There are four return value types:
1.1 project integration
1.1.1 create project
1.1.2 import jar package
Description: in POM Add jar package file to XML file
<!--mybatis Dependent package-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.2.0</version>
</dependency>
<!--jdbc Dependent package-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--add to lombok My bag-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>1.1.3 delete redundant files
Note: then copy it to src, delete the redundant files and keep the files in the figure,

2. Modify the name of the configuration file

application.yml mybatis_ config. Replace with XML
1.1.4 description of main startup exceptions
Prompt: "out of the box" principle error message: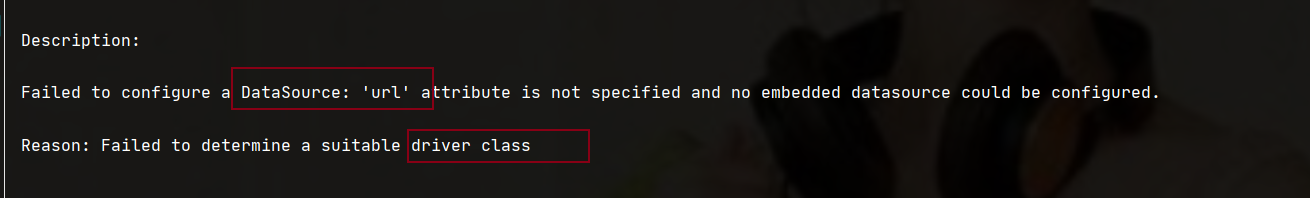
1.1.5 modify YML configuration file
#1. Pay attention to indent when configuring the port number!!!!!
server:
port: 8090
#2. Configure data source
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/jt?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&autoReconnect=true&allowMultiQueries=true
username: root
password: root
mybatis:
type-aliases-package: com.jt.pojo
#Load all mapping files
mapper-locations: classpath:/mappers/*.xml
#Turn on hump mapping
configuration:
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true1.1.7 edit test class
package com.jt;
import com.jt.mapper.UserMapper;
import com.jt.pojo.User;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
public class TestMybatis {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Test
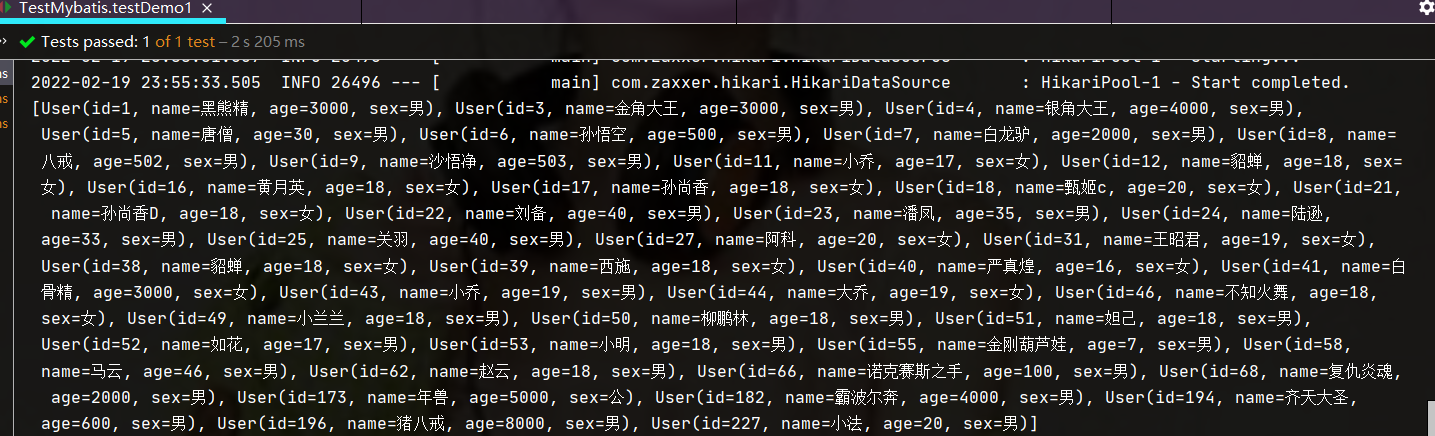
public void testDemo1(){
List<User> all = userMapper.findAll();
System.out.println(all);
}
}
2. Basic usage of mybatis
2.1 query data according to ID
2.1.1 edit test method
@Test
public void testFindUserById(){
int id = 1;
User user = userMapper.findUserById(id);
System.out.println(user);
}2.1.2 editing Mapper interface
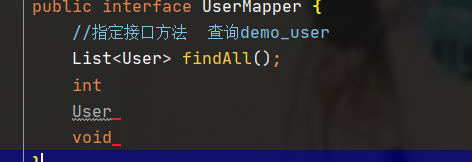
@Mapper //Give the interface to the Spring container to manage map < usermapper, JDK proxy object >
public interface UserMapper {
//Specify interface method query demo_ All data of user
List<User> findAll();
//Query database by ID
User findUserById(int id);
}2.1.3 edit usermapper XML Mapping File
<!-- according to ID query data base
Dynamic value: #{key}
-->
<select id="findUserById" resultType="com.jt.pojo.User">
select * from demo_user where id = #{id}
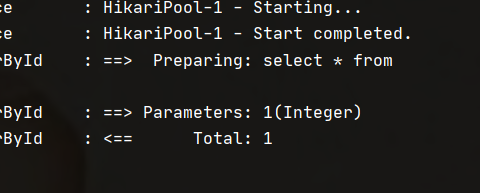
</select>2.2 Sql statement printing
Description: add log operation in YML file
#1. Pay attention to indent when configuring the port number!!!!!
