✍ Catalog brain map

- The official documents explain in detail, but they are also cumbersome. This article aims to record the usage and points for attention of common styles
- Reference video:
1,ECharts
1.1. Ecarts Download
1.1. 1. Github Download
- Download and introduce eckarts js file (the icon depends on this js Library)
Chinese official website: https://echarts.apache.org/zh/index.html
1.1. 2. Gitee Download
- If Github can't get in, we can also go to gitee to download: https://gitee.com/echarts
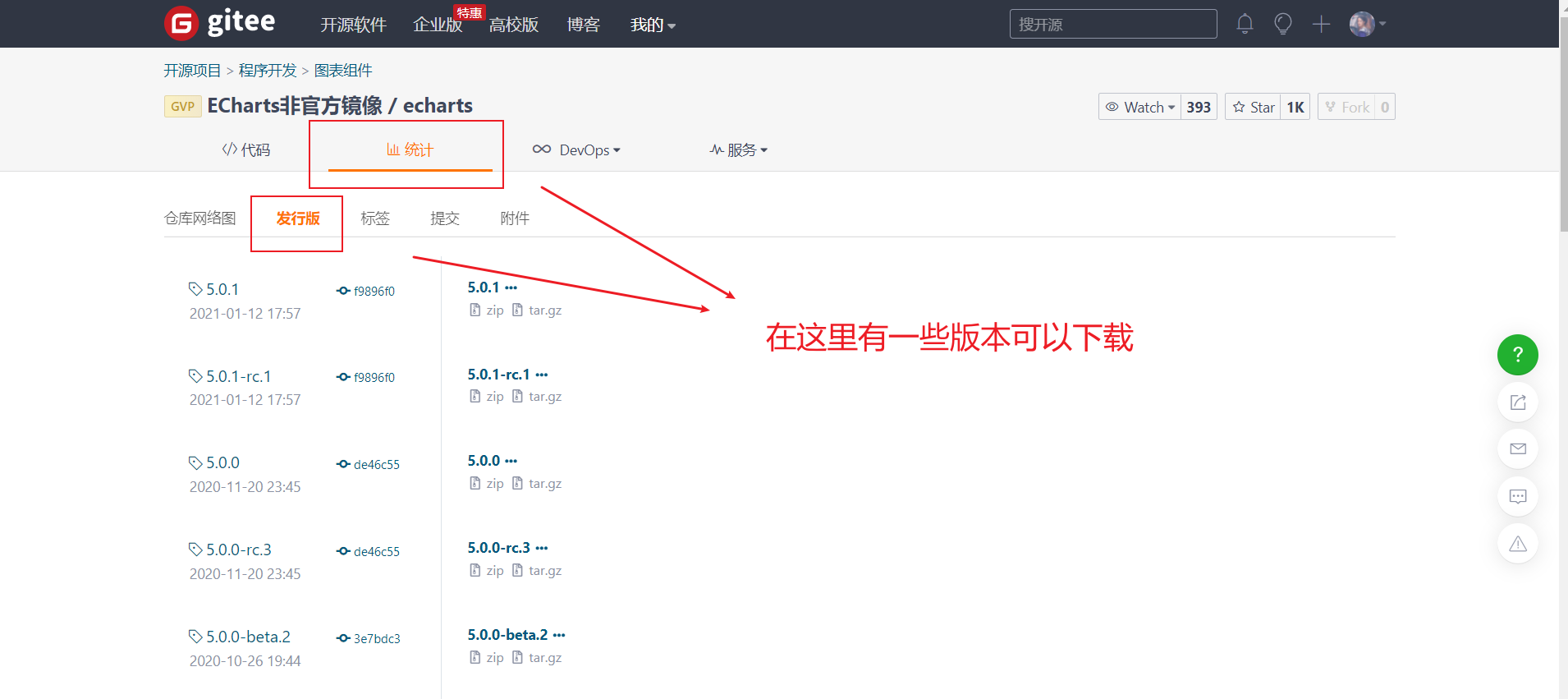
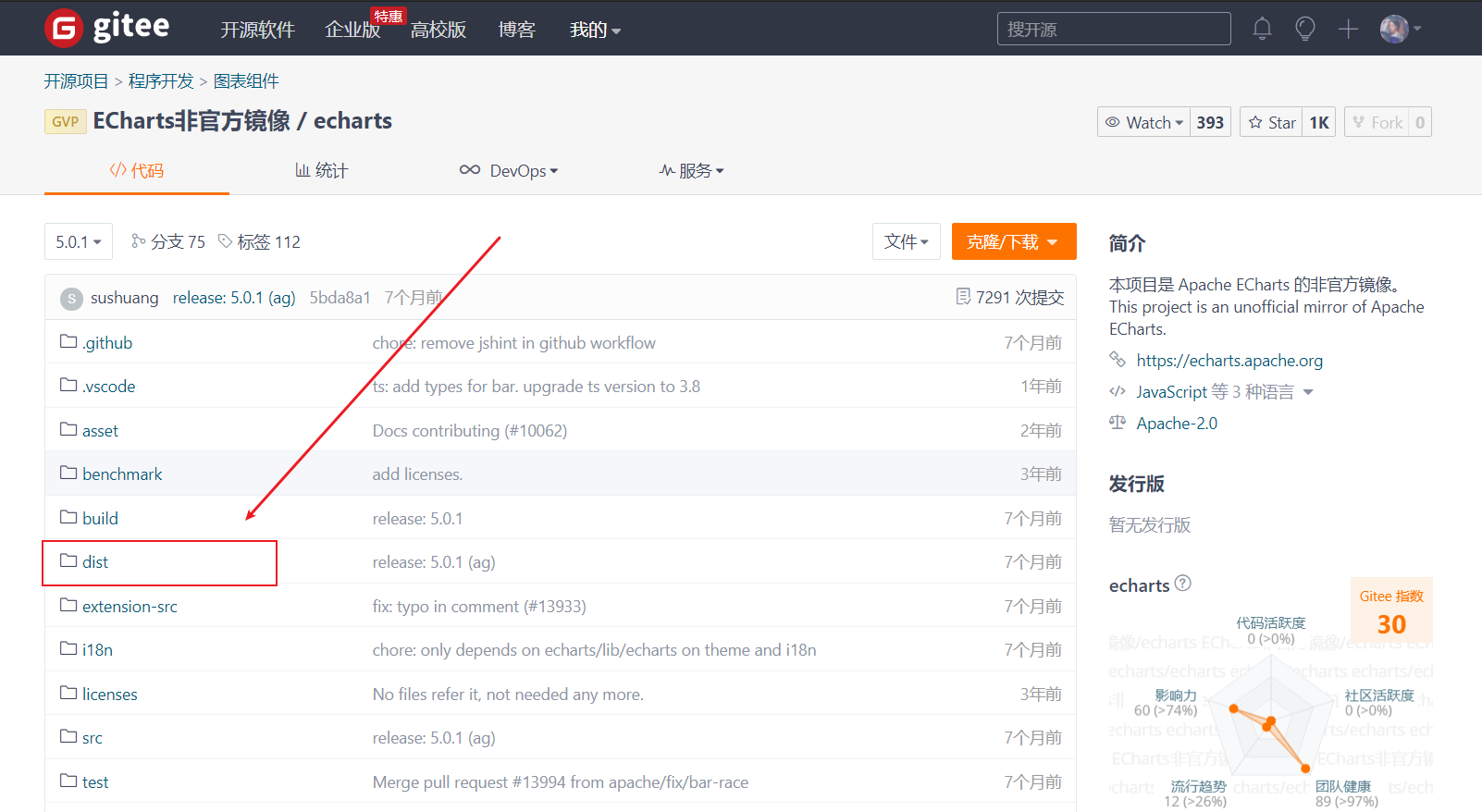
- I'm here at 5.0 Take version 1 as an example
-
We can click clone / download and download zip
-
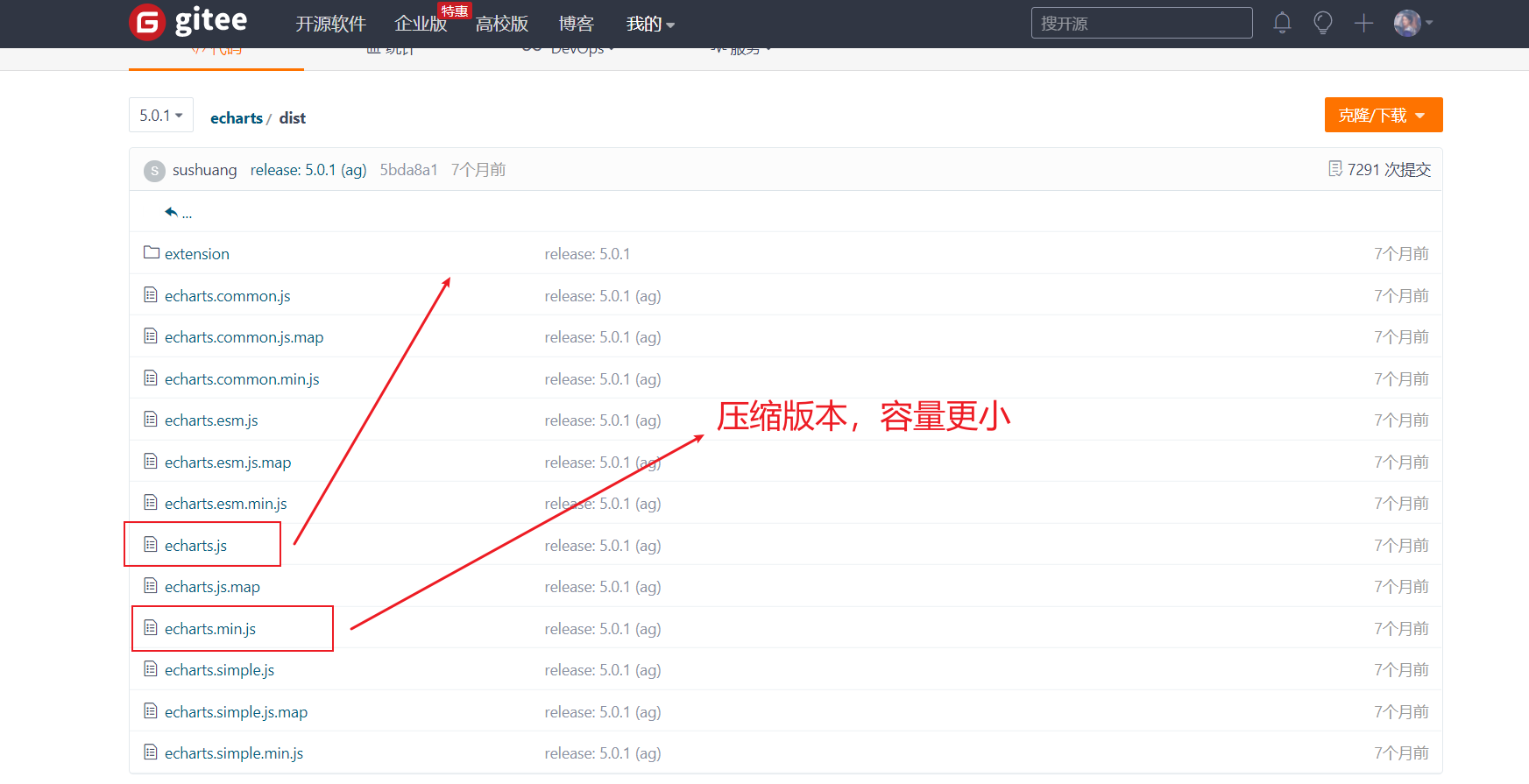
After downloading, unzip the file and find the echorts.com file in the dist folder Copy min.js to our own project structure
-
Then use the script tag to import
1.2 use of ECharts
- Prepare a DOM container with size (the generated icon will be put into this container)
- Initialize the ecarts instance object (instantiate the ecarts object)
- Specify fit item and data (option)
- Set the configuration item to the ecarts instance object
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<script src="../js/echarts.min.js"></script>
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box {
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
background-color: pink;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 1.Prepare a large and small DOM container -->
<div class="box"></div>
<script>
// 2. Initialize the ecarts instantiation object
var myChart = echarts.init(document.querySelector('.box'));
// 3. Specify the configuration items and data of the chart
var option = {
title: {
text: 'ECharts Getting started example'
},
tooltip: {},
legend: {
data: ['sales volume']
},
xAxis: {
data: ["shirt", "cardigan", "Chiffon shirt", "trousers", "high-heeled shoes", "Socks"]
},
yAxis: {},
series: [{
name: 'sales volume',
type: 'bar',
data: [5, 20, 36, 10, 10, 20]
}]
};
// 4. Use the configuration item and data just specified to display the chart.
myChart.setOption(option);
</script>
</body>
</html>
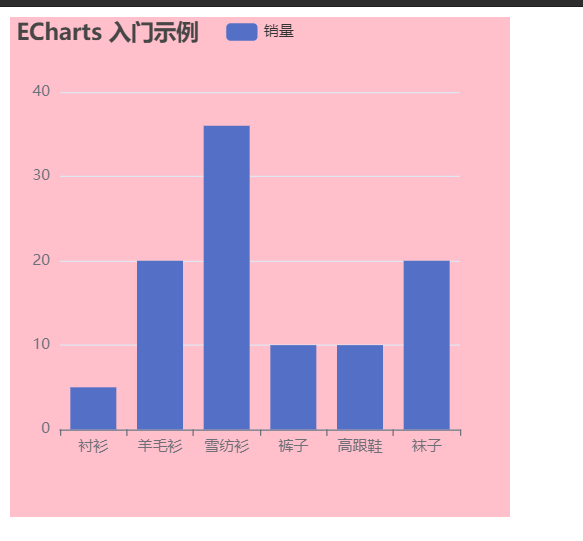
This completes our first example
1.3. Select different charts
- In addition to the column chart, we can also select other charts. The only different step is to specify the configuration items and data of the chart in step 3
- Official website - example. There are many charts in it. We just need to replace the code in step 3. The detailed process is recorded below.
