Zero. Premise of use
Create an aggregation project in which each module is an independent springboot project
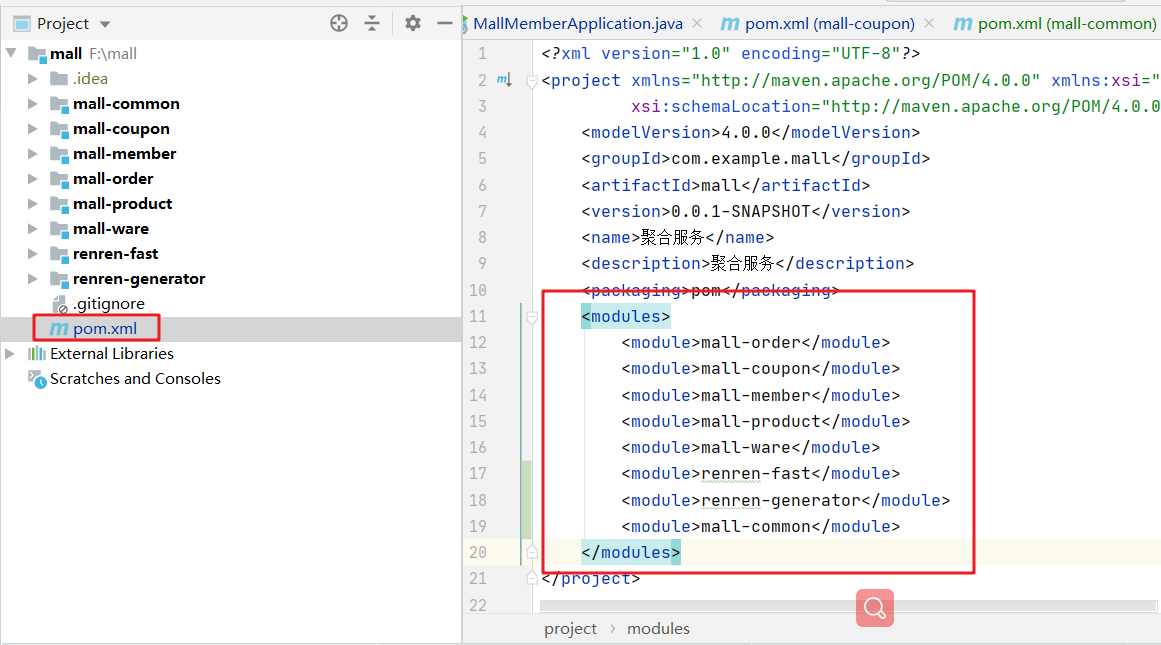
The springcloud version should correspond to the springboot version, otherwise an error will be reported
1, Introduction to components used
| assembly | effect |
|---|---|
| nacos | Registry (service registration and discovery), configuration center (dynamic configuration management) |
| Ribbon | load balancing |
| Feign | Declarative Http client (calling remote services) |
| Sentinel | Service fault tolerance (current limiting, degradation, fusing) |
| Gateway | API gateway (weblux programming mode) |
| Sleuth | Call chain monitoring |
| Seata | Original Fescar, i.e. distributed transaction solution |
2, Introducing dependencies in common modules
1. Each microservice project will have a common module to introduce some common dependencies and configurations
2. When this dependency is introduced, other dependencies of spring cloud Alibaba do not need to write the version number
3. Note that the version number should correspond to the springboot version
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.2.3.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
3, Nacos
1. Download nacos and start
Link: https://github.com/alibaba/nacos/releases
Open the downloaded folder and click Startup in bin CMD run
2. Registration Center
Public module introduces registry dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>
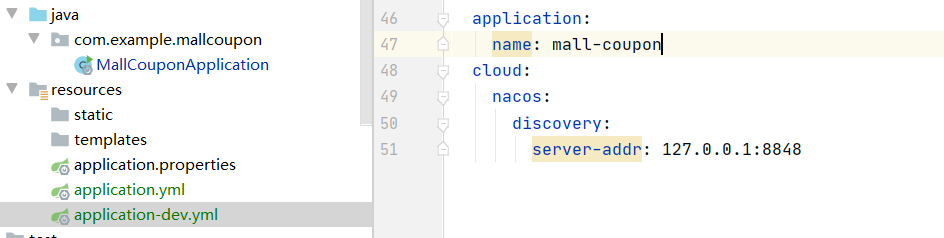
1. Specify the nacos address and service name in each micro service yml (to know which service is registered)
spring:
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
application:
name: mall-coupon
2. Use the @ EnableDiscoveryClient annotation to enable service registration and discovery
