In C + +, all types of data combinations are custom data structures.
Including string, istream, ostream and so on that we often use.
A simple type definition that starts with struct.
//Sales_data.h
#include <string>
struct Sales_data { std::string bookNo; unsigned units_sold = 0; // According to the C++ 11 standard, the data members can be provided with initial values within the class double revenue = 0.0; };
The role of in class initializers: when an object is created, the in class initializers are used to initialize data members.
How to use our custom types
// main.cpp #include <iostream> #include <string> #include "Sales_data.h" int main() { Sales_data data1, data2; // Read in data1 and data2 Code double price = 0; // Unit price entered, used to calculate sales revenue // Read in the first transaction: ISBN,Sales quantity, unit price std::cin >> data1.bookNo >> data1.units_sold >> price; // Calculated as sales revenue data1.revenue = data1.units_sold * price; // Second transaction std::cin >> data2.bookNo >> data2.units_sold >> price; data2.revenue = data2.units_sold * price; // inspect data1 and data2 Of ISBN Same code or not if ( data1.bookNo == data2.bookNo) { unsigned totalCnt = data1.units_sold + data2.units_sold; double totalRevenue = data1.revenue + data2.revenue; // Output: ISBN,Total sales, total sales, average price std::cout << data1.bookNo << " " << totalCnt << " " << totalRevenue << " "; if (totalCnt != 0) std::cout << totalRevenue / totalCnt << std::endl; else std::cout << "(no sales)" << std::endl; return 0; } else { // Two deals ISBN Dissimilarity std::cerr << "Data must refer to the same ISBN" << std::endl; return -1; } // If the same, please data1 and data2 Sum total }

Operation result:
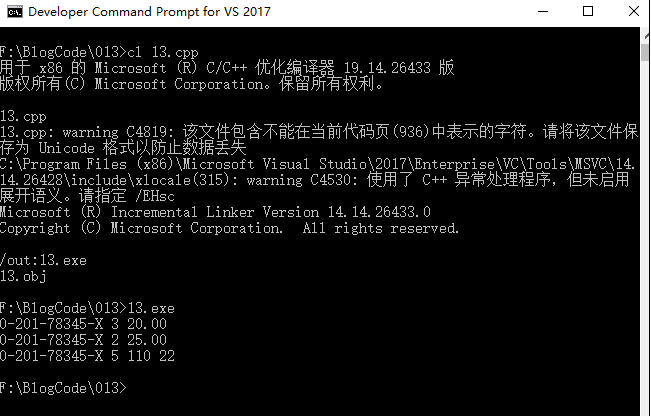
We have basically completed the above procedures.
We also completed a multi file compilation process.
So why do we use a header file to define the type of sales data?
Because if types need to be used more than one in a project, their definitions need to be consistent, and the best way to be consistent is to use the same declaration.
I don't know if you have noticed that string is included in both code files.
If a file is included multiple times, there will be multiple statements in the file. We need some processing to make multiple inclusion work safely and normally.
The processed header file is as follows:
#ifndef SALES_DATA_H // Prevent contained preprocessing statements from being repeated #define SALES_DATA_H #include <string> struct Sales_data { std::string bookNo; unsigned units_sold = 0; double revenue = 0.0; }; #endif //SALES_DATA_H
The role of preprocessing variables
#define sets a name as a preprocessing variable
#ifdef is true only if the variable is defined
#ifndef is true only if the variable is undefined
#endif starts with ifdef or ifndef and ends with this line