ssm framework day 8: Spring MVC
<dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.11</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-web</artifactId> <version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId> <version>2.5</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId> <version>2.0</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency>
2.web.xml configuration
<!--to configure Springmvc DispatcherServlet(Springmvc Core front end controller)--> <servlet> <servlet-name>dispatcherServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <!--Is let spring The front-end controller is loaded when it is created springmvc.xml Create various profiles controller object--> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value> </init-param> <!--Can let Servlet Created when the server starts--> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>dispatcherServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
3. Spring MVC configuration file
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd"> <!--Configure package scanning Create all Controller object --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.bianyiit.web"></context:component-scan> <!--Configure view parser--> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> <!--Specifies the prefix for logical to physical view conversion --> <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/views/"></property> <!--Specifies the suffix for logical to physical view conversion --> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property> </bean> <!--Automatic loading SpringMVC Two other component processor mapper processor adapters --> <mvc:annotation-driven></mvc:annotation-driven> </beans>
4.controller class and jsp page
<%-- Created by IntelliJ IDEA. User: zengl Date: 2019/10/25 Time: 11:21 To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates. --%> <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" isELIgnored="false" %> <html> <head> <title>springmvc introduction</title> </head> <body> <a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/user/helloWorld">springmvc Entry test</a> </body> </html>
package com.bianyiit.web; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; @Controller /** Defines the path prefix for method access in the class */ @RequestMapping("/user") public class UserController { /** * Complete the mapping relationship between request path and method * * A module uses a UserController */ //(path ={"/helloWorld"}, // method ={RequestMethod.GET,RequestMethod.POST}, //Request mode for qualified method access // params={"username"}, //Qualified parameter. If the request parameter name is specified, the request must carry the parameter // headers = {"Accept"}//Qualified request header @RequestMapping("/hello") public String helloWorld(){ System.out.println("UserController Medium helloWorld Yes"); return "hello"; } }
Request process:
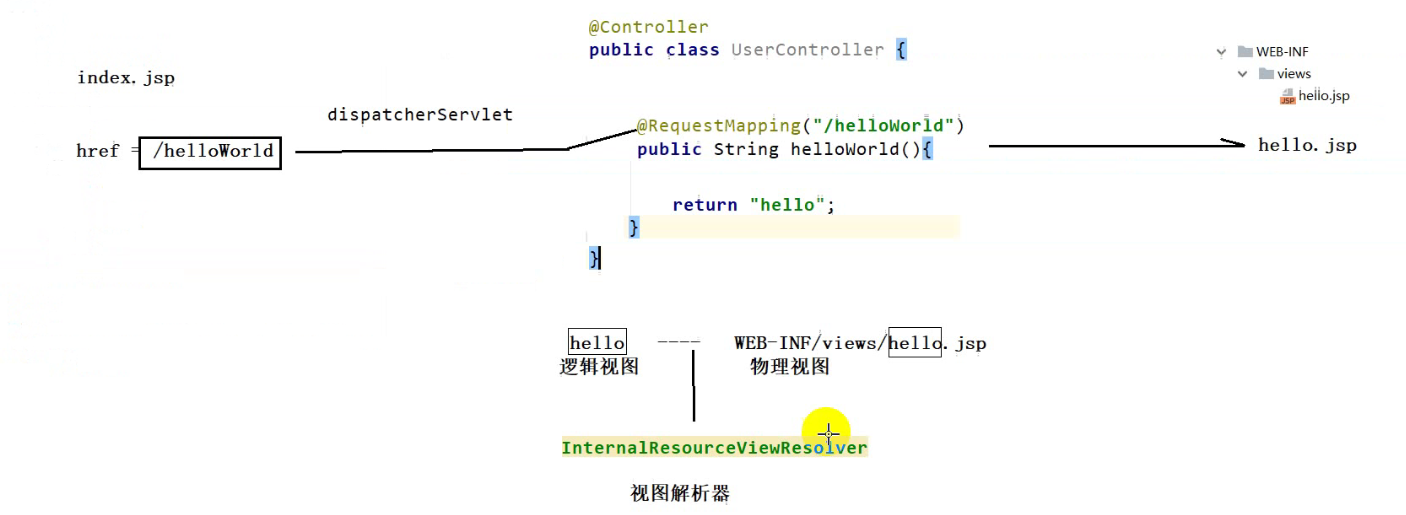
The user sends a request in the browser, which is received by the dispatchServlet, then distributes the request, finds the corresponding mapping path of the controller layer, processes the request, returns the logical view, converts it into a physical view through the configured view parser, returns it to the front-end jsp page, and then sends the data to be displayed to the browser on the jsp page.