After joining, you can register with the registration center

Visit Nacos at http://127.0.0.1:8848/nacos The account and password are all Nacos
You can see that the service has been registered
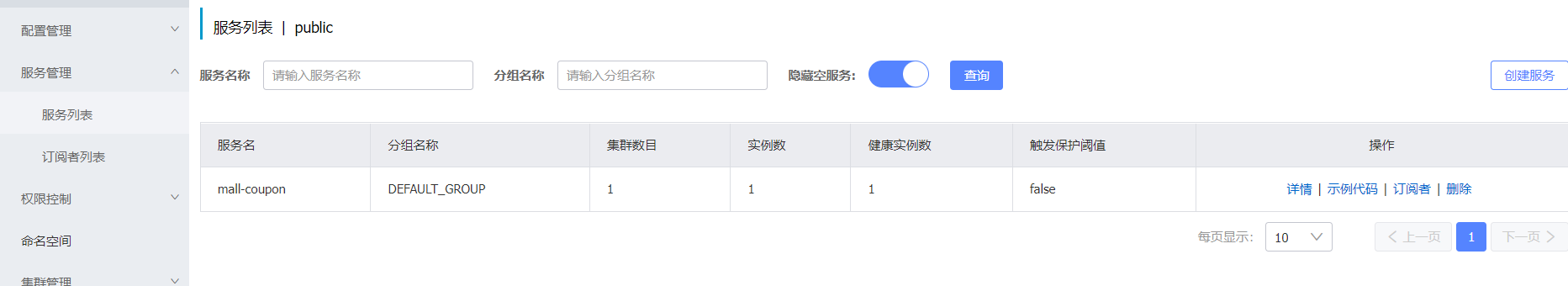
3. Configuration center
1. Import dependency
Import dependency in common module
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
2. Create a new bootstrap yml
Priority is higher than application yml
spring:
application:
name: mall-coupon
cloud:
nacos:
config:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
3. Test the original configuration
1. In application YML new value added
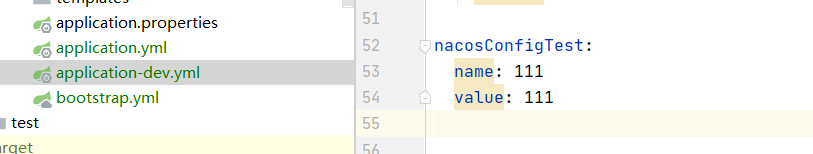
2. @ Value get Value

3. Interface output value

@RestController
@RequestMapping("/coupon")
public class couponController {
@Value("${nacosConfigTest.name}")
private String name;
@Value("${nacosConfigTest.value}")
private String value;
@Resource
MemberFeignService memberFeignService;
@GetMapping("/test")
public String test(){
String s = memberFeignService.memberFeignTest();
String result = "This is the return interface of the caller module calling the callee module:"+s;
return result;
}
@GetMapping("/configTest")
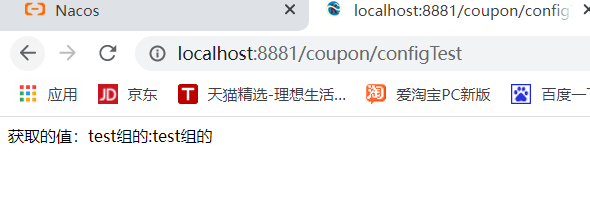
public String configTest(){
return "Value obtained:"+name+":"+value;
}
}
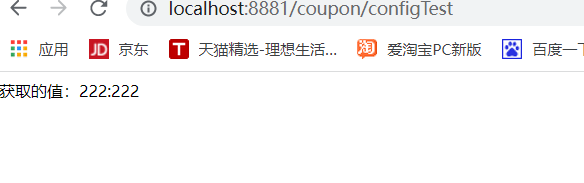
4. The value obtained by the interface at this time

4. nacos new configuration
1. New configuration
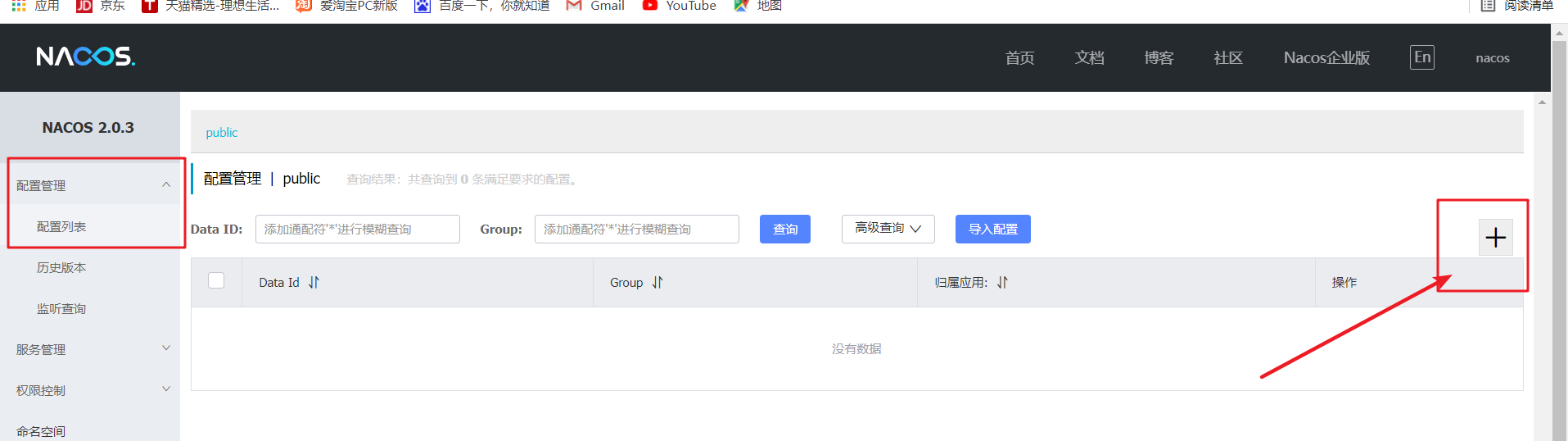
2. Input the information that needs dynamic configuration into the configuration content
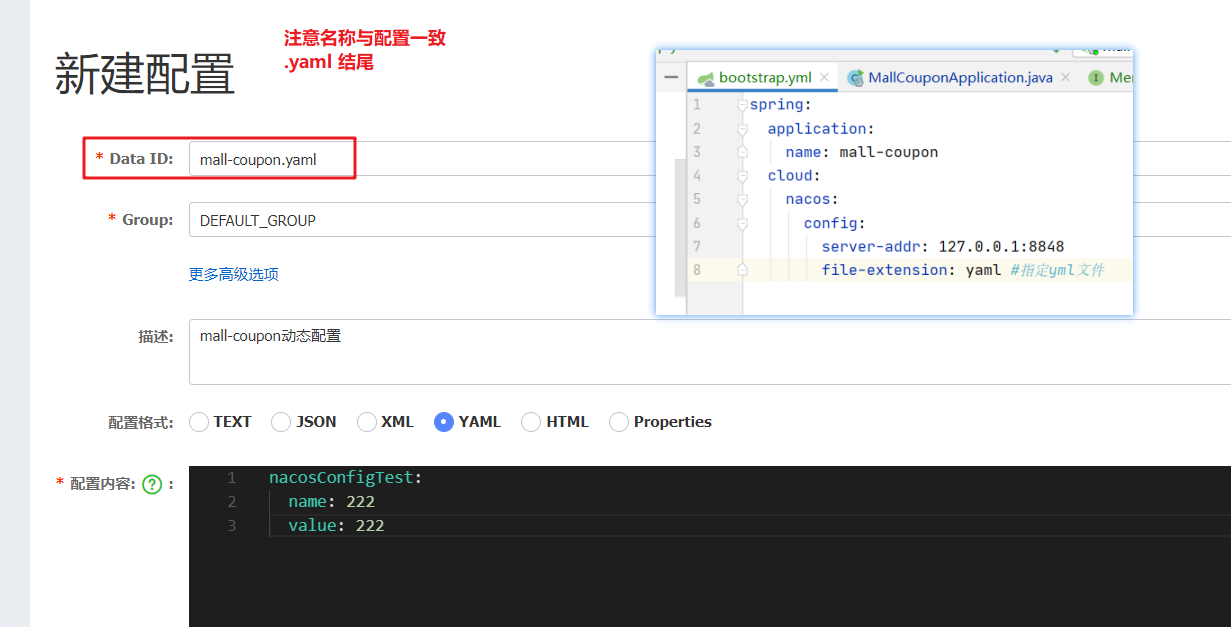
3. Use @ RefreshScope on the interface class
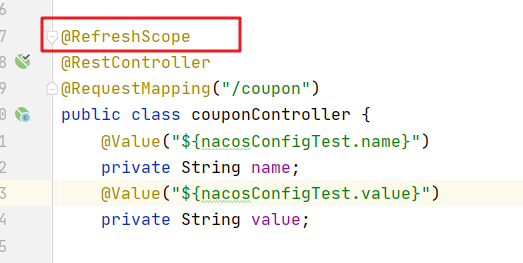
4. At this point, the interface return value becomes dynamic configuration
