Mainstream Message Oriented Middleware
ActiveMQ
summary
from Apache Produce,Java development,support JMS1.1 Agreement and J2EE14 standard. Support a wide range of connection protocols: OpenWire/STOMP/REST/XMPP/AMQP Support multiple voice clients,Support Plug-Ins Convenient management,Easy to configure cluster agent
advantage
be based on AVA,Cross platform operation Can use BC Connect to multiple databases It has perfect interface, monitoring and security mechanism Automatic reconnection and error retry
shortcoming
Less active community RabbitMO At present, the focus is on 60 products Apollo,For 5 Bug Less maintenance It is not suitable for application scenarios with thousands of queues
RabbitMQ
summary
The most popular message oriented middleware high reliability,Support sending confirmation,Delivery confirmation and other characteristics High availability,Support image queue Support Plug-Ins
advantage
be based on Erlang,Support high concurrency Support multiple platforms,Multiple clients,Complete documentation High reliability It has a large-scale application in Internet companies,High community activity
shortcoming
Erlang Voice is relatively small,Not conducive to secondary development Under Agent Architecture,The central node adds latency,Affect performance use AMQP agreement,There is a learning cost to use
RocketMQ
summary
Alibaba team development,Stand the test of double 11 It can ensure strict message order 100 million message accumulation capacity Rich message pull mode
advantage
be based on Java,Facilitate secondary development A single machine supports more than 10000 persistent queues Both memory and disk have a copy of data,Guaranteed performance+High availability More active development,The version update is fast
shortcoming
There are not many types of clients,More mature is Java and C++ No, Web Management interface,Provides a CL(Command line interface) Community attention and maturity are not as good as RabbitMQ
Kafka
summary
LinkedIn Developed a distributed log submission system Unique zoning characteristics,Applicable to big data system High performance and good scalability Replicable, fault tolerant
advantage
Native distributed system Zero copy technology,reduce IO Operation steps,Improve system throughput Fast persistence:Can be in O(1)Message persistence under system overhead Support batch data sending and fetching
shortcoming
More than 64 queues per machine/Partition time,Obvious performance degradation Use short polling mode,Real time depends on the polling interval Consumption failed. Retry is not supported Poor reliability
RabbitMQ related terms
Erlang
Erlang language, developed by Ericsson, is a programming language born for switch software development
characteristic
General concurrency oriented programming language,For distributed systems Virtual machine based interpretation run,Cross platform deployment Inter process context switching is much more efficient than C language With and native Socket Same delay
RabbitMQ is implemented in Erlang at the bottom, so it has high-performance characteristics
AMQP protocol
AMQP (Advanced Message Queuing Protocol) is a network protocol for asynchronous message transmission between processes.
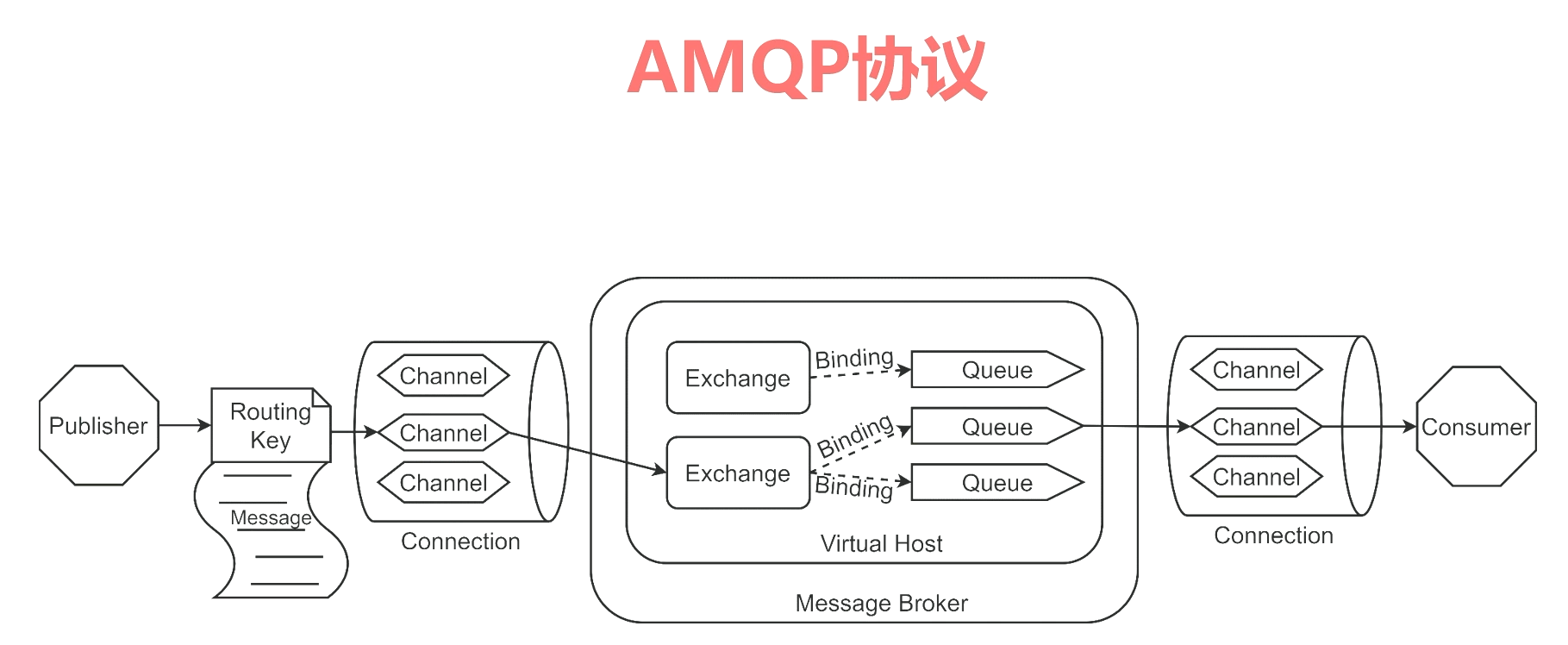
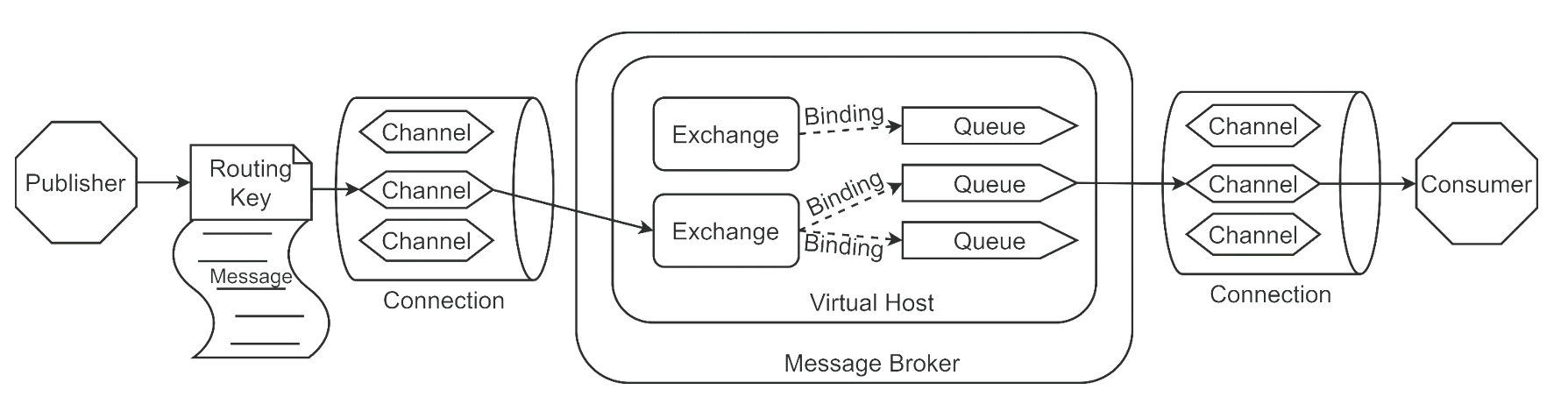
Broker:Applications for receiving and distributing messages, RabbitMQ namely Message Broker Virtual host:fictitious Broker,Isolate multiple units Connection: publisher/ consumer and broker Between TCP connect Channel: connection Internal logical connection,Typically, each thread creates a separate channel Routing Key:Routing key,Used to indicate that the routing forwarding of messages is equivalent to the address of express delivery Exchange:Switch,It is equivalent to the distribution center of express Queue:Message queue,The message was finally sent here to wait consumer Take away Binding: exchange and queue Virtual connection between for message Distribution basis
Exchange
In the implementation of AMQP protocol or RabbitMQ, the core component is Exchange, which undertakes the core function of RabbitMO - routing and forwarding
effect
Exchange yes AMQP Agreement and RabbitMQ Core components of Exchange The function of is to provide a route for the message according to the binding relationship and routing key, and forward the message to the corresponding queue Exchange There are 4 types: Direct/Topic/Fanout/Headers among Headers The former three are mainly used
1.Direct Exchange
Direct Exchange (direct routing). If the Routing Key in the message is consistent with the Binding Key, Direct Exchange sends the message to the corresponding queue
2.Fanout Exchange
For Fanout Exchange (broadcast routing), each message sent to Fanout Exchange will be distributed to all bound queue s
3.Topit Exchange
Topic Exchange: Topic Exchange distributes messages to the target Queue according to the Routing Key and general configuration rules
Full match: similar to Direct
Binding Key Medium#: matches any number of word s Binding Key Medium*:Match any one word
RabbitMQ installation
Windows setup
Installing Erlang OTP https://www.erlang.org/downloads
Install RabbitMQ https://www.rabbitmq.com/
Linux Installation
Docker based installation
docker run -it --rm --name rabbitmq -p 5672:5672 -p 15672:15672 rabbitmq:3-management
Web side management tools
RabbitMQ Web management tools are also called management console and control console The management console is RabbitMQ The most commonly used management and configuration tools The management console is also very useful for business development and debugging
Enable front-end plug-ins
Start application: get into bin Directory execution rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq management Browser open:127.0.0.1:15672 Default user name: guest Default password: guest
function
Overview: viewing nodes/Cluster status Connections: Viewing connection Channels: Viewing channel Switch: view and operate switch status Queue: view and operate queue status Management: advanced management functions
Use of command line tools
Status view
View status: rabbitmqctl status View bindings: rabbitmqctl list_bindings see channel: rabbitmqctl list_channels see connection: rabbitmqctl list_connections View consumer: rabbitmqctl list_consumers View switch: rabbitmqctl list_exchanges View queue: rabbitmqctl list_queues Delete queue: rabbitmqctl delete_queue Empty queue: rabbitmqctl purge_queue
User related
New user: rabbitmqctl add_user Modify user password: rabbitmqctl change_password View user: rabbitmqctl list_users Set user roles: rabbitmqctl rabbitmqctl set_user_tags
Application start stop
Start application: rabbitmqctl start_app Close app: rabbitmqctl stop_app,retain Erlang Virtual machine (paused) Close app: rabbitmqctl stop,And close Erlang virtual machine
Cluster correlation
Join the cluster: rabbitmqctl join_cluster Leave the cluster: rabbitmqctl reset
Mirrored Queues
Set the mirror queue: rabbitmqctl sync_queue Cancel mirror queue: rabbitmqctl cancel_sync_queue
Basic use of RabbitMQ
Add dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
Configuring RabbitMQ
Affirms Exchange Affirms Queue Declare that the switch is bound to the queue
public void initMq(Channel channel) throws IOException, TimeoutException, InterruptedException {
log.info("-------MQ Switch,queue,Binding initialization started---------");
log.info("-------Declare switch start---------");
/**
* Claim switch
* Whether the switch name routing mode is persistent or whether special parameters are automatically deleted
*/
channel.exchangeDeclare("exchange.test", BuiltinExchangeType.DIRECT, true, false, null);
log.info("-------Claim queue start---------");
/**
* Declare a queue
*
* Parameters:
* queue – The name of the queue
* Persistent - true if we declare a persistent queue (the queue will continue to exist after the server is restarted)
* Exclusive – true if we declare an exclusive queue (this connection only)
* autoDelete – true if we declare an auto delete queue (the server will delete it when it is no longer in use)
* Parameters - other properties of the queue (construction parameters)
*/
channel.queueDeclare("queue.test", true, false, false, null);
log.info("-------Declare the binding relationship between switch and queue---------");
/**
* Bind queue to switch
*
* Parameters:
* queue – The name of the queue
* exchange – Name of exchange
* routingKey – Routing key for binding
*/
channel.queueBind("queue.test", "exchange.test", "key.test");
}
Consumer monitoring message
To use asynchronous threads and newly opened threads for message listening, you need to create a thread pool to prevent thread explosion
Configure thread pool
Processing flow of ThredPoolTaskExcutor
When the pool size is less than corePoolSize,Create a new thread and process the request When the pool size is equal to corePoolSize,Put the request in workQueue The idle threads in the pool go workQueue Fetch and process tasks When workQueue When the task cannot be placed, a new thread will be created into the pool and handle the request. If the pool size is too large maximumPoolSize,Just use RejectedExecutionHandler For rejection When the number of threads in the pool is greater than corePoolSize When, extra threads wait keepAliveTime For a long time, if there is no request to deal with, it will be destroyed by itself
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
public class AsyncTaskConfig implements AsyncConfigurer {
@Override
@Bean
public Executor getAsyncExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
//Set the number of core threads
threadPool.setCorePoolSize(10);
//Set the maximum number of threads
threadPool.setMaxPoolSize(100);
//The buffer queue used by the thread pool
threadPool.setQueueCapacity(10);
//Waiting for the task to complete at shutdown -- indicates waiting for all threads to complete execution
threadPool.setWaitForTasksToCompleteOnShutdown(true);
// The waiting time (0 by default, which will stop immediately) is not forced to stop after xx seconds
threadPool.setAwaitTerminationSeconds(60);
// Thread name prefix
threadPool.setThreadNamePrefix("MQ-Async-");
// Initialize thread
threadPool.initialize();
return threadPool;
}
@Override
public AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler() {
return null;
}
}
Message listening method
private void startMessageMonitoring(Channel channel) throws IOException {
log.info("-------Consumer monitoring starts---------");
/**
* Use the server generated consumerTag to start non local and non exclusive consumers.
