The book follows the above two points that I am interested in IoC are
- How does IoC get bean information and manage beans
- IoC prides itself on dependency injection
- How does IoC solve circular dependency (yes, it's entirely because it's said on the Internet that interviewers love to ask questions)
Now that the first problem has been solved, let's analyze the second problem - dependency injection
- How does IoC solve circular dependency (yes, it's entirely because it's said on the Internet that interviewers love to ask questions)
Dependency injection is simply to create your own objects and hand them over to the Spring container for management. Then there must be the following steps
- create object
- Inject the object on which the object depends
- How to solve the problem of circular dependency
This article will also focus on three points.
ps: source code analysis is a personal summary. If there is anything wrong, please contact me for discussion
create object
In the previous article, I learned how Spring obtains various information of beans and stores the information in DefaultListableBeanFactory.
Spring has not been initialized yet. Remember the AbstractApplicationContext#refresh method.
He will create the object in finishBeanFactoryInitialization
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. //Instantiate all remaining (non delayed initialization) singletons. finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
@Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {//Abstract, non singleton, not filter with delayed loading
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) {
FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) bean;
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(
(PrivilegedAction<Boolean>) ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory)::isEagerInit,
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
else {
getBean(beanName);//Ordinary bean s enter this method
}
}
}
// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans... Trigger post initialization callbacks for all applicable beans
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
}
}
}
}
Then you will enter AbstractBeanFactory#doGetBean, which is a very core method. The general process is as follows: first query from this container, if not, query from the parent container, and so on. If you find it, go to the singletonObjects(key is beanName,value is the created bean) in the created bean. If you find it, you can directly return it. If you can't find it, you can create it again. It can be understood that calling this method will get the required bean.
protected <T> T doGetBean(
String name, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly)
throws BeansException {
String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object bean;
// Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.| Query whether the cache
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
logger.trace("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName +
"' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference");
}
else {
logger.trace("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
}
else {
// Fail if we're already creating this bean instance:
// We're assumably within a circular reference.
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
// Check if bean definition exists in this factory.| Check whether the required Bean can be obtained in the current BeanFactory. If it is not found, go to the parent container to get it
BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory();
if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
// Not found -> check parent.
String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name);
if (parentBeanFactory instanceof AbstractBeanFactory) {
return ((AbstractBeanFactory) parentBeanFactory).doGetBean(
nameToLookup, requiredType, args, typeCheckOnly);
}
//If there are beans in the current beanFactory
else if (args != null) {
// Delegation to parent with explicit args.
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args);
}
else if (requiredType != null) {
// No args -> delegate to standard getBean method.
return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType);
}
else {
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup);
}
}
if (!typeCheckOnly) {
markBeanAsCreated(beanName);
}
try {
//Obtain BeanDefinition according to BeanName
RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args);
// Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on.| Gets the bean that the current bean depends on
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn();
if (dependsOn != null) {
for (String dep : dependsOn) {
if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'");
}
registerDependentBean(dep, beanName);
try {
getBean(dep);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"'" + beanName + "' depends on missing bean '" + dep + "'", ex);
}
}
}
// Create bean instance.
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {//TODO creates beans and configures bean core methods
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);//Create bean
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
//Where property bean s are created
else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {
// It's a prototype -> create a new instance.
