1. Strong References (Objects)
Features:
Strong references provide direct access to the target object.
Will not be recycled. 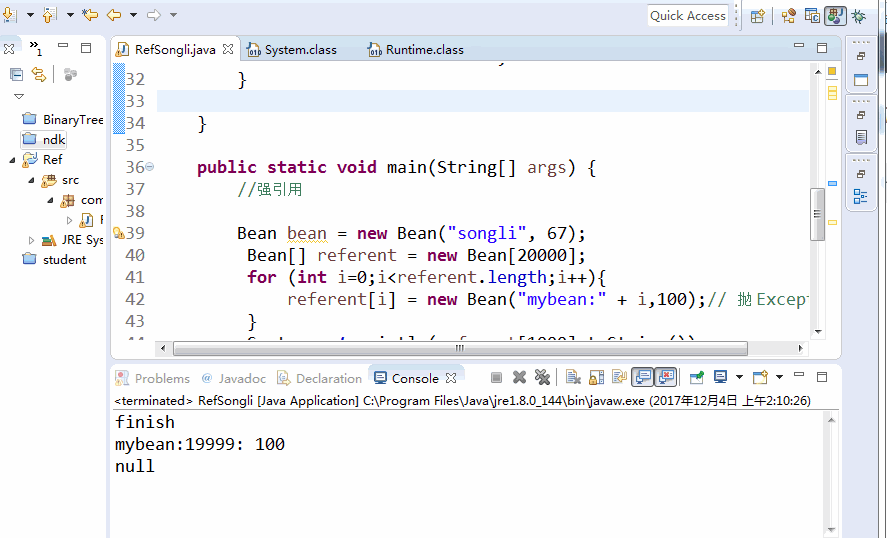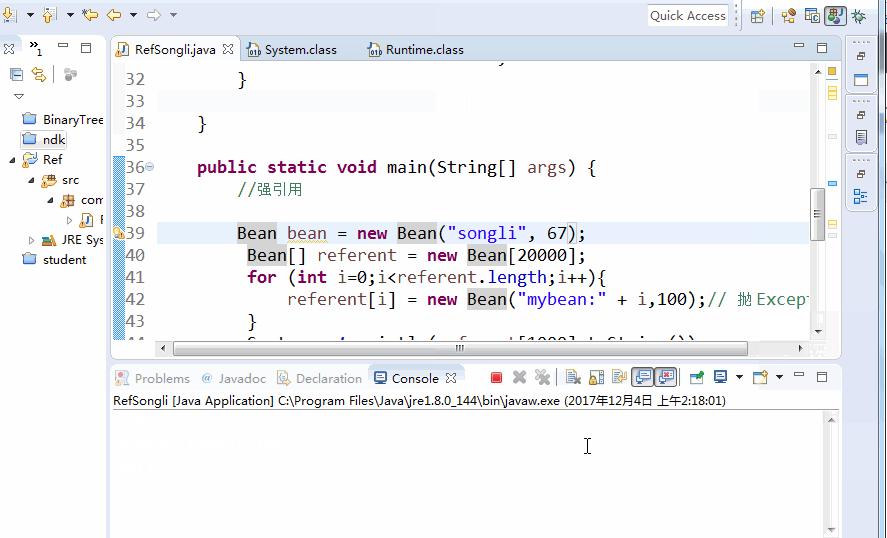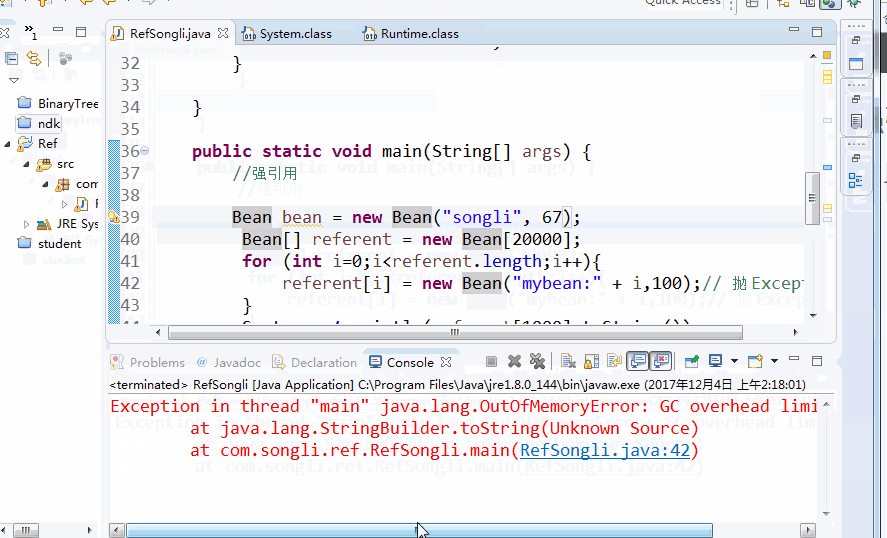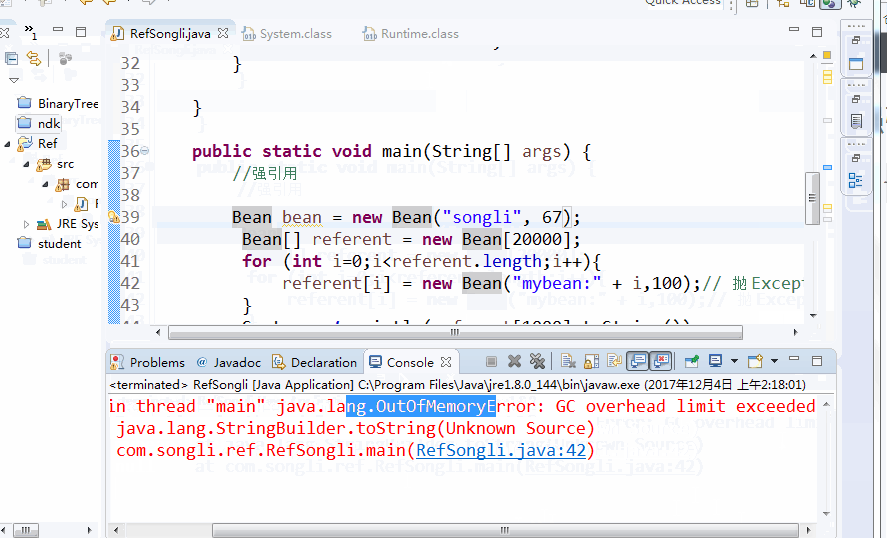
Two, soft reference (SoftReference class)
Features:
When GC reclaims based on JVM memory, JVM reclaims when it finds it is out of memory
Conditions for freeing up space: JVM found insufficient memory.