* Only basic Deliver and basic Cancel access to the AMQP method (this is sufficient for most cases). View the method with the Consumer parameter to access all application callbacks.
*
* Parameters:
* queue – The name of the queue
* autoAck – True if the server should consider that the message is confirmed once sent; false if the server should expect explicit confirmation
* DeliverCallback – Callback when delivering message
* cancelCallback – Callback when consumer cancels
*/
channel.basicConsume("queue.test", true, deliverCallback, cancelCallback);
while (true) {
}
}
DeliverCallback deliverCallback = (consumerTag, message) -> {
log.info("-------Consumer receives message,Start processing---------");
String messageBody = new String(message.getBody());
log.info("Received message:{}", messageBody);
};
CancelCallback cancelCallback = (consumerTag) -> {
log.info("-------Callback when consumer cancels---------");
};
Listening call configuration
/**
* Add @ Configuration annotation to this class
*
* When the project starts, asynchronously obtain a thread from the thread pool to perform MQ initialization and queue listening
*
* @throws IOException
* @throws TimeoutException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
@Async
@Autowired
public void messageMonitoring() throws IOException, TimeoutException, InterruptedException {
log.info("-------Create connection start---------");
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost("IP");
try (Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel()) {
this.initMq(channel);
this.startMessageMonitoring(channel);
}
}
Producer sends message
public static void sendMsg(long number) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost("IP");
try (Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel()) {
log.info("Producer sends message:{}", number);
channel.basicPublish("exchange.test", "key.test", null, String.valueOf(number).getBytes());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
sendMsg(i);
}
}
Perform test
Start project
INFO 14360 --- [ restartedMain] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : -------Create connection start--------- INFO 14360 --- [ restartedMain] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : -------MQ Switch,queue,Binding initialization started--------- INFO 14360 --- [ restartedMain] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : -------Declare switch start--------- INFO 14360 --- [ restartedMain] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : -------Claim queue start--------- INFO 14360 --- [ restartedMain] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : -------Declare the binding relationship between switch and queue--------- INFO 14360 --- [ restartedMain] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : -------Consumer monitoring starts---------
send message
[main] INFO com.example.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig - Producer sends message:0 [main] INFO com.example.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig - Producer sends message:1 [main] INFO com.example.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig - Producer sends message:2 [main] INFO com.example.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig - Producer sends message:3 [main] INFO com.example.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig - Producer sends message:4
Message listening
INFO 14360 --- [pool-1-thread-4] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : -------Consumer receives message,Start processing--------- INFO 14360 --- [pool-1-thread-4] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Received message:0 INFO 14360 --- [pool-1-thread-5] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : -------Consumer receives message,Start processing--------- INFO 14360 --- [pool-1-thread-5] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Received message:1 INFO 14360 --- [pool-1-thread-6] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : -------Consumer receives message,Start processing--------- INFO 14360 --- [pool-1-thread-6] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Received message:2 INFO 14360 --- [pool-1-thread-7] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : -------Consumer receives message,Start processing--------- INFO 14360 --- [pool-1-thread-7] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Received message:3 INFO 14360 --- [pool-1-thread-8] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : -------Consumer receives message,Start processing--------- INFO 14360 --- [pool-1-thread-8] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Received message:4
How to ensure the reliability of messages
Sender
use RabbitMQ The sender side confirms that the confirmation message is successfully sent to RabbitMQ And processed use RabbitMQ Message return mechanism. If the target queue is not found, the middleware will notify the sender
Sender acknowledgement mechanism
After the message is sent, if the middleware receives the message, it will give a reply to the sender The producer receives the response to confirm whether the message is sent to the middleware normally
Three confirmation mechanisms
Single synchronization confirmation Multiple synchronization confirmation Asynchronous acknowledgement
###Single synchronization confirmation mechanism
to configure channel,Enable confirmation mode: channel.confirmSelect() Each time a message is sent, call channel.waitForConfirms()Method, waiting for confirmation
public static void sendMsg(long number) throws IOException, TimeoutException, InterruptedException {
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost("IP");
try (Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel()) {
channel.confirmSelect();
log.info("Producer sends message:{}", number);
channel.basicPublish("exchange.test", "key.test", null, String.valueOf(number).getBytes());
if (channel.waitForConfirms()){
log.info("MQ confirm success");
}else {
log.info("MQ confirm failed");
}
}
}
22:56:05.072 [main] INFO com.example.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig - Producer sends message:0 22:56:05.151 [main] INFO com.example.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig - MQ confirm success 22:56:05.714 [main] INFO com.example.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig - Producer sends message:1 22:56:05.776 [main] INFO com.example.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig - MQ confirm success
Multiple synchronization confirmation mechanism
to configure channel,Enable confirmation mode: channel.confirmSelect() After sending multiple messages, call channel.waitForConfirms()Method, waiting for confirmation
public static void sendMsg(long number) throws IOException, TimeoutException, InterruptedException {
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost("IP");
try (Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel()) {
channel.confirmSelect();
log.info("Producer sends message:{}", number);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
channel.basicPublish("exchange.test", "key.test", null, String.valueOf(number).getBytes());
}
if (channel.waitForConfirms()){
log.info("MQ confirm success");
}else {
log.info("MQ confirm failed");
}
}
}
Producer sends message
22:59:36.793 [main] INFO com.example.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig - Producer sends message:0 22:59:36.893 [main] INFO com.example.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig - MQ confirm success
Consumer monitoring message
INFO 2692 --- [ool-1-thread-12] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : -------Consumer receives message,Start processing--------- INFO 2692 --- [ool-1-thread-12] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Received message:0 INFO 2692 --- [ool-1-thread-13] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : -------Consumer receives message,Start processing--------- INFO 2692 --- [ool-1-thread-13] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Received message:0 INFO 2692 --- [ool-1-thread-13] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : -------Consumer receives message,Start processing--------- INFO 2692 --- [ool-1-thread-13] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Received message:0 INFO 2692 --- [ool-1-thread-13] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : -------Consumer receives message,Start processing--------- INFO 2692 --- [ool-1-thread-13] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Received message:0 INFO 2692 --- [ool-1-thread-13] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : -------Consumer receives message,Start processing--------- INFO 2692 --- [ool-1-thread-13] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Received message:0