2. ECharts general configuration
- Official website - Document - configuration item manual, you can view all our configurations
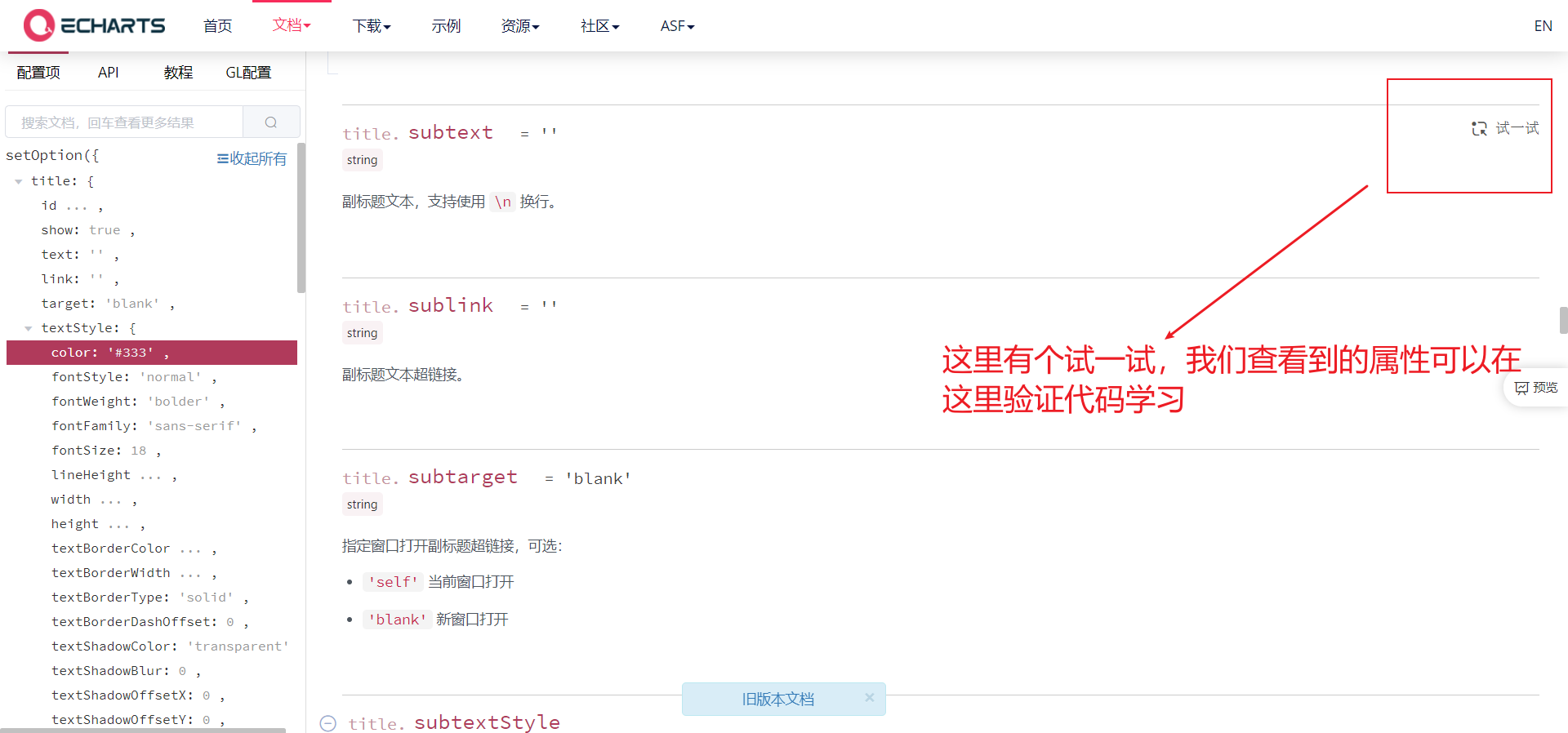
- And we can learn the modified code. We can enter any chart in the example to modify it
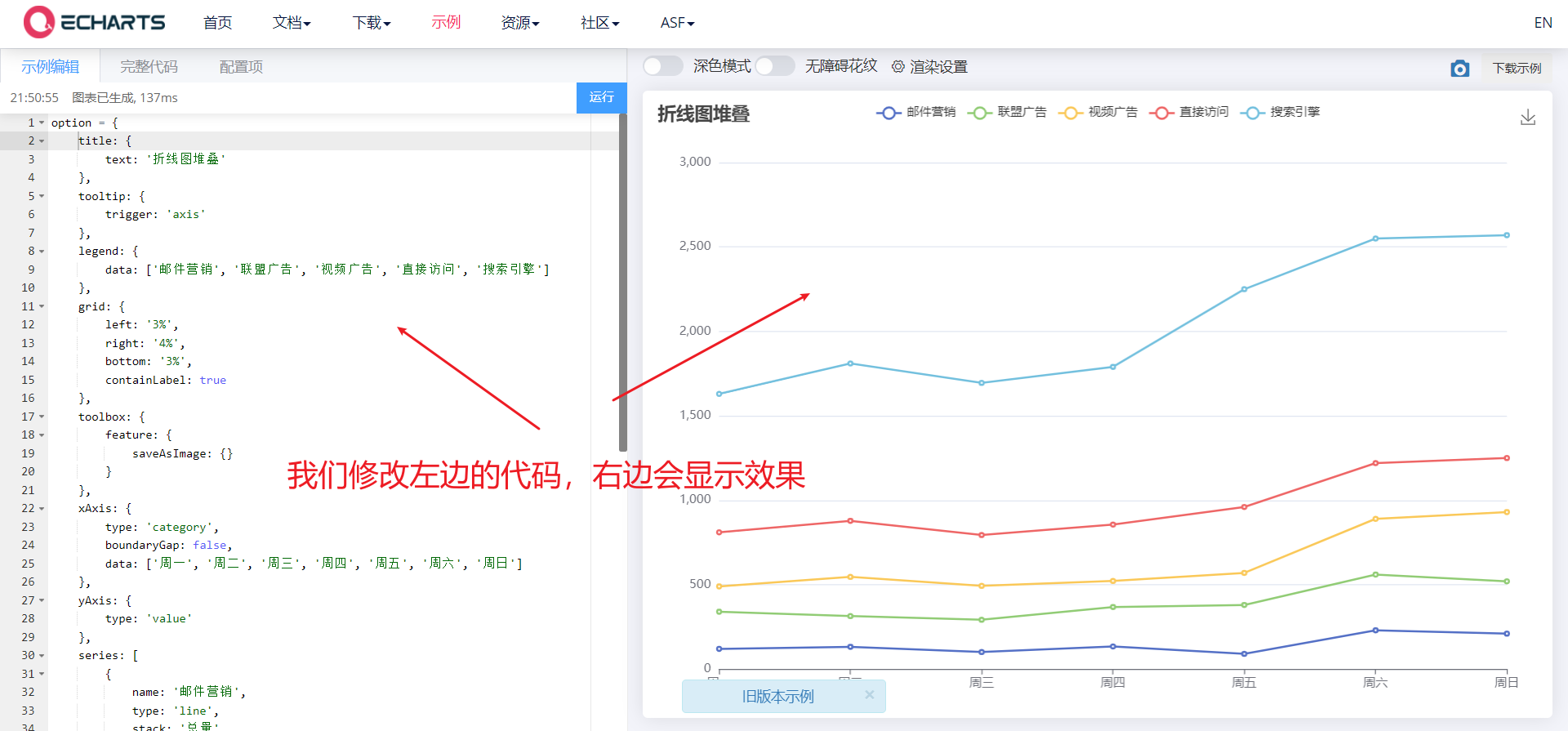
- Unified description code location
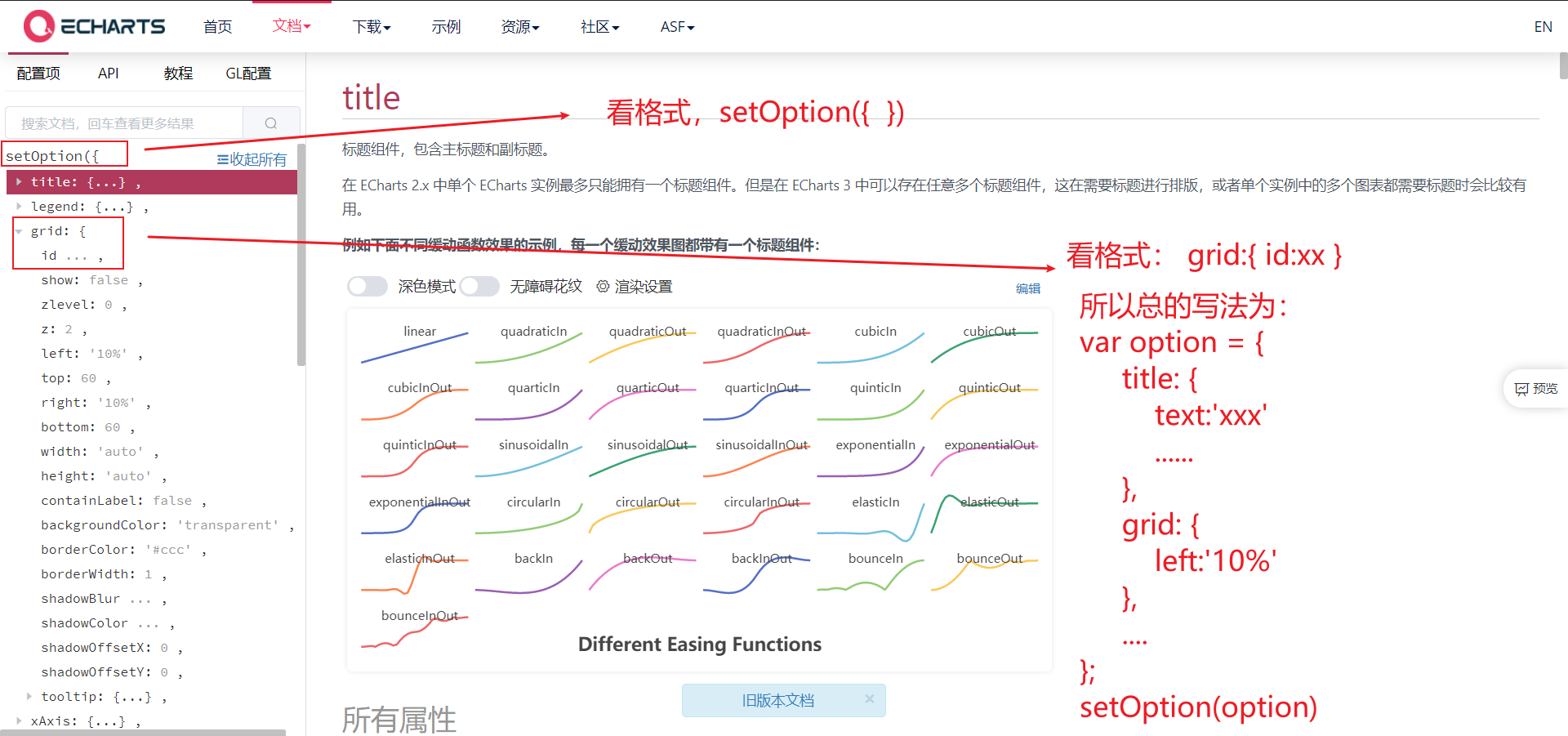
2.1 title Component
- Title component, including main title and subtitle
- Common attributes:
- Text: String type, main title text, supports line feed \ n
- textStyle: Object type, text style
- Title border
- borderWidth: type number, the border line width of the title
- borderRadius: number/Array, fillet radius
- borderColor: the border color of the title
- Title Position
- left,top,right,bottom
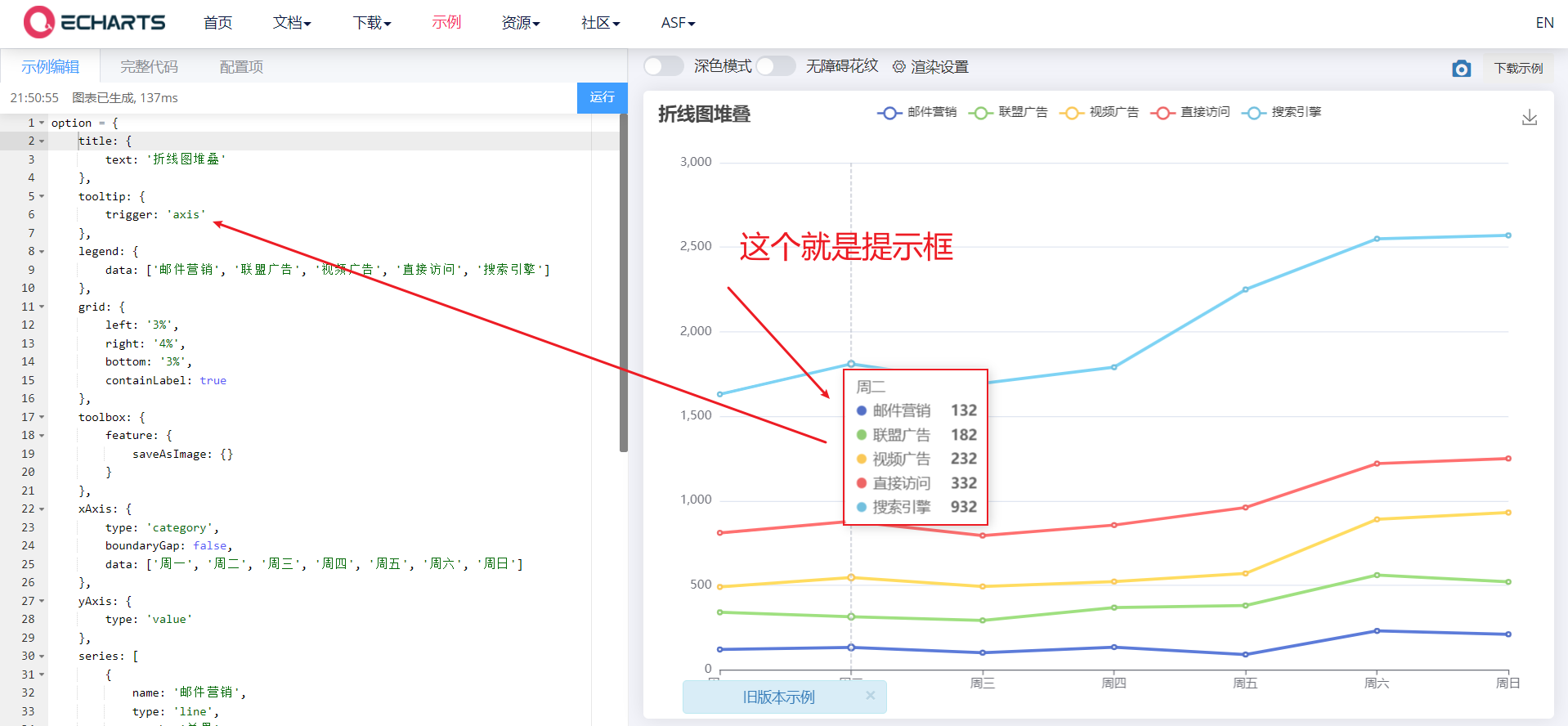
2.2 tooltip prompt box
- The prompt box component is used to configure the display box when the mouse slides over or clicks the chart
- Common attributes:
- Trigger: trigger type, type String, and the following three values are available:
- Item: data item graph trigger, which is mainly used in scatter chart, pie chart and other charts without category axis.
- Axis: coordinate axis trigger, which is mainly used in histogram, line chart and other charts that will use category axis.
- none: nothing triggers.
- Trigger on: trigger timing, type String,
- mousemove: triggered when the mouse moves
- click: triggered when the mouse clicks
- mousemove|click: triggered when the mouse moves and clicks
- Formatter: prompt box floating layer content formatter, which supports two forms: String template and callback function.
