Filter chain analysis
In Spring security, all functions are implemented through filters, which form a complete filter chain.
4.1 initialization process analysis
4.1.1ObjectPostProcessor
/**
* Allows objects to be initialized. Typically, this is used to call the Aware method, initializingbean Afterpropertieset() and ensure disposablebean Destroy() is called.
* It is an object postprocessor, that is, after an object is created successfully, if there are some additional things to be added, it can be processed through ObjectPostProcessor
* Type parameters: <T> – Boundaries of object types supported by this ObjectPostProcessor
*/
public interface ObjectPostProcessor<T> {
// Initializing an object may return a modified instance that should be used instead. Complete the secondary processing of the object
<O extends T> O postProcess(O object);
}
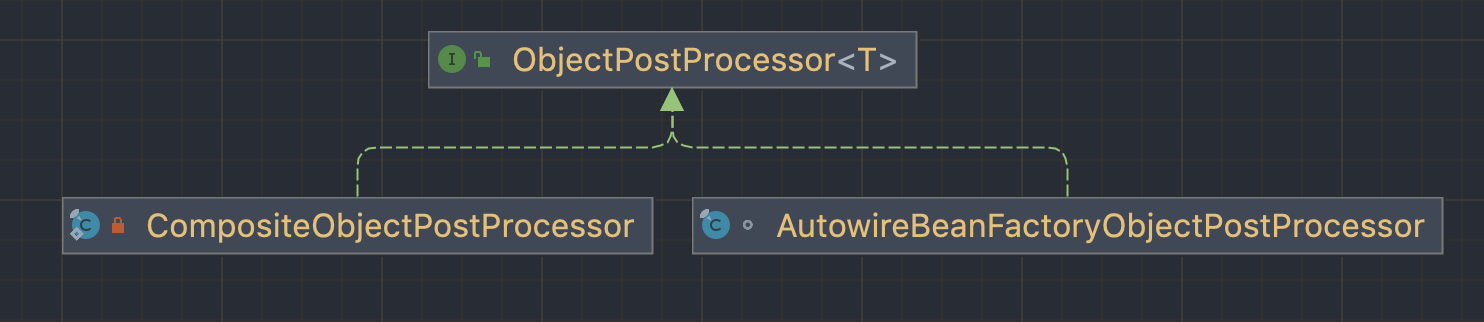
- AutowireBeanFactoryObjectPostProcessor: due to the extensive use of java configuration in spring security, many filters are directly new, and these directly new objects will not be automatically injected into the spring container. Spring security is intended to simplify the configuration, but it brings another problem that a large number of new objects need to be manually registered in the spring container. This is what the autowirebeanfactory objectpostprocessor object undertakes. After an object is new, it can be successfully injected into the spring container by calling the autowirebeanfactory objectpostprocessor #postprocess method, Its implementation principle is to inject a new object into the spring container by calling the AutowireCapableBeanFactory object in the spring container.
- CompositeObjectPostProcessor: an object can have a postprocessor, or you can customize multiple object postprocessors. CompositeObjectPostProcessor is a composite object postprocessor. It maintains a List collection in which all postprocessors of an object are stored. When it is necessary to execute the postprocessor of an object, it will traverse all ObjectPostProcessor instances in the collection and call the postProcess method of the instance respectively for postprocessing of the object. In spring security, the final object postprocessor is actually CompositeObjectPostProcessor. By default, there is only one object in its collection, autowirebeanfactory ObjectPostProcessor.
In spring security, developers can flexibly configure which spring security filters are required in the project. Once the filter is selected, each filter will have a corresponding configurator called xxxconfigurer (for example, CorsConfigurer, csrfconfigurator, etc.). The filters are new in the corresponding configurator, and then processed in the postProcess method, These filters are injected into the spring container.
4.1.2SecurityFilterChain
SecurityFilterChain is the filter chain object in spring security:
/**
* Define a filter chain that can match HttpServletRequest to determine whether it applies to the request.
* Used to configure FilterChainProxy.
