Vue project basic configuration: secondary encapsulation Axios whole process analysis
sketch 📖, I'm a little unfamiliar with axios and the secondary packaging process, so let's sort it out 💻 . arrangement 🖊 Be more detailed, which is convenient for your current study and later review 📘 .
Overview: this chapter mainly includes the basic concepts of axios and the process of secondary packaging axios
-
What is Axios?
- Axios is a promise based HTTP library that can be used in browsers and node JS.
-
install
- npm install axios
- Or npm install axios --S
- Or npm install axios --save
- [note] the above three expressions have the same meaning. Do not add -- save or -- S, which is installed in the dependencies production dependency by default
-
How to introduce axios into the project
-
First:
-
In main JS
-
1. //Introducing axios import axios from 'axios'; //Register axios with the prototype object of vue Vue.prototype.$axios = axios; //Why not use Vue Use(), because the developer of axios did not write the install step 2. //Use method -- > in the called component this.$axios('route','parameter').then().catch()
-
-
-
Second:
- Create a utils – > utils JS file
- Specific reference ⏬ The following is the secondary packaging of axios
-
-
request basic use case (based on cnode community) 🏠 Interface as an example - a good community 😆 )
-
post request
-
axios.post("https://cnodejs.org/api/v1/topics", { accesstoken: "45e7e524-2f99-4e2e-be68-f9c66401a2f1", title: "Late night test axios Secondary packaging-wcc", tab: "dev", content: "I hope we can go further and further on the road of technology!!!", }).then(res => { console.log(res); }) .catch(function (error) { console.log(error); });
-
-
get request
-
In the first way, the input parameter is spliced in the form of query string
-
axios.get("https://cnodejs.org/api/v1/topics?page=1&tab=ask&limit=10&mdrender=false") .then(res =>{ // Execute on success console.log(res); }) .catch(error => { // Execute on error console.log(error); });
-
-
The second method is to pass in {params: {}} as an object
-
axios.get("https://cnodejs.org/api/v1/topics",{ params:{ page:1, tab:'ask', limit:10, mdrender:false } }) .then(res =>{ // Execute on success console.log(res); }) .catch(error => { // Execute on error console.log(error); });
-
-
-
-
Secondary packaging axios
-
New folder utils -- > utils js
-
Step 1: introduce the required configuration
import axios from 'axios'; //Introducing axios import { Message,Loading} from 'element-ui' //Introduce message prompt / load on demand --- use it as a service (service: refer to the element UI official website) import qs from 'qs'; //Parameter serialization, convert the data format to x-www-form-urlencoded (the default format of post) /* qs It is a package managed by npm warehouse, which can be installed by npm install qs command qs.parse()Parse the URL into the form of an object -- a key value pair qs.stringify()Serialize objects into URL s to & splice -- query strings */ -
Step 2: judge the current running environment - this piece of content is linked with * * * proxyTable * * *
let BASE_URL = '',loadingInstance; let HOST = process.env.NODE_ENV; console.log(HOST); switch (HOST) { //Development represents the local development environment case 'development': BASE_URL = '/api'; break; //Production stands for online environment (including dat, uat and production environment) case 'production': BASE_URL = '/'; break; default: BASE_URL = '/api'; } /* In node, the global variable process represents the current node process process.env Contains variables about the system environment, but process Node does not exist in Env_ Env this thing. NODE_ENV Is a user-defined variable. In webpack, it is used to judge the production environment or development environment. [Note] process env. NODE_ Env is a global environment variable added when we execute script commands. */ -
Step 3: configure the default value of * * * axios * * * (in two cases, refer to the official document)
-
Global axios default value (the method used in this example)
-
Custom instance defaults
// Global axios defaults -- more than that axios.defaults.timeout = 5000;//Timeout setting axios.defaults.baseURL = BASE_URL ;//Request root path axios.defaults.headers.post['content-type']='application/x-www-form-urlencoded';//Custom request header
-
-
Step 4: request interceptor
-
Do something before sending the request,
- Add unified cookie
- Request body plus verification
- Set request header
- Or jump to the login page without a token
