📢📢📢📣📣📣
Hello! Hello, everyone. I'm [one heart classmate], a highly motivated [Java domain blogger]! 😜😜😜
✨ Writing style of [one heart students]: I like to explain every knowledge point in [easy to understand] writing, rather than using [tall and tall] official statement.
✨ The field of the blog is the learning of back-end technology, and more back-end technology and learning experience will be continuously updated in the future.
✨ If there is [xiaocute] who is interested in [back-end technology], please pay attention to [one heart students] 💞💞💞
❤️❤️❤️ Thank you, little cute! ❤️❤️❤️
catalogue
2, Basic operations of Elasticsearch in Java
2.5 judge whether the document exists
1, Spring Boot integration
(1) Create a Spring Boot project and import the following dependencies.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.62</version>
</dependency>
<!--es rely on-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
(2) Ensure uniform version
Ensure that the following version of ES is consistent with our own version of ES.
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<!-- Unified version -->
<elasticsearch.version>7.6.1</elasticsearch.version>
</properties>(3) Write configuration class
package com.yixin.config;
import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class ElasticSearchClientConfig {
// Register rest advanced client
@Bean
public RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient(){
RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(
RestClient.builder(
new HttpHost("127.0.0.1",9200,"http")
)
);
return client;
}
}
(4) Test use
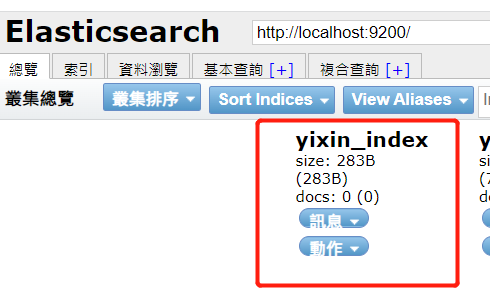
Let's create an index yixin_index to test whether it can be created successfully.
package com.yixin;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RequestOptions;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.CreateIndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.CreateIndexResponse;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.io.IOException;
@SpringBootTest
class DemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("restHighLevelClient")
public RestHighLevelClient client;
// Test index creation, Request PUT liuyou_index
@Test
public void testCreateIndex() throws IOException {
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("yixin_index");
CreateIndexResponse response = client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// System.out.println(response);
System.out.println(response.isAcknowledged());// Check whether the creation is successful
System.out.println(response);// View returned objects
client.close();
}
}
Output:
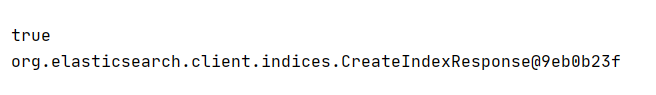
This indicates that our index has been created successfully. We can also go to elasticsearch head to check:
2, Basic operations of Elasticsearch in Java
2.1 index creation
// Test index creation, Request PUT liuyou_index
@Test
public void testCreateIndex() throws IOException {
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("yixin_es");
CreateIndexResponse response = client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// System.out.println(response);
System.out.println(response.isAcknowledged());// Check whether the creation is successful
System.out.println(response);// View returned objects
client.close();
}2.2 get index
// Test to obtain the index and determine whether it exists
@Test
public void testIndexIsExists() throws IOException {
GetIndexRequest request = new GetIndexRequest("yixin_index");
boolean exists = client.indices().exists(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(exists);// Does the index exist
client.close();
}2.3 delete index
// Index deletion
@Test
public void testDeleteIndex() throws IOException {
DeleteIndexRequest request = new DeleteIndexRequest("yixin_index ");
AcknowledgedResponse response = client.indices().delete(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(response.isAcknowledged());// Delete successfully
client.close();
}2.4 adding document data
// Test add document (first create a User entity class and add fastjson dependency)
@Test
public void testAddDocument() throws IOException {
// Create a User object
User user = new User("Wholeheartedly", 18);
// Create request
IndexRequest request = new IndexRequest("yixin_index");
// Make rules PUT /yixin_index/_doc/1
request.id("1");// Set document ID
request.timeout(TimeValue.timeValueMillis(1000));// request.timeout("1s")
// Put our data into the request
request.source(JSON.toJSONString(user), XContentType.JSON);
// The client sends a request and obtains the result of the response
IndexResponse response = client.index(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(response.status());// Get indexed status information CREATED
System.out.println(response);// View the returned content indexresponse [index = liuyou_index, type = _doc, id = 1, version = 1, result = created, seqno = 0, primaryterm = 1, shares = {"total": 2, "successful": 1, "failed": 0}]
