Sentinel overview
Sentinel: traffic guard of distributed system
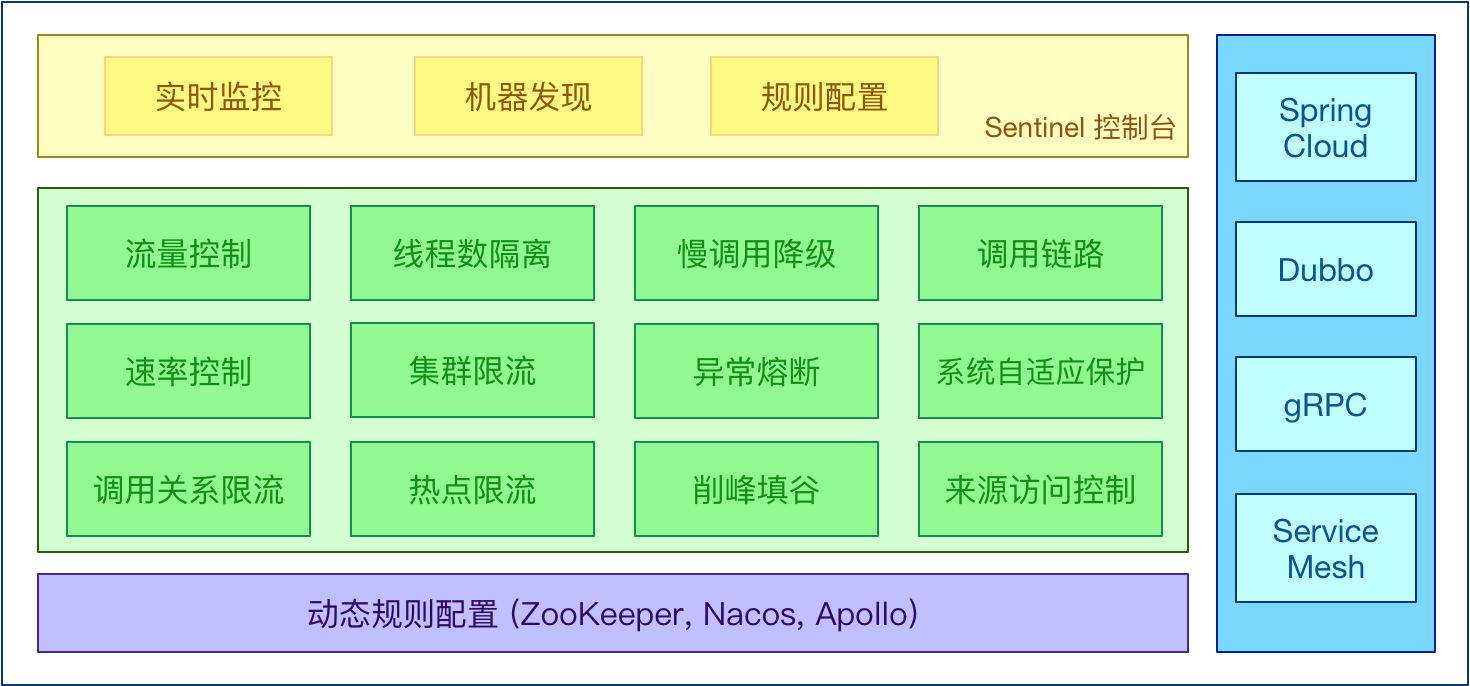
Sentinel takes traffic as the starting point to protect the stability of services from multiple dimensions such as traffic control, fuse degradation and system load protection.
Sentinel is divided into two parts:
Core library( Java Client) does not depend on any framework/Library, which can run on all Java Runtime environment, and Dubbo / Spring Cloud And other frameworks also have good support. Console( Dashboard)be based on Spring Boot Development can be run directly after packaging without additional Tomcat And other application containers.
Sentinel's main features:
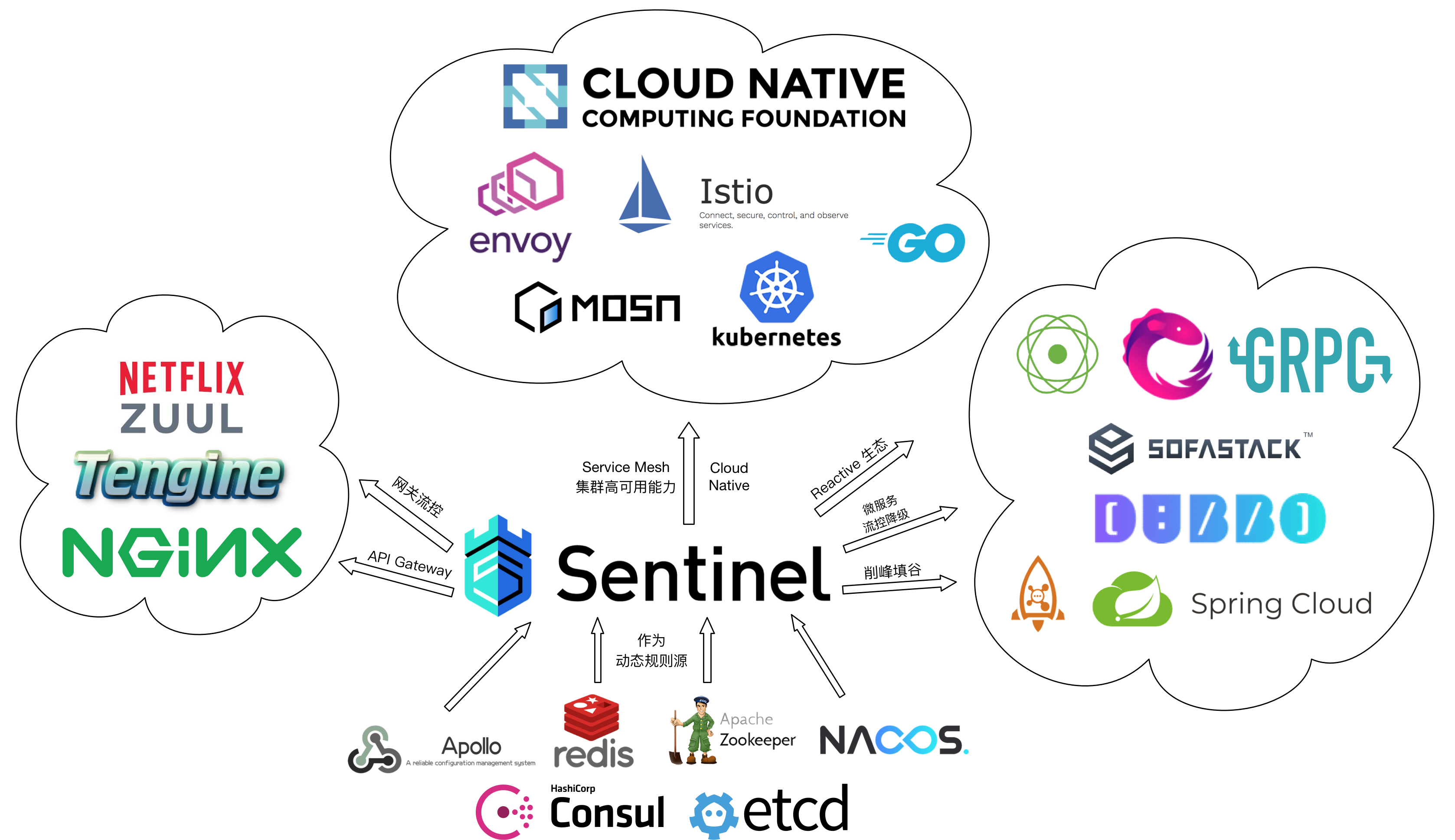
Sentinel's open source ecosystem:
GitHub address: https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel
Official website: https://sentinelguard.io/zh-cn/
Project integration Sentinel
Correlation dependency
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<!--integration spring cloud-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>Hoxton.SR9</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<!--integration spring cloud alibaba-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.2.6.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
Configure Sentinel after the Sentinel console is successfully set up
spring:
cloud:
sentinel:
transport:
# Specifies the address of the sentinel console
dashboard: IP:8858
View Sentinel endpoint
Exposure endpoint
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: '*'
visit: http://localhost:8082/actuator/sentinel
{
"blockPage": null,
"appName": "pay-center",
"consoleServer": [
],
"coldFactor": "3",
"rules": {
"systemRules": [
],
"authorityRule": [
],
"paramFlowRule": [
],
"flowRules": [
],
"degradeRules": [
]
},
"metricsFileCharset": "UTF-8",
"filter": {
"order": -2147483648,
"urlPatterns": [
"/**"
],
"enabled": true
},
"totalMetricsFileCount": 6,
"datasource": {
},
"clientIp": "192.168.42.16",
"clientPort": "8719",
"logUsePid": false,
"metricsFileSize": 52428800,
"logDir": "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\logs\\csp\\",
"heartbeatIntervalMs": 10000
}
Sentinel console
First, determine the Sentinel version corresponding to spring cloud Alibaba, and then build the Sentinel console of the corresponding version
<!--click artifactId get into spring-cloud-alibaba View in dependency management nacos Version of-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.2.6.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<sentinel.version>1.8.1</sentinel.version>
Docker deployment Sentine
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38628046/article/details/106875278
Add Sentinel configuration and restart the project
spring:
cloud:
sentinel:
transport:
# Specifies the address of the sentinel console
dashboard: IP:8858
Since Sentinel is lazy loading, you need to access the( http://192.168.179.1:8082/test/1 )The corresponding service will appear only once for any interface

After accessing the interface for many times, it is found that there is no monitoring information
Check the Docker container log and find that it seems to be caused by IP, and the IP is strange.