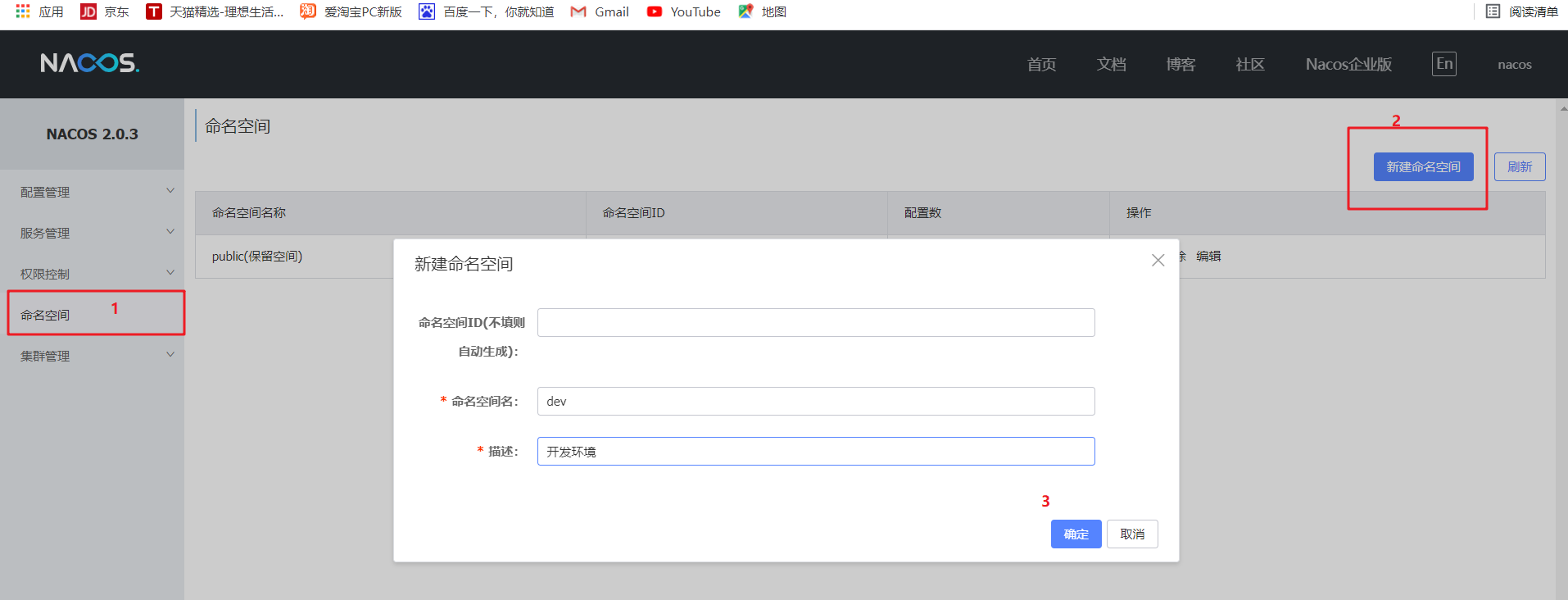
4. Namespace (configuration isolation)
By default, all new configurations are in the public space
For example, during development, we have 1, development environment 2, deployment environment 3 and test environment
1. Add a new development, deployment and test environment in the nacos namespace
 2. Click the configuration list to add several environments
2. Click the configuration list to add several environments
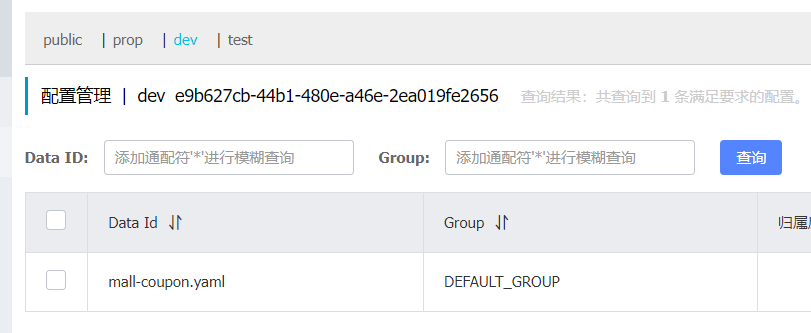
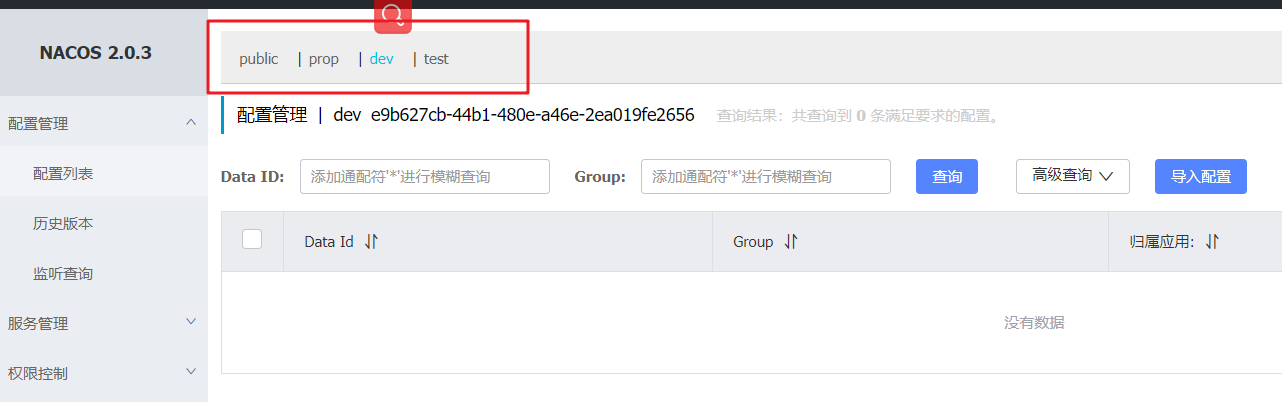 3. Create the same configuration as above in the dev environment
3. Create the same configuration as above in the dev environment
 4. In bootstrap YML new namespace
4. In bootstrap YML new namespace

spring:
application:
name: mall-coupon
cloud:
nacos:
config:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
file-extension: yaml #Specify yml file
namespace: e9b627cb-44b1-480e-a46e-2ea019fe2656 # Namespace id
5. At this time, the configuration in the test environment is taken

5. Configure grouping
1. Fill in groups when adding configurations
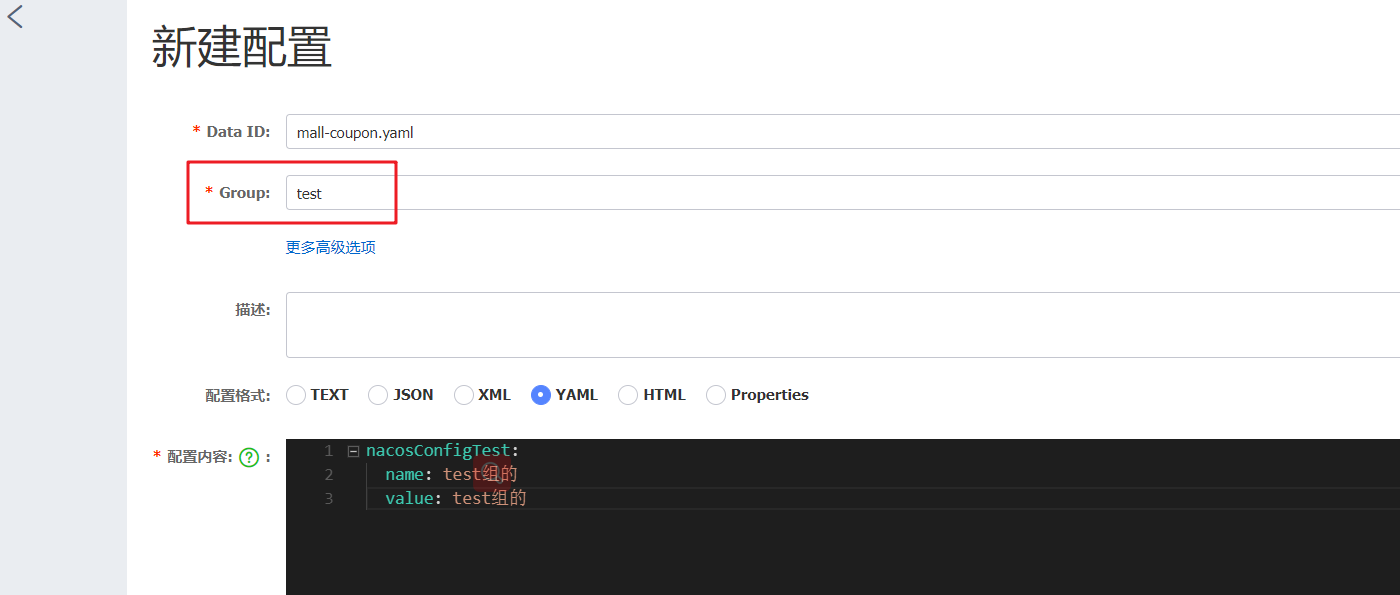
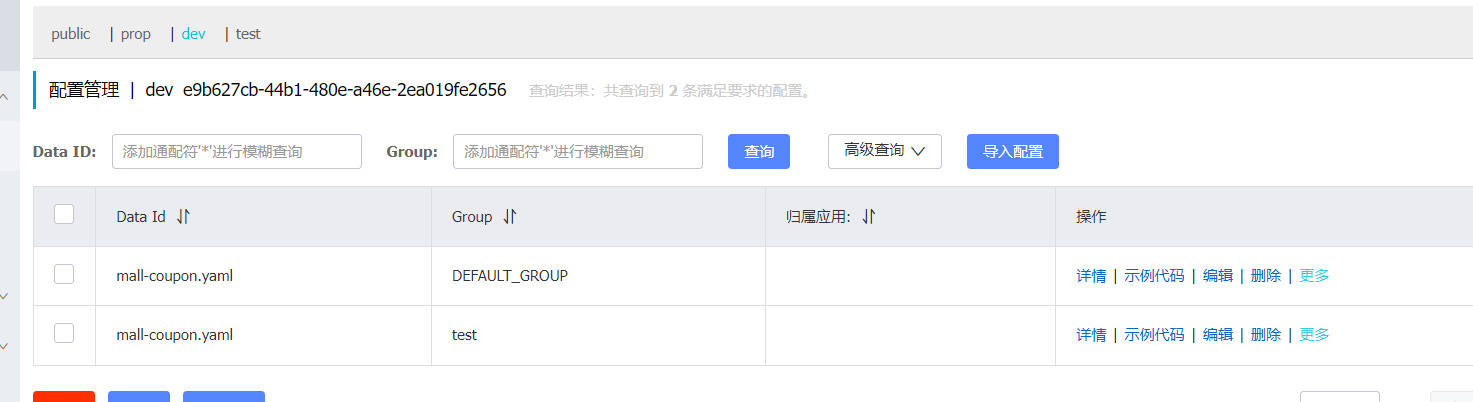 2. In bootstrap YML add specified group
2. In bootstrap YML add specified group

spring:
application:
name: mall-coupon
cloud:
nacos:
config:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
file-extension: yaml #Specify yml file
namespace: e9b627cb-44b1-480e-a46e-2ea019fe2656 # Namespace id
group: test #Group name
3. In this case, the value of the specified group is taken
4, Feign declarative remote call
1. Public module introduces openfeign dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
<version>2.2.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
2. The interface is normally written in one module and called by another module