- Official documents: https://echarts.apache.org/zh/option.html#tooltip.formatter
- Trigger: trigger type, type String, and the following three values are available:
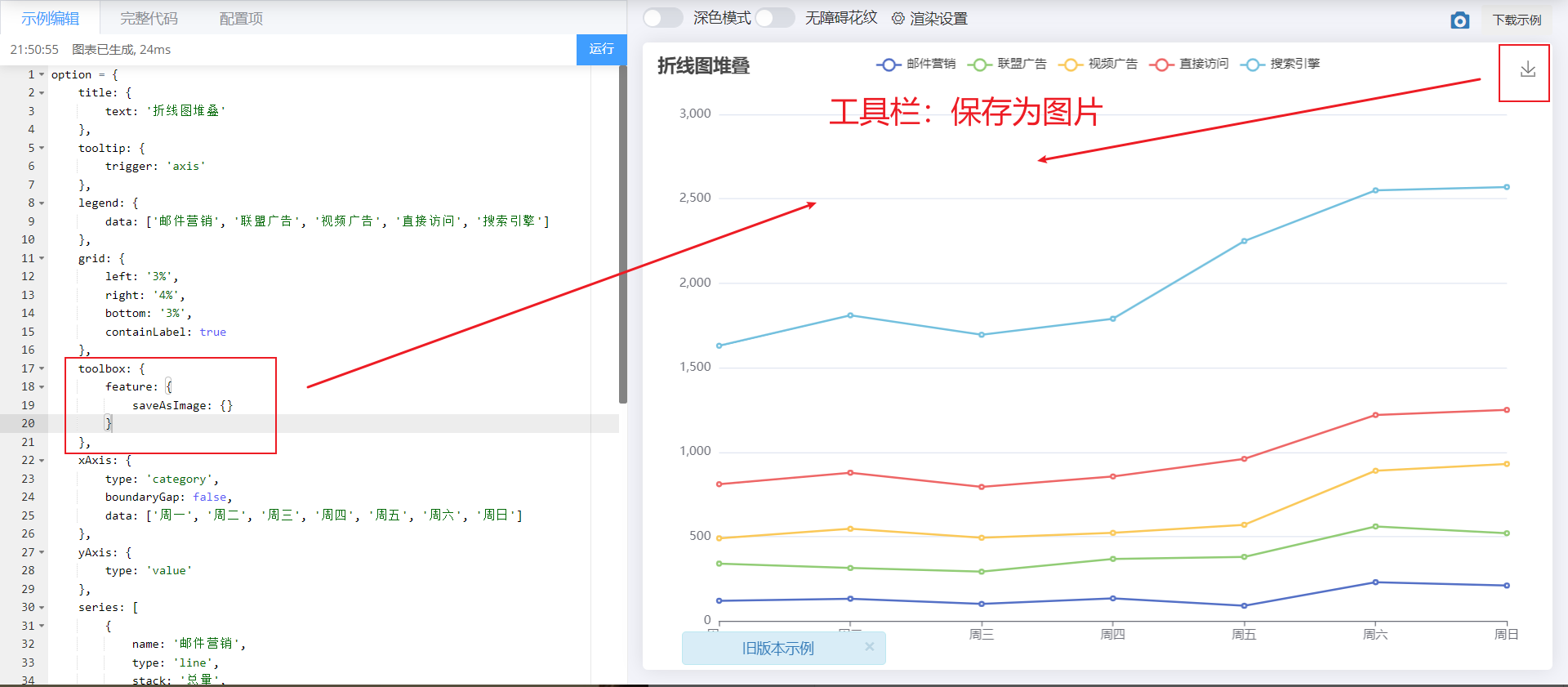
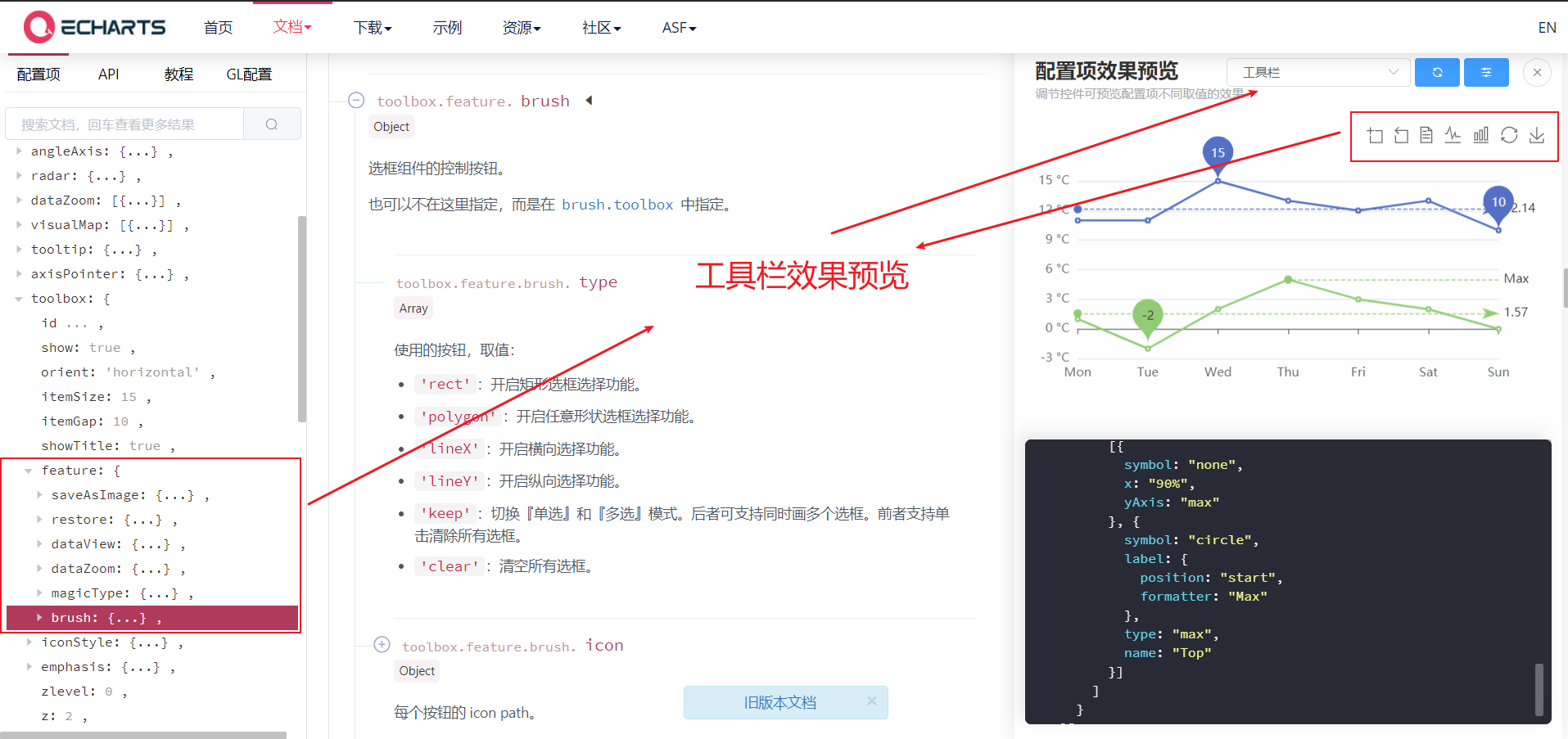
2.3 toolbar
- Toolbar. Built in Export picture,Data view,Dynamic type switching,Data area scaling,Reset Five tools.
- Common attributes are as follows:
- feature, the objects in it can be selected as follows
- saveAsImage {}: save as picture
- Restore {}: configuration item restore
- dataView {}: a data view tool, which can display the data used by the current chart and can be dynamically updated after editing.
- dataZoom {}: data area zoom. At present, only the scaling of rectangular coordinate system is supported.
- magicType {}: dynamic type switching
- feature, the objects in it can be selected as follows
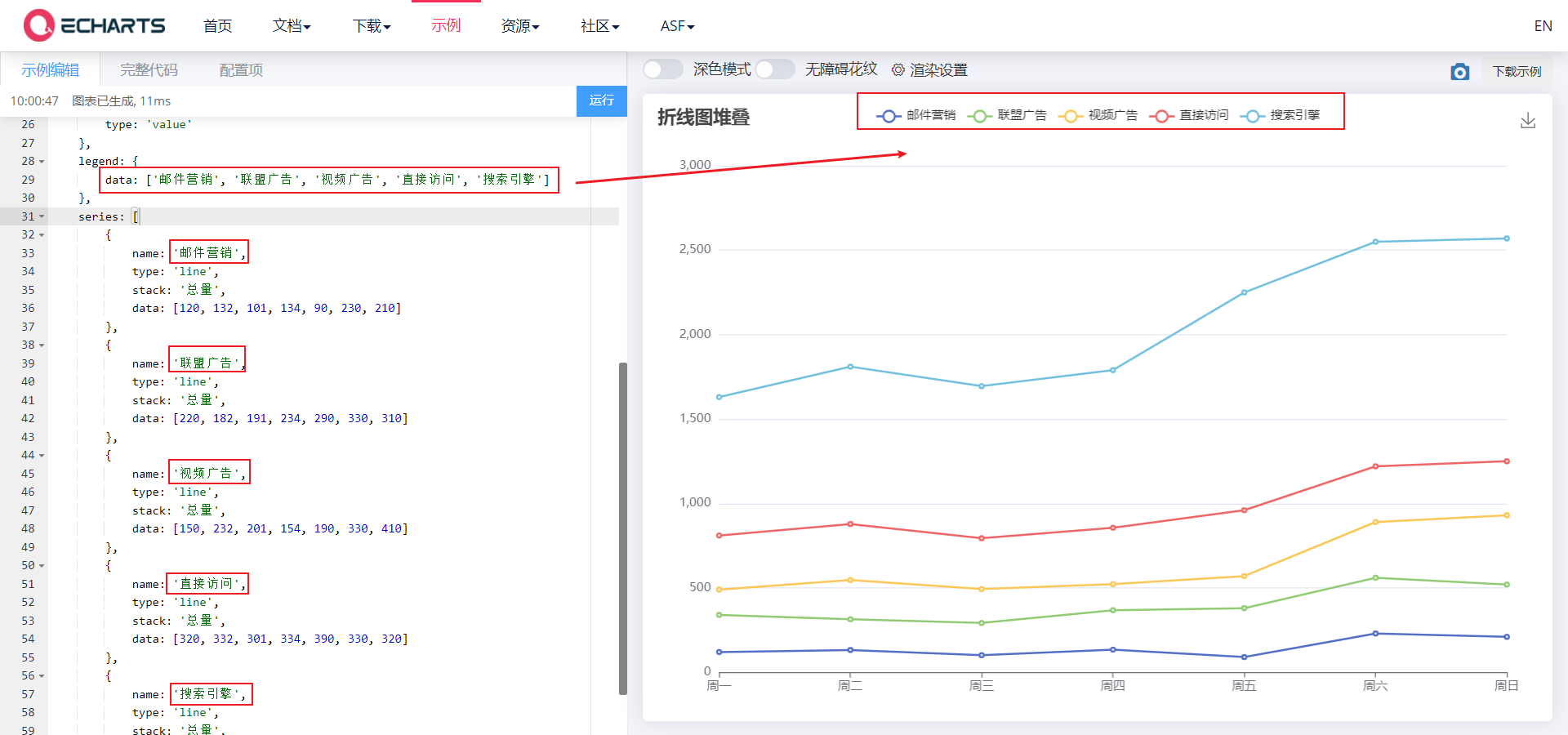
2.4 legend component
- Legend component, used to filter series, needs to be used with series
- Common attributes:
- Data: the data array of the legend, which is an array.
- The value of data in legend must be consistent with the name value of a group of data in the series array.
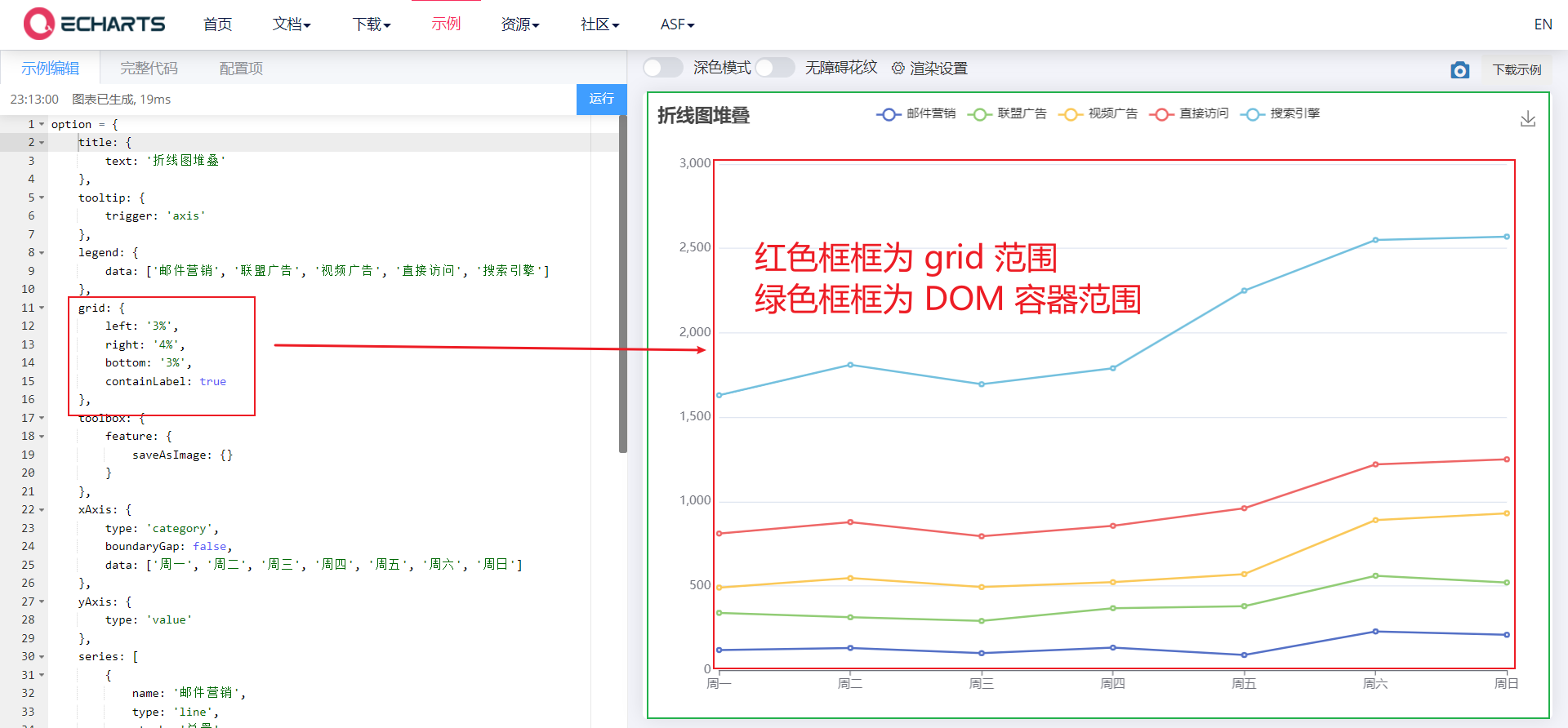
2.5 drawing grid in grid rectangular coordinate system
-
For the drawing grid in the rectangular coordinate system, the upper and lower X axes and the left and right Y axes can be placed in a single grid. You can draw line chart, column chart and scatter chart on the grid
-
Common attributes: https://echarts.apache.org/zh/option.html#grid
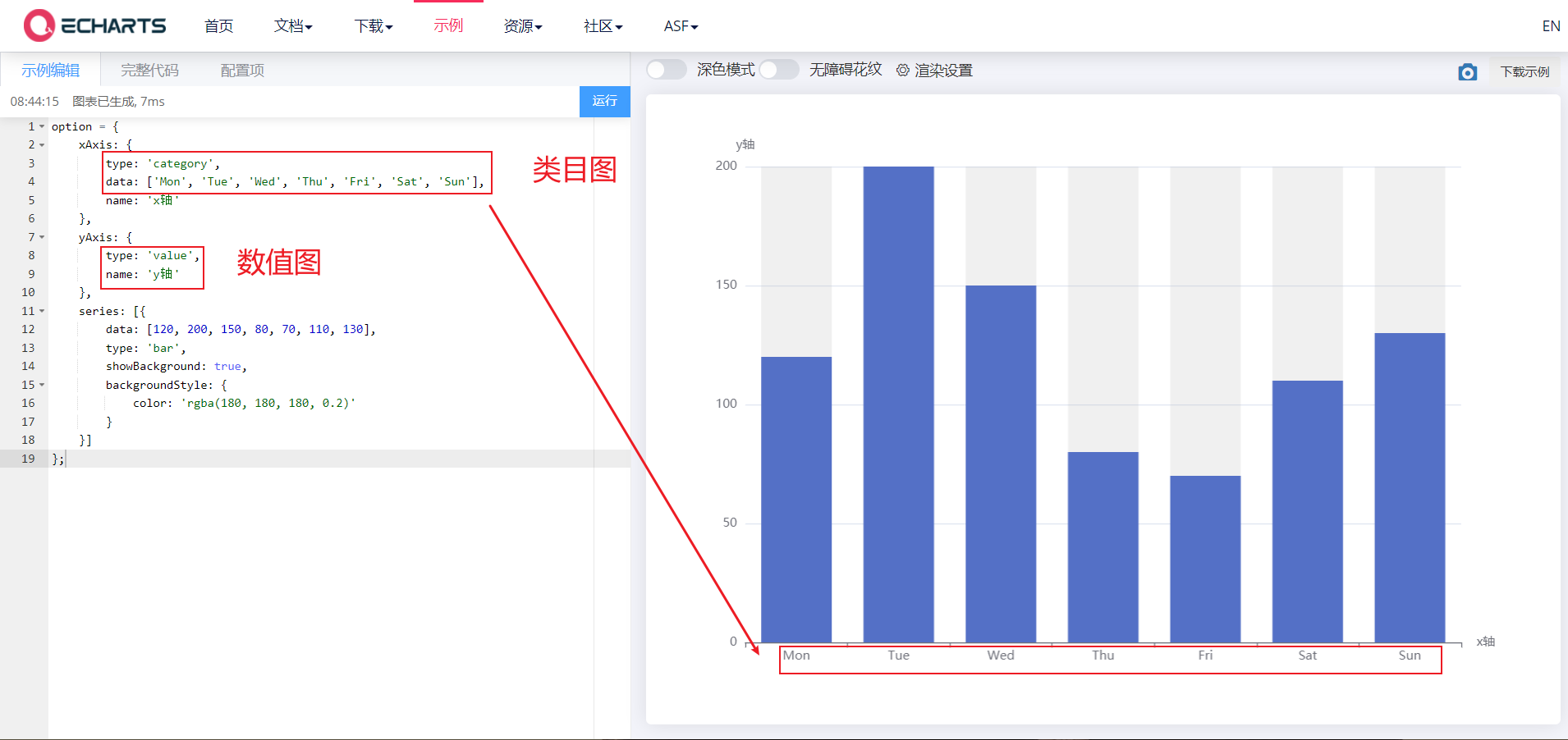
2.5. 1. xAxis and yAxis
-
Official documents: https://echarts.apache.org/zh/option.html#xAxis
-
xAxis is the x axis in the rectangular coordinate system grid, and yAxis is the y axis in the rectangular coordinate system grid
-
Its common attributes are as follows:
- Type: type String, indicating the coordinate axis type. The optional values are as follows:
- Value: value axis, applicable to continuous data
- Category: category axis, applicable to discrete category data. When this type is selected, category data can be automatically retrieved from series.data or dataset.source Medium, or through yAxis.data Set category data.