Asynchronous synchronous acknowledgement mechanism
to configure channel,Enable confirmation mode: channel.confirmSelect() stay channel Add listening on: addConfirmListener,After sending a message, this method will be called back to notify whether the message was sent successfully Asynchronous acknowledgement may be a single message,It can also be multiple,depend on MQ
public static void sendMsg(long number) throws IOException, TimeoutException, InterruptedException {
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost("IP");
try (Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel()) {
channel.confirmSelect();
ConfirmListener confirmListener=new ConfirmListener() {
/**
*
* @param deliveryTag The number of the message sent, the number of the item
* @param multiple Confirm multiple messages, TRUE: confirm multiple messages
* @throws IOException
*/
@Override
public void handleAck(long deliveryTag, boolean multiple) throws IOException {
log.info("handleAck,deliveryTag:{},multiple:{}",deliveryTag,multiple);
}
@Override
public void handleNack(long deliveryTag, boolean multiple) throws IOException {
log.info("handleNack,deliveryTag:{},multiple:{}",deliveryTag,multiple);
}
};
channel.addConfirmListener(confirmListener);
log.info("Producer sends message:{}", number);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
channel.basicPublish("exchange.test", "key.test", null, String.valueOf(number).getBytes());
}
Thread.sleep(5000);
}
}
INFO 2692 --- [ool-1-thread-12] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : -------Consumer receives message,Start processing--------- INFO 2692 --- [ool-1-thread-12] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Received message:0 INFO 2692 --- [ool-1-thread-13] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : -------Consumer receives message,Start processing--------- INFO 2692 --- [ool-1-thread-13] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Received message:0 INFO 2692 --- [ool-1-thread-13] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : -------Consumer receives message,Start processing--------- INFO 2692 --- [ool-1-thread-13] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Received message:0 INFO 2692 --- [ool-1-thread-13] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : -------Consumer receives message,Start processing--------- INFO 2692 --- [ool-1-thread-13] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Received message:0 INFO 2692 --- [ool-1-thread-13] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : -------Consumer receives message,Start processing--------- INFO 2692 --- [ool-1-thread-13] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Received message:0
23:07:14.580 [main] INFO com.example.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig - Producer sends message:0 23:07:14.657 [AMQP Connection ip:5672] INFO com.example.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig - handleAck,deliveryTag:1,multiple:false 23:07:14.666 [AMQP Connection ip:5672] INFO com.example.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig - handleAck,deliveryTag:5,multiple:true
Message return mechanism
Opening method
stay RabbitMQ There is a key configuration item in the basic configuration: Mandatory Mandatory if it is false,RabbitMQ Messages that cannot be routed will be discarded directly Mandatory if it is true,RabbitMQ Will process messages that cannot be routed
public static void sendMsg(long number) throws IOException, TimeoutException, InterruptedException {
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost("IP");
try (Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel()) {
channel.confirmSelect();
ConfirmListener confirmListener=new ConfirmListener() {
/**
*
* @param deliveryTag The number of the message sent, the number of the item
* @param multiple Confirm multiple messages, TRUE: confirm multiple messages
* @throws IOException
*/
@Override
public void handleAck(long deliveryTag, boolean multiple) throws IOException {
log.info("handleAck,deliveryTag:{},multiple:{}",deliveryTag,multiple);
}
@Override
public void handleNack(long deliveryTag, boolean multiple) throws IOException {
log.info("handleNack,deliveryTag:{},multiple:{}",deliveryTag,multiple);
}
};
channel.addConfirmListener(confirmListener);
//Add message return mechanism
// channel.addReturnListener(new ReturnListener() {
// @Override
// public void handleReturn(int replyCode, String replyText, String exchange, String routingKey, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
// log.info("handleReturn,replyCode:{},replyText:{},exchange:{},routingKey:{},properties:{},replyText:{}",replyCode,replyText,exchange,routingKey,properties,new String(body));
// }
// });
channel.addReturnListener(new ReturnCallback() {
@Override
public void handle(Return returnMessage) {
log.info("handleReturn,replyCode:{},replyText:{},exchange:{},routingKey:{},properties:{},replyText:{}",returnMessage.getReplyCode(),returnMessage.getReplyText(),returnMessage.getExchange(),returnMessage.getRoutingKey(),returnMessage.getProperties(),new String(returnMessage.getBody()));
}
});
log.info("Producer sends message:{}", number);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
// Mandatory: enable message return mechanism
channel.basicPublish("exchange.test", "key.test222222", true,null, String.valueOf(number).getBytes());
}
Thread.sleep(5000);
}
}
23:31:29.263 [main] INFO com.example.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig - Producer sends message:0 23:31:29.339 [AMQP Connection ip:5672] INFO com.example.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig - handleReturn,replyCode:312,replyText:NO_ROUTE,exchange:exchange.test,routingKey:key.test222222,properties:#contentHeader<basic>(content-type=null, content-encoding=null, headers=null, delivery-mode=null, priority=null, correlation-id=null, reply-to=null, expiration=null, message-id=null, timestamp=null, type=null, user-id=null, app-id=null, cluster-id=null),replyText:0 23:31:29.339 [AMQP Connection ip:5672] INFO com.example.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig - handleAck,deliveryTag:1,multiple:false 23:31:29.346 [AMQP Connection ip:5672] INFO com.example.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig - handleReturn,replyCode:312,replyText:NO_ROUTE,exchange:exchange.test,routingKey:key.test222222,properties:#contentHeader<basic>(content-type=null, content-encoding=null, headers=null, delivery-mode=null, priority=null, correlation-id=null, reply-to=null, expiration=null, message-id=null, timestamp=null, type=null, user-id=null, app-id=null, cluster-id=null),replyText:0 23:31:29.346 [AMQP Connection ip:5672] INFO com.example.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig - handleAck,deliveryTag:2,multiple:false 23:31:29.346 [AMQP Connection ip:5672] INFO com.example.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig - handleReturn,replyCode:312,replyText:NO_ROUTE,exchange:exchange.test,routingKey:key.test222222,properties:#contentHeader<basic>(content-type=null, content-encoding=null, headers=null, delivery-mode=null, priority=null, correlation-id=null, reply-to=null, expiration=null, message-id=null, timestamp=null, type=null, user-id=null, app-id=null, cluster-id=null),replyText:0 23:31:29.346 [AMQP Connection ip:5672] INFO com.example.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig - handleAck,deliveryTag:3,multiple:false 23:31:29.347 [AMQP Connection ip:5672] INFO com.example.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig - handleReturn,replyCode:312,replyText:NO_ROUTE,exchange:exchange.test,routingKey:key.test222222,properties:#contentHeader<basic>(content-type=null, content-encoding=null, headers=null, delivery-mode=null, priority=null, correlation-id=null, reply-to=null, expiration=null, message-id=null, timestamp=null, type=null, user-id=null, app-id=null, cluster-id=null),replyText:0 23:31:29.347 [AMQP Connection ip:5672] INFO com.example.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig - handleAck,deliveryTag:4,multiple:false 23:31:29.347 [AMQP Connection ip:5672] INFO com.example.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig - handleReturn,replyCode:312,replyText:NO_ROUTE,exchange:exchange.test,routingKey:key.test222222,properties:#contentHeader<basic>(content-type=null, content-encoding=null, headers=null, delivery-mode=null, priority=null, correlation-id=null, reply-to=null, expiration=null, message-id=null, timestamp=null, type=null, user-id=null, app-id=null, cluster-id=null),replyText:0 23:31:29.347 [AMQP Connection ip:5672] INFO com.example.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig - handleAck,deliveryTag:5,multiple:false