ERROR 1 --- [pool-2-thread-1] c.a.c.s.dashboard.metric.MetricFetcher : Failed to fetch metric from <http://192.168.42.16:8719/metric?startTime=1638617140000&endTime=1638617146000&refetch=false> (ConnectionException: Connection timed out) ERROR 1 --- [pool-2-thread-1] c.a.c.s.dashboard.metric.MetricFetcher : Failed to fetch metric from <http://192.168.42.16:8719/metric?startTime=1638617147000&endTime=1638617153000&refetch=false> (ConnectionException: Connection timed out) ERROR 1 --- [pool-2-thread-1] c.a.c.s.dashboard.metric.MetricFetcher : Failed to fetch metric from <http://192.168.42.16:8719/metric?startTime=1638617154000&endTime=1638617160000&refetch=false> (ConnectionException: Connection timed out) ERROR 1 --- [pool-2-thread-1] c.a.c.s.dashboard.metric.MetricFetcher : Failed to fetch metric from <http://192.168.42.16:8719/metric?startTime=1638617161000&endTime=1638617167000&refetch=false> (ConnectionException: Connection timed out)
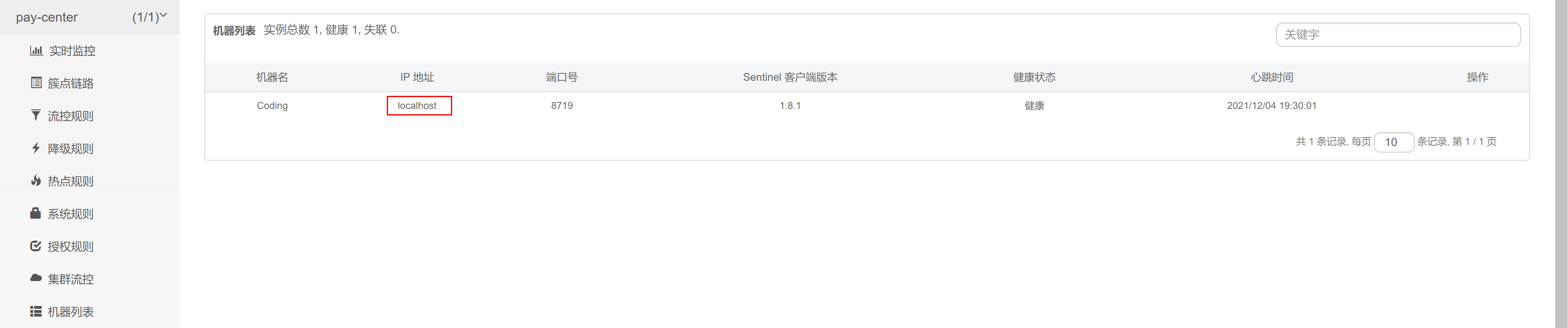
Shut down the service and remove the wrong machine IP from the list of machines on the sentinel console
Modify Sentinel configuration
spring:
cloud:
sentinel:
transport:
# Specifies the address of the sentinel console
dashboard: IP:8858
#Specify the ip to communicate with the console. If it is not configured, an ip registration will be automatically selected, which may cause errors
clientIp: localhost
Restart service
Multiple visits http://192.168.179.1:8082/test/1 Interface service
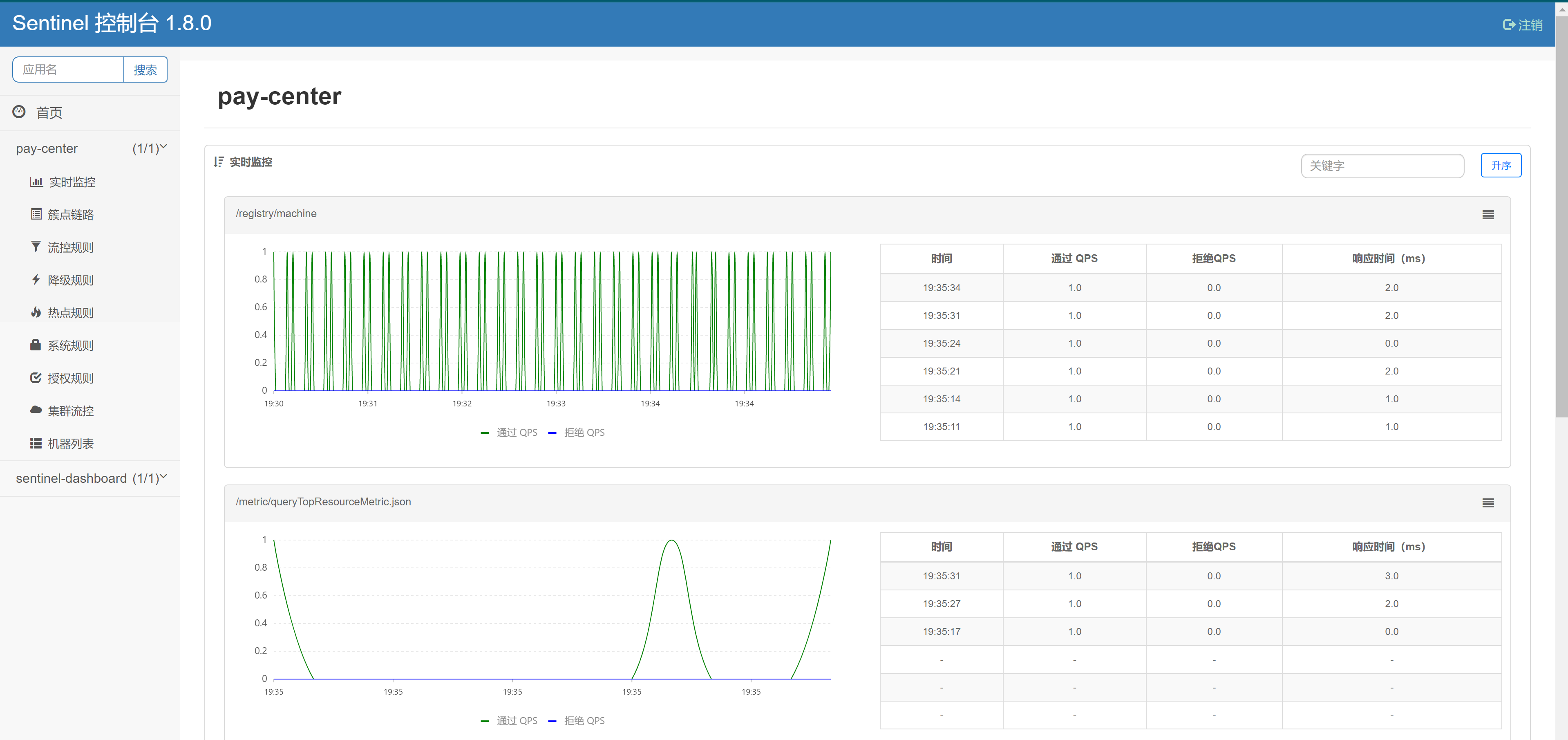
The test/{id} interface was requested. The interface was not found in the real-time monitoring. The reason was not found for a long time. Therefore, the Jar was directly downloaded and run locally.
