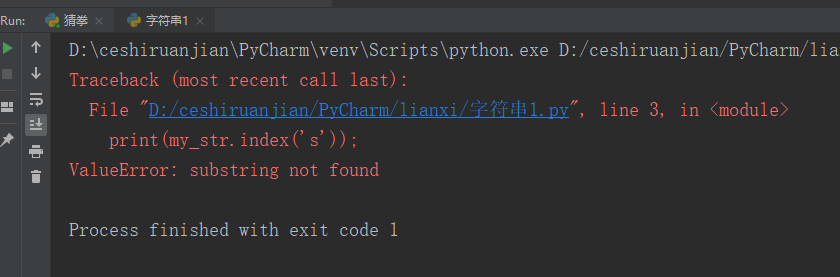
Operating instructions: detect hello Whether it is included in my_str string. If it is, the initial index value will be returned. Otherwise, an error will be reported
code:
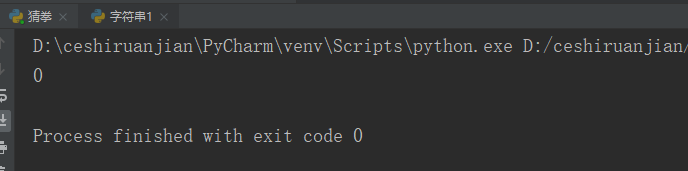
my_str = 'hello world hello python';
print(my_str.index('hello'));#The result 1 containing "hello" displays its subscript. When it is found, it will not continue to find it
# print(my_str.index('s'));#The string does not contain "s", so the result 2 displays an errorResult 1:
Result 2:
3. Operation method: count()
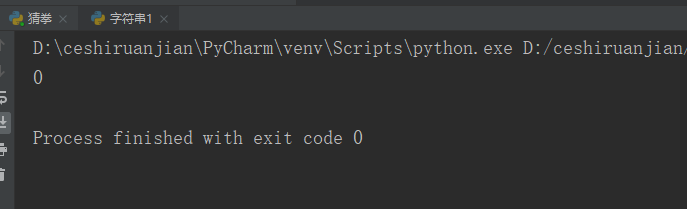
Operation instructions: returns the number of times "h" appears in my_str string between start (head) and end (tail)
code:
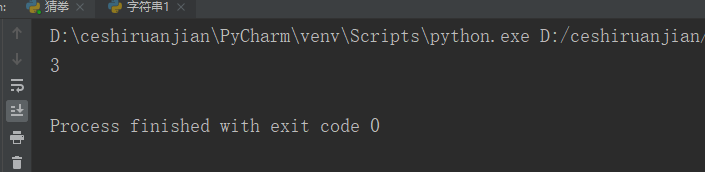
my_str = 'hello world hello python';
print(my_str.count('h'));#Result 1 shows 3
# print(my_str.count('s'));#If result 2 is not available, 0 is displayedResult 1:
Result 2:
4. Operation method: replace()
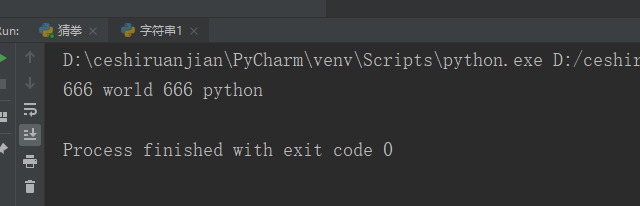
Operation instructions: put "hello" in my_str string Replace with "666". If count is specified, the replacement shall not exceed count times
code:
my_str = 'hello world hello python';
print(my_str.replace('hello','666',2));#Result 1 displayResult 1:
5. Operation method: split()
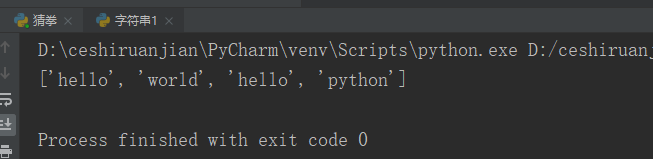
Operating instructions: slice my_str strings with spaces as separators. If maxplit has a specified value, only maxplit value strings will be separated
code:
my_str = 'hello world hello python';
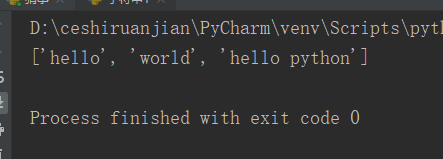
print(my_str.split(" "));#Result 1 display
print(my_str.split(" ",2));#Result 2 showsResult 1:
Result 2:
6. Operation method: startswitch()
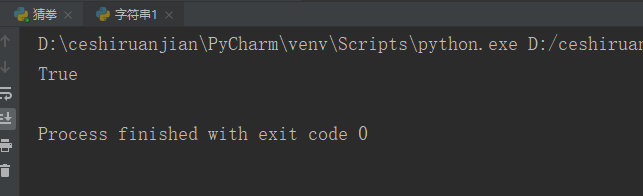
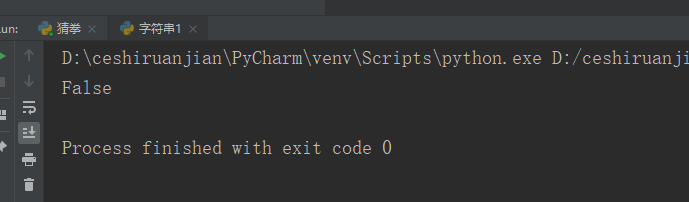
Operating instructions: check whether the string my_str starts with h. if yes, it returns True; otherwise, it returns False
code:
my_str = 'hello world hello python';
print(my_str.startswith('h'));#Result 1 shows True
# print(my_str.startswith('s'));#Result 2 shows FalseResult 1:
Result 2:
7. Operation method: endswitch ()
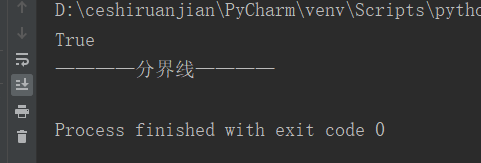