Object prototypeInstance = null;
try {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
else {
String scopeName = mbd.getScope();
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(scopeName)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No scope name defined for bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName);
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'");
}
try {
Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, () -> {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; consider " +
"defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton",
ex);
}
}
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
//At this point, the bean already contains the dependent bean
// Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance.| Check whether the required type matches the type of the actual bean instance
if (requiredType != null && !requiredType.isInstance(bean)) {
try {
T convertedBean = getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType);
if (convertedBean == null) {
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
return convertedBean;
}
catch (TypeMismatchException ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type '" +
ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "'", ex);
}
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
}
return (T) bean;
}
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean is then called
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean. Holds the created Bean object
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {//For single instance, first clear the Bean with the same name in the cache
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
//TODO actually creates bean s
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
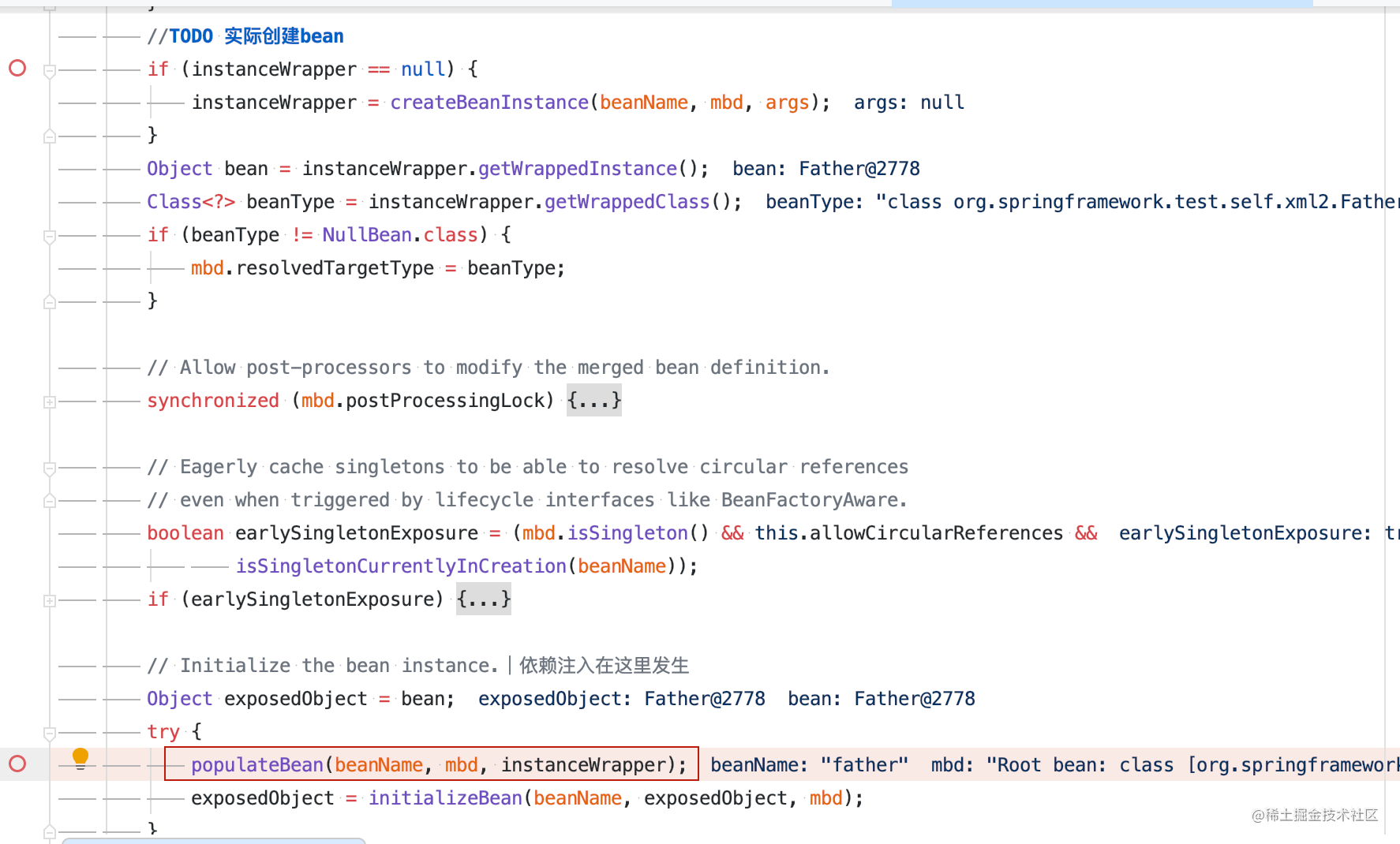
// Initialize the bean instance.| Dependency injection occurs here
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesForType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}
If the bean has no dependencies, it will be created smoothly through reflection. Call the following method.