Download address: https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/releases
java -jar sentinel-dashboard-1.8.1.jar
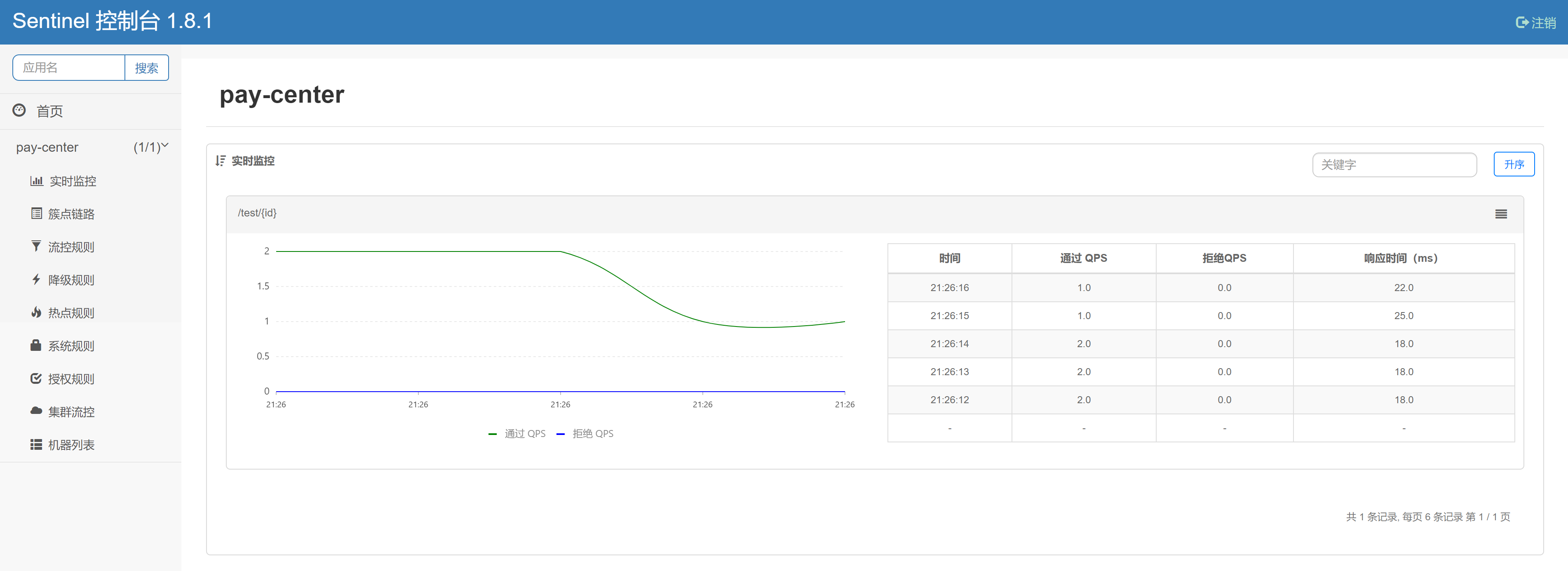
Modify Sentinel configuration (change Sentinel service address to local machine) and access http://localhost:8082/test/1 Service address, last access http://localhost:8080/
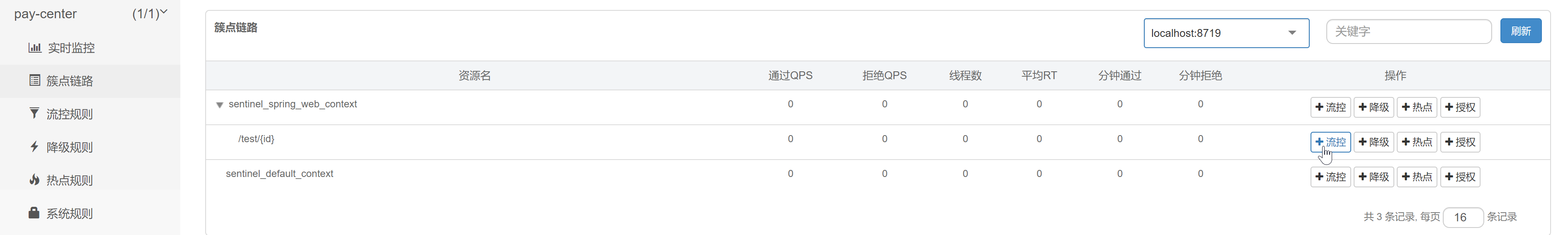
Sentinel's rules
Flow control rules
The principle of flow control is to monitor the QPS or the number of concurrent threads of application traffic, and control the traffic when the specified threshold is reached, so as to avoid being overwhelmed by the instantaneous traffic peak, so as to ensure the high availability of the application.
A current limiting rule is mainly composed of the following factors, which can be combined to achieve different current limiting effects:
resource: The resource name, that is, the object of the flow restriction rule count: Current limiting threshold grade: Current limiting threshold type( QPS Or concurrent threads) limitApp: Call source for flow control, if yes default The call source is not distinguished strategy: Call relation current limiting policy controlBehavior: Flow control effect (direct rejection Warm Up,Uniform speed queue)
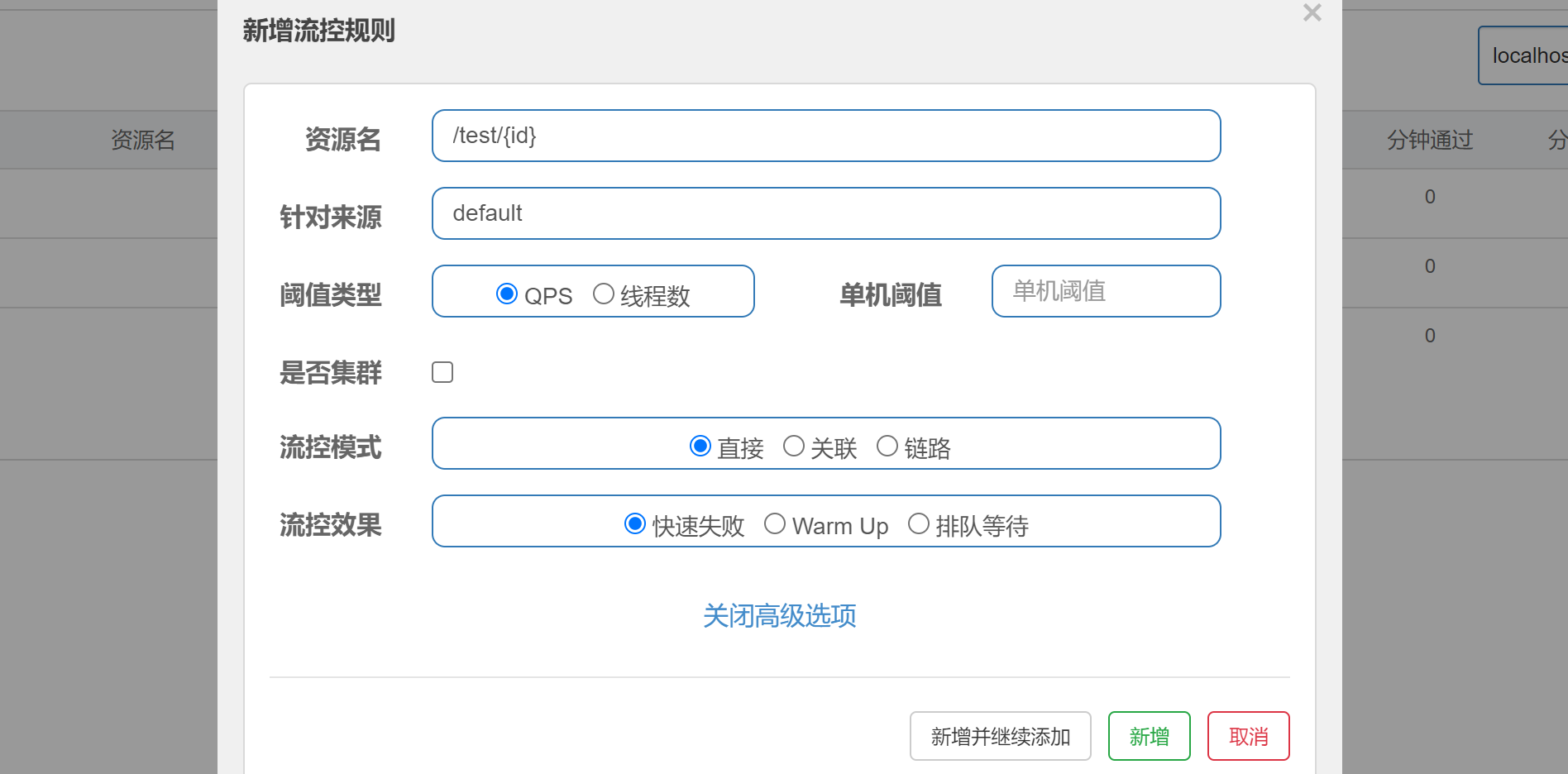
There are two main statistical types of flow control
Count the number of concurrent threads Statistics QPS
Flow control based on call relation
direct relation link
When the QPS exceeds a certain threshold, measures shall be taken to control the flow
Direct rejection Warm Up Uniform queue
Direct rejection
The direct reject (RuleConstant.CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_DEFAULT) method is the default flow control method. When the QPS exceeds the threshold of any rule, the new request will be rejected immediately. The rejection method is to throw a FlowException. This method is applicable when the processing capacity of the system is exactly known, such as when the accurate water level of the system is determined through pressure measurement.
Source class: com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.controller.DefaultController
Warm Up
Warm Up (RuleConstant.CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_WARM_UP) mode, i.e. preheating / cold start mode. When the system is at low water level for a long time, when the flow suddenly increases, directly pull the system to high water level, which may crush the system instantly. Through "cold start" , let the passing flow increase slowly and gradually increase to the upper limit of the threshold within a certain time to give the cold system a warm-up time to avoid the cold system being crushed.
According to the value of codeFactor (default 3), the set QPS threshold is reached after preheating from the threshold / codeFactor
Official principle analysis document
https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/%E9%99%90%E6%B5%81---%E5%86%B7%E5%90%AF%E5%8A%A8
Source code: com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.controller.WarmUpController
Uniform queue
The uniform queuing (ruleconstant. Control_behavior_rate_limit) method will strictly control the interval between requests, that is, let requests pass at a uniform speed, corresponding to the leaky bucket algorithm.