Consumer
Need to use RabbitMQ The consumer side confirms that there is no processing exception for the confirmation message Need to use RabbitMQ The flow limiting mechanism at the consumer end limits the message push speed and ensures the stability of the service at the receiving end
Consumer confirmation mechanism
Consumer ACK type
automatic ACK:After receiving the message, the consumer will automatically sign in the message Manual ACK:After receiving the message, the consumer will not automatically sign in the message, and needs to explicitly sign in the business code
Manual ACK type
Single manual ACK:multiple=false Multiple manual ACK:multiple=true Single is recommended ACK
private void startMessageMonitoring(Channel channel) throws IOException {
log.info("-------Consumer monitoring starts---------");
/**
* Use the server generated consumerTag to start non local and non exclusive consumers.
* Only basic Deliver and basic Cancel access to the AMQP method (this is sufficient for most cases). View the method with the Consumer parameter to access all application callbacks.
*
* Parameters:
* queue – The name of the queue
* autoAck – True if the server should consider that the message is confirmed once sent; false if the server should expect explicit confirmation
* DeliverCallback – Callback when delivering message
* cancelCallback – Callback when consumer cancels
*/
//Autoack: true -- > false, manual sign in
channel.basicConsume("queue.test", false, new DeliverCallback() {
@Override
public void handle(String consumerTag, Delivery message) throws IOException {
log.info("-------Consumer receives message,Start processing---------");
String messageBody = new String(message.getBody());
log.info("Received message:{}", messageBody);
// Manually sign in messages
log.info("Manual sign in DeliveryTa:{}",message.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag());
channel.basicAck(message.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(), false);
// Sign in every 5 messages
//if (message.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag() % 5==0){
// channel.basicAck(message.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(), true);
//}
}
}, cancelCallback);
while (true) {
}
}
DeliverCallback deliverCallback = (consumerTag, message) -> {
log.info("-------Consumer receives message,Start processing---------");
String messageBody = new String(message.getBody());
log.info("Received message:{}", messageBody);
};
CancelCallback cancelCallback = (consumerTag) -> {
log.info("-------Callback when consumer cancels---------");
};
23:58:58.213 [main] INFO com.example.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig - Producer sends message:0 23:58:58.285 [AMQP Connection ip:5672] INFO com.example.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig - handleAck,deliveryTag:1,multiple:false 23:58:58.292 [AMQP Connection ip:5672] INFO com.example.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig - handleAck,deliveryTag:5,multiple:true
INFO 3272 --- [pool-1-thread-4] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : -------Consumer receives message,Start processing--------- INFO 3272 --- [pool-1-thread-4] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Received message:0 INFO 3272 --- [pool-1-thread-4] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Manual sign in DeliveryTa:1 INFO 3272 --- [pool-1-thread-5] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : -------Consumer receives message,Start processing--------- INFO 3272 --- [pool-1-thread-5] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Received message:0 INFO 3272 --- [pool-1-thread-5] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Manual sign in DeliveryTa:2 INFO 3272 --- [pool-1-thread-5] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : -------Consumer receives message,Start processing--------- INFO 3272 --- [pool-1-thread-5] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Received message:0 INFO 3272 --- [pool-1-thread-5] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Manual sign in DeliveryTa:3 INFO 3272 --- [pool-1-thread-5] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : -------Consumer receives message,Start processing--------- INFO 3272 --- [pool-1-thread-5] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Received message:0 INFO 3272 --- [pool-1-thread-5] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Manual sign in DeliveryTa:4 INFO 3272 --- [pool-1-thread-5] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : -------Consumer receives message,Start processing--------- INFO 3272 --- [pool-1-thread-5] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Received message:0 INFO 3272 --- [pool-1-thread-5] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Manual sign in DeliveryTa:5
Return to queue
If the callback queue is set, the message is NACK After that, it will return to the end of the queue and wait for further processing It is generally not recommended to open the replay queue, because it is basically an exception to process an exception message for the first time and again
//Autoack: true -- > false, manual sign in
channel.basicConsume("queue.test", false, new DeliverCallback() {
@Override
public void handle(String consumerTag, Delivery message) throws IOException {
log.info("-------Consumer receives message,Start processing---------");
String messageBody = new String(message.getBody());
log.info("Received message:{}", messageBody);
// Manual sign in message multiple:false: sign in single, true: sign in multiple
//log.info("manually sign in deliveryta: {}", message. Getenvelope() getDeliveryTag());
//channel.basicAck(message.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(), false);
// Sign in every 5 messages
//if (message.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag() % 5==0){
// channel.basicAck(message.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(), true);
//}
//Manually reject and return to the queue
log.info("Manual rejection,Return to queue,rejection DeliveryTa:{}",message.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag());
channel.basicNack(message.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(), false,true);
}
}, cancelCallback);
INFO 11212 --- [ool-1-thread-18] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Manual rejection,Return to queue,rejection DeliveryTa:1365 INFO 11212 --- [ool-1-thread-18] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : -------Consumer receives message,Start processing--------- INFO 11212 --- [ool-1-thread-18] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Received message:0 INFO 11212 --- [ool-1-thread-18] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Manual rejection,Return to queue,rejection DeliveryTa:1366 INFO 11212 --- [ool-1-thread-18] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : -------Consumer receives message,Start processing--------- INFO 11212 --- [ool-1-thread-18] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Received message:0 INFO 11212 --- [ool-1-thread-18] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Manual rejection,Return to queue,rejection DeliveryTa:1367 INFO 11212 --- [ool-1-thread-18] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : -------Consumer receives message,Start processing--------- INFO 11212 --- [ool-1-thread-18] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Received message:0 INFO 11212 --- [ool-1-thread-18] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Manual rejection,Return to queue,rejection DeliveryTa:1368 INFO 11212 --- [ool-1-thread-18] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : -------Consumer receives message,Start processing--------- INFO 11212 --- [ool-1-thread-18] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Received message:0 INFO 11212 --- [ool-1-thread-18] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitMQConfig : Manual rejection,Return to queue,rejection DeliveryTa:1369