1. The member module (called module) writes the interface normally
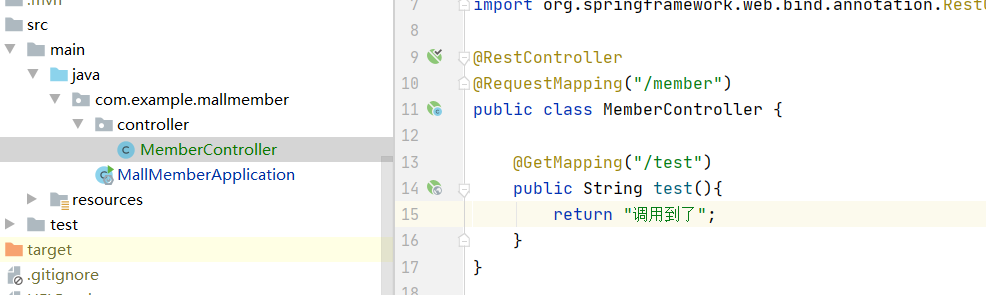
2. coupon module (calling module) creates a feign package and an interface class to specifically call the interface of member module
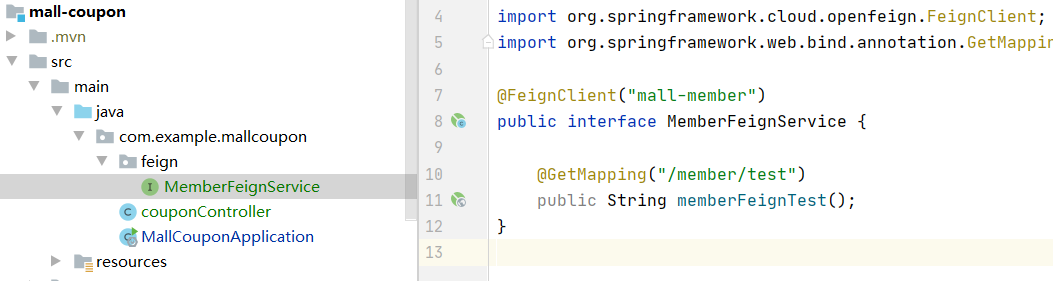
3. Use @ feignclient ("mall member") on the interface class to specify the service name on nacos
 4. Write the interface path of the full member module (called module)
4. Write the interface path of the full member module (called module)
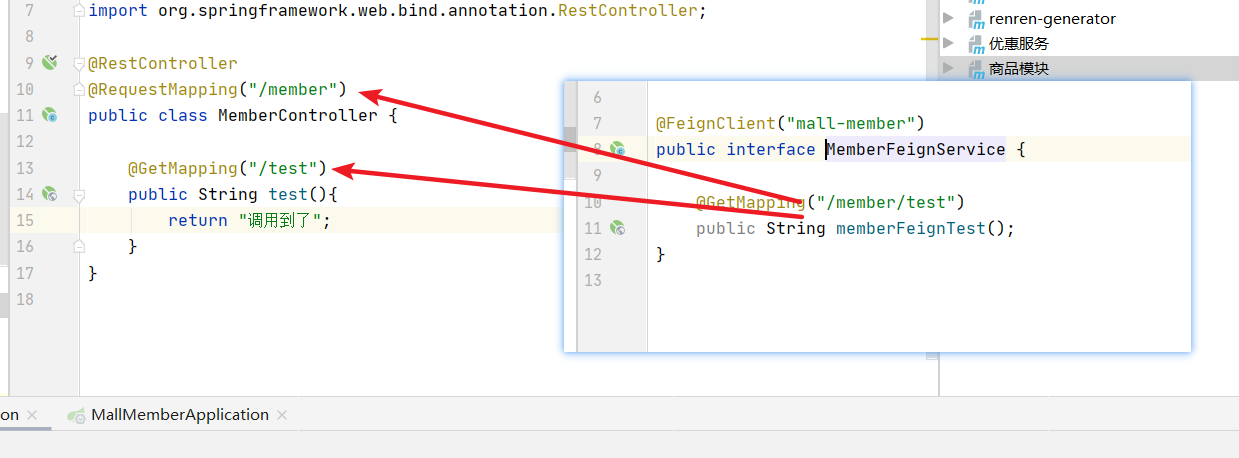
3. Use @ EnableFeignClients on the calling module startup class to open feign
The coupon module (caller) opens feign and specifies the package name
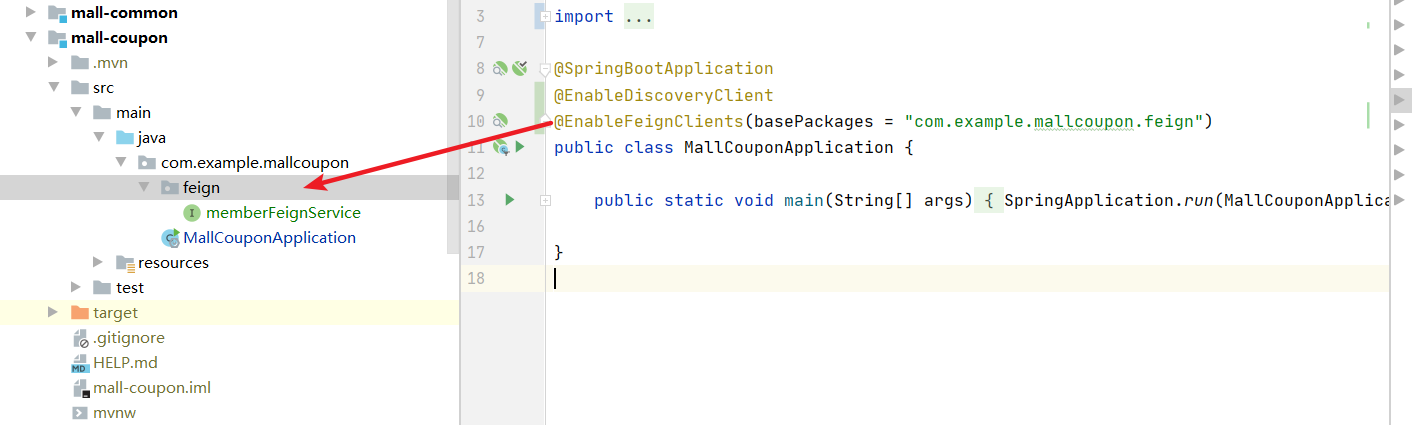
Test call


4. feign performance optimization
Feign's underlying client implementation:
1. URLConnection: the default implementation does not support connection pool
2. Apache HttpClient: support connection pool
3. OKHttp: support connection pool
Therefore, optimizing feign mainly includes:
1. Use the connection pool instead of the default URLConnection
2. Log level, preferably basic or none
Introduce dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>io.github.openfeign</groupId>
<artifactId>feign-httpclient</artifactId>
</dependency>
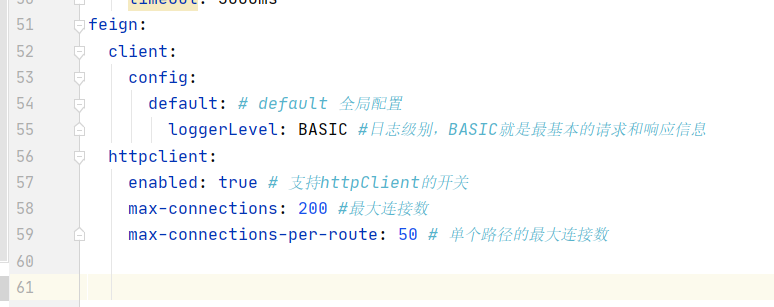
Configure yml
feign:
client:
config:
default: # default global configuration
loggerLevel: BASIC #At the log level, BASIC is the most BASIC request and response information
httpclient:
enabled: true # Switch supporting httpClient
max-connections: 200 #maximum connection
max-connections-per-route: 50 # Maximum connections per path
5, Gateway gateway
Common functions: route forwarding, permission verification, current limit control, etc
1. Build
1. New gateway module