Operation instructions: check whether the string my_str ends with n. if yes, it returns True; otherwise, it returns False
code:
my_str = 'hello world hello python';
print(my_str.endswith('n'));#Result 1 returns true
print('--Dividing line————')
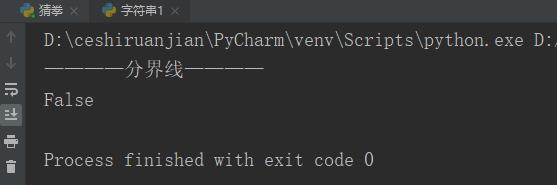
# print(my_str.endswith('s'));#Result 2 returns falseResult 1:
Result 2:
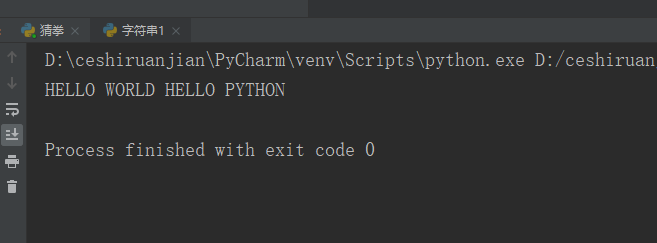
8. Operation method: upper()
Operating instructions: convert the lowercase letters in my_str string to uppercase
code:
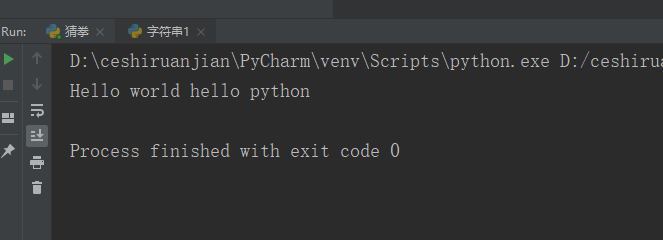
my_str = 'hello world hello python'; print(my_str.upper());#Result 1 display
Result 1:
9. Operation method: lower()
Operating instructions: convert all uppercase characters in my_str string to lowercase
code:
my_str = 'Hello World Hello Python'; print(my_str.lower());#Result 1 display
Result 1:
10. Operation method: title()
Operation instructions: capitalize the first letter of each word of the string
code:
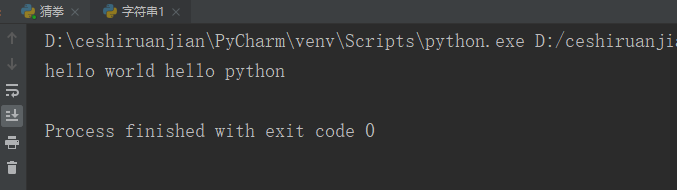
my_str = 'hello world hello python'; print(my_str.title());#Result 1 display
Result 1:
11. Operation method: capitalize()
Operation instructions: capitalize the first character of the string
code:
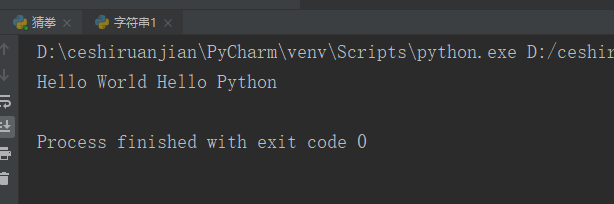
my_str = 'hello world hello python'; print(my_str.capitalize());#Result 1 display
Result 1:
12. Operation method: strip()
Operating instructions: delete the blank characters at both ends of my_str string
code:
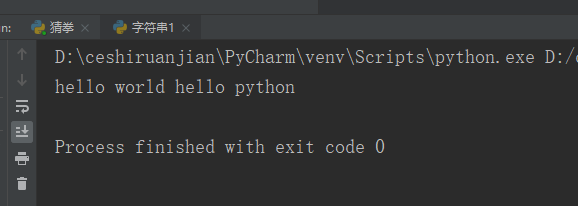
my_str = ' hello world hello python '; print(my_str.strip());#Result 1
Result 1:
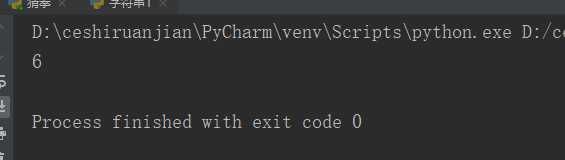
13. Operation method: rfind()
Operating instructions: similar to the find() function, but start from the right
code:
my_str = 'hello world hello python';
print(my_str.rfind('world'))#Result 1Result 1:
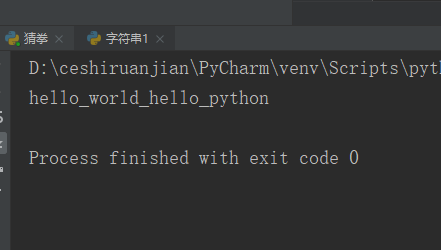
14. Operation method: join()
Operating instructions: insert "underline" after each character to connect my_str strings to construct a new string
code:
my_str = '_'; str = ['hello', 'world', 'hello', 'python']; print(my_str.join(str));#Result 1 display
Result 1:
These are string slicing and common operations in Python