Consumer end current limiting mechanism
QOS of RabbitMQ
QoS Service quality assurance function It ensures that a certain number of messages are not confirmed,Don't consume new news QoS The premise of the function is that automatic confirmation is not used
QoS principle
QoS The principle is that when a certain number of messages on the consumer end are not received ACK When confirming RabbitMQ Do not push new messages to the consumer RabbitMQ use QoS The mechanism realizes the current limit at the consumer end
Parameter setting of consumer end current limiting mechanism
ρrefetch Count:How many unconfirmed messages can be pushed for a consumer global:true Current limiting for the entire consumer end false:For the current channel prefetch size:0(Single message size limit,Generally 0) prefetch Size And globa Two items, RabbitmQ Temporarily not implemented
Current limiting is not used
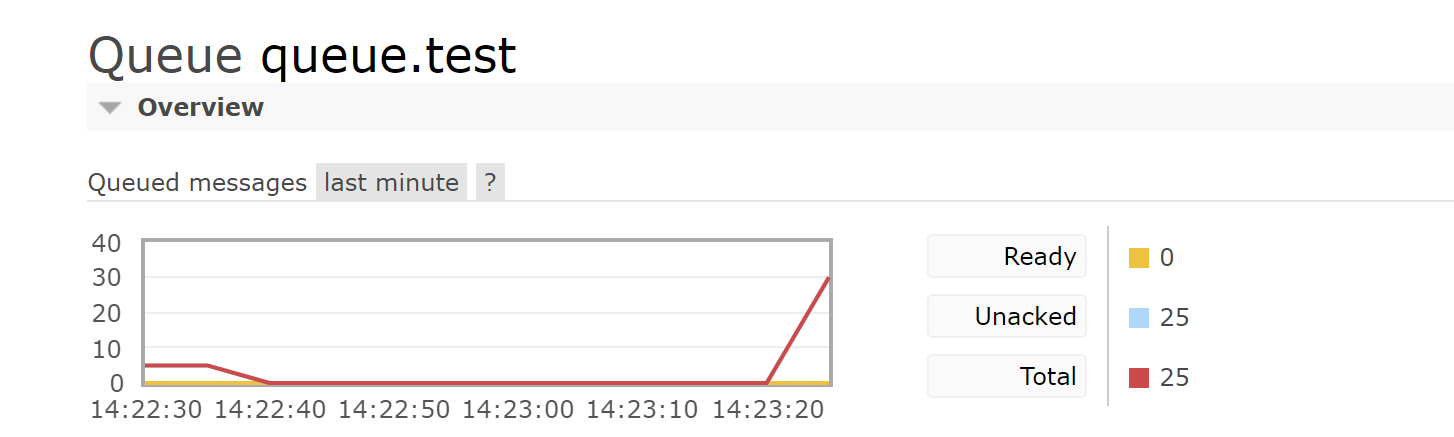
The message producer sends multiple messages at once Message listener thread every 1 s Execute a sign in Consumer initiated service,Receive all sent messages at once
private void startMessageMonitoring(Channel channel) throws IOException {
log.info("-------Consumer monitoring starts---------");
//Autoack: true -- > false, manual sign in
channel.basicConsume("queue.test", false, new DeliverCallback() {
@Override
public void handle(String consumerTag, Delivery message) throws IOException {
log.info("-------Consumer receives message,Start processing---------");
String messageBody = new String(message.getBody());
log.info("Received message:{}", messageBody);
// Sign in every second
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Manually sign in messages
log.info("Manual sign in DeliveryTa:{}",message.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag());
channel.basicAck(message.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
}, cancelCallback);
while (true) {
}
}
DeliverCallback deliverCallback = (consumerTag, message) -> {
log.info("-------Consumer receives message,Start processing---------");
String messageBody = new String(message.getBody());
log.info("Received message:{}", messageBody);
};
CancelCallback cancelCallback = (consumerTag) -> {
log.info("-------Callback when consumer cancels---------");
};
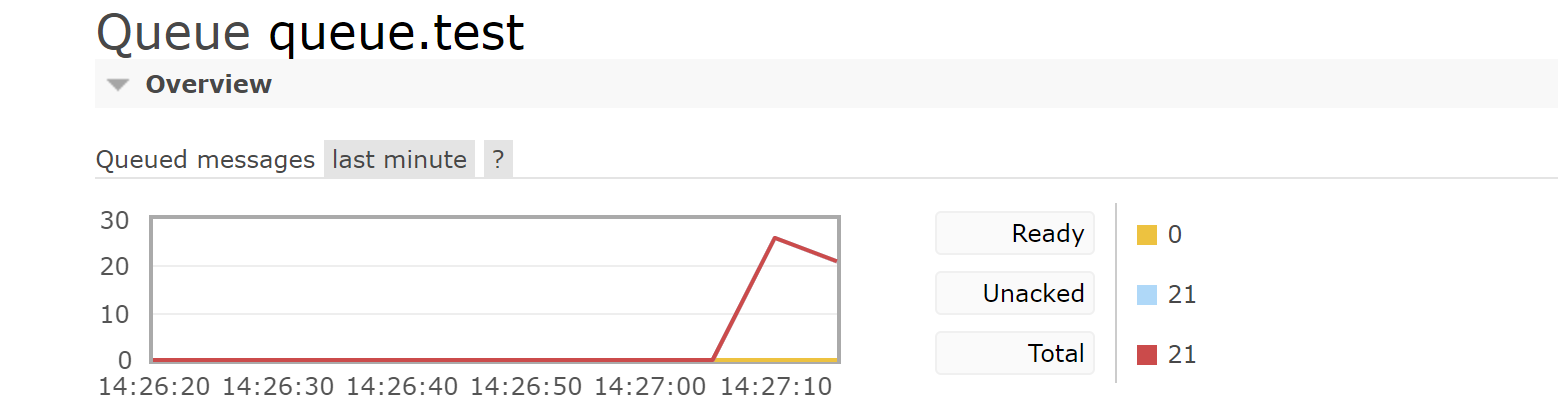
Use current limiting
Set prefetchCount value
private void startMessageMonitoring(Channel channel) throws IOException {
log.info("-------Consumer monitoring starts---------");
// How many unconfirmed messages can be pushed for a consumer
channel.basicQos(2);
//Autoack: true -- > false, manual sign in
channel.basicConsume("queue.test", false, new DeliverCallback() {
@Override
public void handle(String consumerTag, Delivery message) throws IOException {
log.info("-------Consumer receives message,Start processing---------");
String messageBody = new String(message.getBody());
log.info("Received message:{}", messageBody);
// Sign in every second
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Manually sign in messages
log.info("Manual sign in DeliveryTa:{}",message.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag());
channel.basicAck(message.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(), false);
}, cancelCallback);
while (true) {
}
}
DeliverCallback deliverCallback = (consumerTag, message) -> {
log.info("-------Consumer receives message,Start processing---------");
String messageBody = new String(message.getBody());
log.info("Received message:{}", messageBody);
};
CancelCallback cancelCallback = (consumerTag) -> {
log.info("-------Callback when consumer cancels---------");
};
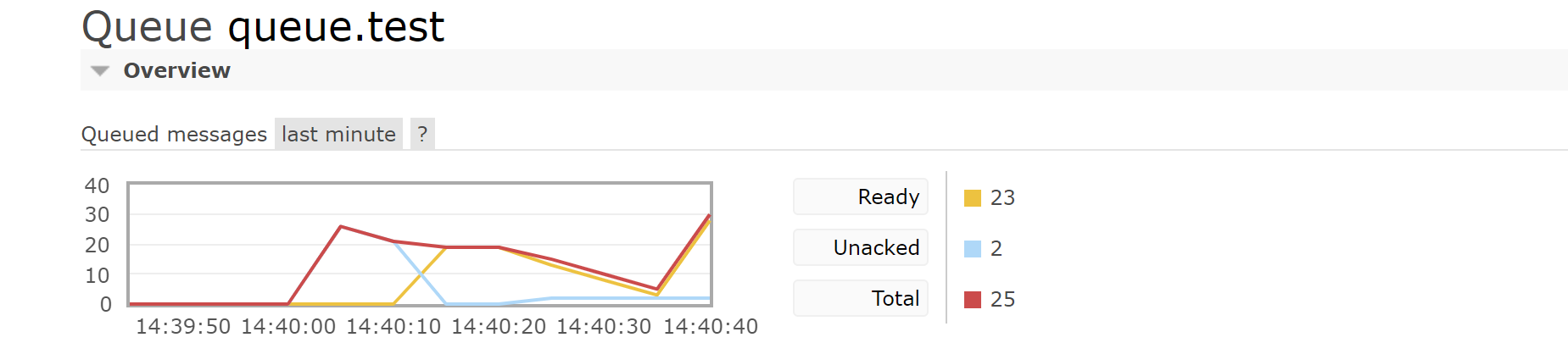
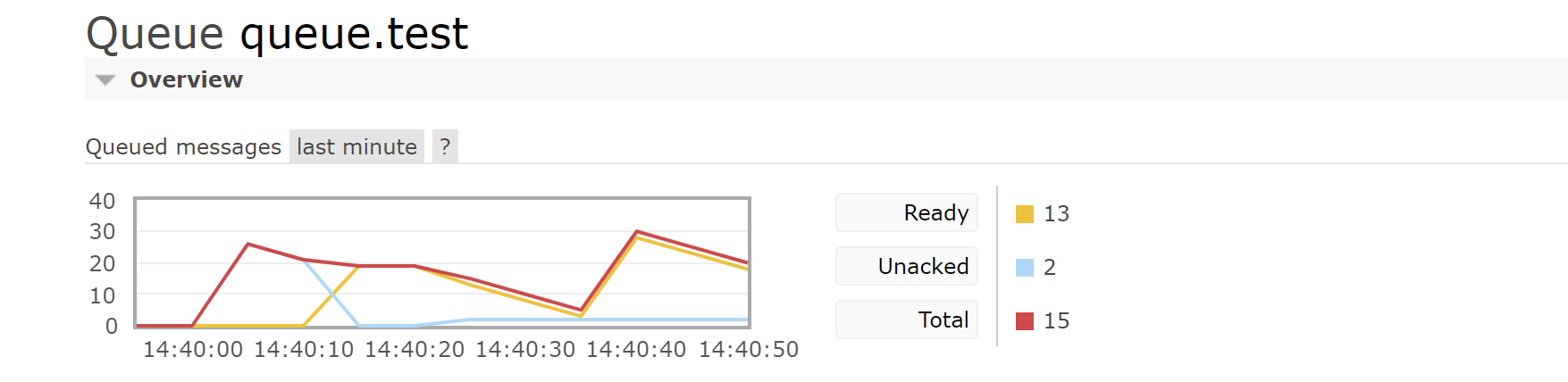
RabbitMQ
A large number of accumulated messages will put great pressure on RabbitMQ. RabbitMQ message expiration mechanism needs to be used to prevent a large number of messages from being overstocked
After expiration, it will be discarded directly and cannot alert the system for abnormal operation. RabbitMQ dead letter queue needs to be used to collect expired messages for analysis
Message expiration mechanism
Expiration time TTL of RabbitMQ
Rabbitmo The expiration time of is called TTL( Time to live),survival time RabbitMQ The expiration time of is divided into messages T And queue TTL news TTL Set the expiration time of a single message queue TTL Set the expiration time of all messages in the queue
Message expiration time
public static void sendMsg(long number) throws IOException, TimeoutException, InterruptedException {
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost("IP");
try (Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel()) {
channel.confirmSelect();
ConfirmListener confirmListener = new ConfirmListener() {
/**
*
* @param deliveryTag The number of the message sent, the number of the item
* @param multiple Confirm multiple messages, TRUE: confirm multiple messages
* @throws IOException
*/
@Override
public void handleAck(long deliveryTag, boolean multiple) throws IOException {
log.info("handleAck,deliveryTag:{},multiple:{}", deliveryTag, multiple);
}
@Override
public void handleNack(long deliveryTag, boolean multiple) throws IOException {
log.info("handleNack,deliveryTag:{},multiple:{}", deliveryTag, multiple);
}
};
channel.addConfirmListener(confirmListener);
//Add message return mechanism
channel.addReturnListener(new ReturnCallback() {
@Override
public void handle(Return returnMessage) {
log.info("handleReturn,replyCode:{},replyText:{},exchange:{},routingKey:{},properties:{},replyText:{}", returnMessage.getReplyCode(), returnMessage.getReplyText(), returnMessage.getExchange(), returnMessage.getRoutingKey(), returnMessage.getProperties(), new String(returnMessage.getBody()));
}
});
// Mandatory: enable message return mechanism
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
log.info("Producer sends message:{}", i);
//Message expires in 5 seconds
AMQP.BasicProperties basicProperties = new AMQP.BasicProperties().builder().expiration("10000").build();
channel.basicPublish("exchange.test", "key.test", true, basicProperties, String.valueOf(i).getBytes());
}
}
}
Producer sends 10 messages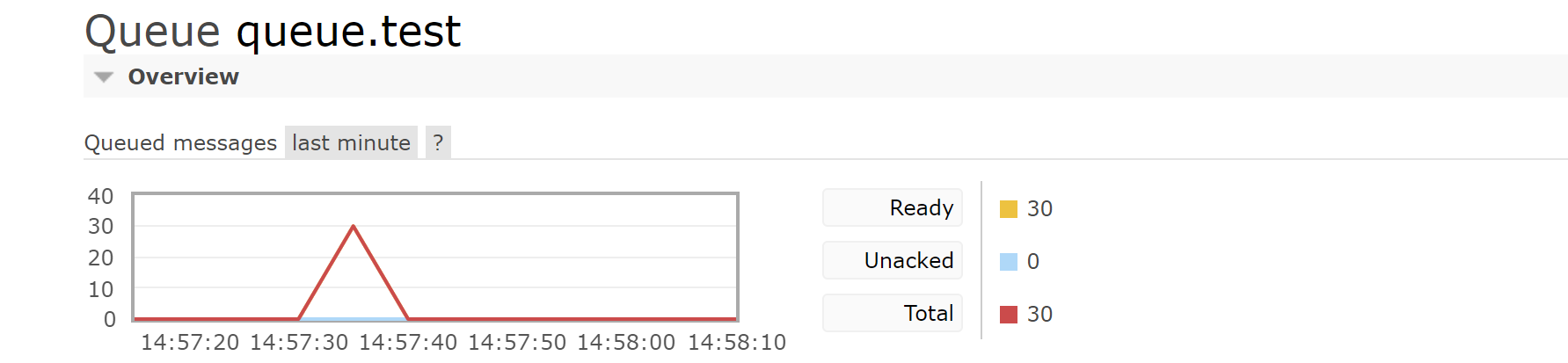
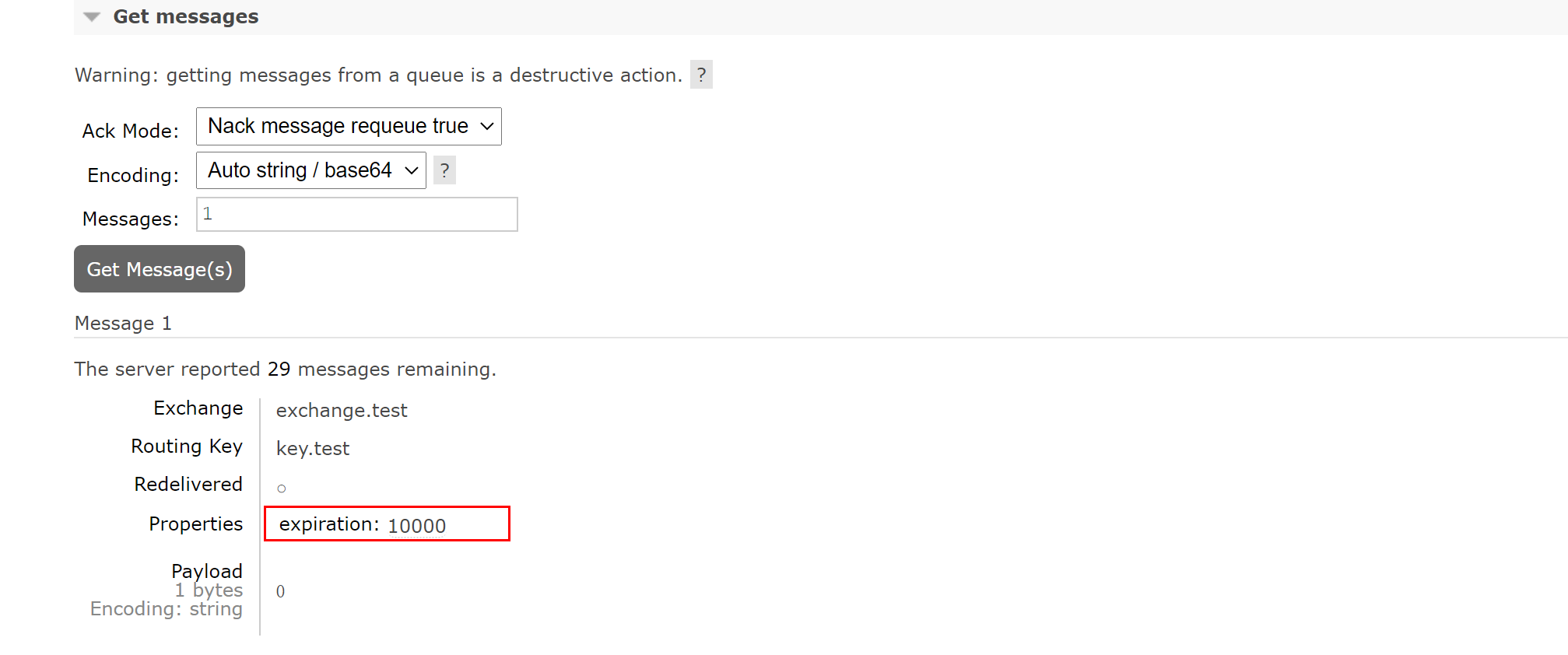
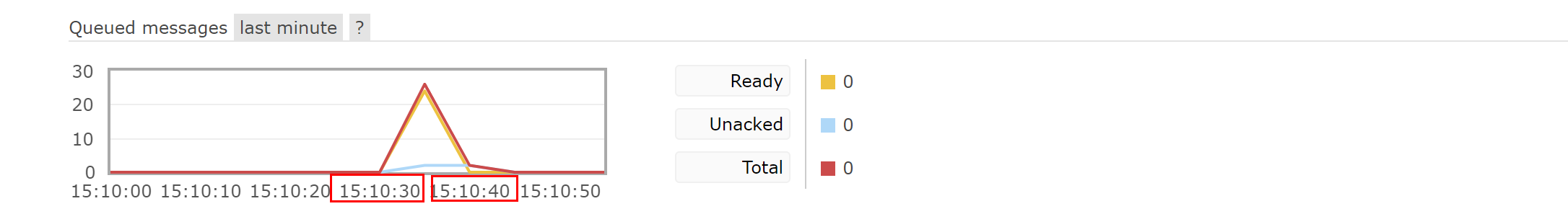
Automatically delete when 10 seconds are up
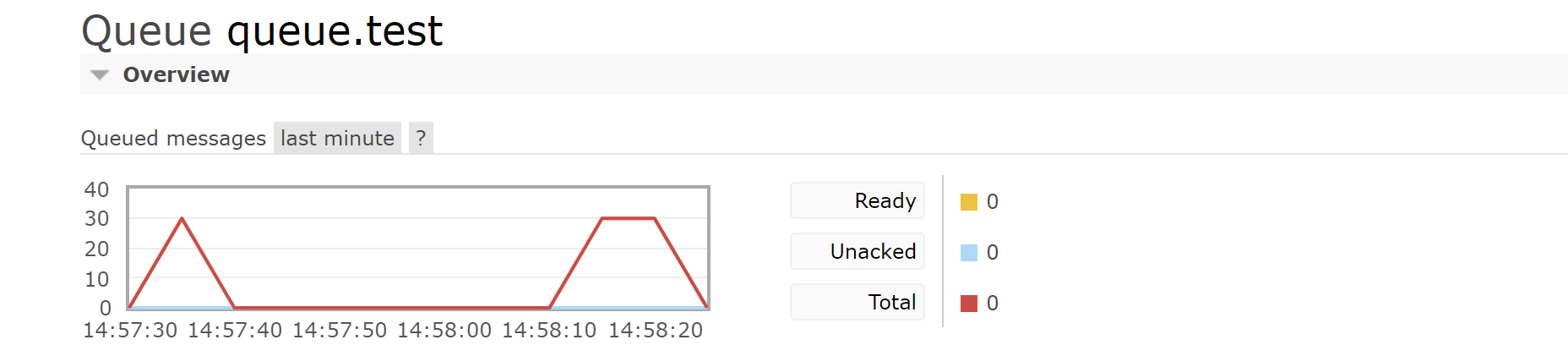
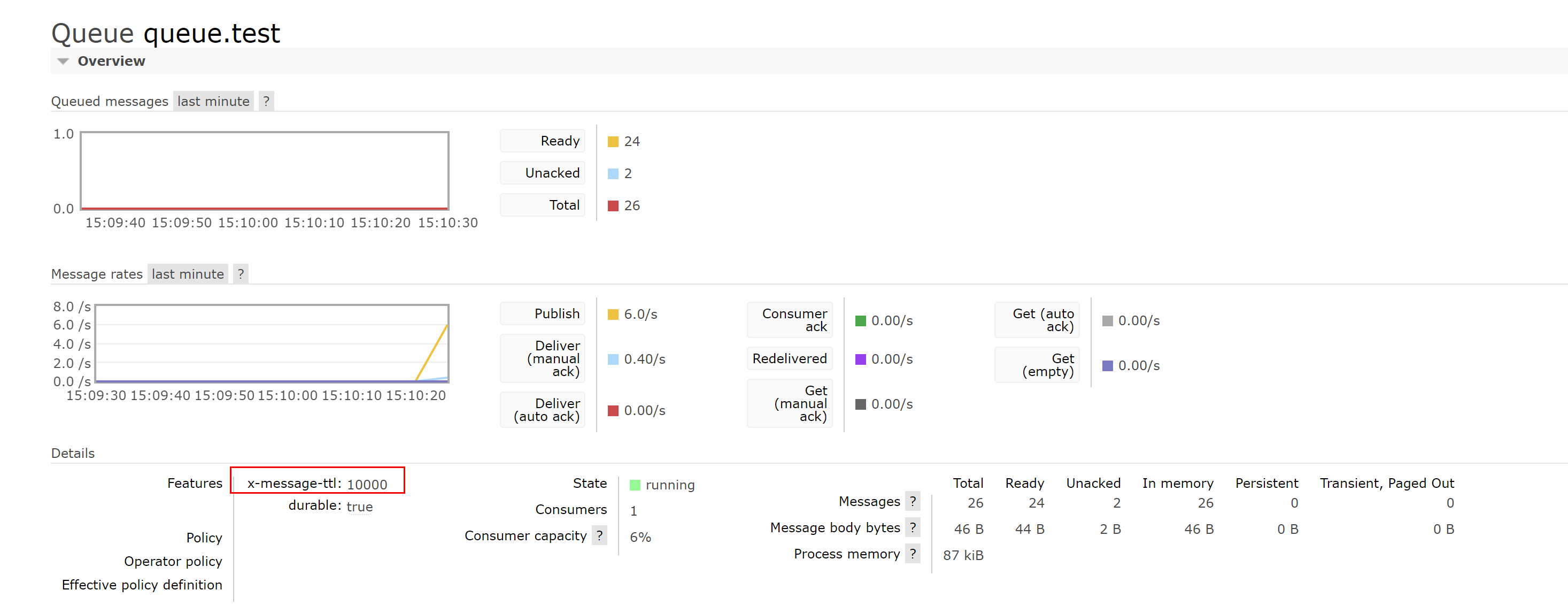
Queue message expiration time
Set queue message expiration time when declaring a queue
public void initMq(Channel channel) throws IOException, TimeoutException, InterruptedException {
log.info("-------MQ Switch,queue,Binding initialization started---------");
log.info("-------Declare switch start---------");
channel.exchangeDeclare("exchange.test", BuiltinExchangeType.DIRECT, true, false, null);
log.info("-------Claim queue start---------");
//Set queue expiration time
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("x-message-ttl",10000);
channel.queueDeclare("queue.test", true, false, false, map);
log.info("-------Declare the binding relationship between switch and queue---------");
channel.queueBind("queue.test", "exchange.test", "key.test");
}
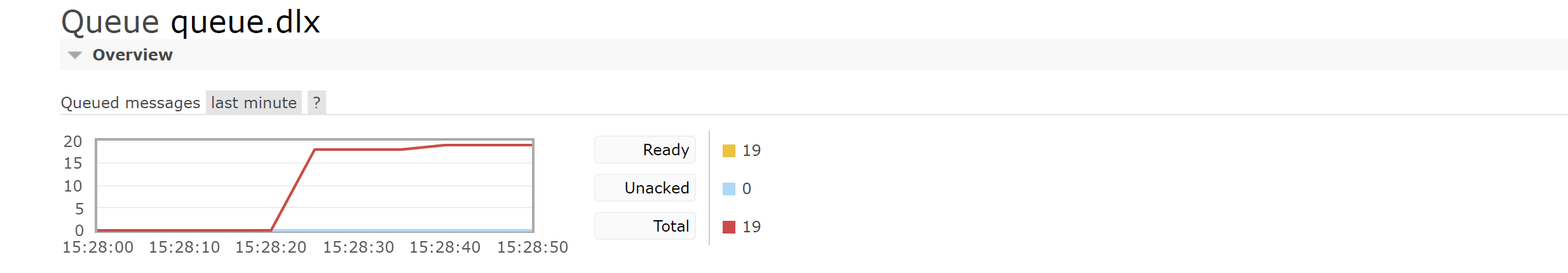
After 10 seconds, all queue messages are deleted
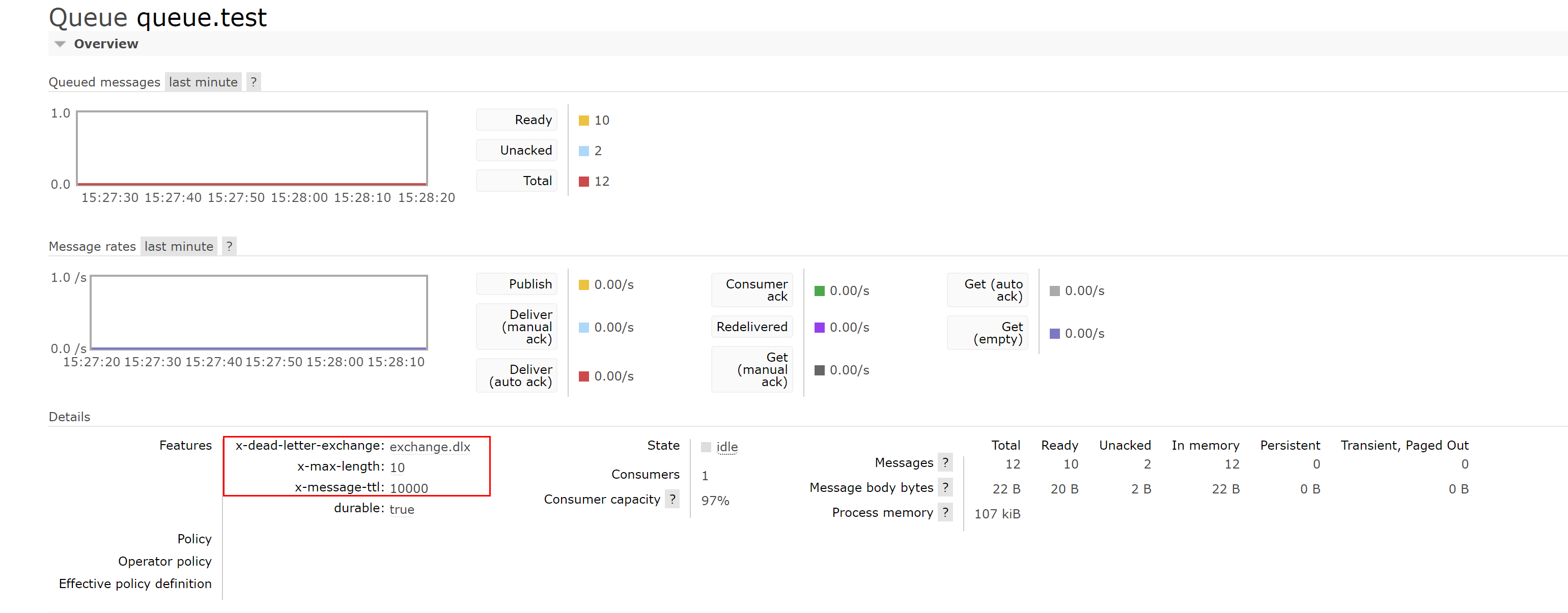
Dead letter queue
Dead letter queue:The queue is configured DLX attribute(Dead- Letter- Exchange) When a message becomes a dead letter( dead message)after,Can be republished to another Exchange,this Exchange It is also a general switch After the dead letter is routed by the dead letter switch,Generally enter a fixed queue
Become a dead letter
Message rejected( reject/nack)also requeue= false Interest expiration(TTL expire) The queue has reached its maximum length
Set dead letter queue
Set the switch and queue for forwarding and receiving dead letters Exchange: dlx.exchange Queue: dIx.queue RoutingKey:# Add parameters to the queue where dead letter needs to be set x-dead-letter-exchange=dlx.exchange
public void initMq(Channel channel) throws IOException, TimeoutException, InterruptedException {
