Preface
As a cached database, Redis currently has a large usage in the market. Most people use its string format storage in their work. For the rest of the data structure, it is rarely used. The basic data structure of Redis includes: string, hash, list, set, sorted set. These five data structures are often used in different scenarios in our work and are frequently asked during interviews, so mastering the use and scenarios of these five basic data structures is the most fundamental and important part of Redis knowledge.
1.5 Basic Data Structures
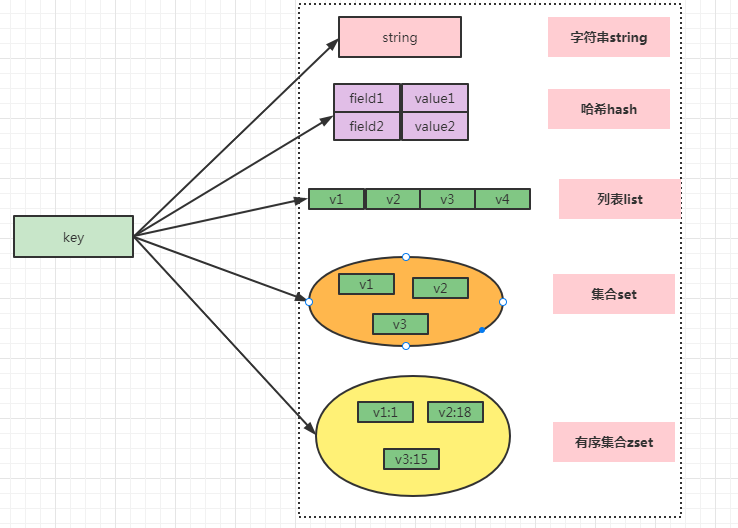
2. String String
2.1. Common operations
SET key value //Save string key-value pairs MSET key value [key value ...] //Bulk Storage of String Key-Value Pairs SETNX key value //Save a non-existent string key-value pair GET key //Gets a string key value MGET key [key ...] //Bulk Get String Key Values DEL key [key ...] //Delete a key EXPIRE key seconds //Set the expiration time of a key (seconds) INCR key //Add 1 to the number stored in the key DECR key //Reduce the number stored in the key by 1 INCRBY key increment //Add increment to the value stored by key DECRBY key decrement //Subtract decrement from value stored in key
2.2. Application Scenarios
2.2.1, Single Value Cache (most commonly used)
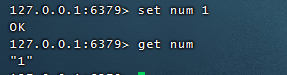
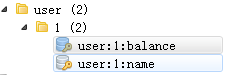
2.2.2, Object Cache
Convert Object to json Storage
SET user:1 value(json Format data)
Each field of the object is stored as available
MSET user:1:name zhuge user:1:balance 1888
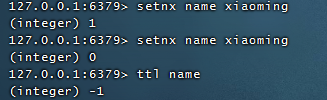
2.2.3, Distributed Lock
SETNX product:10001 true //Return 1 for successful lock acquisition SETNX product:10001 true //Return 0 indicates failure to acquire lock . . . Perform business operations DEL product:10001 //Execute Business Release Lock SET product:10001 true ex 10 nx //Set expiration time to prevent program accidental termination leading to deadlock
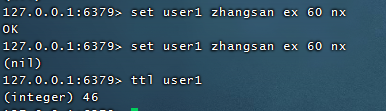
2.2.4, Counters
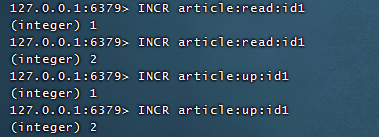
Read, comment on the article

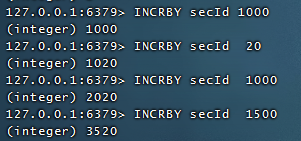
Distributed System Global Sequence Number, which affects performance if each system uses a sequence number from redis, so each system can request N serial numbers in batches for use by the current system at a time, and continue to obtain them after use can improve performance
3. Hashash
3.1. Common Operations
HSET key field value //Stores the key value of a hash table key HSETNX key field value //Stores a key value for a non-existent hash table key HMSET key field value [field value ...] //Storing multiple key-value pairs in a hash table key HGET key field //Gets the field key value corresponding to the hash table key HMGET key field [field ...] //Bulk Get Multiple field key Values in Hash Table key HDEL key field [field ...] //Delete field key value in hash table key HLEN key //Returns the number of field s in the hash table key HGETALL key //Returns all the key values in the hash table key HINCRBY key field increment //Add increment to the value of the field key in the hash table key
3.2. Application Scenarios
3.2.1, Object Cache
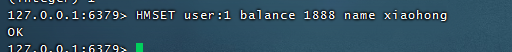
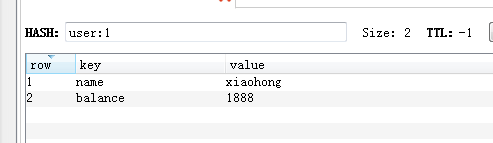
3.2.2, E-commerce shopping cart
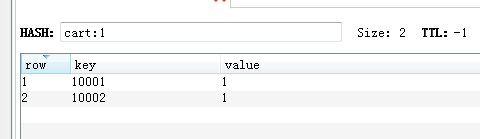
Add shopping cart operation with user id as key, commodity id as field, commodity quantity as value
HSET cart:1 10001 2 //User 1: Commodity 10001 Quantity 2 HSET cart:1 10002 1 //User 1: Commodity 10002 Quantity 1 HINCRBY cart:1 10001 1 //User 1: Commodity 10001 Quantity + 1 HINCRBY cart:1 10001 -2 //User 1: Commodity 10001 Quantity-2 HLEN cart:1 //Get the number of items in User 1 shopping cart HGETALL cart:1 //Get User 1 shopping cart items and quantities hdel cart:1 10001 //Delete User 1's 10001 Merchandise