Queue at a uniform speed to allow requests to pass at a uniform speed, or the value type must be set to QPS, otherwise it is invalid
Official documents
https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/%E6%B5%81%E9%87%8F%E6%8E%A7%E5%88%B6-%E5%8C%80%E9%80%9F%E6%8E%92%E9%98%9F%E6%A8%A1%E5%BC%8F
Source code: com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.controller.RateLimiterController
Flow control test
Direct flow control mode
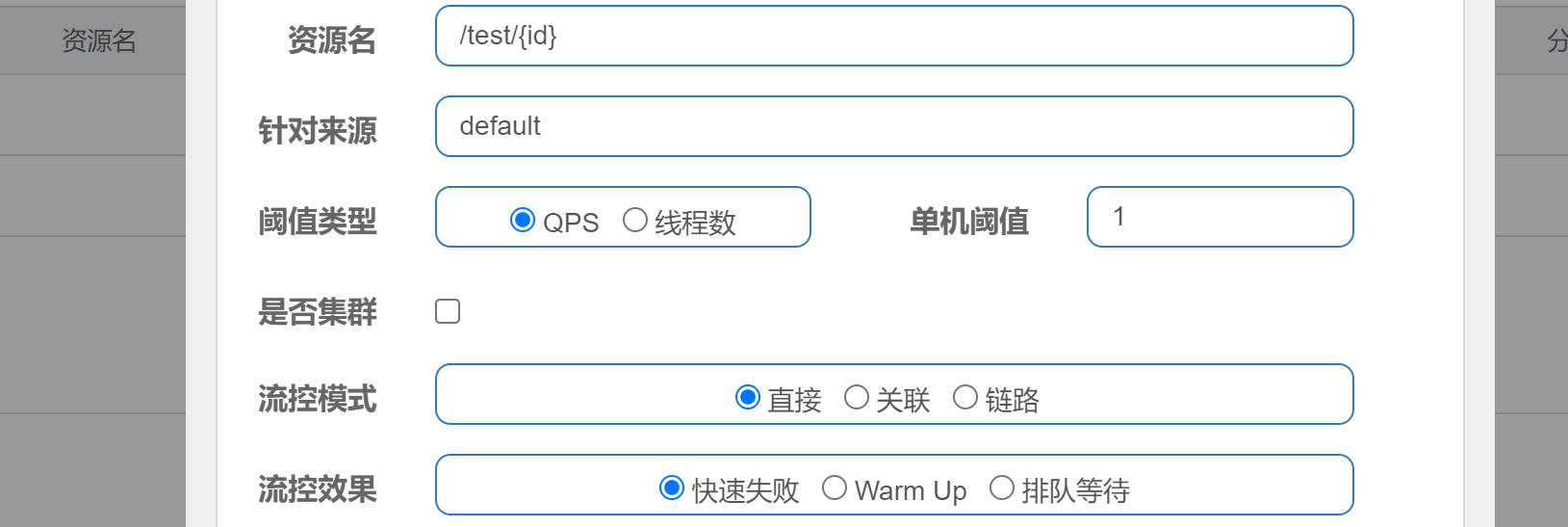
When Qps exceeds 1, an exception is reported and current limiting is performed.

Associated flow control mode
When the associated resource reaches the threshold, it limits itself
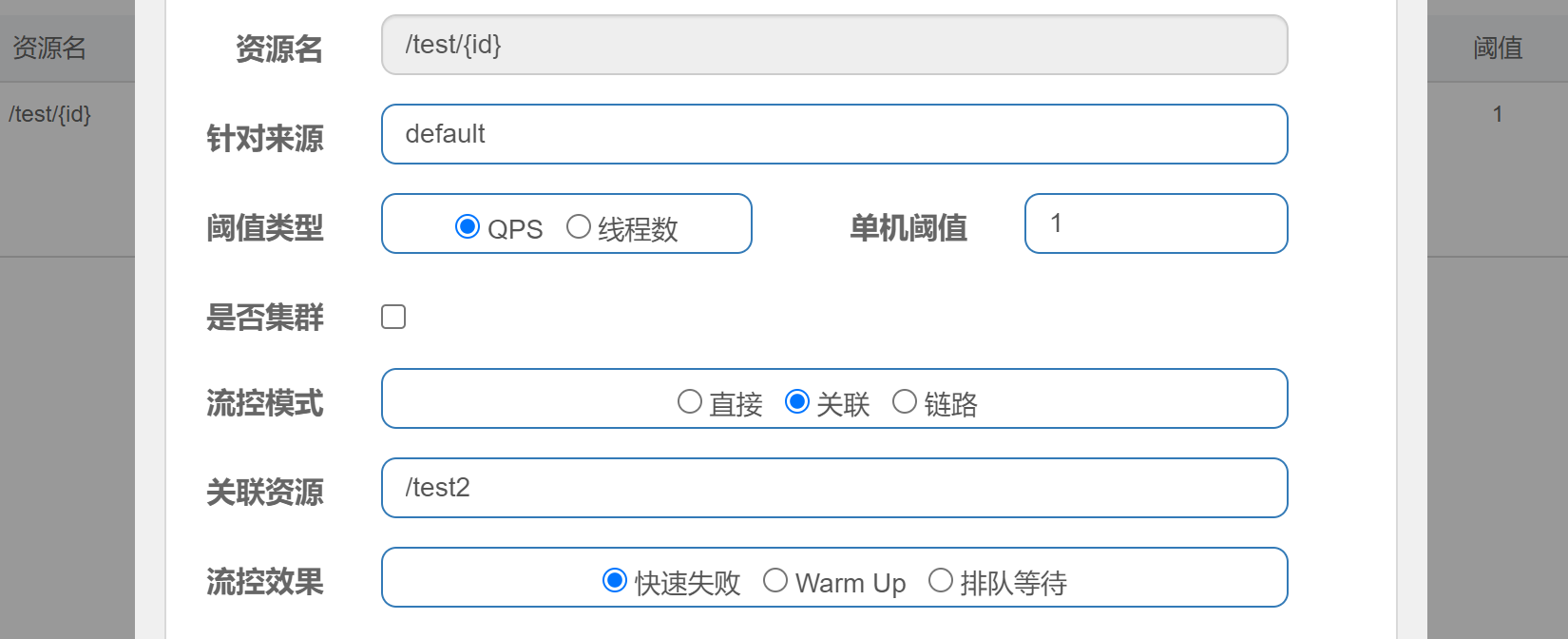
First call the / test2 interface in a loop, and then access the / test/{id} interface. The / test/{id} interface will always be in the current limiting state
Link flow control mode
Only the traffic on the specified link is recorded
@Component
public class TestComponent {
@SentinelResource("common")
public String common() {
return "common";
}
}
@GetMapping("test-a")
public String testA() {
this.testService.common();
return "test-a";
}
@GetMapping("test-b")
public String testB() {
this.testService.common();
return "test-b";
}
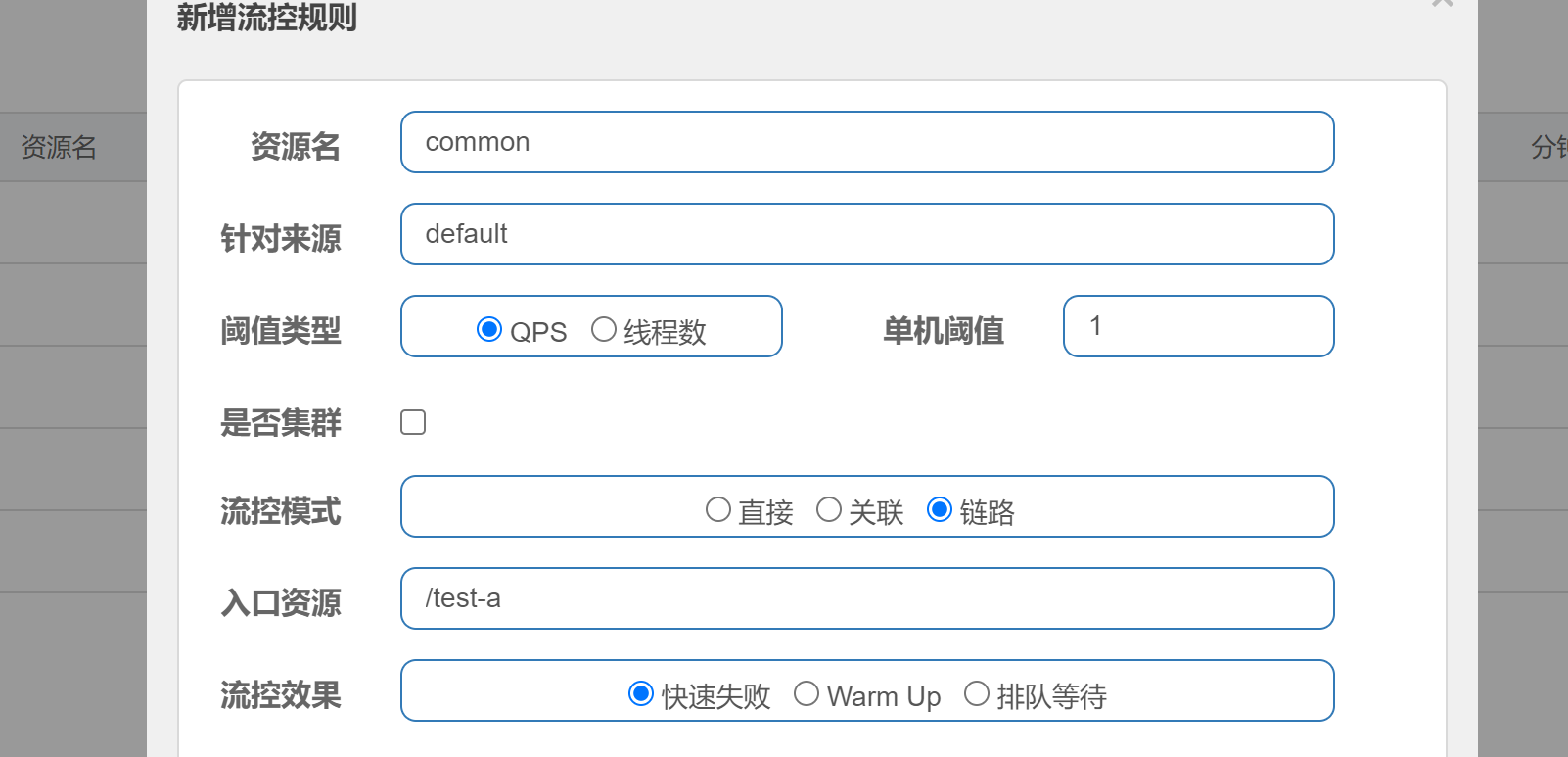
When accessing the test-a interface reaches the Qps time limit, the flow will not be limited by accessing test-b anyway
Degradation rule
A service often calls other modules, such as another remote service, database, or third-party API. For example, when paying, you may need to call the API provided by UnionPay remotely; when querying the price of a commodity, you may need to query the database. However, the stability of the dependent service cannot be guaranteed. If the dependent service appears In case of instability, if the response time of the request becomes longer, the response time of the method calling the service will also become longer, and the threads will accumulate. Finally, the thread pool of the business itself may be exhausted, and the service itself will become unavailable.