2. Rely on
<!-- Common module-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.example.mall</groupId>
<artifactId>mall-common</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
<!-- gateway-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
<version>2.2.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
3. @ EnableDiscoveryClient enable service registration
4. Create a new bootstrap YML and application yml
bootstrap.yml
spring:
application:
name: mall-gateway
cloud:
nacos:
config:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
namespace: 6d405b31-5f62-4105-b8a6-339cc0b8464e
application.yml
server:
port: 88
spring:
application:
name: mall-gateway
cloud:
nacos:
config:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
5. New gateway namespace and configuration
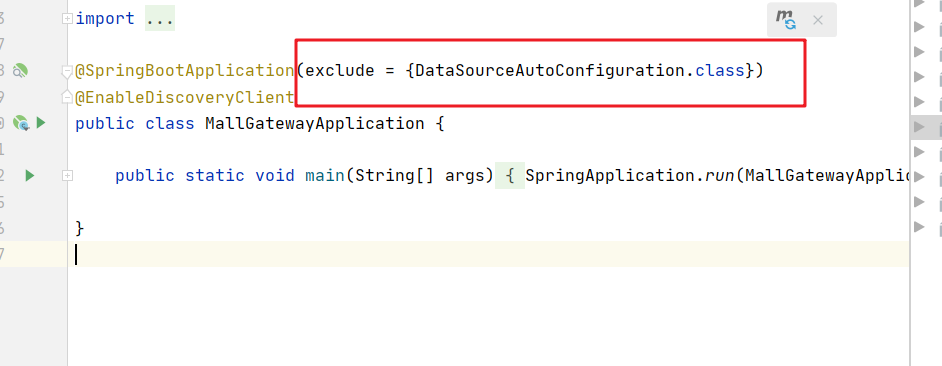
6. Exclude data source related configurations
Because we have introduced the common module, the gateway does not need to configure the data source, and it is not ruled out that the data source configuration will report an error
2. New forwarding gateway configuration (yml)
server:
port: 88
spring:
application:
name: mall-gateway
cloud:
nacos:
config:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
#Gateway configuration
gateway:
routes:
- id: coupon
uri: http://127.0.0.1:8881 / # request address to go
# uri: lb://The target address lb of the mall coupling # route is load balancing, followed by the service name
predicates: # Routing assertion is to judge whether the request meets the conditions of routing rules
- Query=url,coupon # If the URL has / coupon, go to the uri address above. For example: url=coupon
# - Path=/coupon/** # This url is matched according to the path. It meets the requirements as long as it starts with / coupon
#- After=2037-01-20T17:42:47.789-07:00[Asia/Shanghai] # You can access it after this time