- Time: time axis, applicable to continuous time series data
- log: for the number axis, it is applicable to logarithmic data
- Name: type String, name of coordinate axis
- Type: type String, indicating the coordinate axis type. The optional values are as follows:
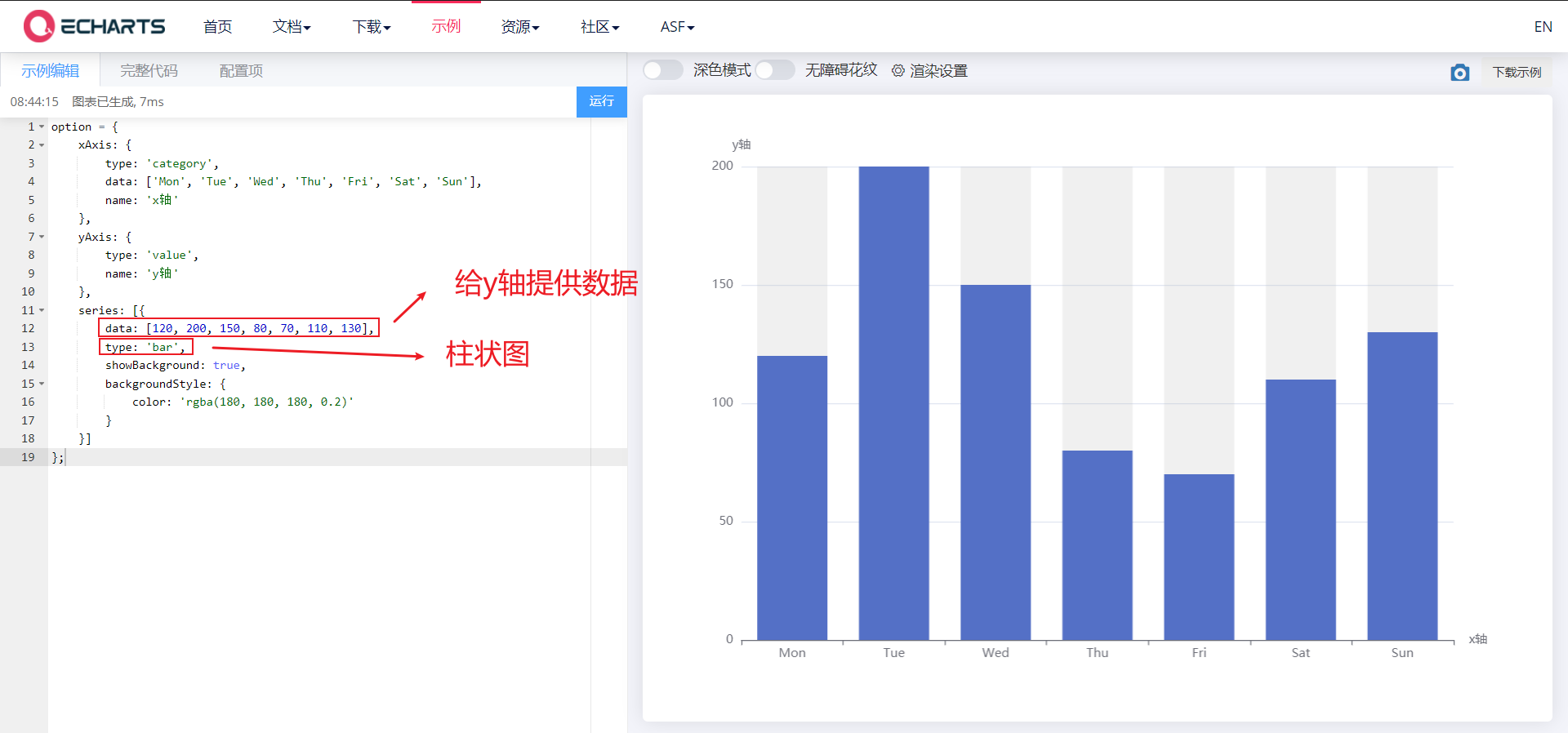
2.5.2,series
-
Official documents: https://echarts.apache.org/zh/option.html#series
-
Series list. Each series determines its own chart type by type, and can provide data for the y-axis
-
Its common attributes are as follows:
- data: https://echarts.apache.org/zh/option.html#series-line.data
- Type: determine your chart type by type
3. Histogram
<body>
<!-- 1.Prepare a large and small DOM container -->
<div style="width: 600px;height: 400px"></div>
<script>
// 2. Initialize the ecarts instantiation object
var myChart = echarts.init(document.querySelector('div'));
// 3. Specify the configuration items and data of the chart
var xDataArr = ['Zhang San','Li Si','Wang Wu','Intercalated soil','Xiao Ming','Moutai','mushroom-shaped umbrella','Wang fried',];
var yDataArr = [88,92,63,77,94,80,72,86];
var option = {
xAxis: {
type: 'category',
data: xDataArr,
},
yAxis: {
type: 'value',
},
series: [
{
name: 'language',
type: 'bar',
data: yDataArr,
}
],
};
// 4. Use the configuration item and data just specified to display the chart.
myChart.setOption(option);
</script>
</body>
3.1 common effects of histogram
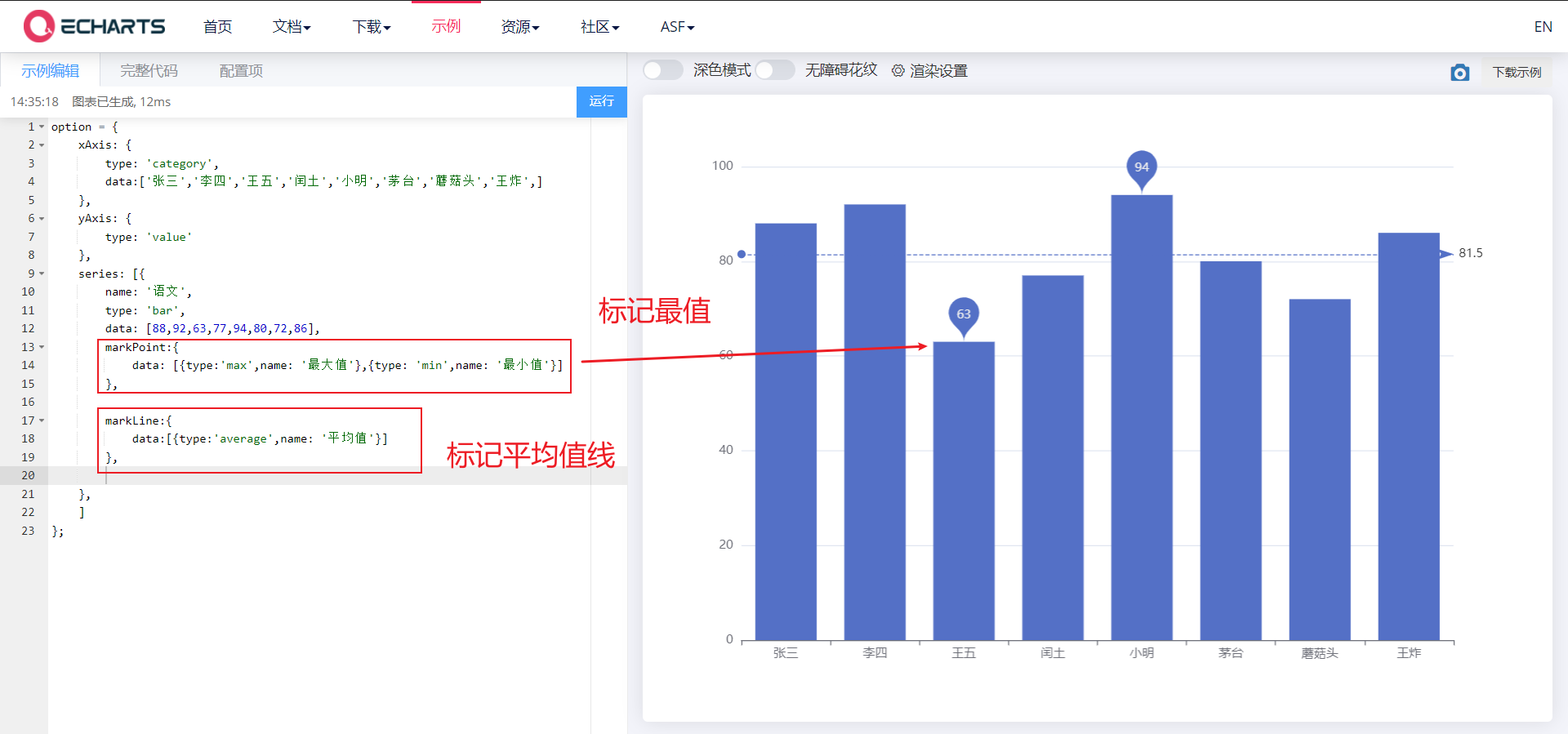
3.1. 1. Mark
- Marking: maximum, minimum, average
- markPoint,markLine,
<body>
<!-- 1.Prepare a large and small DOM container -->
<div style="width: 600px;height: 400px"></div>
<script>
// 2. Initialize the ecarts instantiation object
var myChart = echarts.init(document.querySelector('div'));
// 3. Specify the configuration items and data of the chart
var xDataArr = ['Zhang San','Li Si','Wang Wu','Intercalated soil','Xiao Ming','Moutai','mushroom-shaped umbrella','Wang fried',];
var yDataArr = [88,92,63,77,94,80,72,86];
var option = {
xAxis: {
type: 'category',
data: xDataArr,
},
yAxis: {
type: 'value',
},
series: [
{
name: 'language',
type: 'bar',
markPoint: {
data: [{type: 'max',name: 'Maximum'},{type: 'min',name: 'minimum value'}]
},
markLine : {
data: [{type: 'average',name: 'average value'}]
},
data: yDataArr,
}
],
};
// 4. Use the configuration item and data just specified to display the chart.
myChart.setOption(option);
</script>
</body>
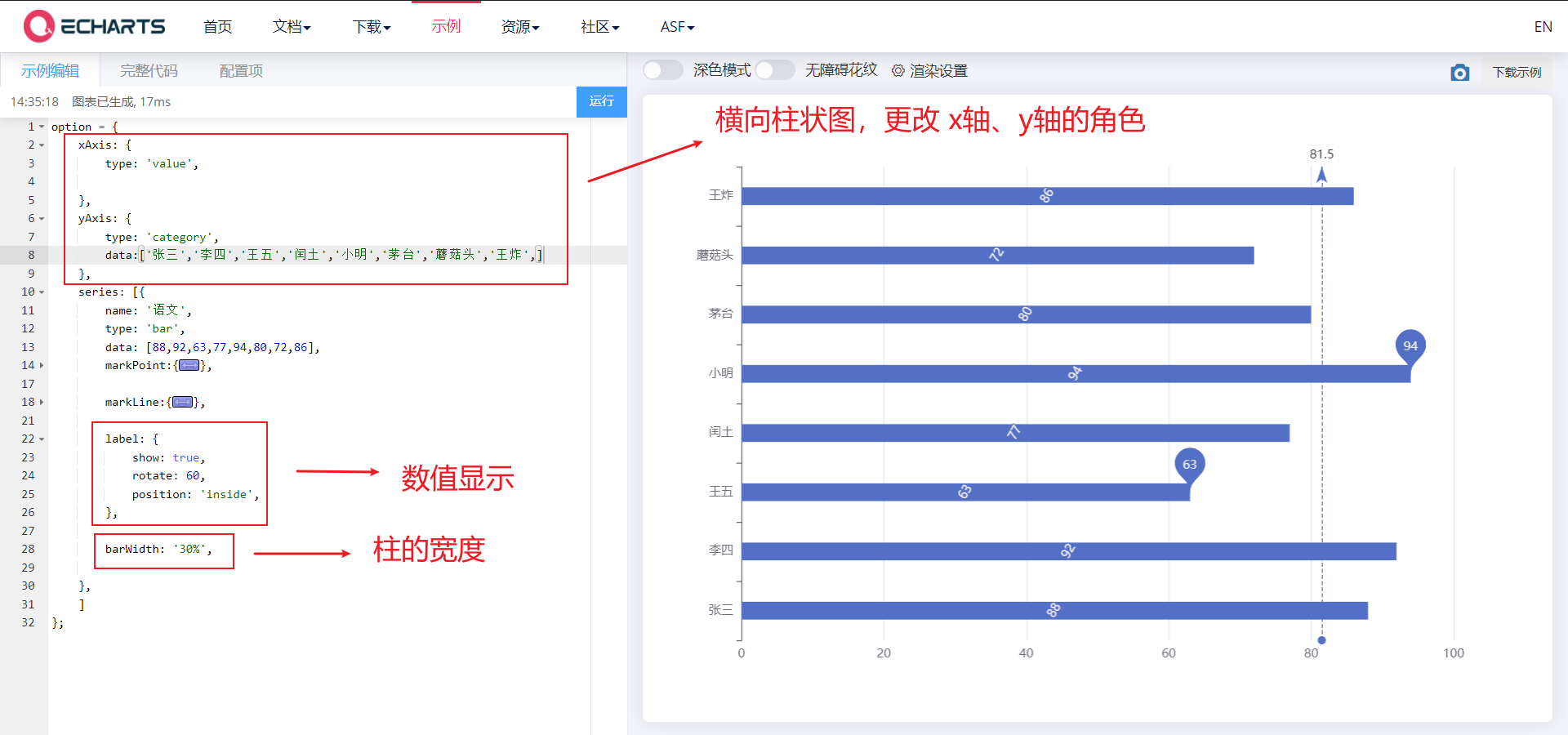
3.1. 2. Show
- Display: numerical display, column width, horizontal histogram
- label, barWidth, changing the role of the x-axis and y-axis
<body>
<!-- 1.Prepare a large and small DOM container -->
<div style="width: 600px;height: 400px"></div>
<script>
// 2. Initialize the ecarts instantiation object
var myChart = echarts.init(document.querySelector('div'));
// 3. Specify the configuration items and data of the chart
var xDataArr = ['Zhang San','Li Si','Wang Wu','Intercalated soil','Xiao Ming','Moutai','mushroom-shaped umbrella','Wang fried',];
var yDataArr = [88,92,63,77,94,80,72,86];
// Transverse histogram
var option = {
xAxis: {
type: 'value',
},
yAxis: {
type: 'category',
data: xDataArr,
},
series: [
{
name: 'language',
type: 'bar',
markPoint: {
data: [{type: 'max',name: 'Maximum'},{type: 'min',name: 'minimum value'}]
},
markLine : {
data: [{type: 'average',name: 'average value'}]
},
// Numerical display
label: {
show: true,
rotate: 60, //Rotate 60 °
position: 'inside',
},
// Column width
barWidth: '30%',
data: yDataArr,
}
],
};
// 4. Use the configuration item and data just specified to display the chart.