*/
public interface SecurityFilterChain {
// Determine whether the request should be processed by the current filter chain
boolean matches(HttpServletRequest request);
// Returns a collection of filters in spring security. If matches returns true, then request
// The request is processed in the collection returned in the getFilters method
List<Filter> getFilters();
}
There is only one default implementation class of SecurityFilterChain, DefaultSecurityFilterChain:
public final class DefaultSecurityFilterChain implements SecurityFilterChain {
private final RequestMatcher requestMatcher;
private final List<Filter> filters;
public DefaultSecurityFilterChain(RequestMatcher requestMatcher, List<Filter> filters) {
logger.info(LogMessage.format("Will secure %s with %s", requestMatcher, filters));
this.requestMatcher = requestMatcher;
this.filters = new ArrayList<>(filters);
}
public RequestMatcher getRequestMatcher() {
return this.requestMatcher;
}
@Override
public List<Filter> getFilters() {
return this.filters;
}
@Override
public boolean matches(HttpServletRequest request) {
return this.requestMatcher.matches(request);
}
}
4.1.3SecurityBuilder
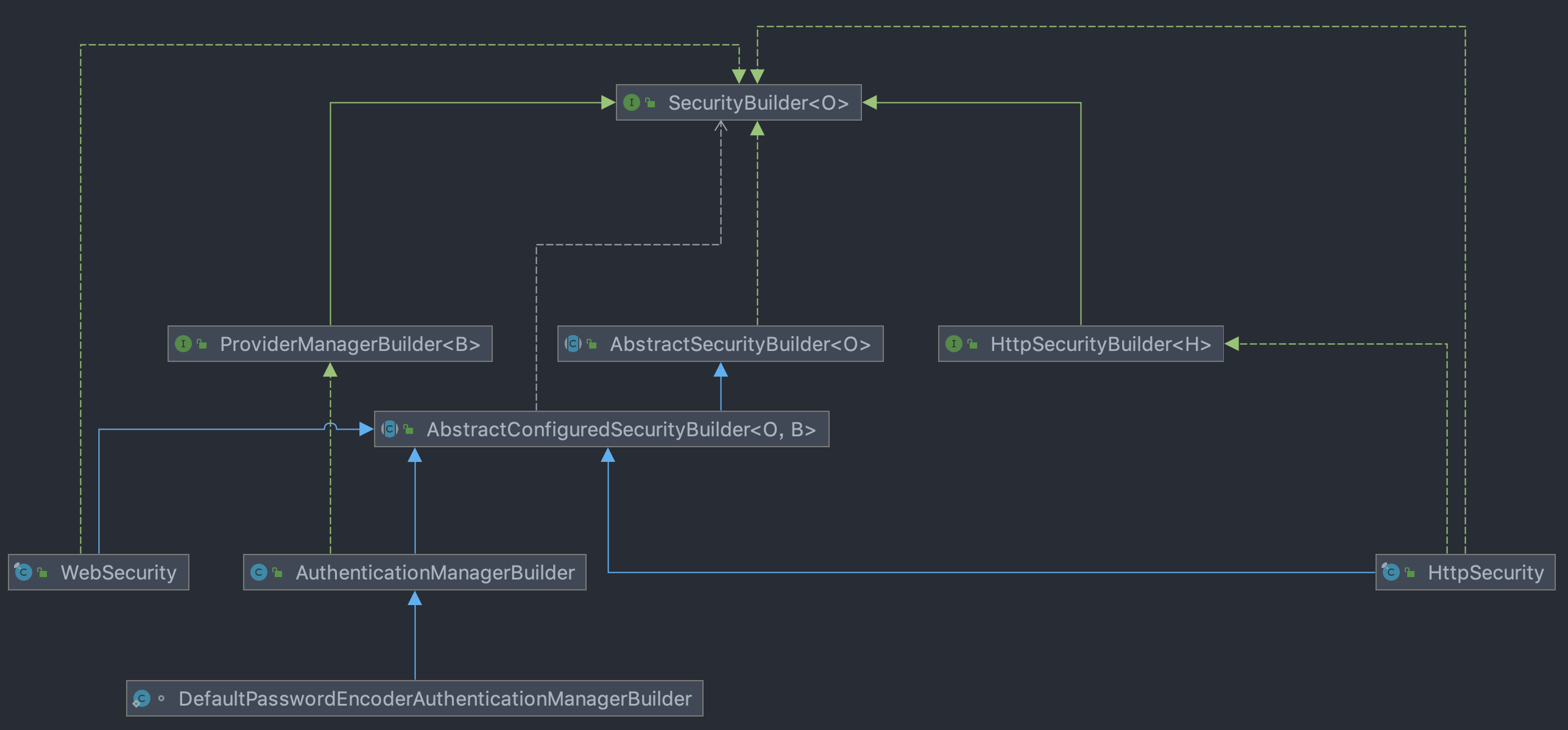
All objects to be built in Spring security can be implemented through SecurityBuilder. The default filter chain, proxy filter, AuthenticationManager, etc. can be built through SecurityBuilder.