log.info("-------MQ Switch,queue,Binding initialization started---------");
log.info("-------Declare switch start---------");
channel.exchangeDeclare("exchange.test", BuiltinExchangeType.DIRECT, true, false, null);
log.info("-------Claim queue start---------");
/**
* If the queue exists, you need to delete the queue after modifying the parameters, otherwise an error will be reported
*/
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
//Set queue expiration time
map.put("x-message-ttl", 10000);
//Set the switch into which messages expire
map.put("x-dead-letter-exchange", "exchange.dlx");
//Sets the maximum length of the queue
map.put("x-max-length", 10);
channel.queueDeclare("queue.test", true, false, false, map);
log.info("-------Declare the binding relationship between switch and queue---------");
channel.queueBind("queue.test", "exchange.test", "key.test");
/*
Dead letter switch
*/
channel.exchangeDeclare("exchange.dlx", BuiltinExchangeType.TOPIC, true, false, null);
/*
* Declare dead letter queue
*/
channel.queueDeclare("queue.dlx", true, false, false, null);
/*
* Declare that the dead letter queue is bound to the dead letter switch
*/
channel.queueBind("queue.dlx", "exchange.dlx", "#");
}
Spring AMQP features
Asynchronous message listening container
Original implementation:Implement thread pool and callback methods by yourself,And register the callback method Spring boot:Automatically implement configurable thread pool,And automatically register callback methods,Just implement the callback method
The native Rabbit template is provided to facilitate sending and receiving messages
comparison basicPublish,More powerful,It can automatically realize message conversion and other functions
Rabbitadmin is provided natively to facilitate queue and switch declaration
Declaratively provide the registration method of queue, switch and binding relationship You don't even need explicit registration code
Spring boot Config supports RabbitMQ natively
make full use of Spring boots The contract is greater than the configured attribute Can be built implicitly Connection, Channel
1.RabbitAdmin
The RabbitAdmin class is used to manage RabbitMQ
CachingConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new CachingConnectionFactory(); RabbitAdmin rabbitAdmin = new RabbitAdmin(connectionFactory);
RebbitAdmin function
declareExchange: Create switch deleteExchange: Delete switch declareQueue: Create queue deleteQueue: Delete queue purgeQueue: Empty queue declareBinding: New binding relationship removeBinding: Delete binding relationship getQueueProperties: Query queue properties
Configure RabbitMQ service
@Configuration
public class RabbitConfig {
@Autowired
public void initRabbit() {
/*
* Create connection
*/
CachingConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new CachingConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost("ip");
connectionFactory.setPort(5672);
connectionFactory.setPassword("guest");
connectionFactory.setUsername("guest");
RabbitAdmin rabbitAdmin = new RabbitAdmin(connectionFactory);
/*
* Claim switch
*/
Exchange exchange = new DirectExchange("exchange.test");
rabbitAdmin.declareExchange(exchange);
/*
* Declaration queue
*/
Queue queue = new Queue("queue.test");
rabbitAdmin.declareQueue(queue);
/*
* Declare binding relationship
*/
Binding binding = new Binding(
"queue.test",
Binding.DestinationType.QUEUE,
"exchange.test",
"key.test",
null);
rabbitAdmin.declareBinding(binding);
}
}
Simplify configuring RabbitMQ services
@Configuration
public class RabbitConfig {
@Bean
public Exchange exchange1() {
return new DirectExchange("exchange.test");
}
@Bean
public Queue queue1() {
return new Queue("queue.test");
}
@Bean
public Binding binding1() {
return new Binding(
"queue.test",
Binding.DestinationType.QUEUE,
"exchange.test",
"key.test",
null);
}
@Bean
public ConnectionFactory connectionFactory() {
CachingConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new CachingConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost("127.0.0.1");
connectionFactory.setPort(5672);
connectionFactory.setPassword("guest");
connectionFactory.setUsername("guest");
// After declarative configuration, it needs to be called manually once, that is, it will be initialized only when it is used. For example, calling the connection method triggers the initialization of the switch queue
connectionFactory.createConnection();
return connectionFactory;
}
@Bean
public RabbitAdmin rabbitAdmin(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
RabbitAdmin rabbitAdmin = new RabbitAdmin(connectionFactory);
// Initialize switch queue, etc
rabbitAdmin.setAutoStartup(true);
return rabbitAdmin;
}
}
2.RabbitTemplate sends a message
use RabbitTemplate send message Rabbittemplate It provides rich functions,Convenient messaging Rabbittemplate Configuration can be explicitly passed in or implicitly declared
Declare RabbitTemplate Bean
@Configuration
public class RabbitConfig {
@Bean
public ConnectionFactory connectionFactory() {
CachingConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new CachingConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost("127.0.0.1");
connectionFactory.setPort(5672);
connectionFactory.setPassword("guest");
connectionFactory.setUsername("guest");
// After declarative configuration, it needs to be called manually once, that is, it will be initialized only when it is used. For example, calling the connection method triggers the initialization of the switch queue
connectionFactory.createConnection();
return connectionFactory;
}
@Bean
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
return new RabbitTemplate(connectionFactory);
}
}
Send a message using the send method
@Slf4j
@Component
public class SendMsg {
@Resource
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void send(String msg) {
log.info("send Method to send a message:{}",msg);
MessageProperties messageProperties = new MessageProperties();
messageProperties.setExpiration("1000");
Message message = new Message(msg.getBytes(), messageProperties);
rabbitTemplate.send("exchange.test", "queue.test", message);
}
}
Send a message using the convertAndSend method
@Slf4j
@Component
public class SendMsg {
@Resource
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void convertAndSend(String msg) {
log.info("convertAndSend Method to send a message:{}",msg);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("exchange.test", "queue.test", msg);
}
}
Perform test
@Test
public void test() {
sendMsg.send("hello world");
sendMsg.convertAndSend("hello world");
}
INFO 13840 --- [ main] com.example.springboot.config.SendMsg : send Method to send a message:hello world INFO 13840 --- [ main] com.example.springboot.config.SendMsg : convertAndSend Method to send a message:hello world
3. Sender confirmation and message return confirmation
RabbitTemplate sets the sender's confirmation and message return methods
@Bean
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate = new RabbitTemplate(connectionFactory);
//Enable message return mechanism
rabbitTemplate.setMandatory(true);
//Message confirmation
rabbitTemplate.setConfirmCallback(new RabbitTemplate.ConfirmCallback() {
@Override
public void confirm(CorrelationData correlationData, boolean ack, String cause) {
log.info("correlationData:{}, ack:{}, cause{}", correlationData, ack, cause);
}
});
// Message return
rabbitTemplate.setReturnCallback(new RabbitTemplate.ReturnCallback() {
@Override
public void returnedMessage(Message message, int replyCode, String replyText, String exchange, String routingKey) {
log.info("message:{}, replyCode:{}, replyText:{}, exchange:{}, routingKey{}", message, replyCode, replyText, exchange, routingKey);
}
});
return rabbitTemplate;
}
When the message is sent again, it is found that the sender's confirmation and message return methods are not executed
Check the source code and find that the publisherConfirms property should be set to TRUE when creating a connection
public void determineConfirmsReturnsCapability(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
this.publisherConfirms = connectionFactory.isPublisherConfirms();
this.confirmsOrReturnsCapable =
this.publisherConfirms || connectionFactory.isPublisherReturns();
}
Modify ConnectionFactory
@Bean
public ConnectionFactory connectionFactory() {
CachingConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new CachingConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost("IP ");
connectionFactory.setPort(5672);
connectionFactory.setPassword("guest");
connectionFactory.setUsername("guest");
// After declarative configuration, it can be called manually once, otherwise it will be initialized when used, such as calling the connection method to trigger the initialization of the switch queue
connectionFactory.createConnection();
connectionFactory.setPublisherConfirmType(CachingConnectionFactory.ConfirmType.SIMPLE);
connectionFactory.setPublisherReturns(true);
return connectionFactory;
}
Create a service and call to send a message (the callback using springBootTest does not take effect)
@RestController
public class TestController {
@Autowired
private SendMsg sendMsg;
@GetMapping("/test")
public String test(){
sendMsg.send("hello world");
sendMsg.convertAndSend("hello world");
return "send success";
}
}
INFO 14576 --- [nio-8888-exec-1] com.example.springboot.config.SendMsg : send Method to send a message:hello world INFO 14576 --- [nio-8888-exec-1] com.example.springboot.config.SendMsg : convertAndSend Method to send a message:hello world INFO 14576 --- [nectionFactory2] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitConfig : correlationData:null, ack:true, causenull INFO 14576 --- [nectionFactory1] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitConfig : correlationData:null, ack:true, causenull
CachingConnectionFactory.ConfirmType.SIMPLE mode cannot determine which message is confirmed
Modify ConnectionFactory
connectionFactory.setPublisherConfirmType(CachingConnectionFactory.ConfirmType.CORRELATED);
Carry CorrelationData when sending messages
public void convertAndSend(String msg) {
log.info("convertAndSend Method to send a message:{}",msg);
CorrelationData correlationData = new CorrelationData();
correlationData.setId("123456");
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("exchange.test", "key.test", msg,correlationData);
}
INFO 14576 --- [nio-8888-exec-1] com.example.springboot.config.SendMsg : send Method to send a message:hello world INFO 14576 --- [nio-8888-exec-1] com.example.springboot.config.SendMsg : convertAndSend Method to send a message:hello world INFO 14576 --- [nectionFactory1] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitConfig : correlationData:null, ack:true, causenull INFO 14576 --- [nectionFactory1] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitConfig : correlationData:CorrelationData [id=123456], ack:true, causenull
4. Message listening container
SimpleMessageListenerContainer is a simple message listener container
characteristic
Set simultaneous listening to multiple queues, automatic start and automatic configuration RabbitMQ Set the number of consumers (maximum quantity, minimum quantity, batch consumption) Set the message confirmation mode, whether to return to the queue, and exception capture Set exclusive, other consumer properties, etc Set specific listeners, message converters, etc Support dynamic settings and modify listener configuration during operation
Using listening containers
@Bean
public SimpleMessageListenerContainer messageListenerContainer(@Autowired ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
SimpleMessageListenerContainer messageListenerContainer = new SimpleMessageListenerContainer(connectionFactory);
// Listening queue
messageListenerContainer.setQueueNames("queue.test");
// Concurrent consumption threads
messageListenerContainer.setConcurrentConsumers(2);
// Maximum concurrent consumption thread
messageListenerContainer.setMaxConcurrentConsumers(5);
// Message confirmation method
//messageListenerContainer.setAcknowledgeMode(AcknowledgeMode.AUTO);
//Manual confirmation
messageListenerContainer.setAcknowledgeMode(AcknowledgeMode.MANUAL);
/*-------------------Message listening method I-----------------------------*/
/*
// Message listening
messageListenerContainer.setMessageListener(new MessageListener() {
@Override
public void onMessage(Message message) {
log.info("Message listening, message:{}", message.toString());
}
});*/
/*-------------------Message listening mode 2-----------------------------*/
messageListenerContainer.setMessageListener(new ChannelAwareMessageListener() {
@Override
public void onMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws Exception {
log.info("Message listening,message:{}", message.toString());
log.info("news Ack,DeliveryTag:{}", message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag());
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
});
// Consumer end current limiting
messageListenerContainer.setPrefetchCount(2);
return messageListenerContainer;
}
Send a message and start listening
INFO 2544 --- [enerContainer-2] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitConfig : Message listening,message:(Body:'hello world' MessageProperties [headers={spring_listener_return_correlation=85d4df83-af4b-426c-aed9-094d9272c9e9, spring_returned_message_correlation=123456}, contentType=text/plain, contentEncoding=UTF-8, contentLength=0, receivedDeliveryMode=PERSISTENT, priority=0, redelivered=false, receivedExchange=exchange.test, receivedRoutingKey=key.test, deliveryTag=5, consumerTag=amq.ctag-vZcoVv0Jx3Vgm07hQ8iDFA, consumerQueue=queue.test])
INFO 2544 --- [enerContainer-2] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitConfig : news Ack,DeliveryTag:5
5. Customize message listening container
The message listener adapter can be used to implement custom message listening
Simple mode
Define a handleMessage method. This method is used to listen to messages and is also a business processing callback. The method name must be handleMessage
@Slf4j
@Component
public class MsgService {
public void handleMessage(byte[] body){
String msg = new String(body);
log.info("Message listening,implement handleMessage(),msg:{}",msg);
}
}
@Autowired
private MsgService msgService;
@Bean
public SimpleMessageListenerContainer messageListenerContainer(@Autowired ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
SimpleMessageListenerContainer messageListenerContainer = new SimpleMessageListenerContainer(connectionFactory);
// Listening queue
messageListenerContainer.setQueueNames("queue.test");
// Concurrent consumption threads
messageListenerContainer.setConcurrentConsumers(2);
// Maximum concurrent consumption thread
messageListenerContainer.setMaxConcurrentConsumers(5);
messageListenerContainer.setAcknowledgeMode(AcknowledgeMode.MANUAL);
// Consumer end current limiting
messageListenerContainer.setPrefetchCount(2);
MessageListenerAdapter messageListenerAdapter = new MessageListenerAdapter();
messageListenerAdapter.setDelegate(msgService);
messageListenerContainer.setMessageListener(messageListenerAdapter);
return messageListenerContainer;
}
Perform test
INFO 14272 --- [nio-8888-exec-1] com.example.springboot.config.SendMsg : send Method to send a message:hello world INFO 14272 --- [nio-8888-exec-1] com.example.springboot.config.SendMsg : convertAndSend Method to send a message:hello world INFO 14272 --- [enerContainer-2] c.example.springboot.config.MsgService : Message listening,implement handleMessage(),msg:hello world
Why must the method name be: handleMessage?
MessageListenerAdapter class, see getListenerMethodName() in onMessage() method
@Override
public void onMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws Exception { // NOSONAR
// Check whether the delegate is a MessageListener impl itself.
// In that case, the adapter will simply act as a pass-through.
Object delegateListener = getDelegate();
if (delegateListener != this) {
if (delegateListener instanceof ChannelAwareMessageListener) {
((ChannelAwareMessageListener) delegateListener).onMessage(message, channel);
return;
}
else if (delegateListener instanceof MessageListener) {
((MessageListener) delegateListener).onMessage(message);
return;
}
}
// Regular case: find a handler method reflectively.
Object convertedMessage = extractMessage(message);
String methodName = getListenerMethodName(message, convertedMessage);
if (methodName == null) {
throw new AmqpIllegalStateException("No default listener method specified: "
+ "Either specify a non-null value for the 'defaultListenerMethod' property or "
+ "override the 'getListenerMethodName' method.");
}
// Invoke the handler method with appropriate arguments.
