pytesser is an open source project of Google, which can be used for text recognition in pictures
Here we will use it for simple verification code identification. The code is as follows:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
__author__ = 'admin'
from pytesser import *
flag = 140
table = []
for i in range(256):
if i < flag:
table.append(0)
else:
table.append(1)
# Since they are all numbers, if there are letters, use this table for correction, and take the similar letters and values as the mapping
rep = {'O': '0',
'I': '1',
'L': '1',
'Z': '2',
'S': '8',
'Q': '0'}
class AuthCode(object):
def __init__(self, img_name):
self.img = img_name
def tran_to_str(self):
# Open the picture.
im = Image.open(self.img)
# Image to gray
img_ry = im.convert('L')
# Save grayscale image
img_ry.save('g'+self.img)
# Binarization to remove image noise
out = img_ry.point(table, '1')
# Save the image after noise removal
out.save('b'+self.img)
# Distinguish
text = image_to_string(out)
# Processing of recognized characters
text = text.strip()
text = text.upper()
for r in rep:
text = text.replace(r, rep[r])
# out.save(text+'.jpg')
print text
return text
if __name__ == '__main__':
i = AuthCode('r2.jpg')
i.tran_to_str()Specific process description:
- Download the picture verification code to the local area. The verification code is roughly as follows


2 convert code to grayscale image
img_ry = im.convert('L')
Here RBG is used to convert to HSI color space, and L component is used
Now the gray image looks like this 

3 again, we remove the noise in the image:
We set the pixels greater than the threshold value to 1, and the others to 0. To solve this problem, Mr. Zhang made a look-up table and asked the library function to help us with the mapping process.
flag = 140
table = []
for i in range(256):
if i < flag:
table.append(0)
else:
table.append(1)
Now the image looks like this 

Finally, save the image as text
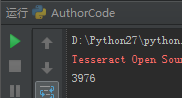
text = image_to_string(out)
Output result