SecurityBuilder
/**
* The interface used to create an object. Different securitybuilders will build different objects in the future.
* Type parameters: <O> – Concrete construction object
*/
public interface SecurityBuilder<O> {
O build() throws Exception;
}
HttpSecurityBuilder
HttpSecurityBuilder is used to build HttpSecurity objects:
/**
* By default, the implementation class of HttpSecurityBuilder has only one HttpSecurity, so H can be understood as HttpSecurity.
* The final object to build is DefaultSecurityFilterChain.
*/
public interface HttpSecurityBuilder<H extends HttpSecurityBuilder<H>>
extends SecurityBuilder<DefaultSecurityFilterChain> {
<C extends SecurityConfigurer<DefaultSecurityFilterChain, H>> C getConfigurer(Class<C> clazz);
<C extends SecurityConfigurer<DefaultSecurityFilterChain, H>> C removeConfigurer(Class<C> clazz);
// Set up an object that can be shared among multiple configurators
<C> void setSharedObject(Class<C> sharedType, C object);
<C> C getSharedObject(Class<C> sharedType);
// Configure an authenticator
H authenticationProvider(AuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider);
// Configure a data source
H userDetailsService(UserDetailsService userDetailsService) throws Exception;
H addFilterAfter(Filter filter, Class<? extends Filter> afterFilter);
H addFilterBefore(Filter filter, Class<? extends Filter> beforeFilter);
// Adding a filter must be an instance or extension of the filter provided by spring security
H addFilter(Filter filter);
}
AbstractSecurityBuilder
AbstractSecurityBuilder implements the SecurityBuilder interface and improves the build to ensure that it is built only once.
public abstract class AbstractSecurityBuilder<O> implements SecurityBuilder<O> {
// Ensure that the configuration class can only be built once even in a multithreaded environment
private AtomicBoolean building = new AtomicBoolean();
private O object;
// Set to final, subclasses cannot be overridden
@Override
public final O build() throws Exception {
if (this.building.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
this.object = doBuild();
return this.object;
}
throw new AlreadyBuiltException("This object has already been built");
}
public final O getObject() {
if (!this.building.get()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("This object has not been built");
}
return this.object;
}
protected abstract O doBuild() throws Exception;
}
AbstractConfiguredSecurityBuilder
Firstly, an enumeration class is declared in AbstractConfiguredSecurityBuilder to describe the different states of the construction process:
private enum BuildState {
// Before configuration class construction
UNBUILT(0),
// Initializing (in this state before initialization is completed)
INITIALIZING(1),
// In configuration (in this state before starting the build)
CONFIGURING(2),
// Under construction
BUILDING(3),
// Build complete
BUILT(4);
private final int order;
BuildState(int order) {
this.order = order;
}
// Determine whether initialization is in progress
public boolean isInitializing() {
return INITIALIZING.order == this.order;
}
// Determine whether the configuration has been completed
public boolean isConfigured() {
return this.order >= CONFIGURING.order;
}
}
The relevant methods of AbstractConfiguredSecurityBuilder class are as follows:
public abstract class AbstractConfiguredSecurityBuilder<O, B extends SecurityBuilder<O>>
extends AbstractSecurityBuilder<O> {
private final LinkedHashMap<Class<? extends SecurityConfigurer<O, B>>, List<SecurityConfigurer<O, B>>> configurers = new LinkedHashMap<>();
public <C extends SecurityConfigurerAdapter<O, B>> C apply(C configurer) throws Exception {
configurer.addObjectPostProcessor(this.objectPostProcessor);
configurer.setBuilder((B) this);
add(configurer);
return configurer;
}
public <C extends SecurityConfigurer<O, B>> C apply(C configurer) throws Exception {
add(configurer);
return configurer;
}
private <C extends SecurityConfigurer<O, B>> void add(C configurer) {
Assert.notNull(configurer, "configurer cannot be null");