Therefore, it is necessary to fuse and downgrade the unstable weak dependent service calls, temporarily cut off the unstable calls, and avoid the overall avalanche caused by local unstable factors.
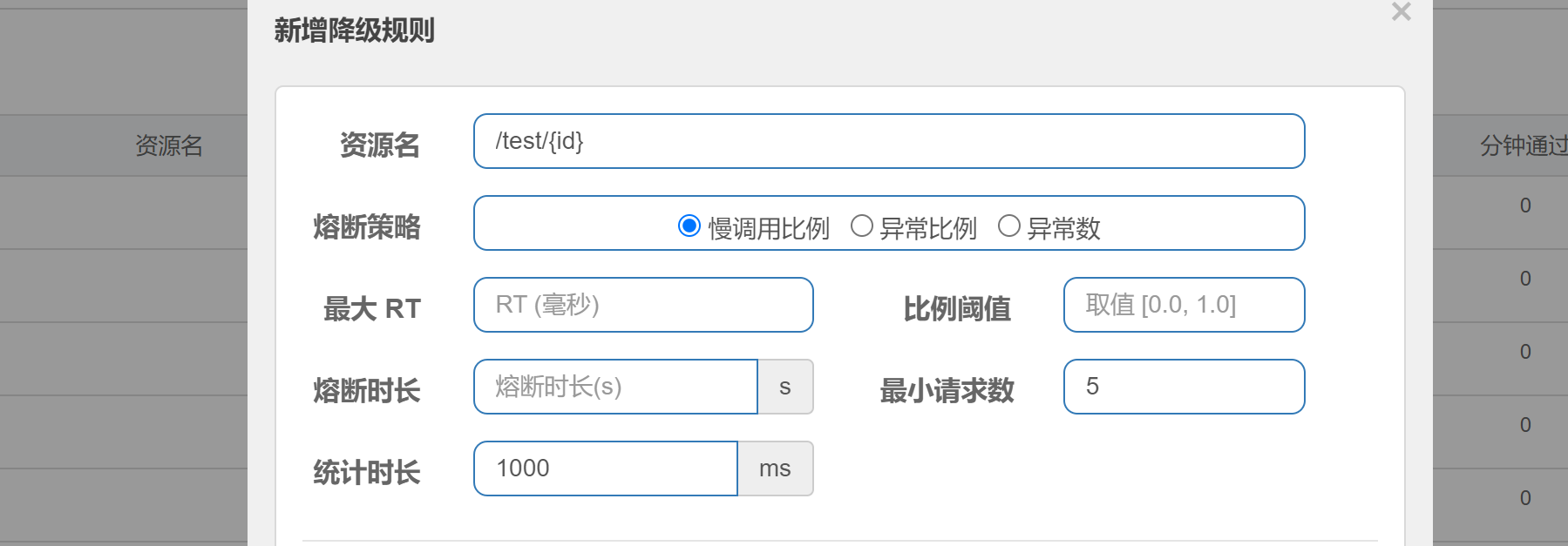
Sentinel fusing strategy:
Slow_request_ratio: select the slow call ratio as the threshold. You need to set the allowed slow call RT (i.e. the maximum response time). If the response time of the request is greater than this value, it will be counted as slow call. When the unit statistics time (statIntervalMs) If the number of internal requests is greater than the set minimum number of requests and the proportion of slow calls is greater than the threshold value, the internal requests in the next fusing time will be blown automatically. After the fusing time, the fuse will enter the detection recovery state (HALF-OPEN state) , if the response time of the next request is less than the set slow call RT, the fuse will end. If it is greater than the set slow call RT, it will be blown again.
Error_ratio: when the number of requests in the unit statistical duration (statIntervalMs) is greater than the set minimum number of requests, and the proportion of exceptions is greater than the threshold, the requests in the next fusing duration will be blown automatically. After fusing for a long time, the fuse will enter the detection recovery state (HALF-OPEN state). If the next request is successfully completed (no error), the fusing will be ended, otherwise it will be blown again. The threshold range of abnormal ratio is [0.0, 1.0], representing 0% - 100%.
Error_count: when the number of exceptions in the unit statistical time exceeds the threshold, it will automatically fuse. After fusing for a long time, the fuse will enter the detection recovery state (HALF-OPEN state). If the next request is successfully completed (no error), the fusing will be ended, otherwise it will be blown again.
Important attributes of the degradation rule:
| Field | explain | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| resource | Resource name, that is, the object of the rule | |
| grade | Fusing strategy, supporting slow call proportion / exception proportion / different constant strategy | Slow call ratio |
| count | In slow call proportional mode, it is slow call critical RT (exceeding this value is counted as slow call); It is the corresponding threshold in the exception proportion / exception number mode | |
| timeWindow | Fusing duration, unit: s | |
| minRequestAmount | The minimum number of requests triggered by fusing. When the number of requests is less than this value, it will not fuse even if the abnormal ratio exceeds the threshold (introduced by 1.7.0) | 5 |
| statIntervalMs | Statistical duration (unit: ms), for example, 60 * 1000 represents minute level (introduced in 1.8.0) | 1000 ms |
| slowRatioThreshold | Slow call proportional threshold. Only slow call proportional mode is valid (introduced in 1.8.0) |
Reference source code: com alibaba. csp. sentinel. slots. block. degrade. DegradeRule
Hot spot parameter current limiting
Hotspot parameter current limiting will count the hotspot parameters in the incoming parameters, and limit the current of resource calls containing hotspot parameters according to the configured current limiting threshold and mode. Hotspot parameter current limiting can be regarded as a special flow control, which is only effective for resource calls containing hotspot parameters.