Advantage
1) Classification and integrated storage of similar data to facilitate data management
2) string consumes less memory than cpu
3) Save more space than string storage
shortcoming
Expired functionality cannot be used on field, it can only be used on key
Redis cluster architecture is not suitable for large-scale use (the same key will only fall on one of these machines after hash)
4. list
4.1. Common Operations
LPUSH key value [value ...] //Insert one or more value values into the header of the key list (leftmost) RPUSH key value [value ...] //Insert one or more value values at the end of the key list (rightmost) LPOP key //Remove and return the header element of the key list RPOP key //Remove and return the tail element of the key list LRANGE key start stop //Returns the elements within a specified interval in the list key, specified by offsets start and stop LINSERT key BEFORE|AFTER pivot element // Insert pivot before and after element element element element LREM key count element //Remove count > 0 from the list of elements equal to the parameter VALUE based on the value of the parameter COUNT: Search from the header to the tail, remove elements equal to the VALUE, number COUNT //Count < 0: Search the header from the end of the table, removing elements equal to VALUE, in absolute COUNT. //count = 0: Remove all values in the table that are equal to VALUE. BLPOP key [key ...] timeout //Pop up an element from the header of the key list. If there are no elements in the list, block the wait for timeout seconds. If timeout=0, block the wait all the time BRPOP key [key ...] timeout //Pop up an element from the end of the key list table. If there are no elements in the list, block waiting for timeout seconds. If timeout=0, block waiting all the time
4.2. Application Scenarios
Stack(Stack FILO) = LPUSH + LPOP Queue(queue FIFO)= LPUSH + RPOP Blocking MQ(Blocking queue)= LPUSH + BRPOP
4.2.1 Weibo and WeChat Business Number Messages
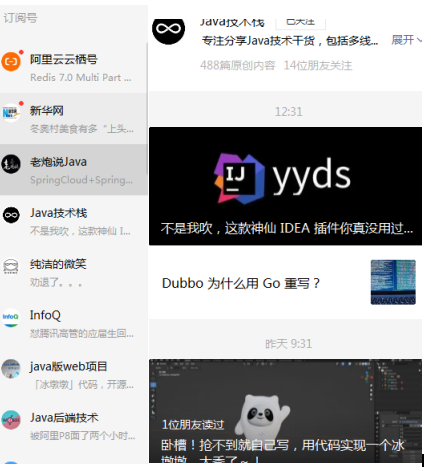
As the public number in the picture above: I subscribed to Ali Yunyunqi (id10001), Xinhua (id10002), infoQ (id10003), etc.
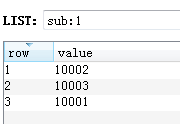
1. First add 10001, 10002, 10003 to the msg:1 list, and the corresponding messages for each user
LPUSH sub:1 10001 10002 10003 LPUSH msg:10001 1 2 3 LPUSH msg:10002 4 5 6 LPUSH msg:10003 8 9
2. At this time 10002 sends a message id: 11, first remove 10002 from the collection I subscribe to, then add 10002 first, and then 11 from the msg
LREM sub:1 0 10002 LPUSH sub:1 10002 LPUSH msg:10002 11
5. Collection set
5.1 Common Operations
SADD key member [member ...] //Save an element in the collection key, ignore it if it exists, and create a new one if the key does not exist SREM key member [member ...] //Remove element from collection key SMEMBERS key //Gets all the elements in the collection key SCARD key //Gets the number of elements of the collection key SISMEMBER key member //Determine if member element exists in collection key SRANDMEMBER key [count] //Select count elements from the set key, and do not delete elements from the key SPOP key [count] //Select count elements from the set key, delete elements from the key SINTER key [key ...] //intersect SINTERSTORE destination key [key ..] //Save the intersection results in a new set destination SUNION key [key ..] //Union operation SUNIONSTORE destination key [key ...] //Save union results in a new set destination SDIFF key [key ...] //Difference set operation SDIFFSTORE destination key [key ...] //Save the difference result in a new set destination
5.2 Scenarios
5.2.1 Draw
- Participate in the Draw
SADD luck:1001 100001 //Add User 100001 to Participation Pool of Commodity 1001