Class<? extends SecurityConfigurer<O, B>> clazz = (Class<? extends SecurityConfigurer<O, B>>) configurer
.getClass();
synchronized (this.configurers) {
if (this.buildState.isConfigured()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot apply " + configurer + " to already built object");
}
List<SecurityConfigurer<O, B>> configs = null;
// Judge whether the same type of configuration class is allowed to exist. By default, the common configuration class is false, so there is always only one configuration class in the collection
if (this.allowConfigurersOfSameType) {
configs = this.configurers.get(clazz);
}
configs = (configs != null) ? configs : new ArrayList<>(1);
configs.add(configurer);
this.configurers.put(clazz, configs);
if (this.buildState.isInitializing()) {
this.configurersAddedInInitializing.add(configurer);
}
}
}
public <C extends SecurityConfigurer<O, B>> List<C> getConfigurers(Class<C> clazz) {
List<C> configs = (List<C>) this.configurers.get(clazz);
if (configs == null) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
return new ArrayList<>(configs);
}
public <C extends SecurityConfigurer<O, B>> List<C> removeConfigurers(Class<C> clazz) {
List<C> configs = (List<C>) this.configurers.remove(clazz);
if (configs == null) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
return new ArrayList<>(configs);
}
public <C extends SecurityConfigurer<O, B>> C getConfigurer(Class<C> clazz) {
List<SecurityConfigurer<O, B>> configs = this.configurers.get(clazz);
if (configs == null) {
return null;
}
Assert.state(configs.size() == 1,
() -> "Only one configurer expected for type " + clazz + ", but got " + configs);
return (C) configs.get(0);
}
public <C extends SecurityConfigurer<O, B>> C removeConfigurer(Class<C> clazz) {
List<SecurityConfigurer<O, B>> configs = this.configurers.remove(clazz);
if (configs == null) {
return null;
}
Assert.state(configs.size() == 1,
() -> "Only one configurer expected for type " + clazz + ", but got " + configs);
return (C) configs.get(0);
}
private Collection<SecurityConfigurer<O, B>> getConfigurers() {
List<SecurityConfigurer<O, B>> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (List<SecurityConfigurer<O, B>> configs : this.configurers.values()) {
result.addAll(configs);
}
return result;
}
}
The core method is doBuild:
// Execute the build method while updating the build status
@Override
protected final O doBuild() throws Exception {
synchronized (this.configurers) {
this.buildState = BuildState.INITIALIZING;
beforeInit();
init();
this.buildState = BuildState.CONFIGURING;
beforeConfigure();
configure();
this.buildState = BuildState.BUILDING;
O result = performBuild();
this.buildState = BuildState.BUILT;
return result;
}
}
protected void beforeInit() throws Exception {
}
protected void beforeConfigure() throws Exception {
}
// Do the final build operation
protected abstract O performBuild() throws Exception;
// Initialization methods of all configuration classes
private void init() throws Exception {
Collection<SecurityConfigurer<O, B>> configurers = getConfigurers();
for (SecurityConfigurer<O, B> configurer : configurers) {
configurer.init((B) this);
}
for (SecurityConfigurer<O, B> configurer : this.configurersAddedInInitializing) {
configurer.init((B) this);
}
}
// Complete the configuration of all configuration classes
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void configure() throws Exception {
Collection<SecurityConfigurer<O, B>> configurers = getConfigurers();
for (SecurityConfigurer<O, B> configurer : configurers) {
configurer.configure((B) this);
}
}
ProviderManagerBuilder
// The object built is AuthenticationManager
public interface ProviderManagerBuilder<B extends ProviderManagerBuilder<B>>
extends SecurityBuilder<AuthenticationManager> {
B authenticationProvider(AuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider);
}
AuthenticationManagerBuilder
To build the AuthenticationManager:
public class AuthenticationManagerBuilder
extends AbstractConfiguredSecurityBuilder<AuthenticationManager, AuthenticationManagerBuilder>