- id: member
uri: http://127.0.0.1:8882 / # request address to go
# uri: lb://The target address lb of the mall member # route is load balancing, followed by the service name
predicates: # Routing assertion is to judge whether the request meets the conditions of routing rules
- Query=url,member # If the URL has / coupon, go to the upper uri address url=member
# - Path=/member/** # This url is matched according to the path. It meets the requirements as long as it starts with / member
test

Spring provides 11 basic predict factories:
| name | explain | Example |
|---|---|---|
| After | Is a request after a certain point in time | - After=2037-01-20T17:42:47.789-07:00[America/Denver] |
| Before | Is a request before a certain point in time | - Before=2031-04-13T15:14:47.433+08:00[Asia/Shanghai] |
| Between | Is a request before two points in time | - Between=2037-01-20T17:42:47.789-07:00[America/Denver], 2037-01-21T17:42:47.789-07:00[America/Denver] |
| Cookie | The request must contain some cookie s | - Cookie=chocolate, ch.p |
| Header | The request must contain some header s | - Header=X-Request-Id, \d+ |
| Host | The request must be to access a host (domain name) | - Host=.somehost.org,.anotherhost.org |
| Method | The request mode must be the specified mode | - Method=GET,POST |
| Path | The request path must conform to the specified rules | - Path=/red/{segment},/blue/** |
| Query | The request parameter must contain the specified parameter | -Query=name, Jack or - Query=name |
| RemoteAddr | The ip address of the requester must be in the specified range | - RemoteAddr=192.168.1.1/24 |
| Weight | Weight processing |
3. Route filter GatewayFilterFactory
spring provides 31 different routing filter factories.
