reference material
Spring IoC source code learning: detailed explanation of invokebeanfactoryprocessors
Previously:
Spring IOC: obtainFreshBeanFactory call chain
Written at the beginning: This article is a personal study note. The content is relatively casual and mixed with personal understanding. If there are mistakes, you are welcome to correct them.
catalogue
2, Invokebeanfactoryprocessors
1,getBeanFactoryPostProcessors
2,invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
1,getBeanFactoryPostProcessors
2. Add custom beanfactoryprocessor
3, Invokebeanfactoryprocessors
1. Distinguish BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor from beanfactoryprocessor
2. Implement BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor according to priority
3. Instantiate the remaining BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors and some beanfactoryprocessors
4. Repeat steps 2 and 3 for beanfactoryprocessor
1, Overview
The invokebeanfactoryprocessors method instantiates and calls all beanfactoryprocessors (including its subclass BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor).
The beanfactoryprocessor interface is an extension point exposed when Spring initializes BeanFactory. The Spring IoC container allows beanfactoryprocessor to read the bean definition and modify it before the container instantiates any bean.
2, Invokebeanfactoryprocessors
2 important steps:
1,getBeanFactoryPostProcessors
Get the value in the beanfactoryprocessors variable of the current application context
2,invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
Instantiate and call all registered beanfactorypost processors
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Getbeanfactoryprocessors(): get the value in the beanfactoryprocessors variable of the current application context
// Invokebeanfactoryprocessors: instantiate and call all registered beanfactoryprocessors
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
}3, Getbeanfactoryprocessors
1,getBeanFactoryPostProcessors
Get the beanfactoryprocessor that has been registered in the current application context. By default, it returns null.
public List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> getBeanFactoryPostProcessors() {
return this.beanFactoryPostProcessors;
}2. Add custom beanfactoryprocessor
In Spring IOC: from ContextLoaderListener to AbstractApplicationContext The customizeContext method described in will read the web through the determineContextInitializerClasses method The parameters in XML (globalInitializerClasses and contextInitializerClasses) initialize the classes that implement the ApplicationContextInitializer interface.
protected void customizeContext(ServletContext sc, ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
//Gets the initializer class collection
List<Class<ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>>> initializerClasses =
determineContextInitializerClasses(sc);
for (Class<ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>> initializerClass : initializerClasses) {
Class<?> initializerContextClass =
GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(initializerClass, ApplicationContextInitializer.class);
if (initializerContextClass != null && !initializerContextClass.isInstance(wac)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(String.format(
"Could not apply context initializer [%s] since its generic parameter [%s] " +
"is not assignable from the type of application context used by this " +
"context loader: [%s]", initializerClass.getName(), initializerContextClass.getName(),
wac.getClass().getName()));
}
//Instantiate the initializer and add it to the collection
this.contextInitializers.add(BeanUtils.instantiateClass(initializerClass));
}
//Sort and execute. The smaller the number, the earlier the execution
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.contextInitializers);
for (ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext> initializer : this.contextInitializers) {
initializer.initialize(wac);
}
}
protected List<Class<ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>>>
determineContextInitializerClasses(ServletContext servletContext) {
List<Class<ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>>> classes =
new ArrayList<Class<ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>>>();
//Configure globalInitializerClasses through the < context param > attribute to obtain the global initialization class name
String globalClassNames = servletContext.getInitParameter(GLOBAL_INITIALIZER_CLASSES_PARAM);
if (globalClassNames != null) {
for (String className : StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(globalClassNames, INIT_PARAM_DELIMITERS)) {
classes.add(loadInitializerClass(className));
}
}
//Configure contextInitializerClasses through the < context param > attribute to obtain the container initialization class name
String localClassNames = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_INITIALIZER_CLASSES_PARAM);
if (localClassNames != null) {
for (String className : StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(localClassNames, INIT_PARAM_DELIMITERS)) {
classes.add(loadInitializerClass(className));
}
}
return classes;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private Class<ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>> loadInitializerClass(String className) {
try {
// Instantiate className
Class<?> clazz = ClassUtils.forName(className, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
if (!ApplicationContextInitializer.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
// Verify whether clazz implements the ApplicationContextInitializer interface. If not, throw an exception
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Initializer class does not implement ApplicationContextInitializer interface: " + clazz);
}
// clazz is strongly converted to ApplicationContextInitializer and returns
return (Class<ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>>) clazz;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Failed to load context initializer class [" + className + "]", ex);
}
}We create a new implementation class of ApplicationContextInitializer and rewrite the initialize method to realize personalized logic, in which we manually add MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor that inherits the BeanFactoryPostProcessor interface. And register it in the context through globalInitializerClasses to realize the pre storage function of beanfactoryprocessors.