implements ProviderManagerBuilder<AuthenticationManagerBuilder> {
// The second parameter is true, which means that configuration classes of the same type are allowed to exist at the same time. Refer to AbstractConfiguredSecurityBuilder
public AuthenticationManagerBuilder(ObjectPostProcessor<Object> objectPostProcessor) {
super(objectPostProcessor, true);
}
// Used to set a parent for an authentication manager
public AuthenticationManagerBuilder parentAuthenticationManager(AuthenticationManager authenticationManager) {
if (authenticationManager instanceof ProviderManager) {
eraseCredentials(((ProviderManager) authenticationManager).isEraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication());
}
this.parentAuthenticationManager = authenticationManager;
return this;
}
// Used to configure the memory based data source, this method will automatically create the InMemoryUserDetailsManagerConfigurer configuration class, and finally add the configuration class to the configurers variable of the parent class.
// The inMemoryAuthentication method can be called repeatedly because the configuration classes of the same type are allowed to exist at the same time
public InMemoryUserDetailsManagerConfigurer<AuthenticationManagerBuilder> inMemoryAuthentication()
throws Exception {
return apply(new InMemoryUserDetailsManagerConfigurer<>());
}
// ditto
public JdbcUserDetailsManagerConfigurer<AuthenticationManagerBuilder> jdbcAuthentication() throws Exception {
return apply(new JdbcUserDetailsManagerConfigurer<>());
}
// ditto
public <T extends UserDetailsService> DaoAuthenticationConfigurer<AuthenticationManagerBuilder, T> userDetailsService(
T userDetailsService) throws Exception {
this.defaultUserDetailsService = userDetailsService;
return apply(new DaoAuthenticationConfigurer<>(userDetailsService));
}
// Used to add an AuthenticationProvider object to the authenticationProviders collection. One AuthenticationManager instance contains multiple AuthenticationProvider instances,
// Then multiple authenticationprovider instances can be added through the authenticationprovider method
@Override
public AuthenticationManagerBuilder authenticationProvider(AuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider) {
this.authenticationProviders.add(authenticationProvider);
return this;
}
// Perform specific construction work. The commonly used instance of AuthenticationManager is ProviderManager, so the ProviderManager object is created here,
// And configure authenticationProviders and parentAuthenticationManager objects. After the ProviderManager object is created successfully,
// Go to the object post processor to process it again and then return
@Override
protected ProviderManager performBuild() throws Exception {
if (!isConfigured()) {
this.logger.debug("No authenticationProviders and no parentAuthenticationManager defined. Returning null.");
return null;
}
ProviderManager providerManager = new ProviderManager(this.authenticationProviders,
this.parentAuthenticationManager);
if (this.eraseCredentials != null) {
providerManager.setEraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication(this.eraseCredentials);
}
if (this.eventPublisher != null) {
providerManager.setAuthenticationEventPublisher(this.eventPublisher);
}
providerManager = postProcess(providerManager);
return providerManager;
}
}
HttpSecurity
The main function of HttpSecurity is to build a filter chain and reflect it on the code, that is, to build a DefaultSecurityFilterChain object.
A DefaultSecurityFilterChain object contains a path matcher and multiple spring security filters. In HttpSecurity, the configuration classes corresponding to the spring security filter are collected by collecting various xxxconfigurers and saved in the configurers variable of the parent class AbstractConfiguredSecurityBuilder. In the subsequent construction process, Then build these xxxconfigurers into specific spring security filters and add them to the filters object of HttpSecurity.