myChart.setOption(option);
</script>
</body>
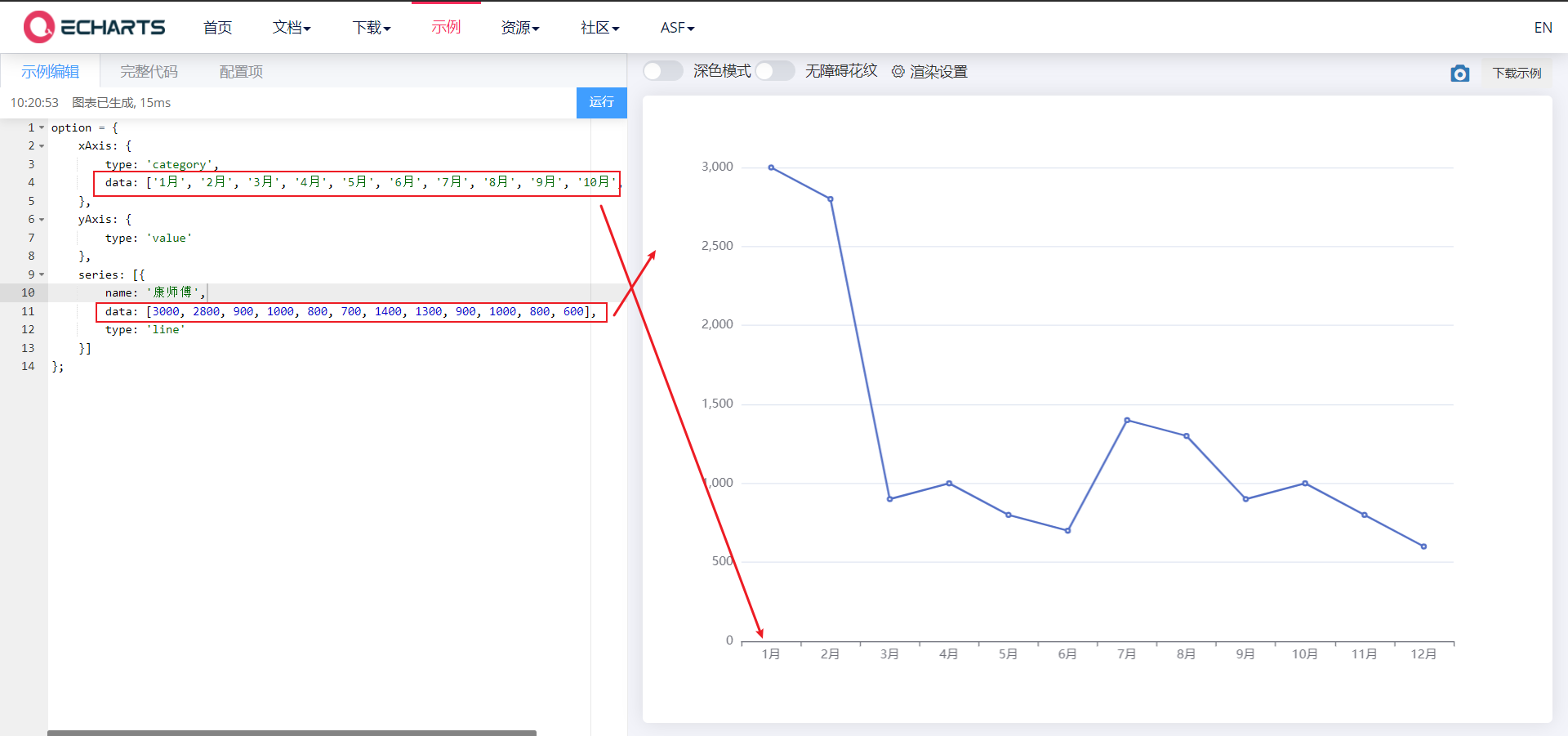
4. Line chart
<body>
<!-- 1.Prepare a large and small DOM container -->
<div style="width: 600px;height: 400px"></div>
<script>
// 2. Initialize the ecarts instantiation object
var myChart = echarts.init(document.querySelector('div'));
// 3. Specify the configuration items and data of the chart
var xDataArr = ['1 month', '2 month', '3 month', '4 month', '5 month', '6 month', '7 month', '8 month', '9 month', '10 month', '11 month', '12 month'];
var yDataArr = [3000, 2800, 900, 1000, 800, 700, 1400, 1300, 900, 1000, 800, 600];
var option = {
xAxis: {
type: 'category',
data: xDataArr
},
yAxis: {
type: 'value'
},
series: [{
name: 'a brand of instant noodles',
data: yDataArr,
type: 'line'
}]
};
// 4. Use the configuration item and data just specified to display the chart.
myChart.setOption(option);
</script>
</body>
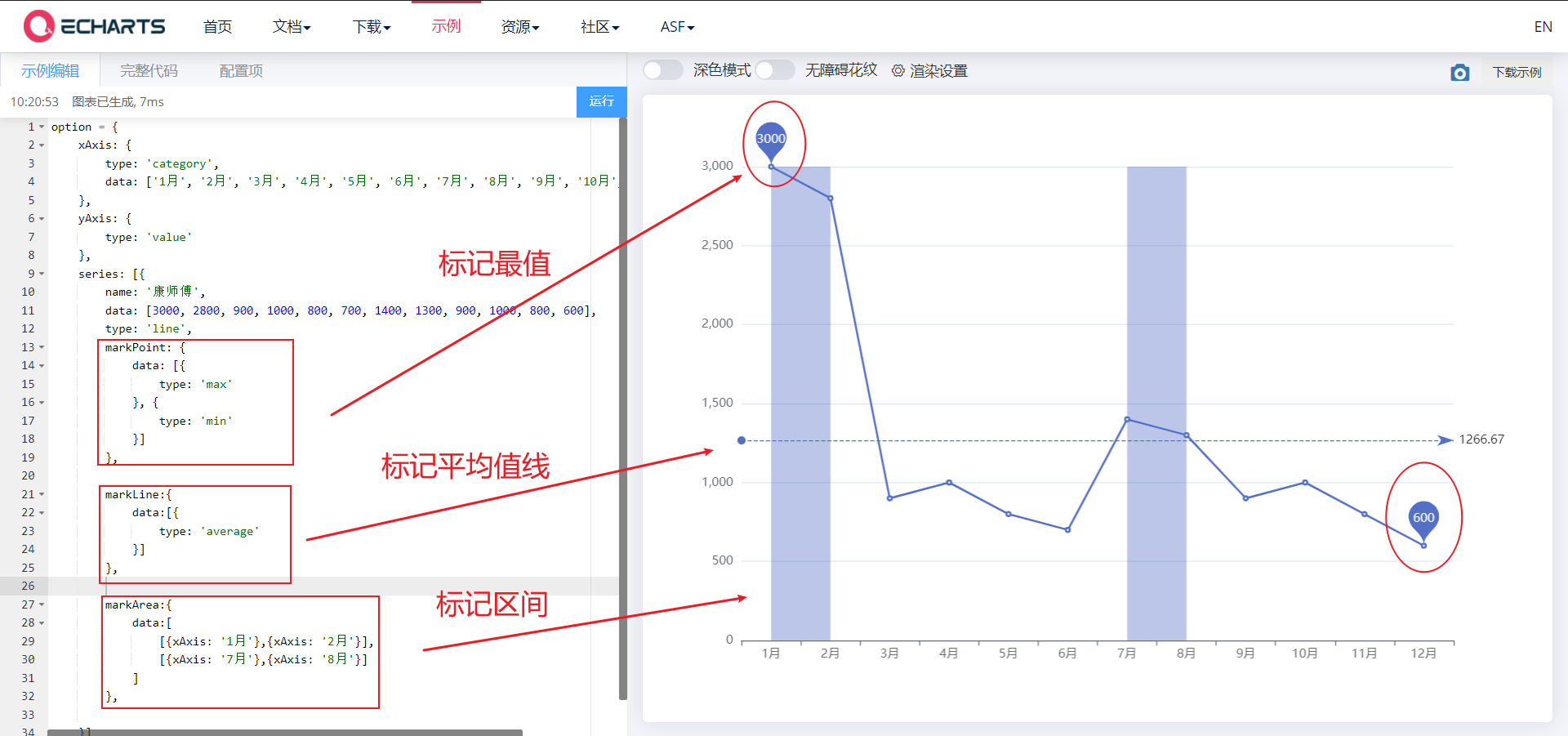
4.1 common effects of line chart
4.1. 1. Mark
- Mark the maximum value, minimum value, average value and marked interval
- markPoint,markLine,markArea
<body>
<!-- 1.Prepare a large and small DOM container -->
<div style="width: 600px;height: 400px"></div>
<script>
// 2. Initialize the ecarts instantiation object
var myChart = echarts.init(document.querySelector('div'));
// 3. Specify the configuration items and data of the chart
var xDataArr = ['1 month', '2 month', '3 month', '4 month', '5 month', '6 month', '7 month', '8 month', '9 month', '10 month', '11 month', '12 month'];
var yDataArr = [3000, 2800, 900, 1000, 800, 700, 1400, 1300, 900, 1000, 800, 600];
var option = {
xAxis: {
type: 'category',
data: xDataArr
},
yAxis: {
type: 'value'
},
series: [{
name: 'a brand of instant noodles',
data: yDataArr,
type: 'line',
// Mark maximum value
markPoint: {
data: [{
type: 'max'
}, {
type: 'min'
}]
},
// Mark average line
markLine: {
data: [{
type: 'average'
}]
},
// Marker interval
markArea:{
data:[
[{xAxis: '1 month'},{xAxis: '2 month'}],
[{xAxis: '7 month'},{xAxis: '8 month'}]
]
},
}]
};
// 4. Use the configuration item and data just specified to display the chart.
myChart.setOption(option);
</script>
</body>
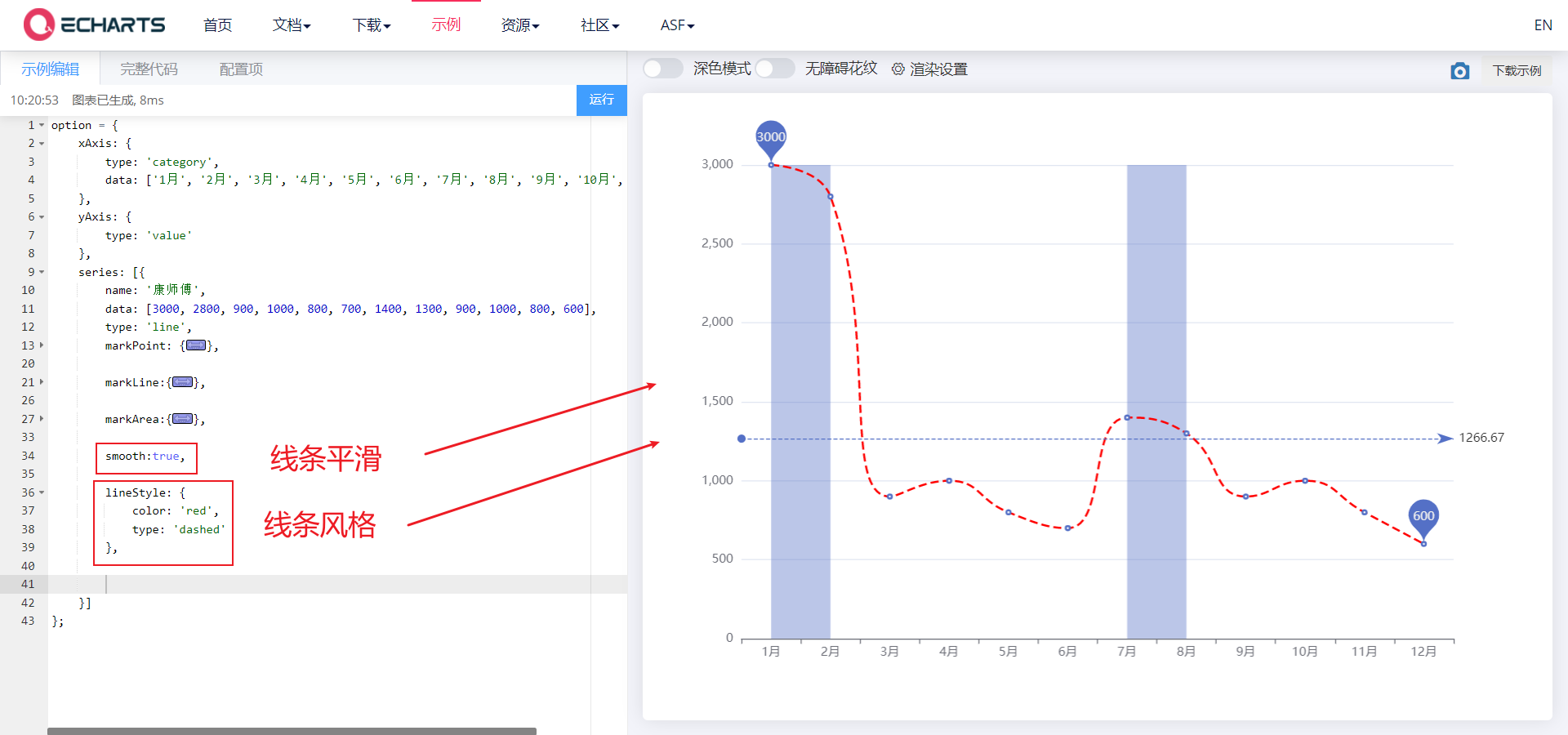
4.1. 2. Line control
- Line control: smoothing style
- smooth,lineStyle
<body>
<!-- 1.Prepare a large and small DOM container -->
<div style="width: 600px;height: 400px"></div>
<script>
// 2. Initialize the ecarts instantiation object
var myChart = echarts.init(document.querySelector('div'));
// 3. Specify the configuration items and data of the chart
var xDataArr = ['1 month', '2 month', '3 month', '4 month', '5 month', '6 month', '7 month', '8 month', '9 month', '10 month', '11 month', '12 month'];
var yDataArr = [3000, 2800, 900, 1000, 800, 700, 1400, 1300, 900, 1000, 800, 600];
var option = {
xAxis: {
type: 'category',
data: xDataArr
},
yAxis: {
type: 'value'
},
series: [{
name: 'a brand of instant noodles',
data: yDataArr,
type: 'line',
markPoint: {
data: [{
type: 'max'
}, {
type: 'min'
}]
},
markLine: {
data: [{
type: 'average'
}]
},
markArea:{
data:[
[{xAxis: '1 month'},{xAxis: '2 month'}],
[{xAxis: '7 month'},{xAxis: '8 month'}]
]
},
// Line smoothing
smooth: true,
// Line style
lineStyle: {
color: 'red',
type: 'dashed', // dashed dotted wire solid wire
}
}
]
};
// 4. Use the configuration item and data just specified to display the chart.
myChart.setOption(option);
</script>
</body>
4.1. 3. Fill style
- Fill style
- areaStyle
<body>
<!-- 1.Prepare a large and small DOM container -->
<div style="width: 600px;height: 400px"></div>
<script>
// 2. Initialize the ecarts instantiation object
var myChart = echarts.init(document.querySelector('div'));
// 3. Specify the configuration items and data of the chart
var xDataArr = ['1 month', '2 month', '3 month', '4 month', '5 month', '6 month', '7 month', '8 month', '9 month', '10 month', '11 month', '12 month'];
var yDataArr = [3000, 2800, 900, 1000, 800, 700, 1400, 1300, 900, 1000, 800, 600];
var option = {
xAxis: {
type: 'category',
data: xDataArr
},
yAxis: {
type: 'value'
},
series: [{
name: 'a brand of instant noodles',
data: yDataArr,
type: 'line',
markPoint: {
data: [{
type: 'max'
}, {
type: 'min'
}]
},
markLine: {
data: [{
type: 'average'
}]
},
markArea:{
data:[
[{xAxis: '1 month'},{xAxis: '2 month'}],
[{xAxis: '7 month'},{xAxis: '8 month'}]
]
},
smooth: true,
lineStyle: {
color: 'red',
type: 'dashed', // dashed dotted wire solid wire
},
areaStyle: {
color: 'blue'
},
}
]
};
// 4. Use the configuration item and data just specified to display the chart.