server:
port: 8090
#2. Configure data source
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/jt?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&autoReconnect=true&allowMultiQueries=true
username: root
#The yml file 0 is not parsed. If the letter begins with 0, it is wrapped in quotation marks
#password: "0123456"
password: root
#3. Configure Mybatis
mybatis:
type-aliases-package: com.jt.pojo
#Load all mapping files
mapper-locations: classpath:/mappers/*.xml
#Turn on hump mapping
configuration:
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
#4. Print Sql com jt. Sql log under mapper
logging:
level:
com.jt.mapper: debug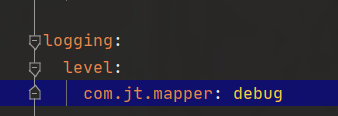
If not compiled (two options):
2.3 query by name and age
2.3.1 edit test class
/**
* Knowledge points:
* 1.If multiple parameters are passed, it is generally encapsulated by object
*/
@Test
public void testFindByNA(){
String name = "Sun Shangxiang";
int age = 18;
User user = new User();
user.setName(name).setAge(age);
List<User> userList = userMapper.findUserByNA(user);
System.out.println(userList);
}2.3.2 editing UserMapper
@Mapper //Give the interface to the Spring container to manage map < usermapper, JDK proxy object >
public interface UserMapper {
//Specify interface method query demo_ All data of user
List<User> findAll();
//Query database by ID
User findUserById(int id);
List<User> findUserByNA(User user);
}2.3.3 edit usermapper XML Mapping File
<!-- according to name and age Query data
Knowledge points: Alias package
Specify the package path in the configuration file: The splicing of package paths can be realized automatically
resultType rule:
1. First, match the package according to the alias.set up..
2. If the match is not successful,Match by path.
Rules for parameter passing:
1. If it is a single parameter,Then use#The value of the parameter obtained by {key}
2. If it is an object parameter,Then use#{property} gets the property value
-->
<select id="findUserByNA" resultType="User">
select * from demo_user where
name = #{name} and age = #{age}
</select>
2.4 query users with age > 18 and age < 100
2.4.1 Sql statement
select * from demo_user where age>18 and age <100
2.4.2 edit test class
/**
* Knowledge point 3:
* Note: if multiple parameters are inconvenient to be encapsulated by User object, the universal set Map should be used
*/
@Test
public void testFindByAge(){
int minAge = 18;
int maxAge = 100;
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("minAge",minAge);
map.put("maxAge",maxAge);
List<User> userList = userMapper.findUserByAge(map);
System.out.println(userList);
}2.4.3 editing Mapper interface
@Mapper //Give the interface to the Spring container to manage map < usermapper, JDK proxy object >
public interface UserMapper {
//Specify interface method query demo_ All data of user
List<User> findAll();
//Query database by ID
User findUserById(int id);
List<User> findUserByNA(User user);
//Habit: there is only one parameter
List<User> findUserByAge(Map<String, Integer> map);
}2.4.4 editing xml Mapping Files
<!--
Query data by age
grammar: If the parameter passed is Map, Then use#{key}
xml Translation character:
1. > >
2. < <
3. & &
-->
<select id="findUserByAge" resultType="User">
select * from demo_user where age > #{minAge}
and age < #{maxAge}
</select>2.4.5 escape label
<!--
Query data by age
grammar: If the parameter passed is Map, Then use#{key}
xml Translation character:
1. > >
2. < <
3. & &
4. Universal translation character
<![CDATA[ Transfer content ]]>
-->
<select id="findUserByAge" resultType="User">
<![CDATA[
select * from demo_user
where age > #{minAge} and age < #{maxAge}
]]>
</select>2.5 realize data encapsulation with annotation @ Param
2.5.1 edit test class
/**
* Knowledge point 4:
* Data encapsulation using annotations
*/
@Test
public void testFindByAge2(){
int minAge = 18;
int maxAge = 100;
List<User> userList = userMapper.findUserByAge2(minAge,maxAge);