// The configuration of other filters is similar to that of form login, so I will only talk about one
// Each set of filter chain will have an AuthenticationManager object to authenticate (if authentication fails, the parent of AuthenticationManager will be called to authenticate again)
public final class HttpSecurity extends AbstractConfiguredSecurityBuilder<DefaultSecurityFilterChain, HttpSecurity>
implements SecurityBuilder<DefaultSecurityFilterChain>, HttpSecurityBuilder<HttpSecurity> {
// Return a FormLoginConfigurer. Developers can continue to improve the configuration of form based on this object
public FormLoginConfigurer<HttpSecurity> formLogin() throws Exception {
return getOrApply(new FormLoginConfigurer<>());
}
// Developers can configure the FormLoginConfigurer object outside in advance, and then directly pass it in for configuration, and can directly configure other filters after the method returns
public HttpSecurity formLogin(Customizer<FormLoginConfigurer<HttpSecurity>> formLoginCustomizer) throws Exception {
formLoginCustomizer.customize(getOrApply(new FormLoginConfigurer<>()));
return HttpSecurity.this;
}
// Configure the AuthenticationProvider object used to perform authentication
@Override
public HttpSecurity authenticationProvider(AuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider) {
getAuthenticationRegistry().authenticationProvider(authenticationProvider);
return this;
}
// Configure UserDetailsService object
@Override
public HttpSecurity userDetailsService(UserDetailsService userDetailsService) throws Exception {
getAuthenticationRegistry().userDetailsService(userDetailsService);
return this;
}
private AuthenticationManagerBuilder getAuthenticationRegistry() {
return getSharedObject(AuthenticationManagerBuilder.class);
}
// Triggers the construction of the AuthenticationManager object
@Override
protected void beforeConfigure() throws Exception {
setSharedObject(AuthenticationManager.class, getAuthenticationRegistry().build());
}
@Override
protected DefaultSecurityFilterChain performBuild() {
this.filters.sort(OrderComparator.INSTANCE);
List<Filter> sortedFilters = new ArrayList<>(this.filters.size());
for (Filter filter : this.filters) {
sortedFilters.add(((OrderedFilter) filter).filter);
}
return new DefaultSecurityFilterChain(this.requestMatcher, sortedFilters);
}
// Add a custom filter after a filter
@Override
public HttpSecurity addFilterAfter(Filter filter, Class<? extends Filter> afterFilter) {
return addFilterAtOffsetOf(filter, 1, afterFilter);
}
// Add a custom filter before a filter
@Override
public HttpSecurity addFilterBefore(Filter filter, Class<? extends Filter> beforeFilter) {
return addFilterAtOffsetOf(filter, -1, beforeFilter);
}
// To add a filter to the filter chain, it must be an instance of the filter provided by the spring security framework or its extension. In fact, in the configure method of each xconfigurer,
// The addFilter method will be called to add the constructed filter to the filters collection in HttpSecurity
@Override
public HttpSecurity addFilter(Filter filter) {
Integer order = this.filterOrders.getOrder(filter.getClass());
if (order == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("The Filter class " + filter.getClass().getName()
+ " does not have a registered order and cannot be added without a specified order. Consider using addFilterBefore or addFilterAfter instead.");
}
this.filters.add(new OrderedFilter(filter, order));
return this;
}
// You can add a filter at a specified location. It should be noted that adding multiple filters at the same location does not overwrite the existing filters
public HttpSecurity addFilterAt(Filter filter, Class<? extends Filter> atFilter) {
return addFilterAtOffsetOf(filter, 0, atFilter);
}
// Call the getConfigurer method of the parent class to check whether there is a corresponding configuration class. If so, return directly; If not, call the apply method to add it to the configurers variable of the parent class
private <C extends SecurityConfigurerAdapter<DefaultSecurityFilterChain, HttpSecurity>> C getOrApply(C configurer)
throws Exception {
C existingConfig = (C) getConfigurer(configurer.getClass());
if (existingConfig != null) {
return existingConfig;
}
return apply(configurer);
}
}
WebSecurity
Compared with HttpSecurity, WebSecurity builds filters on a larger level.