While Android's Andler and Bitmap are in use, they are not released during the life cycle of the Activity, being pointer-to-pointer is empty, and memory is not actually released
Third, WeakReference
Features:
As long as the system is GC-enabled, it will be reclaimed regardless of whether there is enough memory.
Fourth, PhantomReference
get() is an empty null value
Use of storage when null is empty
package com.songli.ref;
import java.lang.ref.Reference;
import java.lang.ref.SoftReference;
import java.lang.ref.WeakReference;
/**
> Author: songli
> QQ: 2734030745
> Mail: 15850774503@163.com
> CSDN: http://my.csdn.net/Poisx
> github: https://github.com/chensongpoixs
*/
public class RefSongli {
public static class Bean {
String name;
Integer va;
public Bean(String name, Integer value) {
this.name = name;
this.va = value;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return name +": " + va;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Strong Reference
Bean bean = new Bean("songli", 67);
Bean[] referent = new Bean[20000];
for (int i=0;i<referent.length;i++){
referent[i] = new Bean("mybean:" + i,100);// Throw Exception
}
System.out.println(referent[1000].toString());
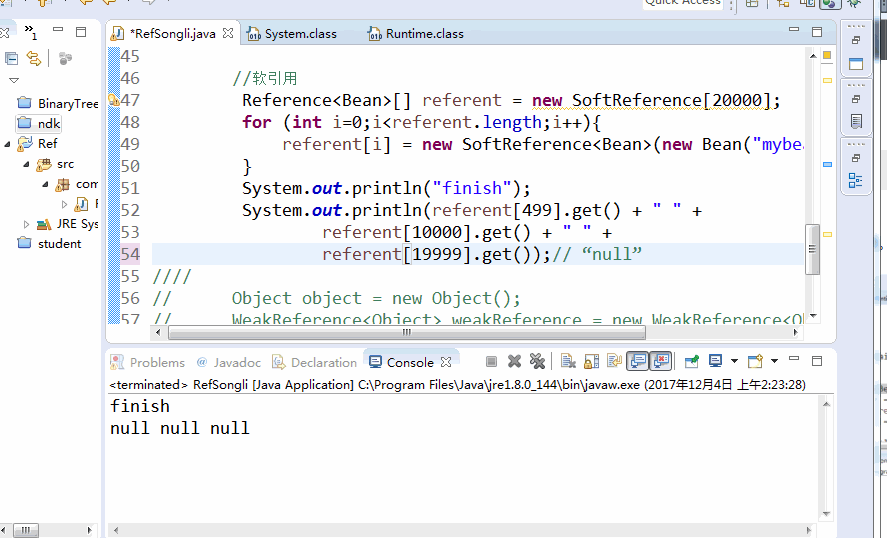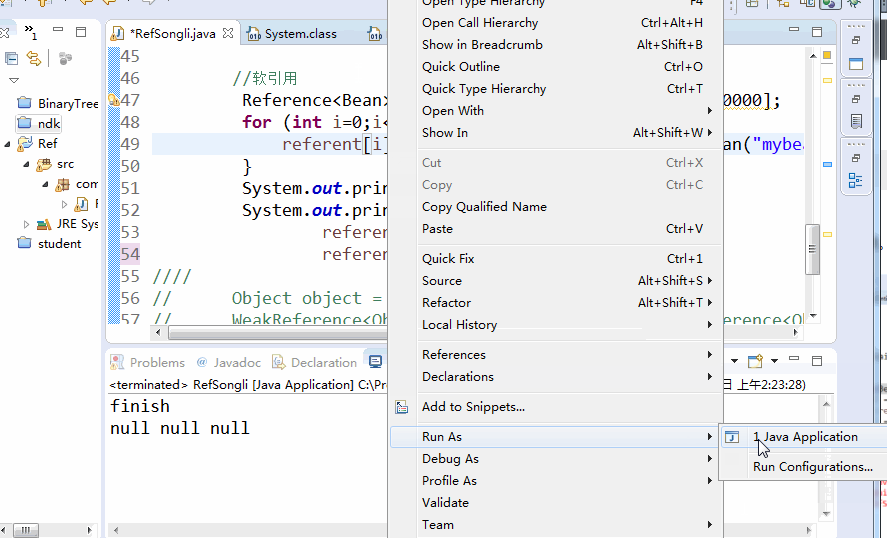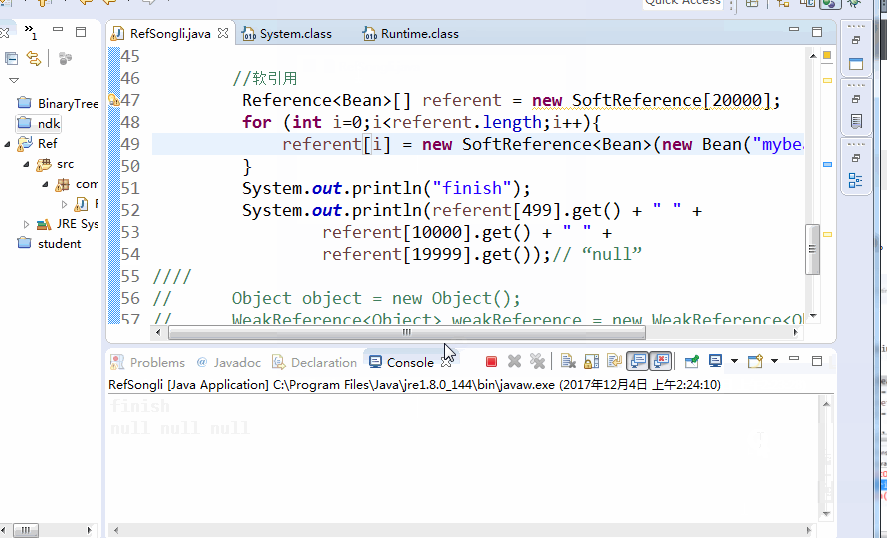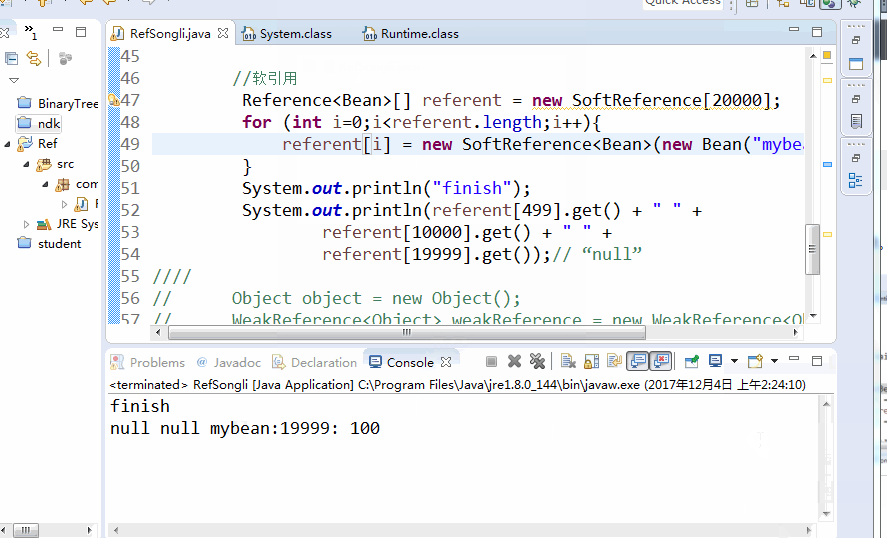
//Soft reference
Reference<Bean>[] referent = new SoftReference[20000];
for (int i=0;i<referent.length;i++){
referent[i] = new SoftReference<Bean>(new Bean("mybean:" + i,100));
}
System.out.println("finish");