- It is equivalent to a package for the same operation in each interface;
axios.interceptors.request.use((config) => { console.log(config); config.data = qs.stringify(config.data); // let token=localStorage.getItem('token'); // token && (config.headers.Authorization=token);// Request to carry token // token &&Object. assign(config.headers,{Authorization:token}); Another way of writing // config.headers = { // 'content type': 'application / x-www-form-urlencoded' / / convert data format // } // Calling loading as a service -- > returns an instance of loading loadingInstance = Loading.service({ lock: true, text: 'Content loading', //The load document displayed below the load icon }); return config; }, error => { // Do something wrong with the request return Promise.reject(error); })
-
-
Step 5: response interceptor
- After the request is responded to, some processing of the response body, such as unified data processing, is often used to judge the login failure, etc
xios.interceptors.response.use(response => { // Do something with the response data setTimeout(() => { // Service mode: method of turning off mask layer loadingInstance.close(); }, 300) return response; }, error => { setTimeout(() => { loadingInstance.close(); }, 300) let { response } = error; if (response) { // The server has returned content let errormsg = ''; switch (response.status) { case 400: errormsg = 'Error request' break; case 401: errormsg = 'Not logged in,Please log in again' break; case 403: errormsg = 'Refuse to visit' break; case 404: errormsg = 'Request error, the resource was not found' break; case 405: errormsg = 'Request method not allowed' break; case 408: errormsg = 'request timeout' break; case 500: errormsg = 'Server error' break; case 501: errormsg = 'Network not implemented' break; case 502: errormsg = 'network error' break; case 503: errormsg = 'Service Unavailable' break; case 504: errormsg = 'Network Timeout ' break; case 505: errormsg = 'http The request is not supported by version' break; default: errormsg = 'Connection error' } // Message global method Message({ type: 'error', message: errormsg }); return false; } else { //The server didn't even return the results. It may be disconnected or the server crashed // window.navigator contains some information such as browser manufacturer and version if (!window.navigator.online) { //Network disconnection treatment Message('Network interruption'); return; } else { //The server crashed Message('The server crashed'); return Promise.reject(error);//Promise pending - > rejected } } }) -
Step 6: GET and POST request encapsulation
-
GET request
/* *GET Method, corresponding to get request *@param {String} url [Requested url address] *@param {Object} params[Parameters carried by the request]] */ export function get(url,params){ return new Promise((resolve,reject) => { axios.get(url,{ params:params }).then(res => { resolve(res.data); }).catch(err =>{ reject(err.data) }) }) } -
POST request
/* *post Method, corresponding to the post request *@param {String} url [Requested url address] *@param {Object} params[Parameters carried by the request]] */ export function post(url, params) { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { axios.post(url, params) .then(res => { resolve(res.data); }).catch(err => { reject(err.data); }) }); }
-
-
Step 7: unified processing interface
-
New api – > index JS file
import { get, post } from '@/utils/utils.js'; // New theme // export const newTheme = params =>post('/api/v1/topics',params); // export const getTopics = params =>get('/api/v1/topics',params); const $CNodeApi = { // New theme newTheme: params =>post('/api/v1/topics',params), // Get topic getTopics:params =>get('/api/v1/topics',params), } export default $CNodeApi;
-
-
Step 8: use interface
-
At HelloWorld Vue is introduced in different ways
// import { newTheme,getTopics } from "@/api/index"; import $CNodeApi from "@/api/index"; //Call in method submit() { $CNodeApi.newTheme({ accesstoken:'45e7e524-2f99-4e2e-be68-f9c66401a2f1', title:'Late night test axios Secondary packaging-wcc', tab:'dev', content:'I hope we can go further and further on the road of technology!!!' }).then(res => { console.log(res); // this.$message({ // message: 'Congratulations, the new theme is successful', // type: 'success' // }); })
-
-
Step 9: call succeeded
- 😆 Finish
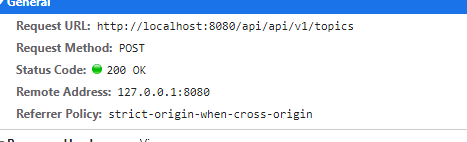
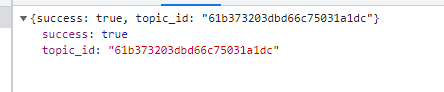
- 😆 Finish
-
-
It's not the mountain we conquer, but ourselves.
What we want to overcome is not mountains, but ourselves.