System.out.println(userList);
}2.5.2 editing interface documents
//Principle: Mybatis only supports single value reference and encapsulates multiple values into single values
//Comments: @ param ("key") int minage (value)
// Function: encapsulate data into Map
List<User> findUserByAge2(@Param("minAge") int minAge, @Param("maxAge") int maxAge);2.5.3 editing xml Mapping Files
<select id="findUserByAge2" resultType="User">
<![CDATA[
select * from demo_user
where age > #{minAge} and age < #{maxAge}
]]>
</select>2.6 fuzzy query
2.6.1 business requirements
Query the user whose name field contains "Jun" Sql statement:
SELECT * FROM demo_user WHERE NAME LIKE "%King%"
2.6.2 edit test method
/**
* Knowledge point 5:
* Data encapsulation using annotations
*/
@Test
public void testFindUserByLike(){
String name = "%" + "King" + "%";
List<User> userList = userMapper.findUserByLike(name);
System.out.println(userList);
}2.6.3 editing interface method
List<User> findUserByLike(String name);
2.6.4 editing xml Mapping Files
<!--Fuzzy queries pay special attention to the case of table names!!!!!
windows In the system: Case insensitive
Linux In the system: Case sensitive.
-->
<select id="findUserByLike" resultType="User">
SELECT * FROM demo_user WHERE NAME LIKE #{name}
</select>
Mode 2: xml Profile dynamic splicing%
<!--Fuzzy queries pay special attention to the case of table names!!!!!
windows In the system: Case insensitive
Linux In the system: Case sensitive.
grammar: "%" In this way
-->
<select id="findUserByLike" resultType="User">
SELECT * FROM demo_user WHERE NAME LIKE "%"#{name}"%"
</select>2.7 Sql tag usage
2.7.1 business requirements
Note: duplicate data often appears in Sql statements If you write your own handwriting every time you repeat The efficiency of development is low Optimization: extract public Sql. Advantages: Sql tags can save code. Disadvantages: poor readability. If it is an association operation, it depends on the situation
2.7.2 Sql tag usage
<!--Fuzzy queries pay special attention to the case of table names!!!!!
windows In the system: Case insensitive
Linux In the system: Case sensitive.
grammar: "%" In this way
-->
<select id="findUserByLike" resultType="User">
SELECT <include refid="tableColumn"/> FROM demo_user WHERE NAME LIKE "%"#{name}"%"
</select>
<!--Sql label: Extract public Sql sentence -->
<sql id="tableColumn">
id,name,age,sex
</sql>2.8 set parameter writing in mybatis
2.8.1 business requirements
Query data with id=1,2,3,5,7
select * from demo_user where id in (1,2,3,5,7........)
2.8.2 edit test class
//Front end: URL? After id = 1,2,3,4,5 is obtained, it is generally received by array
@Test
public void testFindListByIn(){
int[] array = {1,2,3,5,7};
List<User> userList = userMapper.findListByIn(array);
System.out.println(userList);
}2.8.3 editing Mapper interface
List<User> findListByIn(int[] array);
2.8.4 edit Mapper mapping file
<!--
about Mybatis Traversal of
foreach:
1. collection Collection to traverse
1.1 array keyword: array/list
1.2 list Set keyword: list/array
1.3 Map<key,array/list> keyword:key
2. open/close The beginning and end of the loop body can be written to the simplified label outside the loop
3. item Variable name of the current traversal data
4. separator Separator
-->
<select id="findListByIn" resultType="User">
select * from demo_user where id in (
<foreach collection="array" item="id" separator=",">
#{id}
</foreach>
)
</select>2.9 user addition
2.9.1 edit test method
<insert id="saveUser">
insert into demo_user(id,name,age,sex)
value (null, #{name},#{age},#{sex})
</insert>@Test
public void testInsertUser(){
User user = new User();
user.setName("Zhang San").setAge(18).setSex("male");
userMapper.saveUser(user);
System.out.println("Successfully added!!!!");
}2.9.2 editing interface method
void saveUser(User user);
2.9.3 editing xml Mapping Files
<insert id="saveUser">
insert into demo_user(id,name,age,sex)
value (null, #{name},#{age},#{sex})
</insert>