Object[] listenerArguments = buildListenerArguments(convertedMessage, channel, message);
Object result = invokeListenerMethod(methodName, listenerArguments, message);
if (result != null) {
handleResult(new InvocationResult(result, null, null, null, null), message, channel);
}
else {
logger.trace("No result object given - no result to handle");
}
}
getListenerMethodName() returns this defaultListenerMethod
protected String getListenerMethodName(Message originalMessage, Object extractedMessage) {
if (this.queueOrTagToMethodName.size() > 0) {
MessageProperties props = originalMessage.getMessageProperties();
String methodName = this.queueOrTagToMethodName.get(props.getConsumerQueue());
if (methodName == null) {
methodName = this.queueOrTagToMethodName.get(props.getConsumerTag());
}
if (methodName != null) {
return methodName;
}
}
return getDefaultListenerMethod();
}
protected String getDefaultListenerMethod() {
return this.defaultListenerMethod;
}
Default method name: handleMessage
public static final String ORIGINAL_DEFAULT_LISTENER_METHOD = "handleMessage"; private Object delegate; private String defaultListenerMethod = ORIGINAL_DEFAULT_LISTENER_METHOD;
Higher order mode
Customize the mapping relationship between queue name and method name
Message listening and callback business processing class
@Slf4j
@Component
public class MsgService {
public void test1(byte[] body){
String msg = new String(body);
log.info("Message listening,implement handleMessage(),msg:{}",msg);
}
}
@Autowired
private MsgService msgService;
@Bean
public SimpleMessageListenerContainer messageListenerContainer(@Autowired ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
SimpleMessageListenerContainer messageListenerContainer = new SimpleMessageListenerContainer(connectionFactory);
// Listening queue
messageListenerContainer.setQueueNames("queue.test");
// Concurrent consumption threads
messageListenerContainer.setConcurrentConsumers(2);
// Maximum concurrent consumption thread
messageListenerContainer.setMaxConcurrentConsumers(5);
messageListenerContainer.setAcknowledgeMode(AcknowledgeMode.MANUAL);
// Consumer end current limiting
messageListenerContainer.setPrefetchCount(2);
MessageListenerAdapter messageListenerAdapter = new MessageListenerAdapter();
messageListenerAdapter.setDelegate(msgService);
// Customize the mapping relationship between queue name and method name
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("queue.test","test1");
// map.put("queue.test2","test2");
messageListenerAdapter.setQueueOrTagToMethodName(map);
messageListenerContainer.setMessageListener(messageListenerAdapter);
return messageListenerContainer;
}
Perform test
INFO 7100 --- [nio-8888-exec-1] com.example.springboot.config.SendMsg : send Method to send a message:hello world INFO 7100 --- [nio-8888-exec-1] com.example.springboot.config.SendMsg : convertAndSend Method to send a message:hello world INFO 7100 --- [enerContainer-2] c.example.springboot.config.MsgService : Message listening,implement handleMessage(),msg:hello world
Core this queueOrTagToMethodName. size() > 0
protected String getListenerMethodName(Message originalMessage, Object extractedMessage) {
if (this.queueOrTagToMethodName.size() > 0) {
MessageProperties props = originalMessage.getMessageProperties();
String methodName = this.queueOrTagToMethodName.get(props.getConsumerQueue());
if (methodName == null) {
methodName = this.queueOrTagToMethodName.get(props.getConsumerTag());
}
if (methodName != null) {
return methodName;
}
}
return getDefaultListenerMethod();
}
6.MessageConverter message conversion
MessageConverter Used to automatically convert messages when sending and receiving messages Jackson2JsonMessageConverter Is the most commonly used MessageConverter Used to convert Json Format message,coordination ClassMapper Can be directly converted to POJO object
Using Jackson2JsonMessageConverter
Jackson2JsonMessageConverter messageConverter = new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter(); messageListenerAdapter.setMessageConverter(new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter()); messageListenerAdapter.setMessageConverter(messageConverter);
The receiving parameter of the message listening callback method is a LinkedHashMap
public void test1(Map<String,Object> map){
log.info("Message listening,implement handleMessage(),msg:{}",map);
}
Using ClassMapper
@Autowired
private MsgService msgService;
@Bean
public SimpleMessageListenerContainer messageListenerContainer(@Autowired ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
SimpleMessageListenerContainer messageListenerContainer = new SimpleMessageListenerContainer(connectionFactory);
// Listening queue
messageListenerContainer.setQueueNames("queue.test");
// Concurrent consumption threads
messageListenerContainer.setConcurrentConsumers(2);
// Maximum concurrent consumption thread
messageListenerContainer.setMaxConcurrentConsumers(5);
// Consumer end current limiting
messageListenerContainer.setPrefetchCount(2);
MessageListenerAdapter messageListenerAdapter = new MessageListenerAdapter();
messageListenerAdapter.setDelegate(msgService);
Jackson2JsonMessageConverter messageConverter = new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter();
messageConverter.setClassMapper(new ClassMapper() {
@Override
public void fromClass(Class<?> clazz, MessageProperties properties) {
}
@Override
public Class<?> toClass(MessageProperties properties) {
return UserDTO.class;
}
});
messageListenerAdapter.setMessageConverter(messageConverter);
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("queue.test", "test1");
// map.put("queue.test2","test2");
messageListenerAdapter.setQueueOrTagToMethodName(map);
messageListenerContainer.setMessageListener(messageListenerAdapter);
return messageListenerContainer;
}
When sending a message, convert the POJO object to JSON and then to byte object, otherwise there is a pit
@Autowired
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
public void convertAndSend(String msg) throws JsonProcessingException {
log.info("convertAndSend Method to send a message:{}", userDTO);
CorrelationData correlationData = new CorrelationData();
correlationData.setId("123456");
String writeValueAsString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(userDTO);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("exchange.test", "key.test", writeValueAsString.getBytes(), correlationData);
}
INFO 10636 --- [nio-8888-exec-1] com.example.springboot.config.SendMsg : send Method to send a message:UserDTO(id=1, name=MQ) INFO 10636 --- [nio-8888-exec-1] com.example.springboot.config.SendMsg : convertAndSend Method to send a message:UserDTO(id=1, name=MQ) INFO 10636 --- [enerContainer-2] c.example.springboot.config.MsgService : Message listening,implement handleMessage(),msg:UserDTO(id=1, name=MQ) INFO 10636 --- [enerContainer-1] c.example.springboot.config.MsgService : Message listening,implement handleMessage(),msg:UserDTO(id=1, name=MQ)
7.RabbitListener
RabbitListener is the final scheme of message listening in SpringBoot. It uses annotation declaration and has no intrusion into business code. It can also be configured in the SpringBoot configuration file
@Use of RabbitListener annotation
@RabbitListener Is a composite annotation. The following annotations can be nested @Exchange: Automatic declaration Exchange @Queue: Automatic declaration queue @QueueBinding: Automatically declare binding relationships
bean declaring RabbitListenerContainerFactory
@Bean
public RabbitListenerContainerFactory rabbitListenerContainerFactory(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory){
SimpleRabbitListenerContainerFactory factory = new SimpleRabbitListenerContainerFactory();
factory.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
return factory;
}
Act on class
@Slf4j
@Component
@RabbitListener(containerFactory = "rabbitListenerContainerFactory", queues = "queue.test")
public class MsgService {
@RabbitHandler(isDefault = true)
public void test1(@Payload Message message) {
log.info("Message listening,implement handleMessage(),msg:{}", new String(message.getBody()));
}
}
Act on the method
@RabbitListener(containerFactory = "rabbitListenerContainerFactory", queues = "queue.test")
public void test1(@Payload Message message) {
log.info("Message listening,implement handleMessage(),msg:{}", new String(message.getBody()));
}
Automatically declare switch, queue, binding relationship, parameter attribute
@Slf4j
@Configuration
public class RabbitConfig {
@Bean
public ConnectionFactory connectionFactory() {
CachingConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new CachingConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost("ip");
connectionFactory.setPort(5672);
connectionFactory.setPassword("guest");
connectionFactory.setUsername("guest");
connectionFactory.setPublisherConfirmType(CachingConnectionFactory.ConfirmType.CORRELATED);
connectionFactory.setPublisherReturns(true);
// After declarative configuration, it can be called manually once, otherwise it will be initialized when used, such as calling the connection method to trigger the initialization of the switch queue
connectionFactory.createConnection();
return connectionFactory;
}
@Bean
public RabbitAdmin rabbitAdmin(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
return new RabbitAdmin(connectionFactory);
}
@Bean
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate = new RabbitTemplate(connectionFactory);
//Enable message return mechanism
rabbitTemplate.setMandatory(true);
// Message return
rabbitTemplate.setReturnCallback(new RabbitTemplate.ReturnCallback() {
@Override
public void returnedMessage(Message message, int replyCode, String replyText, String exchange, String routingKey) {
log.info("message:{}, replyCode:{}, replyText:{}, exchange:{}, routingKey{}", message, replyCode, replyText, exchange, routingKey);
}
});
//Message confirmation
rabbitTemplate.setConfirmCallback(new RabbitTemplate.ConfirmCallback() {
@Override
public void confirm(CorrelationData correlationData, boolean ack, String cause) {
log.info("correlationData:{}, ack:{}, cause{}", correlationData, ack, cause);
}
});
return rabbitTemplate;
}
@Bean
public RabbitListenerContainerFactory rabbitListenerContainerFactory(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory){
SimpleRabbitListenerContainerFactory factory = new SimpleRabbitListenerContainerFactory();
factory.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
return factory;
}
}
@Slf4j
@Component
public class MsgService {
@RabbitListener(containerFactory = "rabbitListenerContainerFactory", admin = "rabbitAdmin",
bindings = {
@QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = "queue.test",
arguments = {
@Argument(name = "x-message-ttl", value = "1000", type = "java.lang.Integer"),
@Argument(name = "x-dead-letter-exchange", value = "exchange.dlx"),
}),
exchange = @Exchange(name = "exchange.test", type = ExchangeTypes.FANOUT),
key = "key.test"
),
@QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = "exchange.dlx"),
exchange = @Exchange(name = "exchange.dlx", type = ExchangeTypes.DIRECT),
key = "key.dlx"
),
}
)
public void test1(@Payload Message message) {
log.info("Message listening,implement handleMessage(),msg:{}", new String(message.getBody()));
}
}
Delete existing switches and queues and restart the project
INFO 11692 --- [nio-8888-exec-1] com.example.springboot.config.SendMsg : send Method to send a message:UserDTO(id=1, name=MQ)
INFO 11692 --- [nio-8888-exec-1] com.example.springboot.config.SendMsg : convertAndSend Method to send a message:UserDTO(id=1, name=MQ)
INFO 11692 --- [nectionFactory1] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitConfig : correlationData:null, ack:true, causenull
INFO 11692 --- [ntContainer#0-1] c.example.springboot.config.MsgService: Message listening, execute handleMessage(),msg:{"id":1,"name":"MQ"}
INFO 11692 --- [ntContainer#0-1] c.example.springboot.config.MsgService: Message listening, execute handleMessage(),msg:{"id":1,"name":"MQ"}
INFO 11692 --- [nectionFactory1] c.e.springboot.config.RabbitConfig : correlationData:CorrelationData [id=123456], ack:true, causenull
Comment / delete the RabbitConfig configuration class created in application Properties configure MQ information. If the SpringBoot convention is greater than the configuration, the settings related to the RabbitConfig configuration class will be set automatically
spring.rabbitmq.addresses=ip spring.rabbitmq.username=guest spring.rabbitmq.password=guest spring.rabbitmq.port=6379 # Enable send confirmation spring.rabbitmq.publisher-confirm-type=correlated # Start sending failed return spring.rabbitmq.publisher-returns=true # Manual sign in spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.acknowledge-mode=manual
Add message confirmation and fallback listening
@Configuration
@Slf4j
public class MqConfig {
/**
* Enable the callback processing of confirm and return mechanisms
*
* @return RabbitTemplate
*/
@Bean
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate = new RabbitTemplate(connectionFactory);
//Enable message return mechanism
rabbitTemplate.setMandatory(true);
// Message return
rabbitTemplate.setReturnCallback(new RabbitTemplate.ReturnCallback() {
@Override
public void returnedMessage(Message message, int replyCode, String replyText, String exchange, String routingKey) {
log.info("message:{}, replyCode:{}, replyText:{}, exchange:{}, routingKey{}", message, replyCode, replyText, exchange, routingKey);
}
});
//Message confirmation
rabbitTemplate.setConfirmCallback(new RabbitTemplate.ConfirmCallback() {
@Override
public void confirm(CorrelationData correlationData, boolean ack, String cause) {
log.info("correlationData:{}, ack:{}, cause{}", correlationData, ack, cause);
}
});
return rabbitTemplate;
}
}
Note admin = "rabbitAdmin", the bean created by spring does not have the entire name of rabbitAdmin
containerFactory = "rabbitListenerContainerFactory" can be annotated or not. In fact, this Bean will be created, which can be directly referenced or not referenced
@Slf4j
@Component
public class MsgService {
@RabbitListener(
//containerFactory = "rabbitListenerContainerFactory", admin = "rabbitAdmin",
bindings = {
@QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = "queue.test",
arguments = {
@Argument(name = "x-message-ttl", value = "1000", type = "java.lang.Integer"),
@Argument(name = "x-dead-letter-exchange", value = "exchange.dlx"),
}),
exchange = @Exchange(name = "exchange.test", type = ExchangeTypes.FANOUT),
key = "key.test"
),
@QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = "exchange.dlx"),
exchange = @Exchange(name = "exchange.dlx", type = ExchangeTypes.DIRECT),
key = "key.dlx"
),
}
)
public void test1(@Payload Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
log.info("Message listening,implement handleMessage(),msg:{}", new String(message.getBody()));
log.info("Prepare for signing in,Sign in message Id:{}",message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag());
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
}
Delete existing switches and queues and restart the project
INFO 14028 --- [nio-8888-exec-1] com.example.springboot.config.SendMsg : send Method to send a message:UserDTO(id=1, name=MQ)
INFO 14028 --- [nio-8888-exec-1] com.example.springboot.config.SendMsg : convertAndSend Method to send a message:UserDTO(id=1, name=MQ)
INFO 14028 --- [ntContainer#0-1] c.example.springboot.config.MsgService: Message listening, execute handleMessage(),msg:{"id":1,"name":"MQ"}
INFO 14028 --- [ntContainer#0-1] c.example.springboot.config.MsgService: ready to execute sign in, sign in message Id:1
INFO 14028 --- [ntContainer#0-1] c.example.springboot.config.MsgService: Message listening, execute handleMessage(),msg:{"id":1,"name":"MQ"}
INFO 14028 --- [ntContainer#0-1] c.example.springboot.config.MsgService: ready to execute sign in, sign in message Id:2