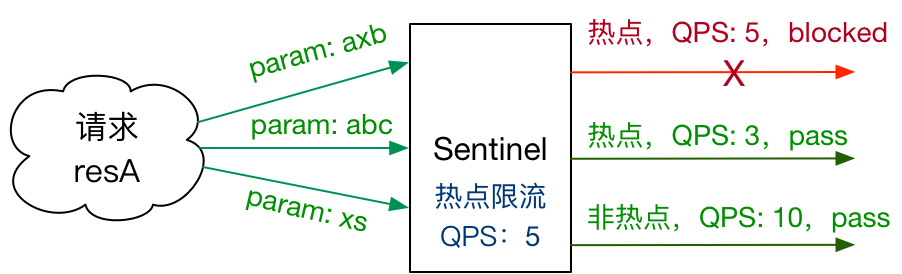
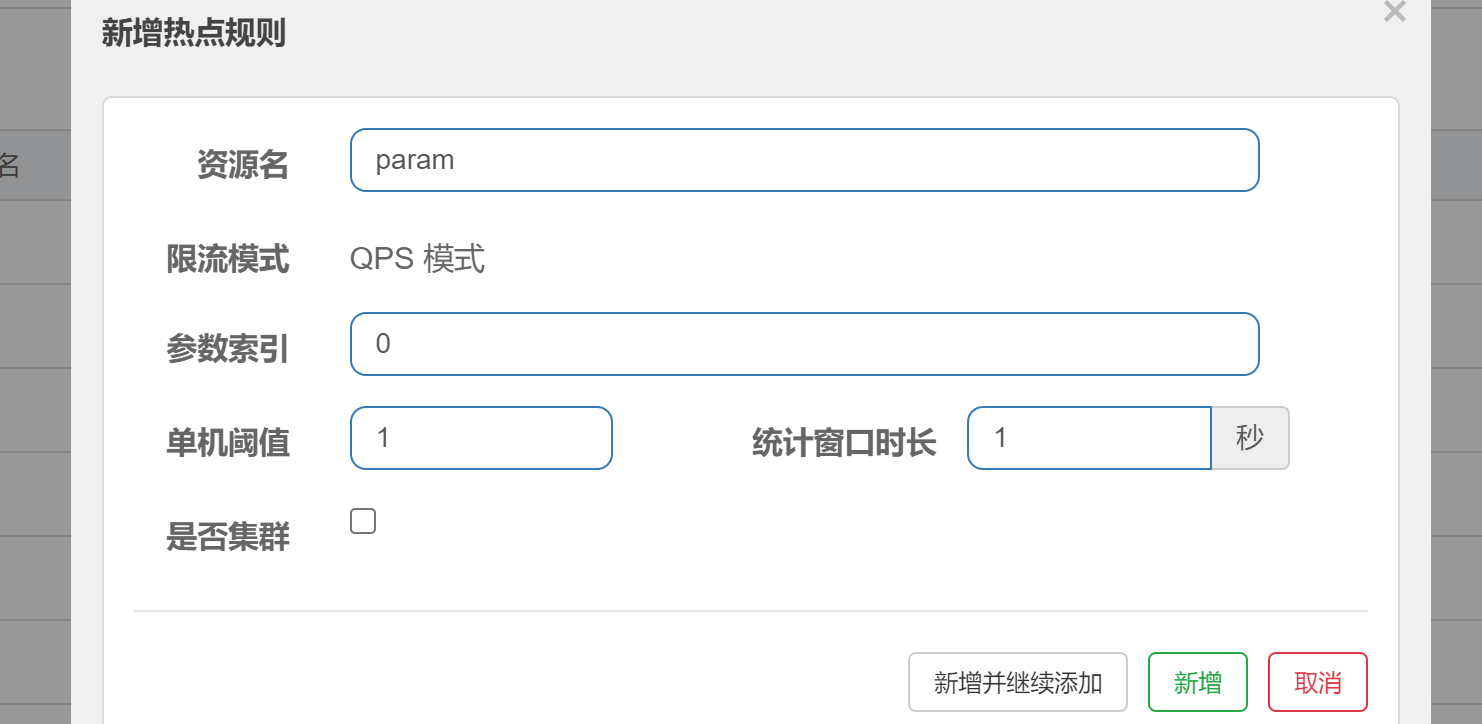
Add / testParam interface
@GetMapping("/testParam")
@SentinelResource("param")
public String testParam(Integer a,String b){
return a + "-------------" +b;
}
request http://localhost:8082/testParam?a=1&b=Sentinel , due to the limitation on the first parameter, when Qps reaches 1, the current limit throws an exception
request http://localhost:8082/testParam?a=&b=Sentinel In any case, the request will not be throttled

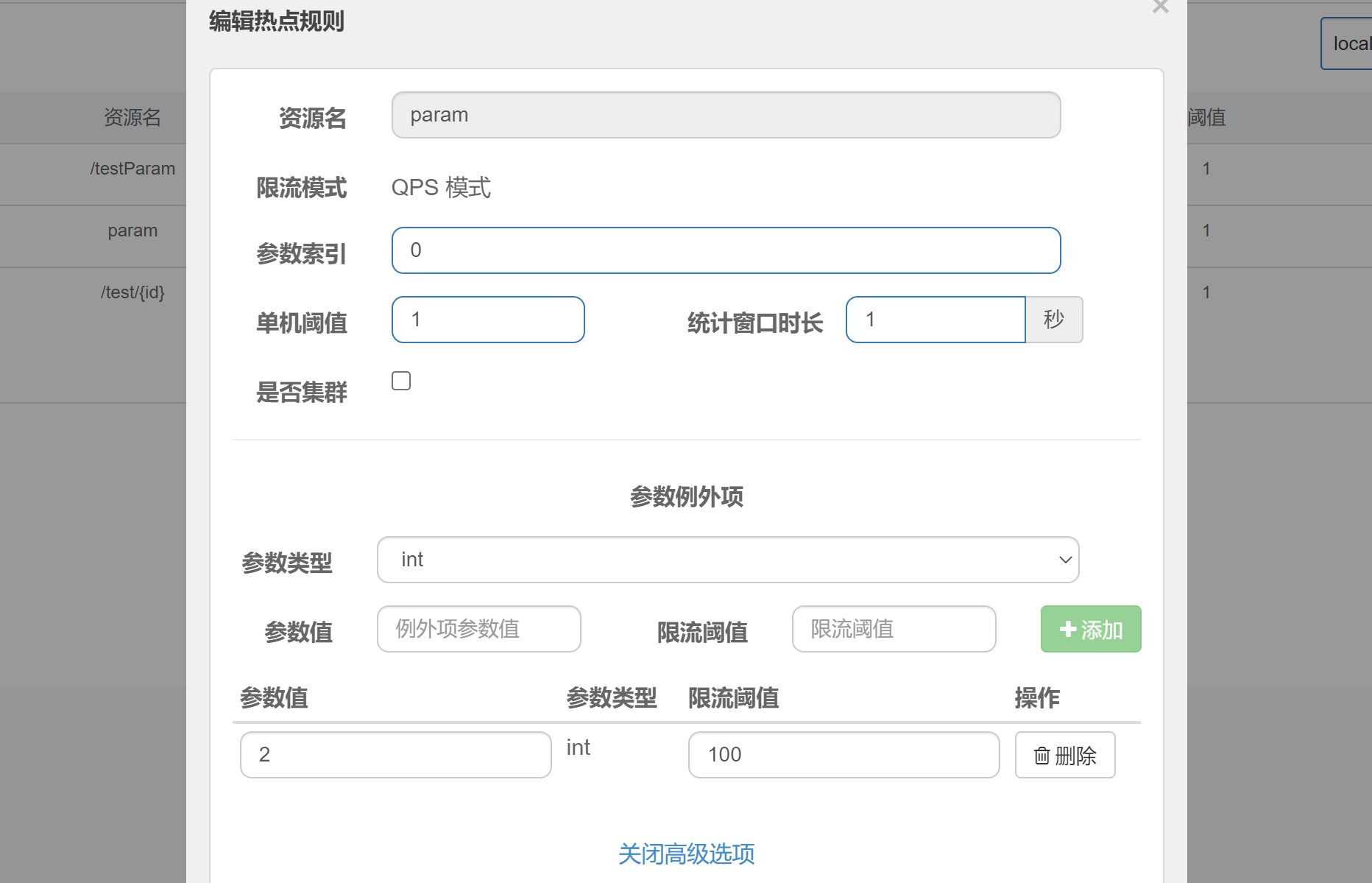
When the first parameter value is not 2, Qps Current limit when 1 is reached When the first parameter value is 2, Qps Current limit when reaching 100
Reference source code: com alibaba. csp. sentinel. slots. block. flow. param. ParamFlowChecker
System rules
The system protection rule is to control the entrance flow at the application level, and monitor the application indicators from the dimensions of load, CPU utilization, average RT, entrance QPS and the number of concurrent threads of a single machine, so as to make the system run at the maximum throughput and ensure the overall stability of the system.