public class MyApplicationContextInitializer implements ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>
{
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor myBeanFactoryPostProcessor = new MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor();
applicationContext.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(myBeanFactoryPostProcessor);
System.out.println("Will be customized MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor Add to application context");
}
}<context-param>
<param-name>globalInitializerClasses</param-name>
<param-value>
com.test.MyApplicationContextInitializer
</param-value>
</context-param>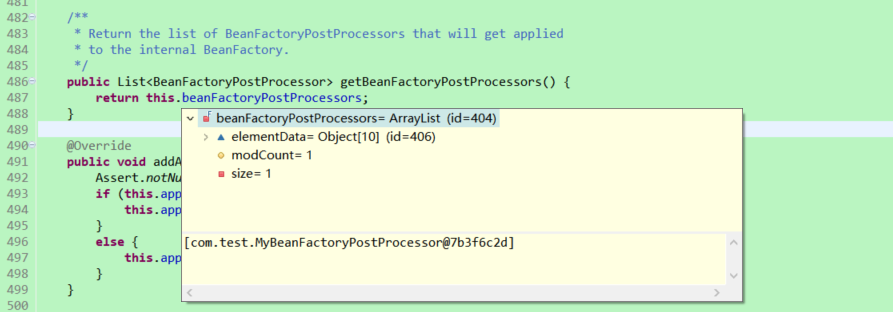
3, Invokebeanfactoryprocessors
First, let's introduce BeanFactoryPostProcessor and its subclass BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.

The beanfactoryprocessor interface is an extension point exposed when Spring initializes BeanFactory. The Spring IoC container allows beanfactoryprocessor to read the bean definition and modify it before the container instantiates any bean.
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor inherits from beanfactoryprocessor and has higher priority than beanfactoryprocessor. It is mainly used to execute before the start of conventional beanfactoryprocessor detection. In particular, you can register some regular beanfactorypost processors through BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor. Because at this time, all conventional beanfactoryprocessor have not started to be processed.
For the introduction of beanfactoryprocessor, please refer to the article I wrote before Portal
Because the whole code of invokebeanfactoryprocessors is long, it is divided into several sections according to the execution steps, as shown in the following figure.
public static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) {
1,distinguish BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor And BeanFactoryPostProcessor
2,Implement according to priority BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
3,Instantiate surplus BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors And part BeanFactoryPostProcessor
4,in the light of BeanFactoryPostProcessor Repeat steps 2 and 3
}1. Distinguish BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor from beanfactoryprocessor
Traverse the parameter beanfactoryprocessors and distinguish BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor from beanfactoryprocessor. The former directly executes its postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry method one step more than the latter, and then stores it in registryProcessors and regularPostProcessors respectively.
Note: what is stored and implemented here is the beanfactoryprocessors passed as parameters, that is, the beanfactoryprocessor extended and implemented by ApplicationContextInitializer described earlier, excluding the beanfactoryprocessor registered in the container.
Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<String>();
// Judge whether beanFactory is BeanDefinitionRegistry, and beanFactory is DefaultListableBeanFactory,
// The DefaultListableBeanFactory implements the BeanDefinitionRegistry interface, so it is true here
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;
// It is used to store ordinary beanfactoryprocessor
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new LinkedList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();
// Used to store BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new LinkedList<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor>();
// First, process the bean factorypostprocessors in the parameter
// Traverse all beanfactoryprocessors to distinguish BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor from ordinary beanfactoryprocessor
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
// If it is BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
// Directly execute the postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry method of BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor interface
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
// Added to registryprocessors (used to finally execute the postProcessBeanFactory method)
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
} else {
// Otherwise, it's just an ordinary beanfactoryprocessor
// Added to regularpostprocessors (used to execute the postProcessBeanFactory method last)
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
2. Implement BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor according to priority
(1) find out the beannames of all beans that implement the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor interface and store them in postProcessorNames (here, the beanName is found from the beanName registered in the obtainFreshBeanFactory method in the previous step through beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType)
(2) traverse the postProcessorNames and filter out the beanName that implements the PriorityOrdered interface (for sorting).
(3) use beanfactory The getBean method creates the bean object corresponding to the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor. Store the created bean object in currentRegistryProcessors and the beanName in processedBeans.
(4) sort currentRegistryProcessors according to the implementation of PriorityOrdered interface, and then store currentRegistryProcessors into registryProcessors.
(5) traverse currentRegistryProcessors and execute the postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry method. After execution, clear currentRegistryProcessors.
(6) repeat steps 1-5, but the postProcessorNames will be retrieved. This is because after executing the postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry method of BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor above, other beandefinitionregistrypostprocessors may be added, so it needs to be searched again. And this step is for the Ordered interface, not the PriorityOrdered interface.