| name | explain |
|---|---|
| AddRequestHeader | Add a request header to the current request |
| RemoveRequestHeader | Remove a request header from the request |
| AddResponseHeader | Add a response header to the response result |
| RemoveResponseHeader | There is a response header removed from the response result |
| RequestRateLimiter | Limit requested traffic |
| . . . |
test
1. Add configuration
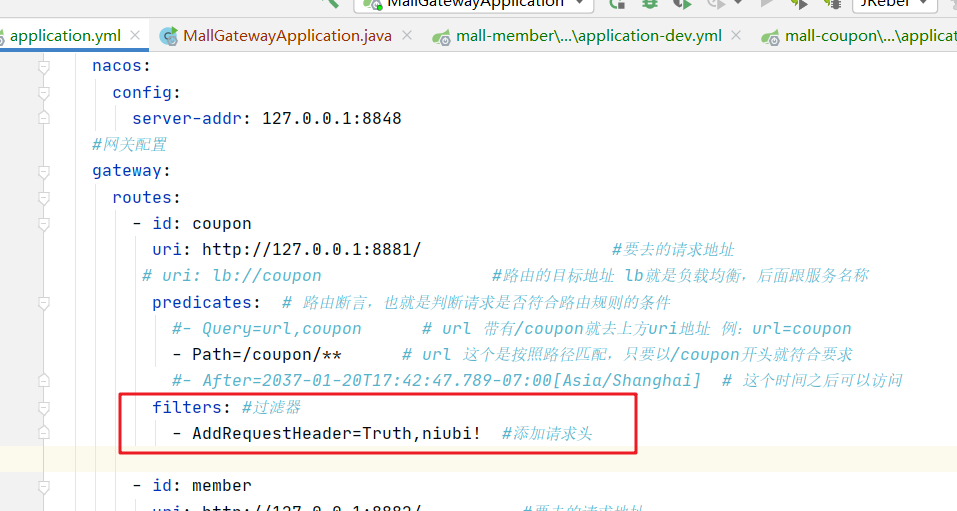 2. Get request header in interface
2. Get request header in interface
 3. Added to request header
3. Added to request header
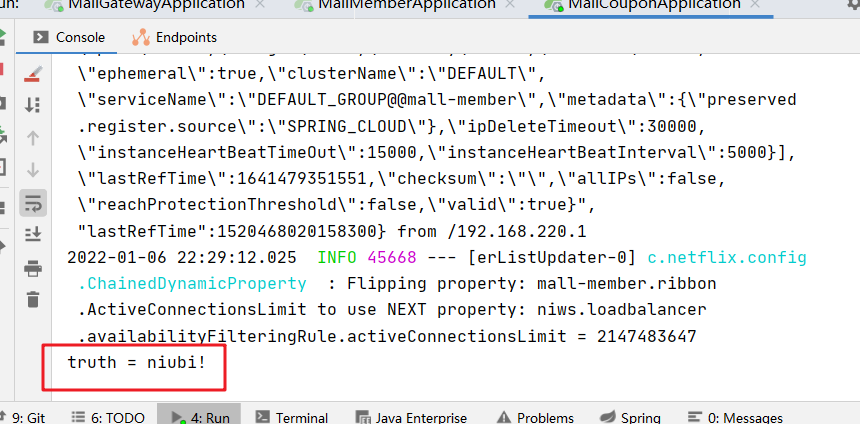 4. Effective for all routing requests
4. Effective for all routing requests
 5. Code
5. Code
server:
port: 88
spring:
application:
name: mall-gateway
cloud:
nacos:
config:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
#Gateway configuration
gateway:
routes:
- id: coupon
uri: http://127.0.0.1:8881 / # request address to go
# uri: lb://The destination address lb of the coupon # route is load balancing, followed by the service name
predicates: # Routing assertion is to judge whether the request meets the conditions of routing rules
#- Query=url,coupon # If the URL has / coupon, go to the uri address above. For example: url=coupon
- Path=/coupon/** # This url is matched according to the path. It meets the requirements as long as it starts with / coupon
#- After=2037-01-20T17:42:47.789-07:00[Asia/Shanghai] # You can access it after this time
#filters: #filter
#- AddRequestHeader=Truth,niubi! #Add request header
- id: member
uri: http://127.0.0.1:8882 / # request address to go
# uri: lb://The target address lb of the member # route is load balancing, followed by the service name
predicates: # Routing assertion is to judge whether the request meets the conditions of routing rules
#- Query=url,member # If the URL has / coupon, go to the upper uri address url=member
- Path=/member/** # This url is matched according to the path. It meets the requirements as long as it starts with / member
default-filters: #The default filter will take effect for all routing requests
- AddRequestHeader=Truth,niubi!
4. Global filter
The difference between GetewayFilter and GetewayFilter is that GetewayFilter is defined through configuration, and the processing logic is fixed. The logic of GlobalFilter needs to be implemented by writing code.
This is defined by implementing the GlobalFilter interface.