}2.5 judge whether the document exists
// Get the document and judge whether there is get /index/_doc/1
@Test
void testIsExists() throws IOException {
GetRequest request = new GetRequest("yixin_index", "1");
// Do not get returned_ The context of source
request.fetchSourceContext(new FetchSourceContext(false));
request.storedFields("_none_");
boolean exists = client.exists(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(exists);
}2.6 obtaining document data
// Test to obtain document information
@Test
public void testGetDocument() throws IOException {
GetRequest request = new GetRequest("yixin_index","1");
GetResponse response = client.get(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(response.getSourceAsString());// Print document content
System.out.println(request);// All the contents returned are the same as the command
client.close();
}2.7 update document data
// Test update document content
@Test
public void testUpdateDocument() throws IOException {
UpdateRequest request = new UpdateRequest("yixin_index", "1");
User user = new User("One heart classmate",18);
request.doc(JSON.toJSONString(user),XContentType.JSON);
UpdateResponse response = client.update(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(response.status()); // OK
client.close();
}2.8 deleting document data
// remove document
@Test
public void testDeleteDocument() throws IOException {
DeleteRequest request = new DeleteRequest("yixin_index", "1");
request.timeout("1s");
DeleteResponse response = client.delete(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(response.status());// OK
}2.9 batch insert data
// Batch insert data
@Test
public void testBulk() throws IOException {
BulkRequest bulkRequest = new BulkRequest();
bulkRequest.timeout("10s");
ArrayList<User> users = new ArrayList<>();
users.add(new User("One heart classmate-1",1));
users.add(new User("One heart classmate-2",2));
users.add(new User("One heart classmate-3",3));
users.add(new User("One heart classmate-4",4));
users.add(new User("One heart classmate-5",5));
users.add(new User("One heart classmate-6",6));
// Batch request processing
for (int i = 0; i < users.size(); i++) {
bulkRequest.add(
// Here is the data information
new IndexRequest("yixin_index")
.id(""+(i + 1)) // If the id is not set, a random id will be generated
.source(JSON.toJSONString(users.get(i)),XContentType.JSON)
);
}
BulkResponse bulk = client.bulk(bulkRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(bulk.status());// ok
}2.10 query operation
// query
// SearchRequest search request
// SearchSourceBuilder condition construction
// HighlightBuilder highlight
// TermQueryBuilder exact query
// MatchAllQueryBuilder
// xxxQueryBuilder ...
@Test
public void testSearch() throws IOException {
// 1. Create query request object
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("yixin_index");
// 2. Build search criteria
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
// (1) Query criteria are created using the QueryBuilders tool class
// Precise query
TermQueryBuilder termQueryBuilder = QueryBuilders.termQuery("age", "1");
// Matching query
// MatchAllQueryBuilder matchAllQueryBuilder = QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery();
// (2) Other < optional >: (you can refer to the field section of SearchSourceBuilder)
// Set highlight
searchSourceBuilder.highlighter(new HighlightBuilder());
// //Pagination
// searchSourceBuilder.from();
// searchSourceBuilder.size();
searchSourceBuilder.timeout(new TimeValue(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
// (3) Conditional input
searchSourceBuilder.query(termQueryBuilder);
// 3. Add condition to request
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
// 4. Client query request
SearchResponse search = client.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 5. View the returned results
SearchHits hits = search.getHits();
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(hits));
System.out.println("=======================");
for (SearchHit documentFields : hits.getHits()) {
System.out.println(documentFields.getSourceAsMap());
}
}
Summary
The above is the steps of integrating Spring Boot with ElasticSearch sorted out by [one heart students], and how to perform basic operations on [es] in [Java]. For more operations on ES, we can check the [official document] for detailed reading.
If this [article] is helpful to you, I hope I can praise [one heart classmate] 👍, It's not easy to create. Compared with the official statement, I prefer to use [easy to understand] to explain every knowledge point. If there are cute people who are interested in [back-end technology], they are also welcome to pay attention ❤️❤️❤️ [one heart students] ❤️❤️❤️, I will bring you great [harvest and surprise] 💕💕!