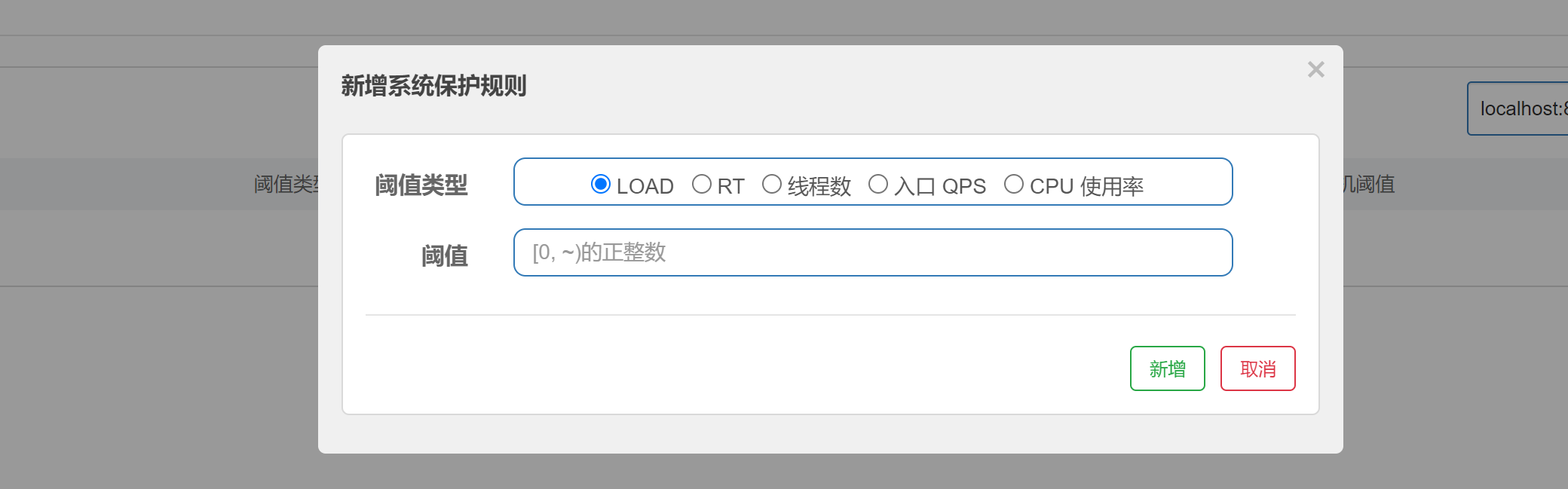
Load adaptation (only valid for Linux / Unix like machines): load1 of the system is used as the heuristic index for adaptive system protection. When system load1 exceeds the set heuristic value and the current number of concurrent threads exceeds the estimated system capacity, system protection will be triggered (BBR stage). The system capacity is estimated from the maxQps * minRt of the system. The setting reference value is generally CPU cores * 2.5.
CPU usage (version 1.5.0 +): when the system CPU utilization exceeds the threshold, the system protection is triggered (value range 0.0-1.0), which is sensitive.
Average RT: when the average RT of all inlet flows on a single machine reaches the threshold, the system protection is triggered, and the unit is milliseconds.
Number of concurrent threads: system protection is triggered when the number of concurrent threads of all inlet traffic on a single machine reaches the threshold.
Inlet QPS: when the QPS of all inlet flows on a single machine reaches the threshold, the system protection is triggered.
Reference source code: com alibaba. csp. sentinel. slots. system. SystemRuleManager
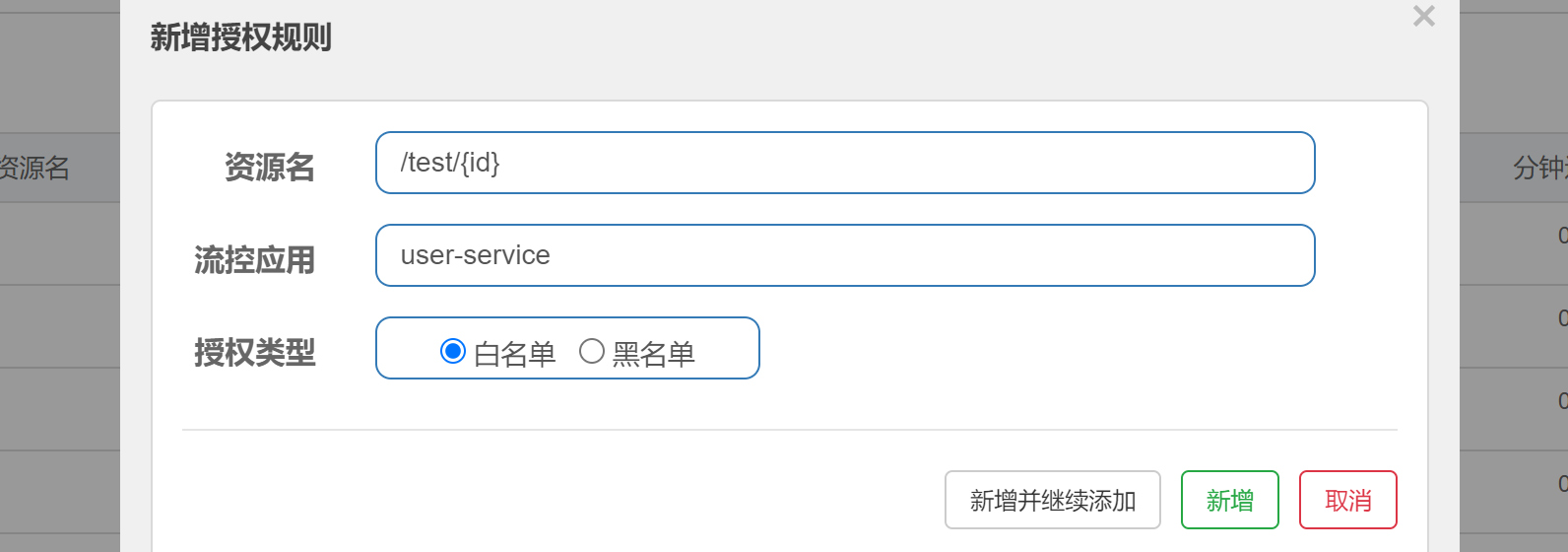
Authorization rules
Whether the resource can pass is limited according to the request origin of the resource. If the white list is configured, it can pass only when the request source is in the white list; If the blacklist is configured, the request will not pass if the request source is in the blacklist, and the other requests will pass.
Sentinel's rule persistence
Pull mode:
The client actively polls and pulls rules from a rule management center, which can be RDBMS, files, or even VCS. The way to do this is simple, but the disadvantage is that changes cannot be obtained in time;
Push mode:
The rule center is pushed uniformly, and the client monitors changes at any time by registering a listener, such as using Nacos, Zookeeper and other configuration centers. This method has better real-time and consistency guarantee.
Specific implementation reference: https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/%E5%8A%A8%E6%80%81%E8%A7%84%E5%88%99%E6%89%A9%E5%B1%95
Sentinel configuration
Configuration of application side connection console
spring:
cloud:
sentinel:
transport:
# Specifies the address of the sentinel console
dashboard: IP:8858
#Specify the ip to communicate with the console. If it is not configured, an ip registration will be automatically selected, which may cause errors
clientIp: localhost
# Specifies the port to communicate with the console. The default value is 8719
# If not set, it will automatically start scanning from 8719 and + 1 in turn until an unoccupied port is found
port: 8719
# Heartbeat sending cycle, the default value is null, but the default value is 10 seconds in SimpleHttpHeartbeatSender
heartbeat-interval-ms: 10000
Console configuration
| Configuration item | Default value | describe |
|---|---|---|
| server.port | 8080 | Specify port |
| csp.sentinel.dashboard.server | localhost:8080 | Specify address |
| project.name | Specifies the name of the program | |
| sentinel.dashboard.auth.username | sentinel | Dashboard login account |
| sentinel.dashboard.auth.password | sentinel | Dashboard login password |
| server.servlet.session.timeout | 30 Minutes | Login Session expiration time If it is configured as 7200, it means 7200 seconds 60m indicates 60 minutes |
Use of Sentinel
API mode
Three core API s:
SphU : Define resources, make resources monitored, and protect resources Tacer: Count the exceptions you want ContextUtil: Implement the call source and mark the call
Note that exception degradation is only for business exceptions, and does not take effect for the exception (BlockException) of Sentinel current limiting degradation itself. In order to count the proportion or number of exceptions, you need to use tracer Trace (Ex) records business exceptions.