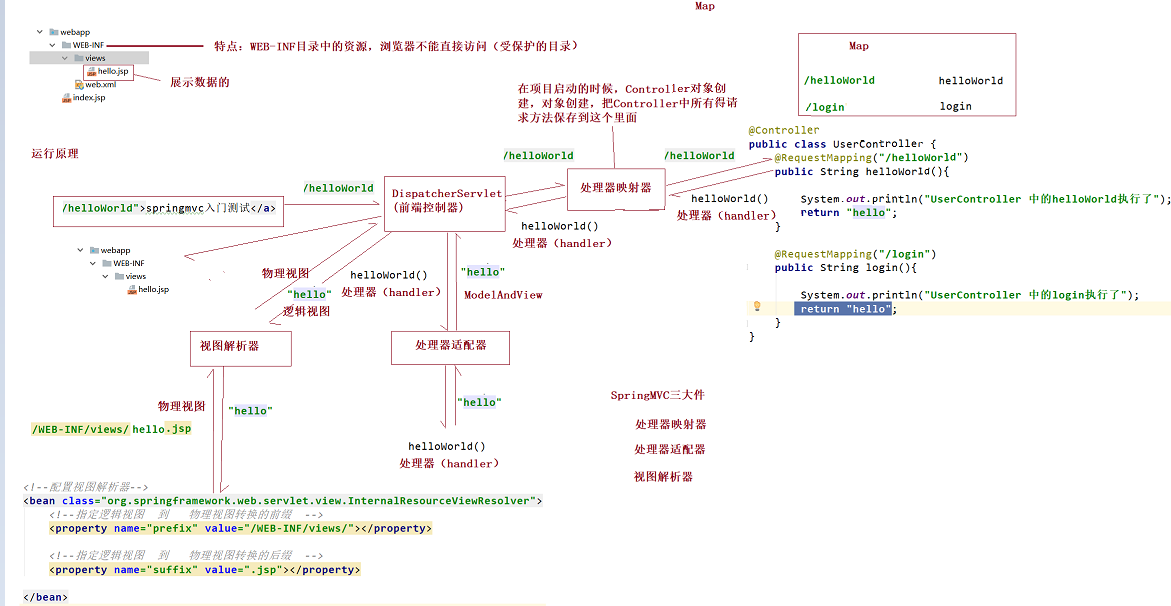
3. Operating principle of spring MVC
As shown in the figure:
4. Receipt of request parameters
The code is as follows:
package com.bianyiit.web; import com.bianyiit.domian.User; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession; @Controller @RequestMapping("/param") public class ParamController { /** * Controller Methods can accept Servlet related API s * @param request * @param response * @return */ @RequestMapping("/hello") public String hello(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response){ //1. Get request parameters System.out.println(request.getParameter("username")); System.out.println(request.getParameter("password")); return "hello"; } @RequestMapping("/hello1") public String hello1(String username,String password){ //1. Get request parameters System.out.println(username+ " :: " + password); return "hello"; } @RequestMapping("/hello2") public String hello2(User user){ //1. Get request parameters System.out.println(user.getUsername()+ " :: " + user.getPassword()); return "hello"; } }
Note: the parameter name (name) requested by the front end should be consistent with the attribute name of the back end (one-to-one correspondence)
Today's learning experience: learning is not only a part of life, but also a very important part. The above is only personal understanding. If there is any improper understanding, I hope you can correct me. Thank you! Last sentence: I hope you become the person you want to be!