An HttpSecurity can build a filter chain, that is, a DefaultSecurityFilterChain, while a project can have multiple HttpSecurity objects, which can build multiple DefaultSecurityFilterChain filter chains.
WebSecurity is responsible for rebuilding the DefaultSecurityFilterChain object (there may be multiple) built by HttpSecurity and other requests that need to be ignored into a FilterChainProxy object, and adding an HTTP firewall at the same time.
public final class WebSecurity extends AbstractConfiguredSecurityBuilder<Filter, WebSecurity>
implements SecurityBuilder<Filter>, ApplicationContextAware {
// Save all ignored requests, because in the actual project, for example, some static resources do not need to go through the spring security filter chain
private final List<RequestMatcher> ignoredRequests = new ArrayList<>();
// Used to save all HttpSecurity objects
private final List<SecurityBuilder<? extends SecurityFilterChain>> securityFilterChainBuilders = new ArrayList<>();
// Configure request firewall
public WebSecurity httpFirewall(HttpFirewall httpFirewall) {
this.httpFirewall = httpFirewall;
return this;
}
// After each HttpSecurity object is created successfully, it is added to the securityFilterChainBuilders collection through this method
public WebSecurity addSecurityFilterChainBuilder(
SecurityBuilder<? extends SecurityFilterChain> securityFilterChainBuilder) {
this.securityFilterChainBuilders.add(securityFilterChainBuilder);
return this;
}
@Override
protected Filter performBuild() throws Exception {
int chainSize = this.ignoredRequests.size() + this.securityFilterChainBuilders.size();
List<SecurityFilterChain> securityFilterChains = new ArrayList<>(chainSize);
for (RequestMatcher ignoredRequest : this.ignoredRequests) {
// Only the request matcher is passed in without the corresponding filter chain, which means that these ignored requests do not have to go through the spring security filter chain in the future
securityFilterChains.add(new DefaultSecurityFilterChain(ignoredRequest));
}
// Traverse the collection and call the build method to build the DefaultSecurityFilterChain object
for (SecurityBuilder<? extends SecurityFilterChain> securityFilterChainBuilder : this.securityFilterChainBuilders) {
securityFilterChains.add(securityFilterChainBuilder.build());
}
FilterChainProxy filterChainProxy = new FilterChainProxy(securityFilterChains);
if (this.httpFirewall != null) {
filterChainProxy.setFirewall(this.httpFirewall);
}
if (this.requestRejectedHandler != null) {
filterChainProxy.setRequestRejectedHandler(this.requestRejectedHandler);
}
filterChainProxy.afterPropertiesSet();
Filter result = filterChainProxy;
this.postBuildAction.run();
// Return the constructed FilterChainProxy object, and then embed it into the web filter (native filter chain) through the DelegatingFilterProxy provided by spring
return result;
}
}
4.1.4FilterChainProxy
FilterChainProxy is integrated into web filter through DelegatingFilterProxy proxy filter. DelegatingFilterProxy, as a proxy object, does not carry specific business.
Therefore, the final execution of the filter in spring security is in FilterChainProxy.