- View all users participating in the lottery
SMEMBERS luck:1001
- Draw a winner
SPOP luck:1001 1
5.2.2 Microblog Comments, Collections, Labels
- Give the thumbs-up
SADD like:1 1001
- Cancel a favor
SREM like:1 1001
- Check if the user has overrated
SISMEMBER like:1 1001
5.2.3 Weibo Weixin Focus Model
Liu Haoran pays attention to: Zhang Jie, Liu Tao, Wang Baoqiang
SADD follow:lhr zj lt wbq
Zhang Jie pays attention to: Liu Haoran, Liu Tao, Wang Baoqiang, Wang Yuezheng, Xiena, Hu Ge
SADD follow:zj lhr lt wbq wlz xl hg
Liu Tao pays attention to: Liu Haoran, Zhang Jie, Chen Yixun, Xu Song
SADD follow:lt lhr zj cyx xs
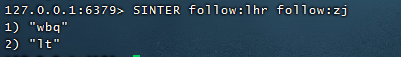
Model 1: Shared focus
People that Liu Haoran and Zhang Jie pay attention to
SINTER follow:lhr follow:zj
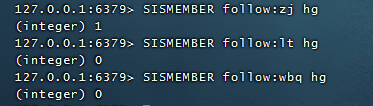
Model 2: People I care about also have concerns
Liu Haoran's concerned people are also concerned about Hu Ge
SISMEMBER follow:zj hg SISMEMBER follow:lt hg SISMEMBER follow:wbq hg
Model 2: People who might be interested
When Liu Haoran visits Zhang Jie's homepage, he will recommend people who are interested. People who Zhang Jie cares about go and not in Liu Haoran's attention can be recommended.
SDIFF follow:zj follow:lhr

5.2.4 Merchandise Screening on Shopping Sites

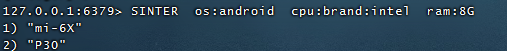
SADD brand:huawei P30 //p30 in Huawei Brand Collection SADD brand:xiaomi mi-6X //mi-6X in Millet brand collection SADD brand:iPhone iphone8 //iphone8 in Apple Brand Collection SADD os:android P30 mi-6X //P30 mi-6X in the Android Collection SADD cpu:brand:intel P30 mi-6X //P30 mi-6X in the cpu Intel collection SADD ram:8G P30 mi-6X iphone8 //P30 mi-6X iphone8 in 8G memory collection
Find handsets with 8G of memory, Intel CPU and Android:
SINTER os:android cpu:brand:intel ram:8G
6. Ordered set sorted
6.1 Common Operations
ZADD key score member [[score member]...] //Add a score element to an ordered set key ZREM key member [member ...] //Delete element from ordered collection key ZSCORE key member //Returns the score of an element member in an ordered set key ZINCRBY key increment member //Add increment to the score of the member of the element in the ordered set key ZCARD key //Returns the number of elements in an ordered set key ZRANGE key start stop [WITHSCORES] //Get ordered set key s from start subscript to stop subscript elements in positive order ZREVRANGE key start stop [WITHSCORES] //Gets the elements of the ordered set key from the start subscript to the stop subscript in reverse order ZUNIONSTORE destkey numkeys key [key ...] //Union calculation ZINTERSTORE destkey numkeys key [key ...] //Intersection calculation
6.2 Application Scenarios
6.2.1 microblog hot search list
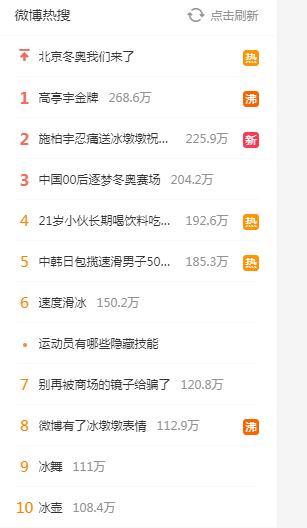
Take daily hot search news as a collection, and when a user clicks on a topic that day, the score is + 1
Click News
ZINCRBY hotnews:20220201 1 dawmll //2022-02-01 Click Winter Olympics We're coming+1 ZINCRBY hotnews:20220201 1 gtljp //2022-02-01 Click on Gold Medals in Gao Tingyu+1
- Show Top Ten of the Day
ZREVRANGE hotnews:20220201 0 10 WITHSCORES [WITHSCORES]
- 2-day Search List Calculation
ZUNIONSTORE newhots 2 hotnews:20220201 hotnews:20220202 //Add the fractions of the same value from two or more together and place the result in newhots
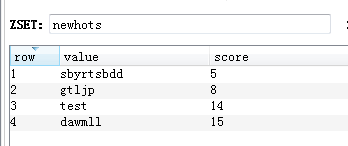
- Show 2nd Top Ten
ZREVRANGE newhots 0 10 //Remove the top 10 from the new set of statistics above

summary
Tip: Here is a summary of the article:
Through this article, you have a better understanding of the five Redis data structures, including the use in real-world scenarios. We hope to help you solve the problems in your work, and we will update the Redis architecture related articles in the future.
Thank you for your interest