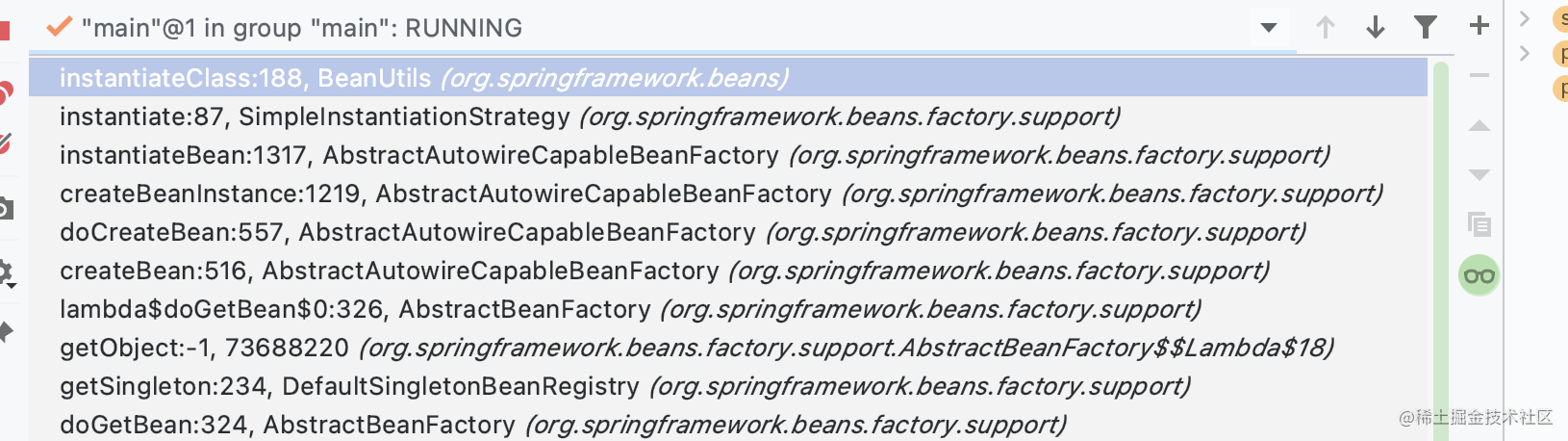
public static <T> T instantiateClass(Constructor<T> ctor, Object... args) throws BeanInstantiationException {
Assert.notNull(ctor, "Constructor must not be null");
try {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(ctor);
if (KotlinDetector.isKotlinReflectPresent() && KotlinDetector.isKotlinType(ctor.getDeclaringClass())) {
return KotlinDelegate.instantiateClass(ctor, args);
}
else {
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = ctor.getParameterTypes();
Assert.isTrue(args.length <= parameterTypes.length, "Can't specify more arguments than constructor parameters");
Object[] argsWithDefaultValues = new Object[args.length];
for (int i = 0 ; i < args.length; i++) {
if (args[i] == null) {
Class<?> parameterType = parameterTypes[i];
argsWithDefaultValues[i] = (parameterType.isPrimitive() ? DEFAULT_TYPE_VALUES.get(parameterType) : null);
}
else {
argsWithDefaultValues[i] = args[i];
}
}
return ctor.newInstance(argsWithDefaultValues);
}
}
...slightly
}
Finally, add the created bean to the map
protected void addSingleton(String beanName, Object singletonObject) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
this.singletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
}
}
Dependency injection
Dependency injection will take one more step after creation
If there are bean s, there are properties that need dependency injection
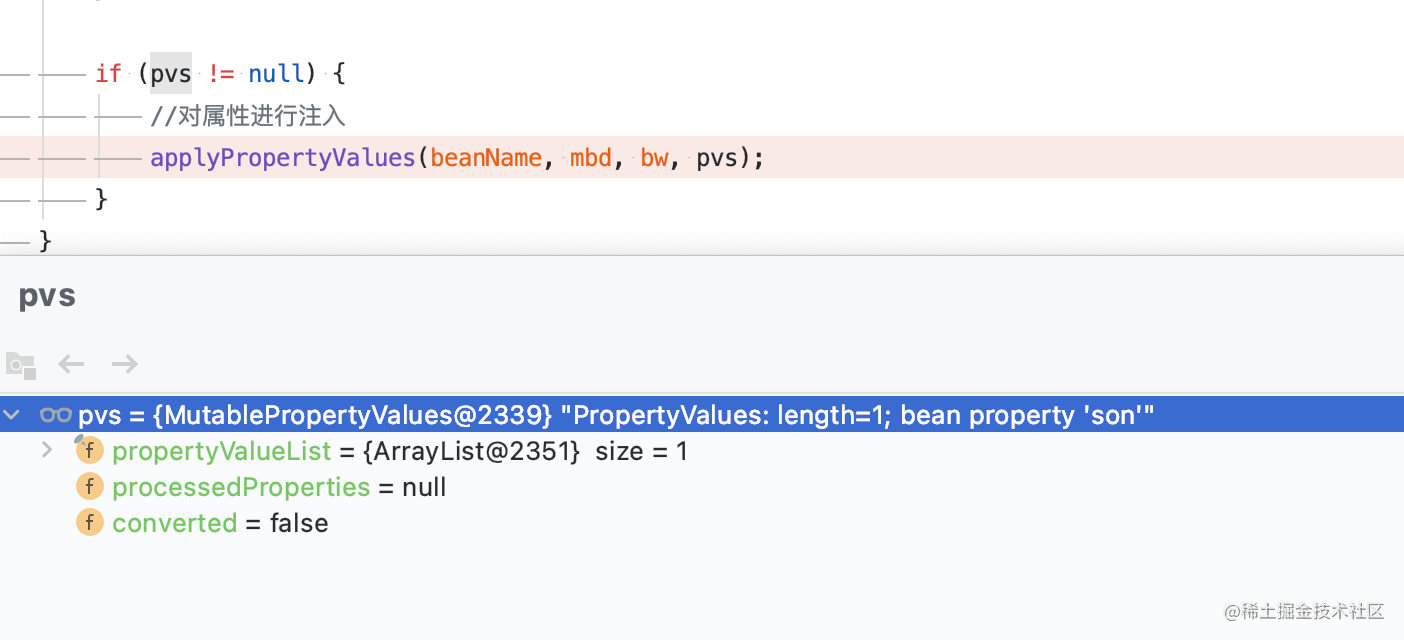
protected void applyPropertyValues(String beanName, BeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw, PropertyValues pvs) {
if (pvs.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && bw instanceof BeanWrapperImpl) {
((BeanWrapperImpl) bw).setSecurityContext(getAccessControlContext());
}
MutablePropertyValues mpvs = null;
List<PropertyValue> original;
if (pvs instanceof MutablePropertyValues) {