System.out.println(referent[499].get() + " " +
referent[10000].get() + " " +
referent[19999].get());// "null"
////
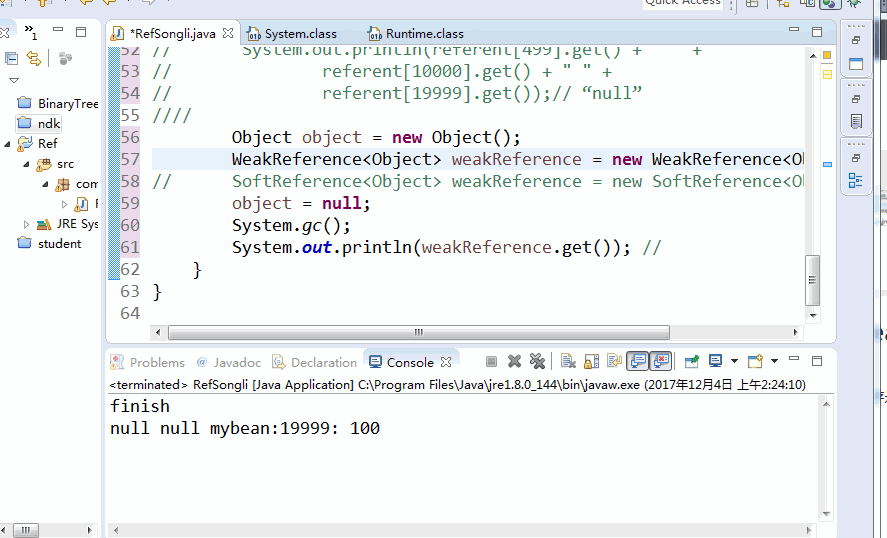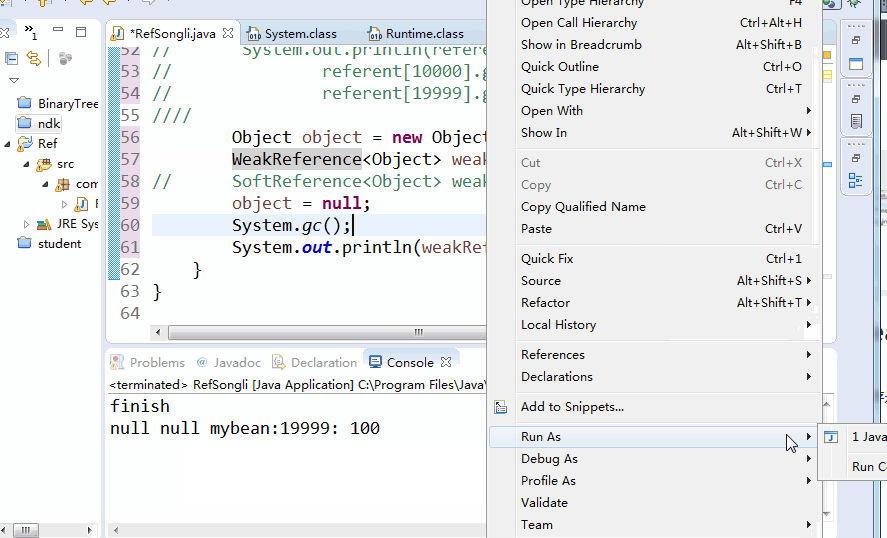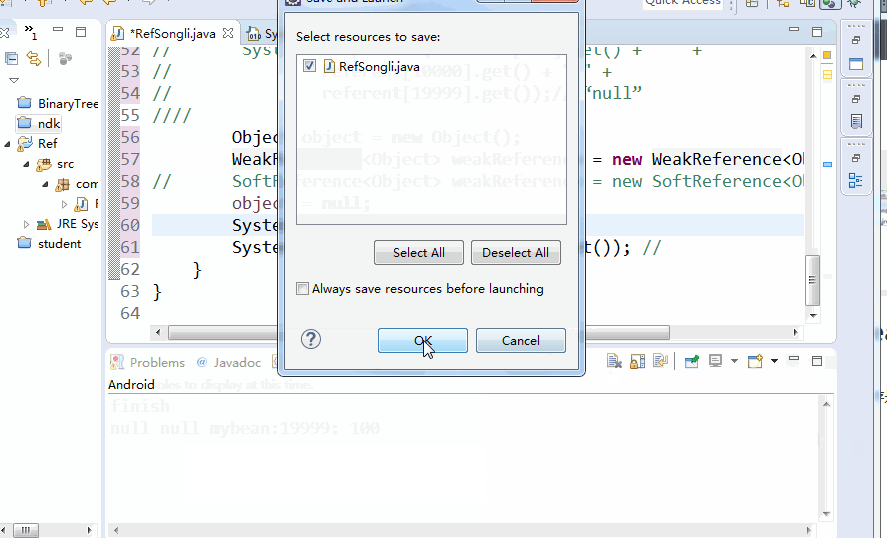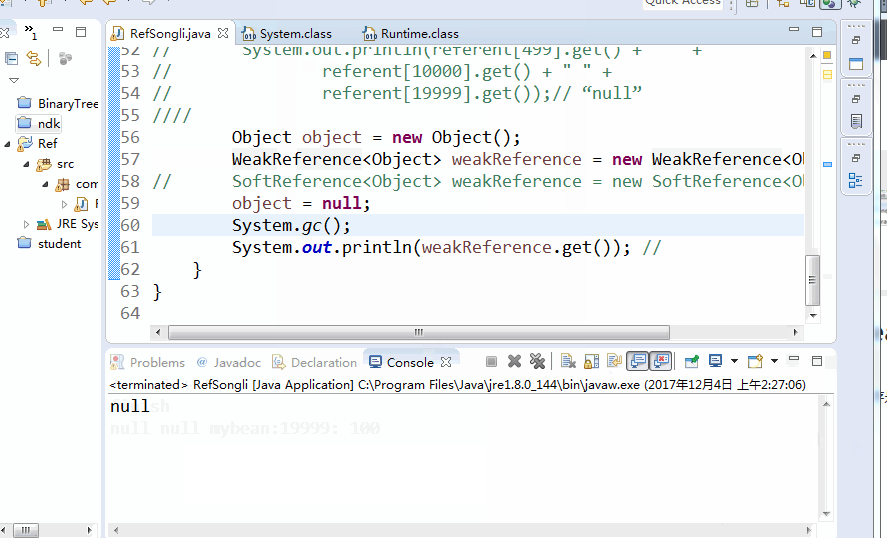
Object object = new Object();
WeakReference<Object> weakReference = new WeakReference<Object>(object);
// SoftReference<Object> weakReference = new SoftReference<Object>(object);
object = null;
System.gc();
System.out.println(weakReference.get()); //
}
}