// Used to save the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor executed this time
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor>();
// Call all BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor implementation classes that implement the PriorityOrdered interface
// Find the beanName of all beans that implement the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor interface
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Traverse postProcessorNames
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
// Verify whether the PriorityOrdered interface is implemented
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
// Get the bean instance corresponding to ppName and add it to currentRegistryProcessors,
// beanFactory.getBean: the getBean method here will trigger the creation of the bean object corresponding to ppName, which will not be deeply resolved at present
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
// Join the processedBeans to be executed to avoid subsequent repeated execution
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
// Sort (sort according to whether PriorityOrdered, Ordered interface and order value are implemented)
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
// Added to registryprocessors (used to finally execute the postProcessBeanFactory method)
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
// Traverse currentRegistryProcessors and execute the postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry method
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
// After execution, clear currentRegistryProcessors
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Call all BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor implementation classes that implement the Ordered interface (the process is basically the same as step 3 above)
// Find out all classes that implement the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor interface. Repeat the search here because the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor above is executed,
// Other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor may be added, so it needs to be searched again
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
// Verify whether the Ordered interface is implemented and has not been executed
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
// Traverse currentRegistryProcessors and execute the postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry method
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
3. Instantiate the remaining BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors and some beanfactoryprocessors
(1) call beanfactory Getbeannamesfortype finds all classes that implement the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor interface and skips those that have already been executed.
(2) repeat steps 3, 4 and 5 in the previous section.
(3) take out all beandefinitionregistrypostprocessors from registryProcessors and execute its postProcessBeanFactory method.
(4) call the postProcessBeanFactory method of beanfactoryprocessor in beanfactoryprocessors.
// Finally, call all the remaining BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors.
boolean reiterate = true;
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
// Find all classes that implement the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor interface
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
// Skip already executed
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
// If a BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor is executed, a new BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor may be generated,
// Therefore, the value of repeat is set to true, which means that it needs to be searched again
reiterate = true;
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
// Traverse currentRegistryProcessors and execute the postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry method
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
}
// 6. Call the postProcessBeanFactory method of all beandefinitionregistrypostprocessors (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor inherits from beanfactoryprocessor)
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);
// Finally, call the postProcessBeanFactory method of the common BeanFactoryPostProcessor in parameter beanFactoryPostProcessors.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
} else {
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
4. Repeat steps 2 and 3 for beanfactoryprocessor
After the first three steps, all beandefinitionregistrypostprocessors have been processed, including the input beanfactoryprocessors and all registered beanfactoryprocessors in the container. Now start processing all beanfactoryprocessors in the container.
Step 4 imitates the operations of the previous two steps, but replaces BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor with beanfactoryprocessor.
// Find all the classes that implement the beanfactoryprocessor interface
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// It is used to store the beanfactorypost processor that implements the PriorityOrdered interface
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();
// The beanName used to store the beanfactoryprocessor that implements the Ordered interface
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>();
// beanName for storing ordinary beanfactoryprocessor
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>();
// Traverse the postProcessorNames and distinguish the beanfactory postprocessor according to the implementation of PriorityOrdered, the implementation of Ordered interface and ordinary
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
// Skip already executed
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
} else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
// Add beanfactoryprocessor that implements the PriorityOrdered interface
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
} else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
// Add the beanName of beanfactoryprocessor that implements the Ordered interface
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
} else {
// Add the beanName of the remaining ordinary beanfactoryprocessor
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// Call all beanfactoryprocessors that implement the PriorityOrdered interface
// Sort priorityOrderedPostProcessors
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Traverse priorityOrderedPostProcessors and execute the postProcessBeanFactory method
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Call all beanfactoryprocessors that implement the Ordered interface
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
// Get the bean instance corresponding to the postProcessorName, add it to orderedPostProcessors, and prepare for execution
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
// Sort orderedPostProcessors
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Traverse orderedPostProcessors and execute the postProcessBeanFactory method
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Call all remaining beanfactoryprocessor
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
// Get the bean instance corresponding to postProcessorName, add it to nonOrderedPostProcessors, and prepare for execution
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
// Traverse the nonOrderedPostProcessors and execute the postProcessBeanFactory method
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Clear the metadata cache (mergedBeanDefinitions, allBeanNamesByType, singletonBeanNamesByType),
// Because the postprocessor may have modified the original metadata, for example, replacing placeholders in values
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
Summary:
The whole process first obtains globalInitializerClasses and contextInitializerClasses from the context, and manually adds them to beanfactoryprocessor and BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor in the context.
Then store them separately and implement the postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry method of BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor. Then obtain the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registered in beanFactory, filter out the beanName that implements the PriorityOrdered interface, and implement it in turn after sorting. Repeat the same steps for the Ordered interface. Finally, execute the postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry method successively for the beanName of the remaining BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor type in beanFactory. Finally, call the postProcessBeanFactory method of BeanFactoryPostProcessor in reference beanFactoryPostProcessors.
Then, repeat the process of BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor and replace the object with beanfactoryprocessor.