mpvs = (MutablePropertyValues) pvs;
if (mpvs.isConverted()) {
// Shortcut: use the pre-converted values as-is.
try {
bw.setPropertyValues(mpvs);
return;
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Error setting property values", ex);
}
}
original = mpvs.getPropertyValueList();
}
else {
original = Arrays.asList(pvs.getPropertyValues());
}
TypeConverter converter = getCustomTypeConverter();
if (converter == null) {
converter = bw;
}
//BeanDefinitionValueResolver the parsing of BeanDefinition is completed in this valueResolver
BeanDefinitionValueResolver valueResolver = new BeanDefinitionValueResolver(this, beanName, mbd, converter);
// Create a deep copy, resolving any references for values.
List<PropertyValue> deepCopy = new ArrayList<>(original.size());
boolean resolveNecessary = false;
for (PropertyValue pv : original) {
if (pv.isConverted()) {
deepCopy.add(pv);
}
else {
String propertyName = pv.getName();
Object originalValue = pv.getValue();
if (originalValue == AutowiredPropertyMarker.INSTANCE) {
Method writeMethod = bw.getPropertyDescriptor(propertyName).getWriteMethod();
if (writeMethod == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Autowire marker for property without write method: " + pv);
}
originalValue = new DependencyDescriptor(new MethodParameter(writeMethod, 0), true);
}
Object resolvedValue = valueResolver.resolveValueIfNecessary(pv, originalValue);//Obtained bean object
Object convertedValue = resolvedValue;
//Judge whether there is a set method
boolean convertible = bw.isWritableProperty(propertyName) &&
!PropertyAccessorUtils.isNestedOrIndexedProperty(propertyName);
if (convertible) {
convertedValue = convertForProperty(resolvedValue, propertyName, bw, converter);
}
// Possibly store converted value in merged bean definition,
// in order to avoid re-conversion for every created bean instance.