myChart.setOption(option);
</script>
</body>
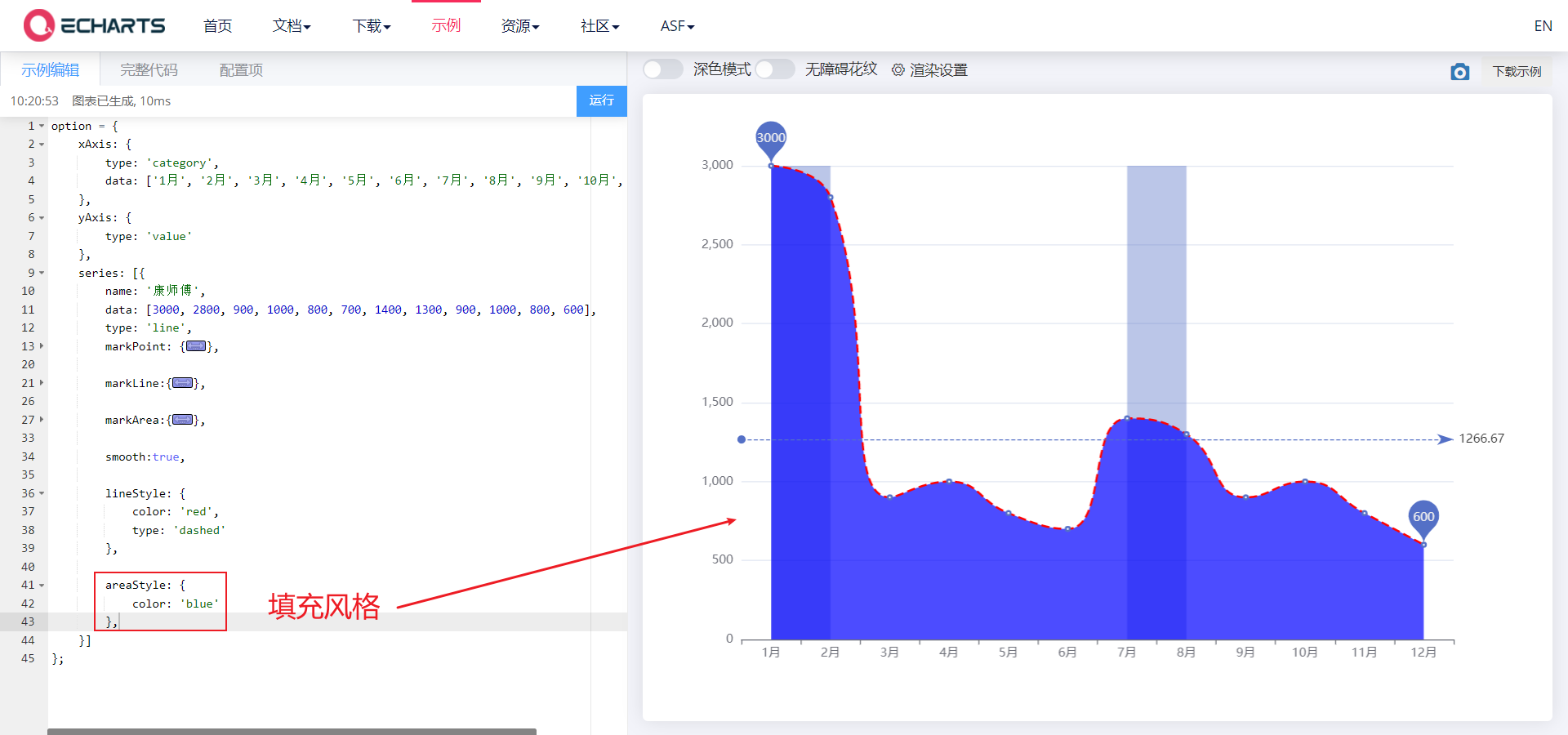
4.1. 4. Next to the edge
- Next to the edge, scale (out of scale of 0 value, that is, don't let the x and y axes start from 0)
- boundaryGap,scale
- Make the line chart close to the left y-axis and start drawing
- If our x and y axes always start from 0, the difference of elements in a column array is very small, and the broken line graph is almost a straight line
<body>
<!-- 1.Prepare a large and small DOM container -->
<div style="width: 600px;height: 400px"></div>
<script>
// 2. Initialize the ecarts instantiation object
var myChart = echarts.init(document.querySelector('div'));
// 3. Specify the configuration items and data of the chart
var xDataArr = ['1 month', '2 month', '3 month', '4 month', '5 month', '6 month', '7 month', '8 month', '9 month', '10 month', '11 month', '12 month'];
//var yDataArr = [3000, 2800, 900, 1000, 800, 700, 1400, 1300, 900, 1000, 800, 600];
var yDataArr = [3005, 3003, 3001, 3002, 3009, 3007, 3003, 3001, 3005, 3004, 3001, 3009];
var option = {
xAxis: {
type: 'category',
data: xDataArr,
// Next to the edge
boundaryGap: false,
},
yAxis: {
type: 'value',
// zoom
scale: true,
},
series: [{
name: 'a brand of instant noodles',
data: yDataArr,
type: 'line',
}
]
};
// 4. Use the configuration item and data just specified to display the chart.
myChart.setOption(option);
</script>
</body>
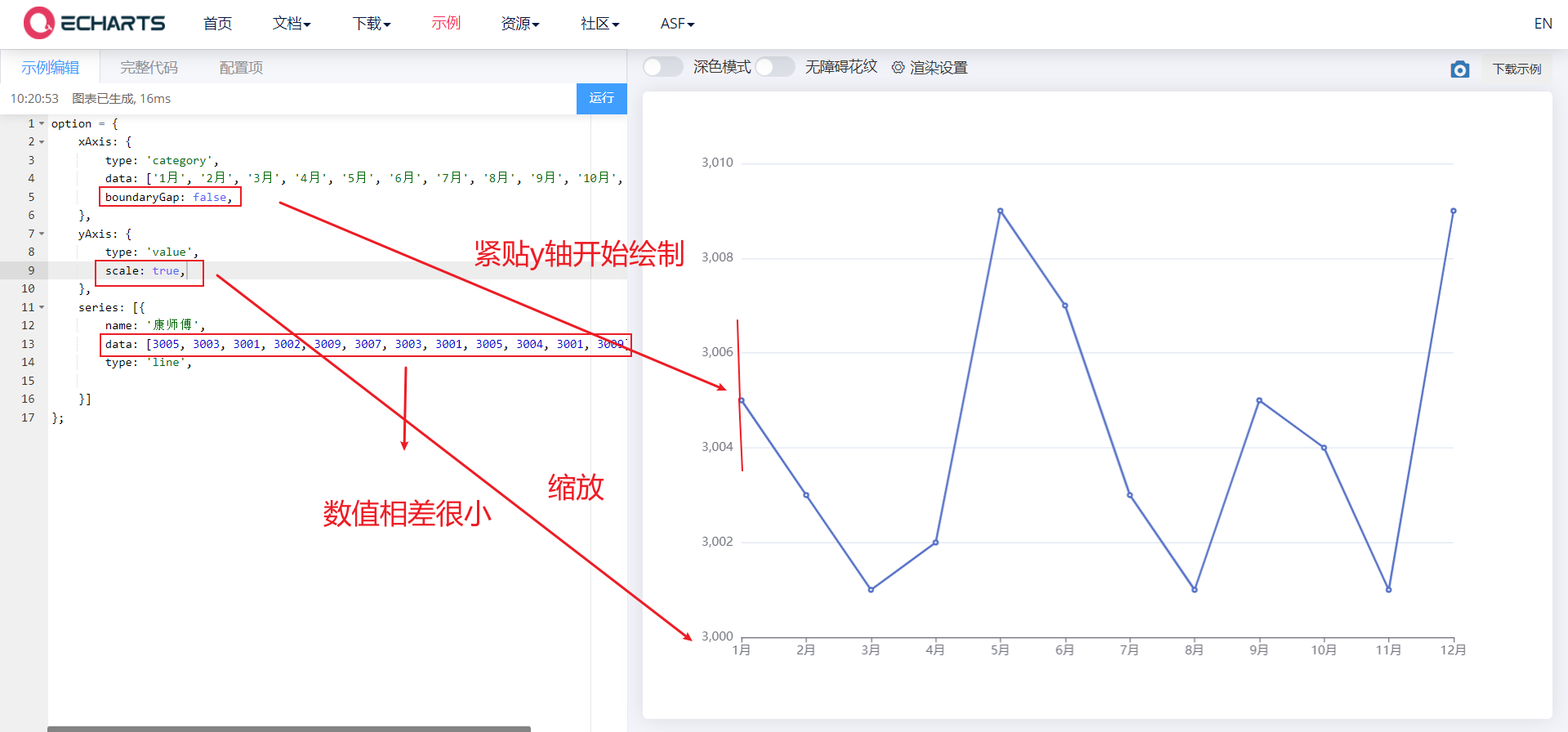
4.1. 5. Stacking diagram
- Stacking diagram
- stack
<body>
<!-- 1.Prepare a large and small DOM container -->
<div style="width: 600px;height: 400px"></div>
<script>
// 2. Initialize the ecarts instantiation object
var myChart = echarts.init(document.querySelector('div'));
// 3. Specify the configuration items and data of the chart
var xDataArr = ['1 month', '2 month', '3 month', '4 month', '5 month', '6 month', '7 month', '8 month', '9 month', '10 month', '11 month', '12 month'];
var yDataArr = [3000, 2800, 900, 1000, 800, 700, 1400, 1300, 900, 1000, 800, 600];
var yDataArr2 = [2000,3800,1900,500,900,1700,2400,300,1900,1500,1800,200];
var option = {
xAxis: {
type: 'category',
data: xDataArr,
},
yAxis: {
type: 'value',
},
series: [{
data: yDataArr,
type: 'line',
stack: 'all',
areaStyle: {},
},
{
data: yDataArr2,
type: 'line',
stack: 'all',
areaStyle: {},
}
]
};
// 4. Use the configuration item and data just specified to display the chart.
myChart.setOption(option);
</script>
</body>
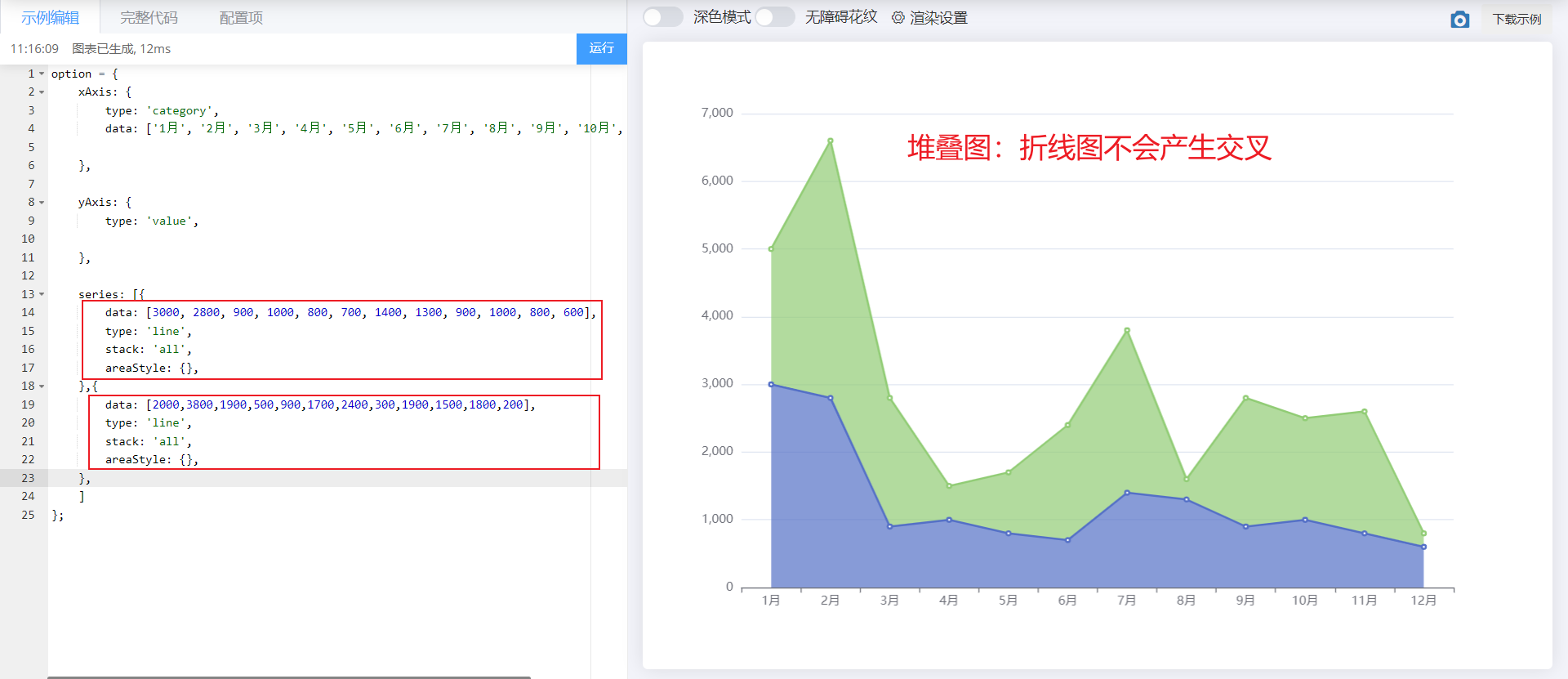
5. Scatter diagram
- X-axis data and Y-axis data: 2D arrays
- Set the type under series: scatter, xaxis and yAxis should be set to value
- Adjust: set the coordinate axes to scale away from the 0 value, scale
<body>
<!-- 1.Prepare a large and small DOM container -->
<div style="width: 600px;height: 400px"></div>
<script>
// 2. Initialize the ecarts instantiation object
var myChart = echarts.init(document.querySelector('div'));
// 3. Specify the configuration items and data of the chart
var axisData = [
[10.0, 8.04],
[8.07, 6.95],
[13.0, 7.58],
[9.05, 8.81],
[11.0, 8.33],
[14.0, 7.66],
[13.4, 6.81],
[10.0, 6.33],
[14.0, 8.96],
[12.5, 6.82],
[9.15, 7.20],
[11.5, 7.20],
[3.03, 4.23],
[12.2, 7.83],
[2.02, 4.47],
[1.05, 3.33],
[4.05, 4.96],
[6.03, 7.24],
[12.0, 6.26],
[12.0, 8.84],
[7.08, 5.82],
[5.02, 5.68]
];
var option = {
xAxis: {
type: 'value',
scale: true,
},
yAxis: {
type: 'value',
scale: true,
},
series: [{
type: 'scatter',
data: axisData,
}]
}
// 4. Use the configuration item and data just specified to display the chart.
myChart.setOption(option);
</script>
</body>
5.1 common effects of scatter diagram
5.1. 1. Bubble chart effect
- The size and color of scatter points are different
- symbolSize ,itemStyle.color
① Different scatter sizes
<body>
<!-- 1.Prepare a large and small DOM container -->
<div style="width: 600px;height: 400px"></div>
<script>
// 2. Initialize the ecarts instantiation object
var myChart = echarts.init(document.querySelector('div'));
// 3. Specify the configuration items and data of the chart
var axisData = [
[161.2, 51.6],
[167.5, 59.0],
[159.5, 49.2],
[157.0, 63.0],
[155.8, 53.6],
[170.0, 59.0],
[159.1, 47.6],
[166.0, 69.8],
[176.2, 66.8],
[160.2, 75.2],
[172.5, 55.2],
[170.9, 54.2],
[172.9, 62.5],
[153.4, 42.0],
[160.0, 50.0],
[147.2, 49.8],
[168.2, 49.2],
[175.0, 73.2],
[157.0, 47.8],
[167.6, 68.8],
[159.5, 50.6]
];
var option = {
xAxis: {
type: 'value',
scale: true,
},
yAxis: {
type: 'value',
scale: true,
},
series: [{
type: 'scatter',
data: axisData,
// symbolSize: 20
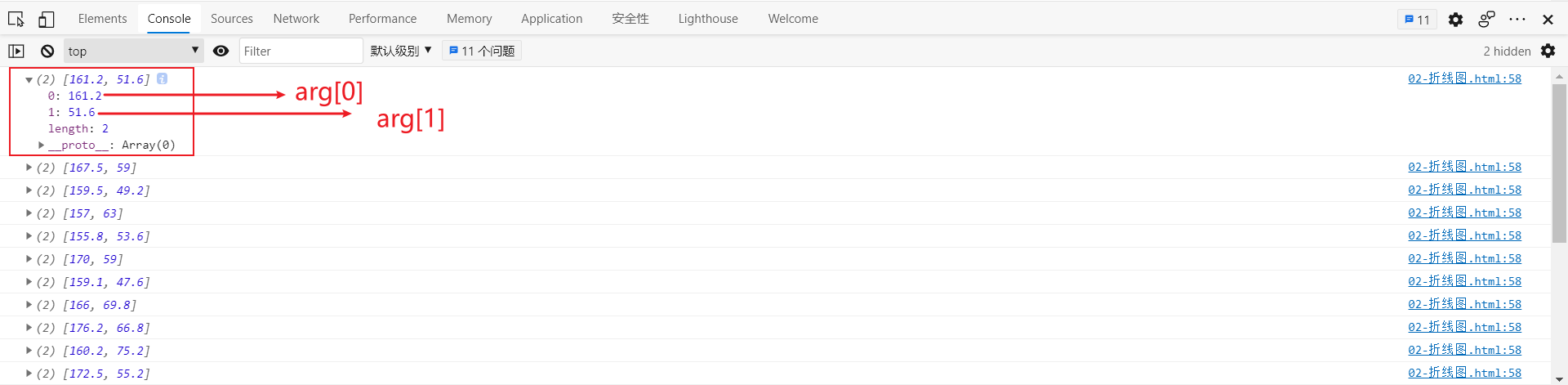
symbolSize: function(arg) {
//console.log(arg);
var height = arg[0] / 100;
var weight = arg[1];
// bmi = weight kg / (height m * height) bmi greater than 28 represents obesity
var bmi = weight / (height * height)
if (bmi > 28) {
return 20;
} else {
return 5;
}
},
}]
}
// 4. Use the configuration item and data just specified to display the chart.