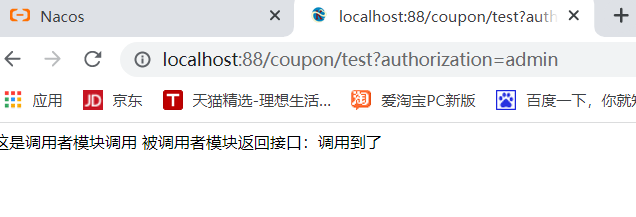
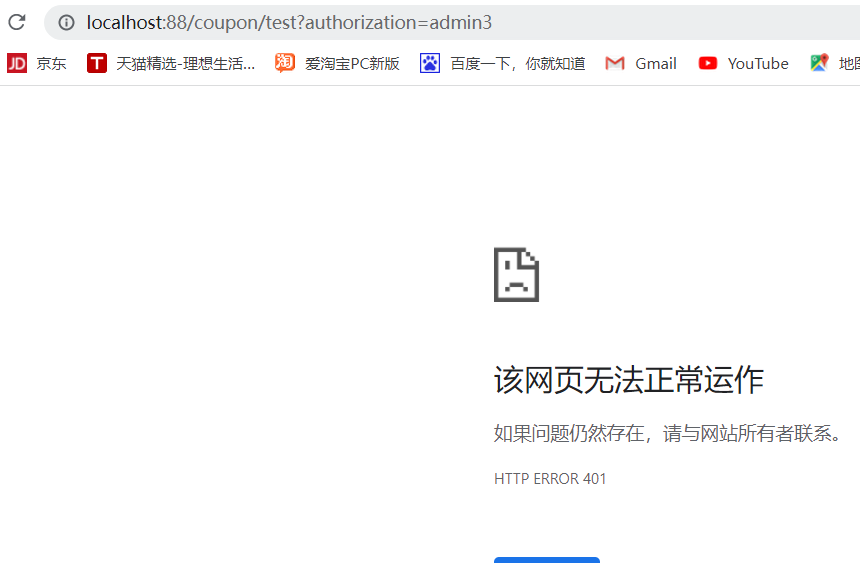
Case: define global filter, intercept and judge user identity
Requirement: define a global filter, intercept the request, and judge whether the requested parameters meet the following conditions:
1. Is there authorization in the parameter
2. Whether the authorization parameter value is admin
If both are met, release, otherwise intercept

@Order(-1) // Multiple filters, the smaller the value, the higher the priority
@Component
public class AuthorizationFilter implements GlobalFilter {
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {
// 1. Get request header
ServerHttpRequest request = exchange.getRequest();
MultiValueMap<String, String> params = request.getQueryParams();
// 2. Gets the authorization parameter in the parameter
String auth = params.getFirst("authorization");
// 3. Judge whether the parameter value is equal to admin
if ("admin".equals(auth)){
// 4. Yes, release
return chain.filter(exchange);
} // 5. No, intercept
// Set status code
exchange.getResponse().setStatusCode(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED);
return exchange.getResponse().setComplete();
}
}
test
correct
 FALSE
FALSE
5. Filter execution sequence

Each filter must specify an order value. The smaller the order value, the higher the priority and the higher the execution order
.
GlobalFilter specifies the order value by implementing the @ order annotation, which we specify ourselves
.
The order of routing filter and defaultFilter is specified by Spring. By default, it is incremented from 1 in the order of declaration (that is, yml configuration. The higher the above, the higher)
.
When the order value of the filter is the same, it will be executed in the order of defaultfilter > routing filter > globalfilter.
6. Cross domain problem handling
Cross domain: domain name inconsistency is cross domain, mainly including
1. Different domain names: www.taobao.com COM and www.taobao.com Org and www.jd.com com
2. The domain name is the same, but the ports are different: 8080 and 8081
Cross domain problem: the browser prohibits cross domain ajax requests between the initiator of the request and the server, and the request is intercepted by the browser
Solution: CORS
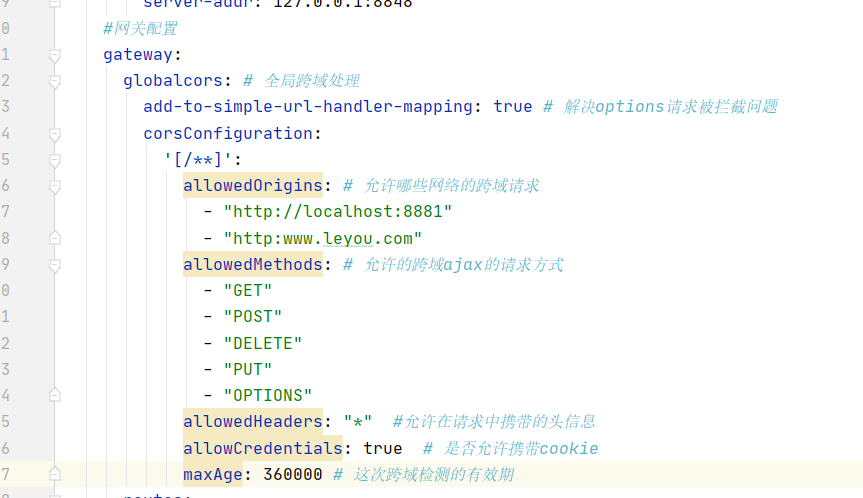
#Gateway configuration
gateway:
globalcors: # Global cross domain processing
add-to-simple-url-handler-mapping: true # Solve the problem that the options request is intercepted
corsConfiguration:
'[/**]':
allowedOrigins: # Which networks are allowed for cross domain requests
- "http://localhost:8881"
- "http:www.leyou.com"
allowedMethods: # Allowed cross domain ajax request mode
- "GET"
- "POST"
- "DELETE"
- "PUT"
- "OPTIONS"
allowedHeaders: "*" #Header information allowed to be carried in the request
allowCredentials: true # Allow cookie s
maxAge: 360000 # Validity of this cross domain detection
8. Configure all codes
server:
port: 88
spring:
application:
name: mall-gateway
cloud:
nacos:
config:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
#Gateway configuration
gateway:
globalcors: # Global cross domain processing
add-to-simple-url-handler-mapping: true # Solve the problem that the options request is intercepted
corsConfiguration:
'[/**]':
allowedOrigins: # Which networks are allowed for cross domain requests
- "http://localhost:8881"
- "http:www.leyou.com"
allowedMethods: # Allowed cross domain ajax request mode
- "GET"
- "POST"
- "DELETE"
- "PUT"
- "OPTIONS"
allowedHeaders: "*" #Header information allowed to be carried in the request
allowCredentials: true # Allow cookie s
maxAge: 360000 # Validity of this cross domain detection
routes:
- id: coupon
uri: http://127.0.0.1:8881 / # request address to go
# uri: lb://The destination address lb of the coupon # route is load balancing, followed by the service name
predicates: # Routing assertion is to judge whether the request meets the conditions of routing rules
#- Query=url,coupon # If the URL has / coupon, go to the uri address above. For example: url=coupon
- Path=/coupon/** # This url is matched according to the path. It meets the requirements as long as it starts with / coupon
#- After=2037-01-20T17:42:47.789-07:00[Asia/Shanghai] # You can access it after this time
#filters: #filter
#- AddRequestHeader=Truth,niubi! #Add request header
- id: member
uri: http://127.0.0.1:8882 / # request address to go
# uri: lb://The target address lb of the member # route is load balancing, followed by the service name
predicates: # Routing assertion is to judge whether the request meets the conditions of routing rules
#- Query=url,member # If the URL has / coupon, go to the upper uri address url=member
- Path=/member/** # This url is matched according to the path. It meets the requirements as long as it starts with / member
default-filters: #The default filter will take effect for all routing requests
- AddRequestHeader=Truth,niubi!
To be added......