if (resolvedValue == originalValue) {
if (convertible) {
pv.setConvertedValue(convertedValue);
}
deepCopy.add(pv);
}
else if (convertible && originalValue instanceof TypedStringValue &&
!((TypedStringValue) originalValue).isDynamic() &&
!(convertedValue instanceof Collection || ObjectUtils.isArray(convertedValue))) {
pv.setConvertedValue(convertedValue);
deepCopy.add(pv);
}
else {
resolveNecessary = true;
deepCopy.add(new PropertyValue(pv, convertedValue));
}
}
}
if (mpvs != null && !resolveNecessary) {
mpvs.setConverted();
}
// Set our (possibly massaged) deep copy.
try {
//Where dependency injection occurs
bw.setPropertyValues(new MutablePropertyValues(deepCopy));
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Error setting property values", ex);
}
}
Finally, the set method will be called for injection
//set method injection
@Override
public void setValue(@Nullable Object value) throws Exception {
Method writeMethod = (this.pd instanceof GenericTypeAwarePropertyDescriptor ?
((GenericTypeAwarePropertyDescriptor) this.pd).getWriteMethodForActualAccess() :
this.pd.getWriteMethod());
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(writeMethod);
return null;
});
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>)
() -> writeMethod.invoke(getWrappedInstance(), value), acc);
}
catch (PrivilegedActionException ex) {
throw ex.getException();
}
}
else {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(writeMethod);
writeMethod.invoke(getWrappedInstance(), value);
}
}

@Autowired is a little different
It is processed here.

Annotation is to directly set the value autowiredannotationbeanpostprocessor through field AutowiredFieldElement#inject
@Override
protected void inject(Object bean, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Field field = (Field) this.member;
Object value;
if (this.cached) {
try {
value = resolvedCachedArgument(beanName, this.cachedFieldValue);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Unexpected removal of target bean for cached argument -> re-resolve
value = resolveFieldValue(field, bean, beanName);
}
}
else {
value = resolveFieldValue(field, bean, beanName);
}
if (value != null) {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
field.set(bean, value);
}
}
Cyclic dependence
The test code is as follows
@Component
public class Father {
@Autowired
private Son son;
public void say(){
son.say();
System.out.println("say hello");
}
}
@Component
public class Son {
@Autowired
private Father father;
public void say(){
System.out.println("abcdefg");
}
}
How to solve circular dependency? spring will cache the bean reference into singletonFactories after creating the reflection and before dependency injection
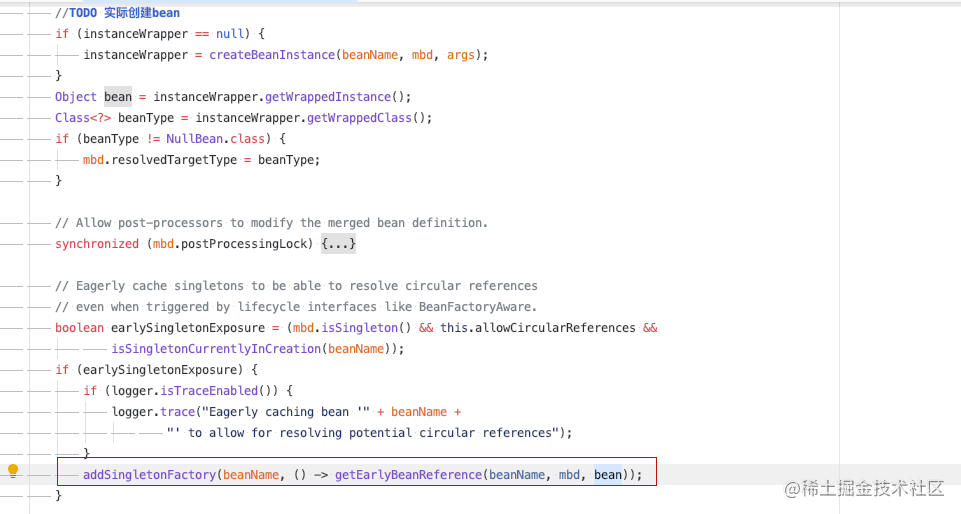
protected void addSingletonFactory(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory) {
Assert.notNull(singletonFactory, "Singleton factory must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
if (!this.singletonObjects.containsKey(beanName)) {
this.singletonFactories.put(beanName, singletonFactory);
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
}
}
}
What's the use of it
When parsing the bean in the class, getBean will be called to get the bean, and the DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry#getSingleton(String, boolean) will be entered to try to get the bean. singletonsCurrentlyInCreation will record the bean being created. For example, in the example I wrote above, father needs son and son needs father. No matter which one is created first, for example, Father creates first, When injection is needed, it is found that son has not been created. At this time, it starts to create son. When son injects, it needs father. At this time, father has not been created. At this time, singletonFactories play a role. singletonFactories store objects that have been created but have been injected into instances, but the reference of father will not change, but the value of son has not been assigned. At this time, the reference of father is given to son first. Son is created and assigned to father. This is roughly such a process. After creation, delete singletonFactories and store them in singletonObjects.