myChart.setOption(option);
</script>
</body>
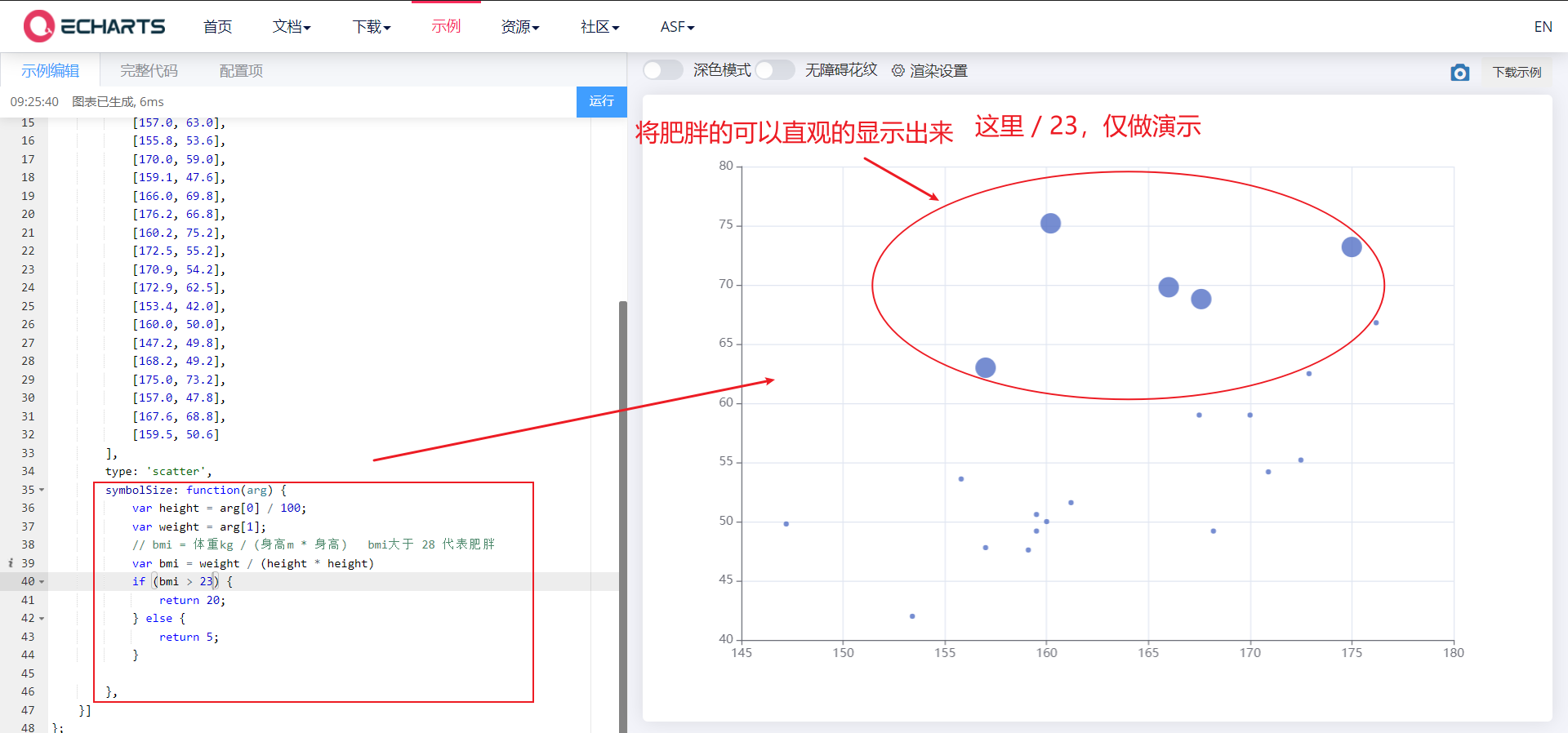
arg is as follows:
② The color of scatter points is different
<body>
<!-- 1.Prepare a large and small DOM container -->
<div style="width: 600px;height: 400px"></div>
<script>
// 2. Initialize the ecarts instantiation object
var myChart = echarts.init(document.querySelector('div'));
// 3. Specify the configuration items and data of the chart
var axisData = [
[161.2, 51.6],
[167.5, 59.0],
[159.5, 49.2],
[157.0, 63.0],
[155.8, 53.6],
[170.0, 59.0],
[159.1, 47.6],
[166.0, 69.8],
[176.2, 66.8],
[160.2, 75.2],
[172.5, 55.2],
[170.9, 54.2],
[172.9, 62.5],
[153.4, 42.0],
[160.0, 50.0],
[147.2, 49.8],
[168.2, 49.2],
[175.0, 73.2],
[157.0, 47.8],
[167.6, 68.8],
[159.5, 50.6]
];
var option = {
xAxis: {
type: 'value',
scale: true,
},
yAxis: {
type: 'value',
scale: true,
},
series: [{
type: 'scatter',
data: axisData,
// Scatter size
// symbolSize: 20
symbolSize: function(arg) {
var height = arg[0] / 100;
var weight = arg[1];
// bmi = weight kg / (height m * height) bmi greater than 28 represents obesity
var bmi = weight / (height * height)
if (bmi > 28) {
return 20;
} else {
return 5;
}
},
// Scatter color
itemStyle: {
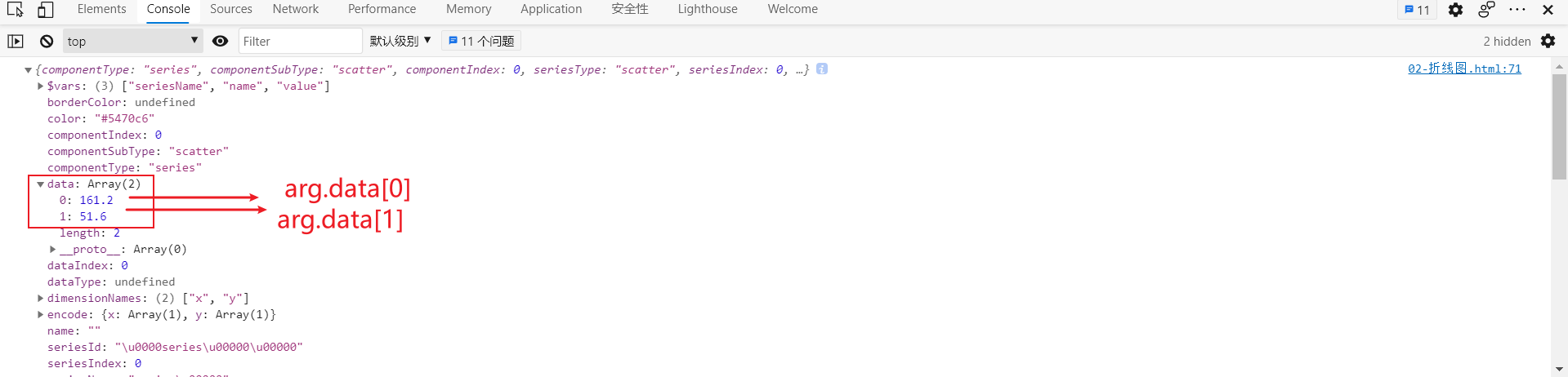
color: function(arg) {
var height = arg.data[0] / 100;
var weight = arg.data[1];
// bmi = weight kg / (height m * height) bmi greater than 28 represents obesity
var bmi = weight / (height * height)
if (bmi > 23) {
return 'red';
} else {
return 'green';
}
}
}
}]
}
// 4. Use the configuration item and data just specified to display the chart.
myChart.setOption(option);
</script>
</body>
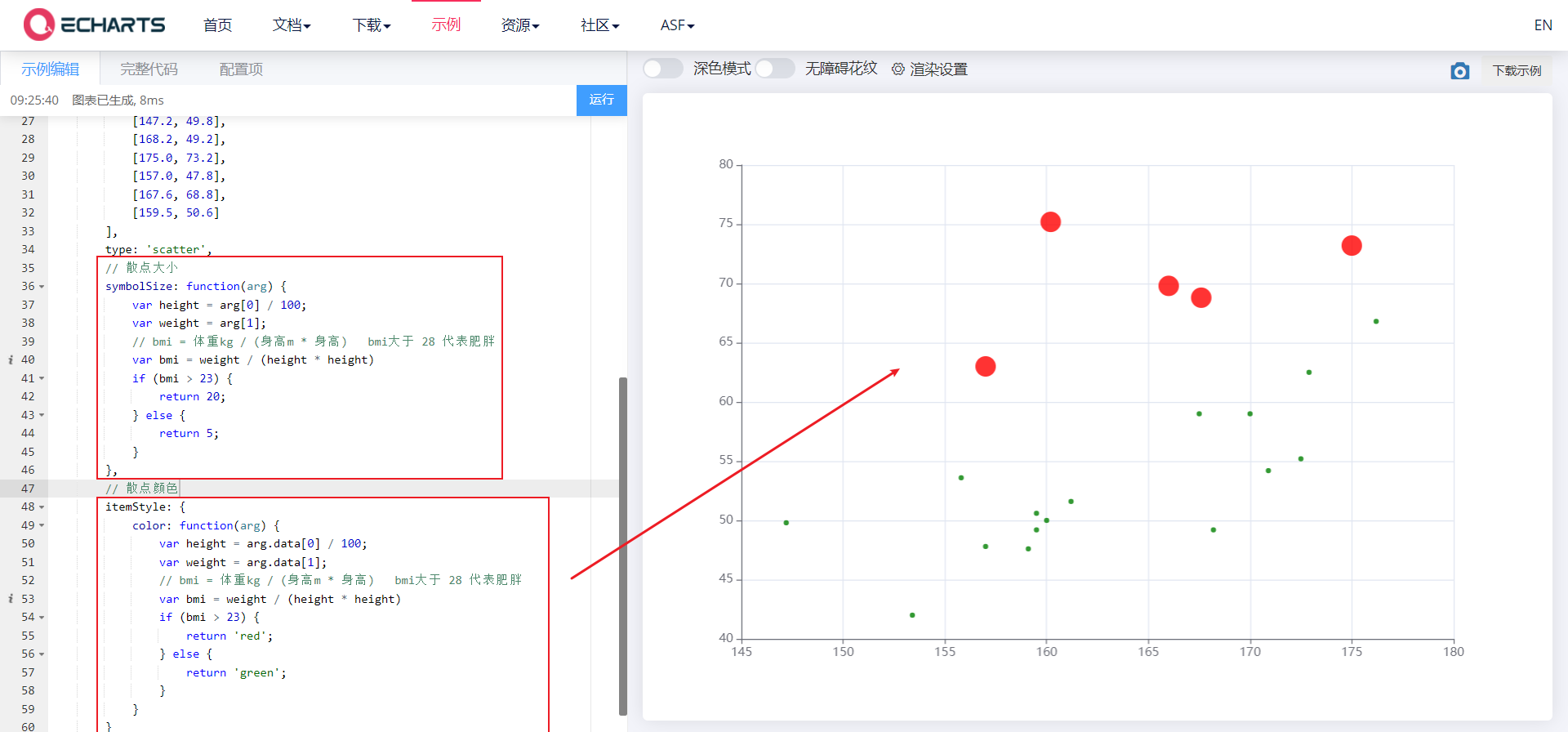
arg is an object as follows:
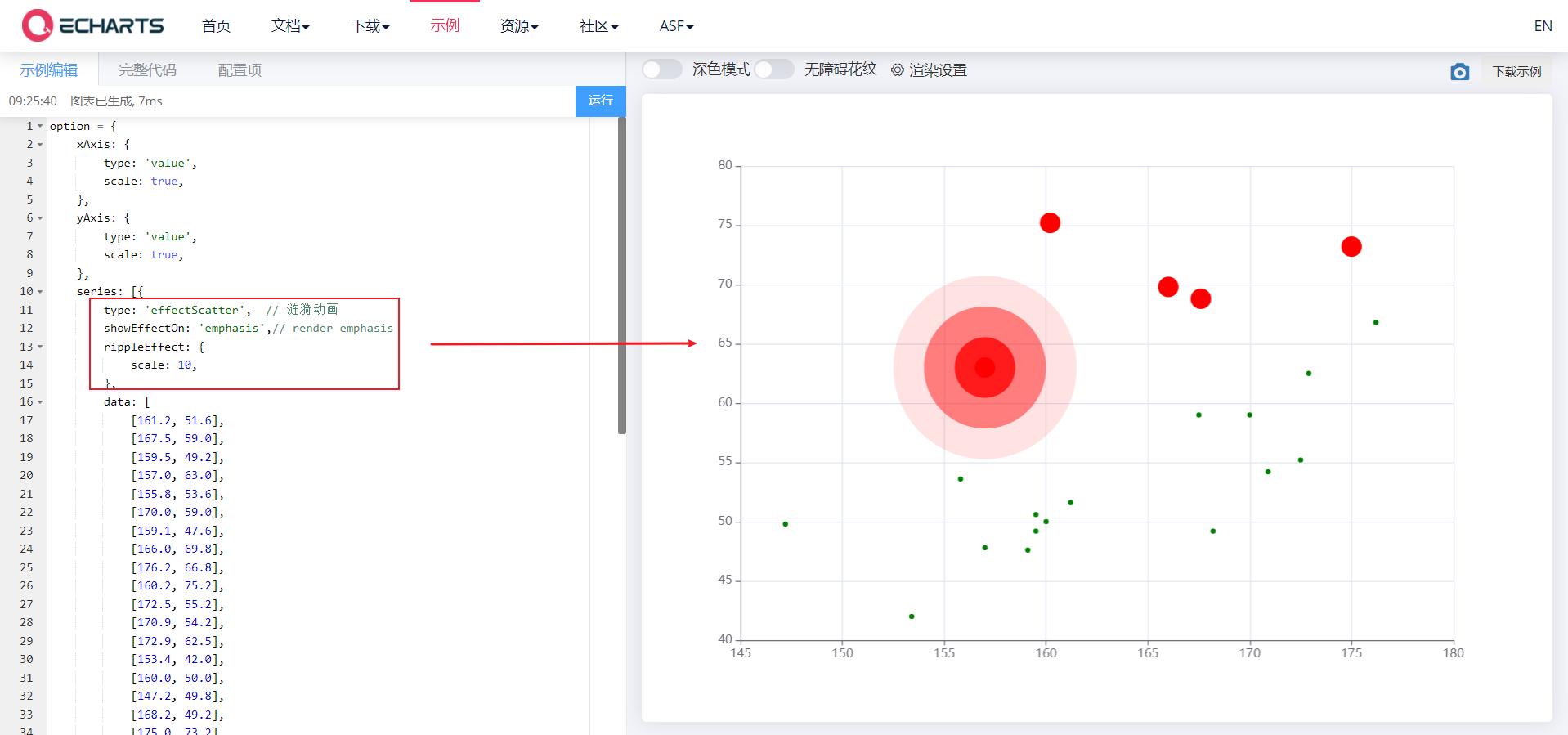
5.1. 2. Ripple animation effect
- type: effectscutter turns on the ripple animation effect
- showEffectOn: 'emphasis' controls the ripple effect when the mouse moves to a scatter point
- rippleEffect: {} controls the ripple animation range
<body>
<!-- 1.Prepare a large and small DOM container -->
<div style="width: 600px;height: 400px"></div>
<script>
// 2. Initialize the ecarts instantiation object
var myChart = echarts.init(document.querySelector('div'));
// 3. Specify the configuration items and data of the chart
var axisData = [
[161.2, 51.6],
[167.5, 59.0],
[159.5, 49.2],
[157.0, 63.0],
[155.8, 53.6],
[170.0, 59.0],
[159.1, 47.6],
[166.0, 69.8],
[176.2, 66.8],
[160.2, 75.2],
[172.5, 55.2],
[170.9, 54.2],
[172.9, 62.5],
[153.4, 42.0],
[160.0, 50.0],
[147.2, 49.8],
[168.2, 49.2],
[175.0, 73.2],
[157.0, 47.8],
[167.6, 68.8],
[159.5, 50.6]
];
var option = {
xAxis: {
type: 'value',
scale: true,
},
yAxis: {
type: 'value',
scale: true,
},
series: [{
//type: 'scatter', / / scatter
type: 'effectScatter', // Ripple animation
showEffectOn: 'emphasis',// render emphasis
rippleEffect: {
scale: 5,
},
data: axisData,
// symbolSize: 20
symbolSize: function(arg) {
var height = arg[0] / 100;
var weight = arg[1];
// bmi = weight kg / (height m * height) bmi greater than 28 represents obesity
var bmi = weight / (height * height)
if (bmi > 28) {
return 20;
} else {
return 5;
}
},
itemStyle: {
color: function(arg) {
var height = arg.data[0] / 100;
var weight = arg.data[1];
// bmi = weight kg / (height m * height) bmi greater than 28 represents obesity
var bmi = weight / (height * height)
if (bmi > 23) {
return 'red';
} else {
return 'green';
}
}
}
}]
}
// 4. Use the configuration item and data just specified to display the chart.