@GetMapping("/test-api")
public String testSentinelAPI(@RequestParam(required = false) String name) {
// Define resource name
String resourceName = "test-api";
// Implement the call source and mark the call
ContextUtil.enter(resourceName, "test-service");
Entry entry = null;
try {
entry = SphU.entry(resourceName);
// Protected business logic
if (StringUtils.isBlank(name)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal parameter");
}
return name;
}
// If the protected resource is restricted or degraded, BlockException will be thrown
catch (BlockException blockException) {
return "Current limiting or degradation";
} catch (IllegalArgumentException illegalArgumentException) {
// Call tracer Trace (Ex) to record business exceptions
Tracer.trace(illegalArgumentException);
return "Illegal parameter";
} finally {
if (entry != null) {
// Exit entry
entry.exit();
}
ContextUtil.exit();
}
}
Annotation method
@SentinelResource is used to define resources and provide optional exception handling and fallback configuration items
Use details refer to: https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/%E6%B3%A8%E8%A7%A3%E6%94%AF%E6%8C%81
@GetMapping("/test-sentinel-resource")
@SentinelResource(
value = "test-sentinel-api",
blockHandler = "block",
//blockHandlerClass = BlockHandlerTestClass.class,
//fallbackClass = FallbackTestClass.class,
fallback = "fallback"
)
public String testSentinelResource(@RequestParam(required = false) String name) {
if (StringUtils.isBlank(name)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal parameter");
}
return name;
}
public String block(String name, BlockException blockException) {
return "Current limiting or degradation---------block";
}
public String fallback(String name, Throwable throwable) {
return "Current limiting or degradation---------fallback";
}
Separate block() and fallback(), and specify them respectively with blockHandlerClass and fallbackClass
@GetMapping("/test-sentinel-resource")
@SentinelResource(
value = "test-sentinel-api",
blockHandler = "block",
blockHandlerClass = BlockHandlerTestClass.class,
fallbackClass = FallbackTestClass.class,
fallback = "fallback"
)
public String testSentinelResource(@RequestParam(required = false) String name) {
if (StringUtils.isBlank(name)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal parameter");
}
return name;
}
blockHandlerClass = BlockHandlerTestClass.clas: the corresponding block function must be in the blockhandlertestclass class and must be a public static function
fallbackClass = FallbackTestClass.class: the corresponding fallback function must be in the fallbacktestclass class and must be a public static function
public class BlockHandlerTestClass{
/**
* Handle current limiting or degradation
*/
public static String block(String name, BlockException blockException) {
return "BlockHandlerTestClass----Current limiting or degradation-------block";
}
}
Integration with RestTemplate and Feign
RestTemplate integration Sentinel
@SentinelRestTemplate annotation also provides fallback and blockHandler processing
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface SentinelRestTemplate {
String blockHandler() default "";
Class<?> blockHandlerClass() default void.class;
String fallback() default "";
Class<?> fallbackClass() default void.class;
String urlCleaner() default "";
Class<?> urlCleanerClass() default void.class;
}
Define current limiting degradation exception handling class
public class BlockHandler {
public static SentinelClientHttpResponse handleException(HttpRequest request, byte[] body, ClientHttpRequestExecution clientHttpRequestExecution, BlockException blockException) {
return new SentinelClientHttpResponse("Current limiting or degradation---------BlockHandler Class");
}
}
public class FallBackHandler {
public static SentinelClientHttpResponse fallBackHandle(HttpRequest request, byte[] body, ClientHttpRequestExecution clientHttpRequestExecution, BlockException blockException){
return new SentinelClientHttpResponse("Current limiting or degradation---------FallBackHandler Class");
}
}
RestTemplate add @ SentinelRestTemplate annotation
@Bean
//Ribbon load balancing
@LoadBalanced
//Let RestTemplate support Sentinel current limiting
@SentinelRestTemplate(blockHandler = "handleException",blockHandlerClass = BlockHandler.class,
fallback = "fallBackHandle", fallbackClass = FallBackHandler.class)
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
RestTemplate template = new RestTemplate();
return template;
}
}
@SentinelRestTemplate annotation configuration can be turned off
resttemplate:
sentinel:
# The development environment can be temporarily shut down: degraded, current limited
# The default value is true. If it is set to false, it means that the @ SentinelRestTemplate annotation is closed
enabled: false
Feign integrated Sentinel
Enable Feign's support for Sentinel
feign:
sentinel:
# Integrate sentinel for feign
enabled: true
Create current limiting degraded fault tolerance class
Implement the fault-tolerant interface directly, and implement the fault-tolerant scheme for each method realization FallbackFactory Interface
@Component
public class UserCenterFeignClientFallback implements UserCenterFeignClient {
@Override
public UserDTO selectUserById(Integer id) {
UserDTO userDTO = new UserDTO();
userDTO.name("Flow control or degradation-------implements UserCenterFeignClient");
return userDTO;
}
}
@Component
public class UserCenterFeignClientFallbackFactory implements FallbackFactory<UserCenterFeignClient> {
@Override
public UserCenterFeignClient create(Throwable cause) {
return new UserCenterFeignClient() {
@Override
public UserDTO selectUserById(Integer id) {
UserDTO userDTO = new UserDTO();
userDTO.name("Flow control or degradation-------implements FallbackFactory");
return userDTO;
}
};
}
}
Specify the fault-tolerant class for the interface degraded by current limiting
@FeignClient(name = "user-center",
// fallback = UserCenterFeignClientFallback.class,
fallbackFactory = UserCenterFeignClientFallbackFactory.class
)
public interface UserCenterFeignClient {
@GetMapping("/users/{id}")
UserDTO selectUserById(@PathVariable Integer id);
}
Sentinel exception handling
Uniformly handle returned exceptions: implement the BlockExceptionHandler interface and override the handle() method.
@Component
public class MyUrlBlockHandler implements BlockExceptionHandler {
@Override
public void handle(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse response, BlockException e) throws Exception {
String msg = null;
if (e instanceof FlowException) {
msg = "Current limiting---------FlowException";
} else if (e instanceof DegradeException) {
msg = ("Demotion---------DegradeException";
} else if (e instanceof ParamFlowException) {
msg = "Hot spot parameter current limiting---------ParamFlowException";
} else if (e instanceof SystemBlockException) {
msg = "System rules---------SystemBlockException";
} else if (e instanceof AuthorityException) {
msg = "Authorization rule failed---------AuthorityException";
}
response.setStatus(500);
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.setHeader("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
new ObjectMapper().writeValue(response.getWriter(), msg);
}
Sentinel implements source differentiation
code implementation
@Component
public class MyRequestOriginParser implements RequestOriginParser {
@Override
public String parseOrigin(HttpServletRequest request) {
// Get the parameter named origin from the request header / request parameters
// String origin = request.getHeader("request");
String origin = request.getParameter("origin");
// Throw an exception if the origin parameter cannot be obtained
if (StringUtils.isBlank(origin)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal request");
}
return origin;
}
}
Current limiting test for source
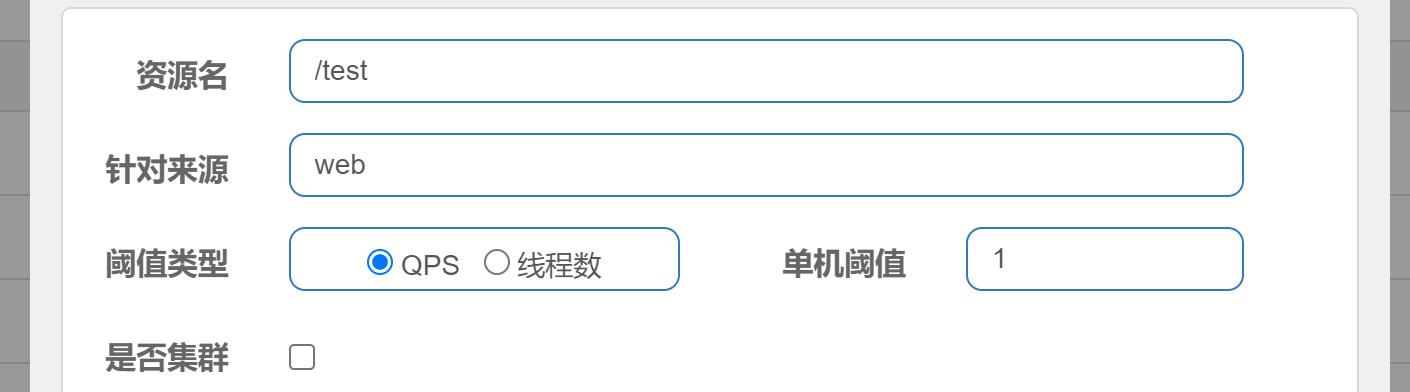
Request: http://localhost:8082/test?origin=web
Current limiting---------FlowException
Request: http://localhost:8082/test?origin=app : casual access
Authorization test for source
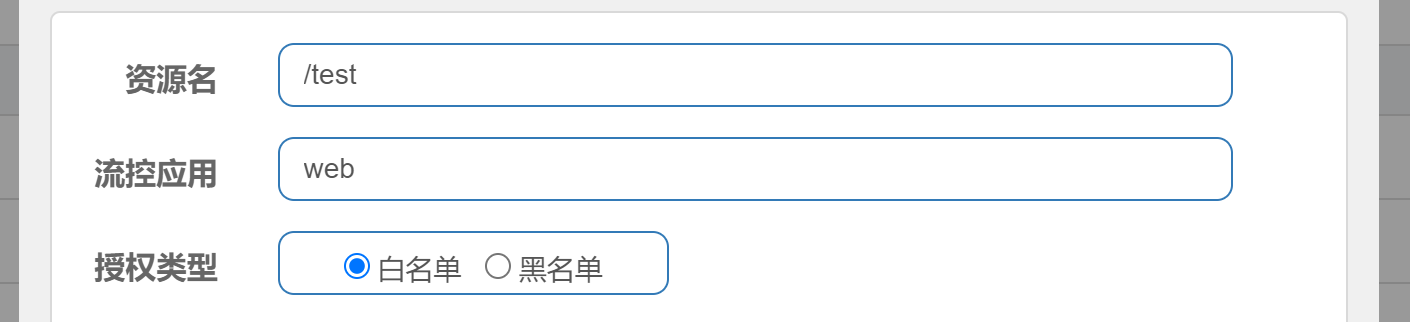
Request: http://localhost:8082/test?origin=app
Authorization rule failed---------AuthorityException
Request: http://localhost:8082/test?origin=web : passed