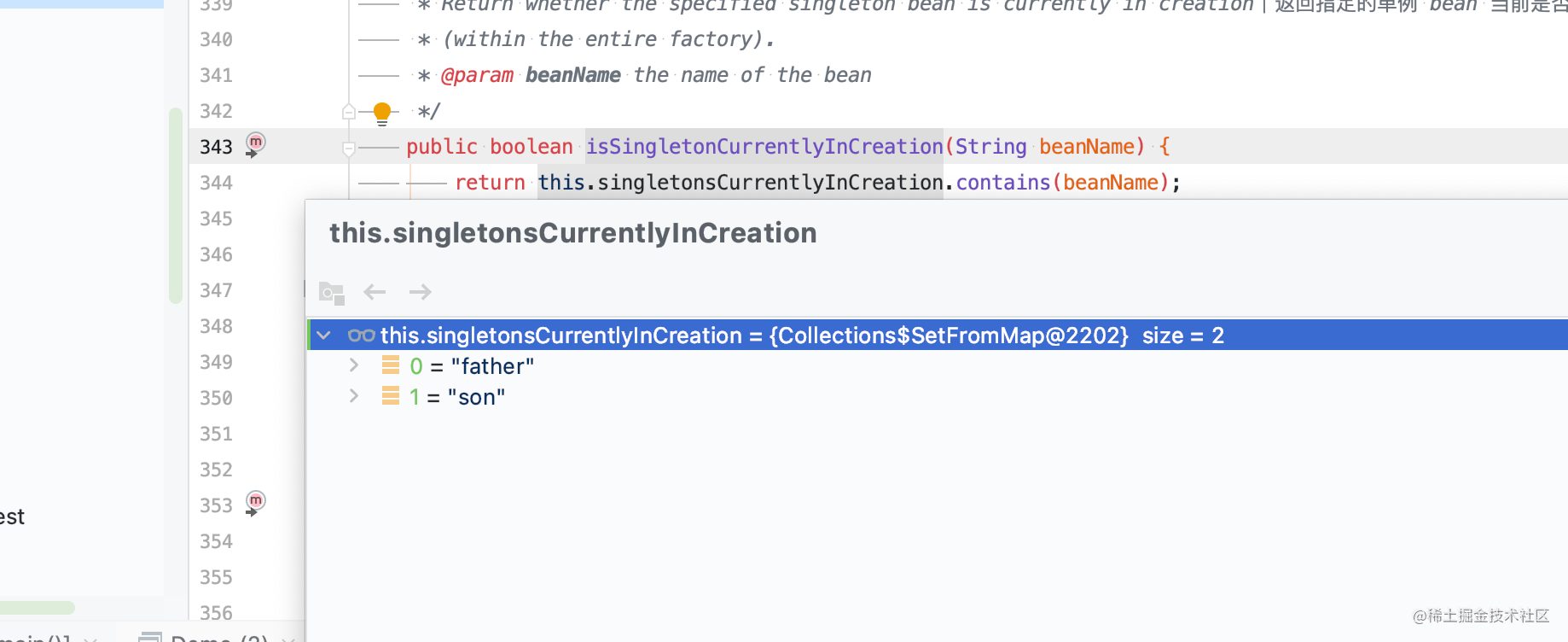
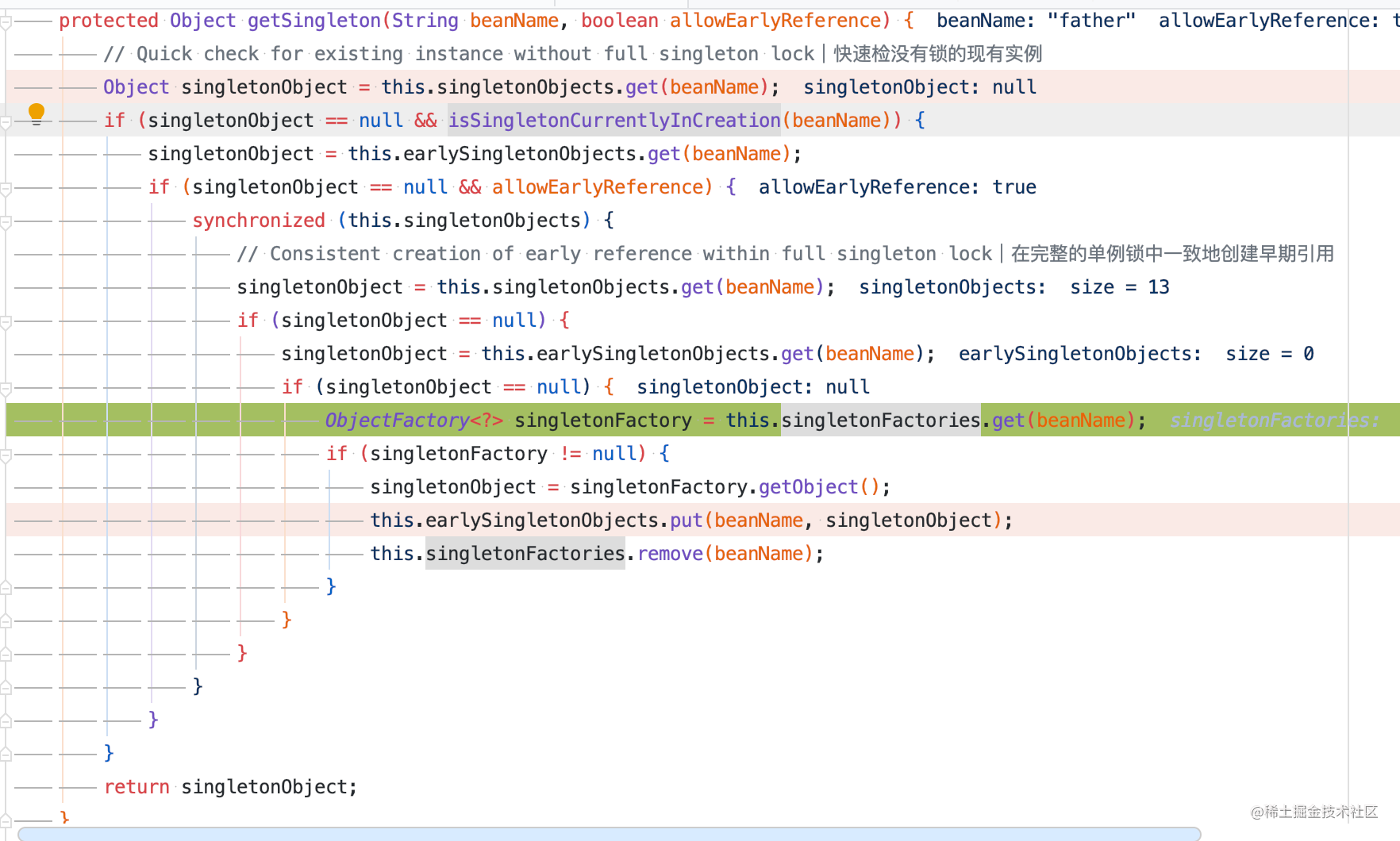
@Nullable
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
// Quick check for existing instance without full singleton lock
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
// Consistent creation of early reference within full singleton lock
singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
After creation, delete it and store it in singletonObjects.
protected void addSingleton(String beanName, Object singletonObject) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
this.singletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
}
}