myChart.setOption(option);
</script>
</body>
6. Rectangular coordinate system
- Rectangular coordinate system chart: histogram, broken line chart and scatter chart
6.1 common configuration of rectangular coordinate system
There are three common configurations
- grid Grid
- axis
- Area zoomdatazoom
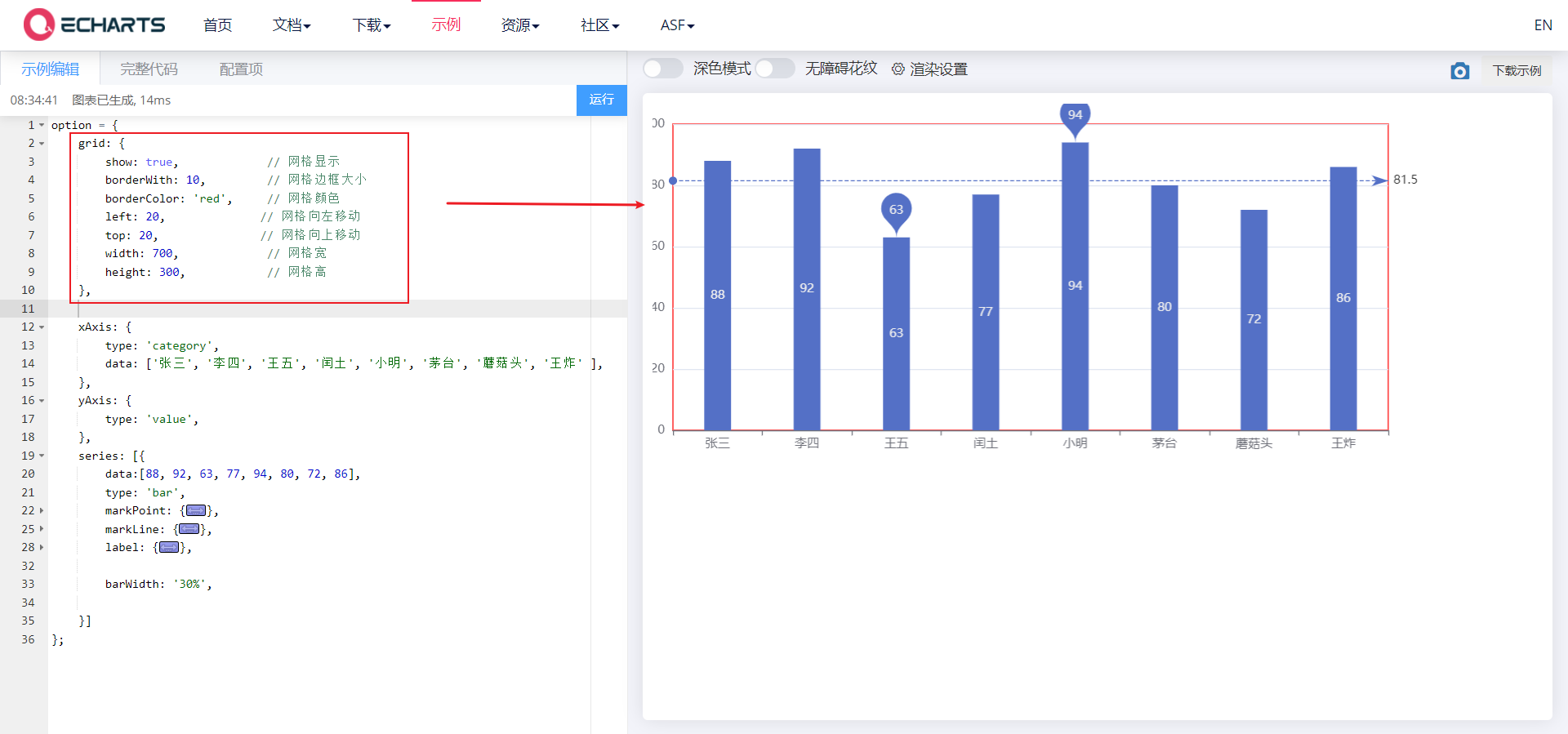
6.1. 1. grid Grid
-
Grid is used to control the layout and size of rectangular coordinate system. x-axis and y-axis are drawn on the basis of grid
-
Display grid
show
-
grid border
borderWidth,borderColor
-
Location and size of grid
left,top,right,bottom | width,height
<body>
<!-- 1.Prepare a large and small DOM container -->
<div style="width: 600px;height: 400px"></div>
<script>
// 2. Initialize the ecarts instantiation object
var myChart = echarts.init(document.querySelector('div'));
// 3. Specify the configuration items and data of the chart
var xDataArr = ['Zhang San', 'Li Si', 'Wang Wu', 'Intercalated soil', 'Xiao Ming', 'Moutai', 'mushroom-shaped umbrella', 'Wang fried', ];
var yDataArr = [88, 92, 63, 77, 94, 80, 72, 86];
var option = {
grid: {
show: true, // Grid display
borderWith: 10, // Grid border size
borderColor: 'red', // Grid color
left: 120, // Move grid left
top: 120, // Move grid up
width: 300, // Grid width
height: 150, // Grid height
},
xAxis: {
type: 'category',
data: xDataArr,
},
yAxis: {
type: 'value',
},
series: [{
name: 'language',
type: 'bar',
data: yDataArr,
markPoint: {
data: [{
type: 'max',
name: 'Maximum'
}, {
type: 'min',
name: 'minimum value'
}]
},
markLine: {
data: [{
type: 'average',
name: 'average value'
}]
},
// Numerical display
label: {
show: true,
rotate: 60, //Rotate 60 °
position: 'inside',
},
// Column width
barWidth: '30%',
}],
};
// 4. Use the configuration item and data just specified to display the chart.
myChart.setOption(option);
</script>
</body>
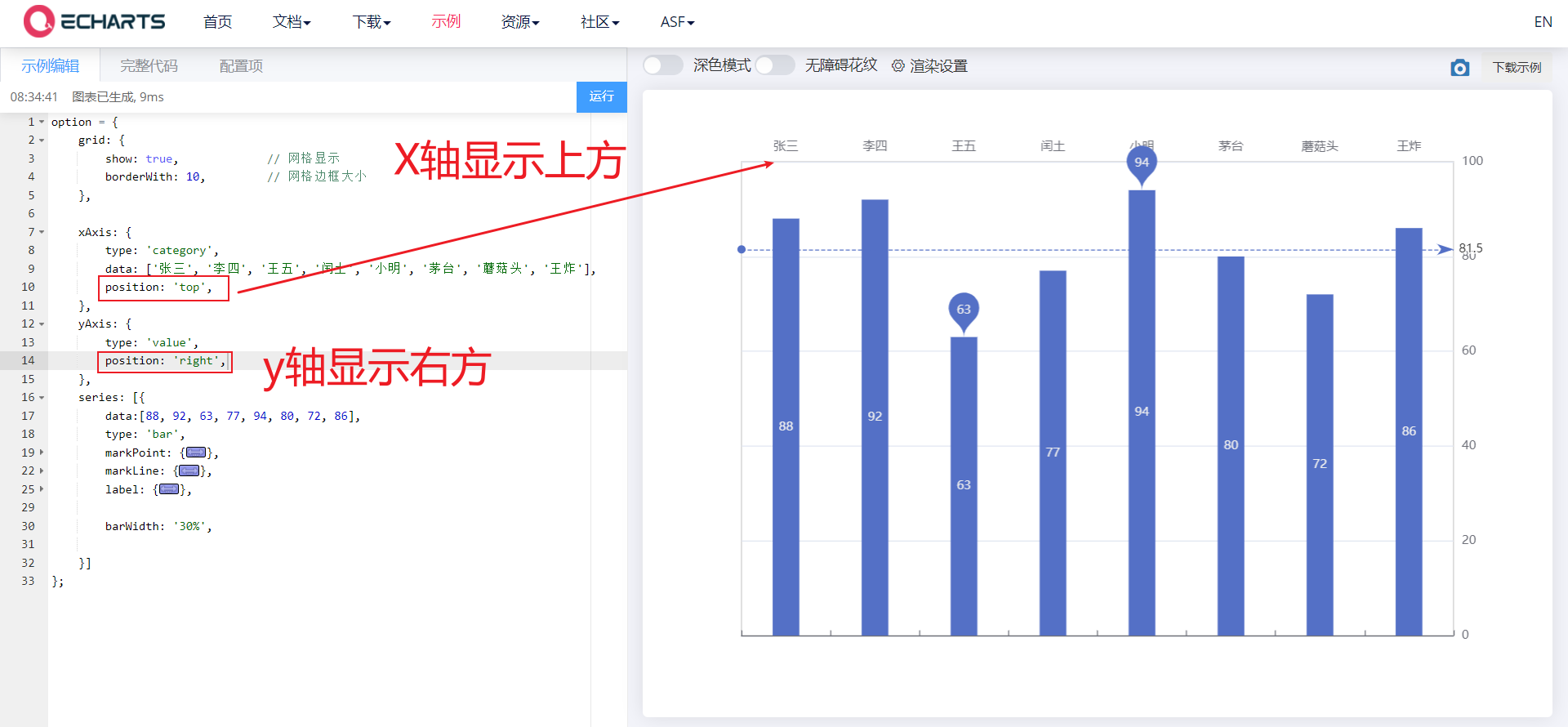
6.1. 2. axis
The coordinate axis is divided into x-axis and y-axis. There are at most two positions of x-axis and y-axis in a grid
- Axis type
- Value: the value axis will be automatically selected from the series Read data from data
- Category: category axis. This type must set category data through data
- Display position
- xAxis: the value can be top or bottom
- yAxis: can be left or right
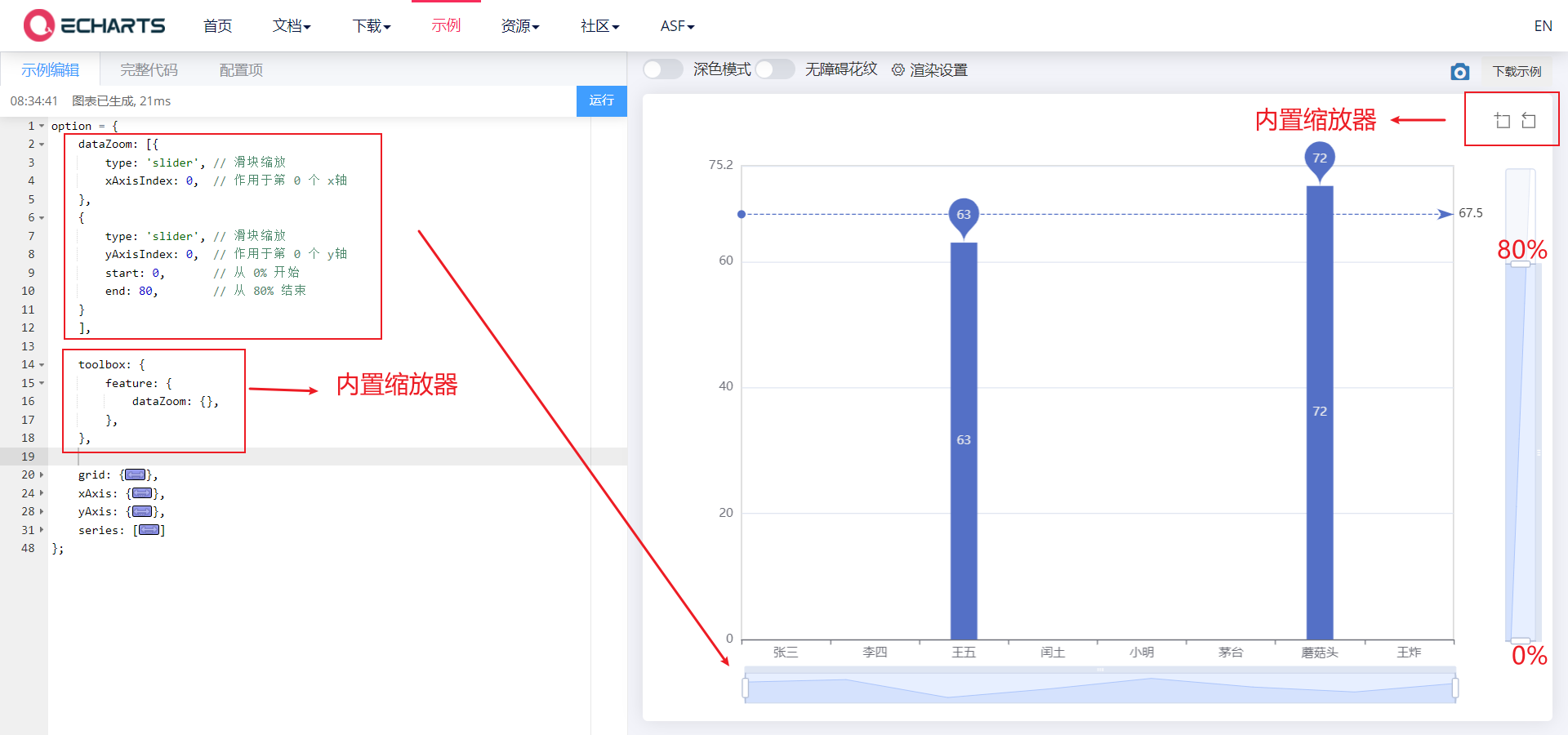
6.1. 3. Area zoomdatazoom
dataZoom is used for area scaling and data range filtering. Both x-axis and y-axis can be used
dataZoom is an array, which means that multiple area scalers can be configured
- Type type
- Slider: slider
- inside: built in, zoom by mouse wheel or two fingers
- Indicates the active axis
- xAxisIndex: set which x-axis is controlled by the scaling component. Generally, write 0
- yAxisIndex: set which y-axis is controlled by the scaling component. Generally, write 0
- Indicates the scaling of the initial state
- start: the starting percentage of the data window range
- End: the end percentage of the data window range
<body>
<!-- 1.Prepare a large and small DOM container -->
<div style="width: 600px;height: 400px"></div>
<script>
// 2. Initialize the ecarts instantiation object
var myChart = echarts.init(document.querySelector('div'));
// 3. Specify the configuration items and data of the chart
var xDataArr = ['Zhang San', 'Li Si', 'Wang Wu', 'Intercalated soil', 'Xiao Ming', 'Moutai', 'mushroom-shaped umbrella', 'Wang fried', ];
var yDataArr = [88, 92, 63, 77, 94, 80, 72, 86];
var option = {
dataZoom: [
{
// type: 'slider', / / slider scaling
type: 'inside', // Mouse Wheel Zoom
xAxisIndex: 0, // Acting on the 0th x-axis
},
{
type: 'inside',
yAxisIndex: 0, // Acting on the 0th y-axis
start: 0,
end: 60,
}
],
toolbox: {
feature: {
// The built-in area scaler needs to be opened before customizing the area scaler
dataZoom: {},
}
},
grid: {
show: true, // Grid display
borderWith: 10, // Grid border size
},
xAxis: {
type: 'category',
data: xDataArr,
position: 'top',
},
yAxis: {
type: 'value',
position: 'right',
},
series: [{
name: 'language',
type: 'bar',
data: yDataArr,
markPoint: {
data: [{
type: 'max',
name: 'Maximum'
}, {
type: 'min',
name: 'minimum value'
}]
},
markLine: {
data: [{
type: 'average',
name: 'average value'
}]
},
// Numerical display
label: {
show: true,
rotate: 60, //Rotate 60 °
position: 'inside',
},
// Column width
barWidth: '30%',
}],
};
// 4. Use the configuration item and data just specified to display the chart.
myChart.setOption(option);
</script>
</body>