The source code of FilterChainProxy is relatively long. It is divided into sections:
// Save the filter chain
private List<SecurityFilterChain> filterChains;
// The validator after the filter chain configuration is completed is NullFilterChainValidator by default. In fact, it does not do any validation
private FilterChainValidator filterChainValidator = new NullFilterChainValidator();
// Default firewall object
private HttpFirewall firewall = new StrictHttpFirewall();
public FilterChainProxy() {
}
public FilterChainProxy(SecurityFilterChain chain) {
this(Arrays.asList(chain));
}
public FilterChainProxy(List<SecurityFilterChain> filterChains) {
this.filterChains = filterChains;
}
Because FilterChainProxy is essentially a filter, its core method is doFilter:
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
boolean clearContext = request.getAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED) == null;
if (!clearContext) {
doFilterInternal(request, response, chain);
return;
}
try {
request.setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED, Boolean.TRUE);
doFilterInternal(request, response, chain);
}
catch (RequestRejectedException ex) {
this.requestRejectedHandler.handle((HttpServletRequest) request, (HttpServletResponse) response, ex);
}
finally {
// If the doFilter method is executed for the first time (clearContext is true), after execution,
// In the finally code block, you need to clear the user information from the SecurityContextHolder,
// This is mainly to prevent users from not configuring SecurityContextPersistenceFilter correctly,
// As a result, the login user information is not correctly cleared, resulting in memory leakage
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
request.removeAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED);
}
}
The doFilter method is equivalent to the entry of the whole spring security filter chain. Some specific filters, such as SecurityContextPersistenceFilter, are executed after this method.
In the doFilter method, the specific implementation of the filter is entrusted to the doFilterInternal method:
private void doFilterInternal(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// Convert the request object into a FirewalledRequest object, and the conversion process will be processed by http firewall
FirewalledRequest firewallRequest = this.firewall.getFirewalledRequest((HttpServletRequest) request);
// At the same time, the response is converted to HttpServletResponse
HttpServletResponse firewallResponse = this.firewall.getFirewalledResponse((HttpServletResponse) response);
// Get the filter chain corresponding to the current request
List<Filter> filters = getFilters(firewallRequest);
// If the filters are null or there are no elements in the filters, the current request does not need to go through the spring security filter chain,
// Execute firewallrequest Reset resets the attributes in the http firewall, and then executes chain Dofilter, go back to the web filter,
// The spring security filter chain will be skipped
if (filters == null || filters.size() == 0) {
firewallRequest.reset();
chain.doFilter(firewallRequest, firewallResponse);
return;
}
// Build the virtual filter chain object VirtualFilterChain and execute doFilter
VirtualFilterChain virtualFilterChain = new VirtualFilterChain(firewallRequest, chain, filters);
virtualFilterChain.doFilter(firewallRequest, firewallResponse);
}
// Traverse the filterChains set to determine which filter chain the current request corresponds to
private List<Filter> getFilters(HttpServletRequest request) {
for (SecurityFilterChain chain : this.filterChains) {
if (chain.matches(request)) {
return chain.getFilters();
}
}
return null;
}
Next, let's take a look at the specific implementation of VirtualFilterChain:
private static final class VirtualFilterChain implements FilterChain {
// Represents the native filter chain, and the doFilter method executing it will return to the web filter
private final FilterChain originalChain;
// Stored Filter of this request
private final List<Filter> additionalFilters;
// Current request object
private final FirewalledRequest firewalledRequest;
// Size of filter chain
private final int size;
// Subscript of filter chain execution
private int currentPosition = 0;
// Assign a value to the corresponding variable
private VirtualFilterChain(FirewalledRequest firewalledRequest, FilterChain chain,
List<Filter> additionalFilters) {
this.originalChain = chain;
this.additionalFilters = additionalFilters;
this.size = additionalFilters.size();
this.firewalledRequest = firewalledRequest;
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) throws IOException, ServletException {
// Judge whether the currently executed subscripts are equal to the size of the filter chain. If they are equal, it means that all filters in the whole filter chain have gone through one by one,
// At this point, the attributes in the http firewall are reset first, then originalChain. is called. The dofilter method jumps out of the spring security filter,
// Go back to the web filter; If they are not equal, the currentPosition will increase automatically, and then take a filter from the filter chain set for execution. Note,
// When executing, the third parameter this represents the current object (i.e. VirtualFilterChain), so after each filter is executed,
// The last chain The doFilter method will return to the current doFilter method and continue to call the next filter
if (this.currentPosition == this.size) {
// Deactivate path stripping as we exit the security filter chain
this.firewalledRequest.reset();
this.originalChain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
this.currentPosition++;
Filter nextFilter = this.additionalFilters.get(this.currentPosition - 1);
nextFilter.doFilter(request, response, this);
}
}
4.1.5SecurityConfigurer
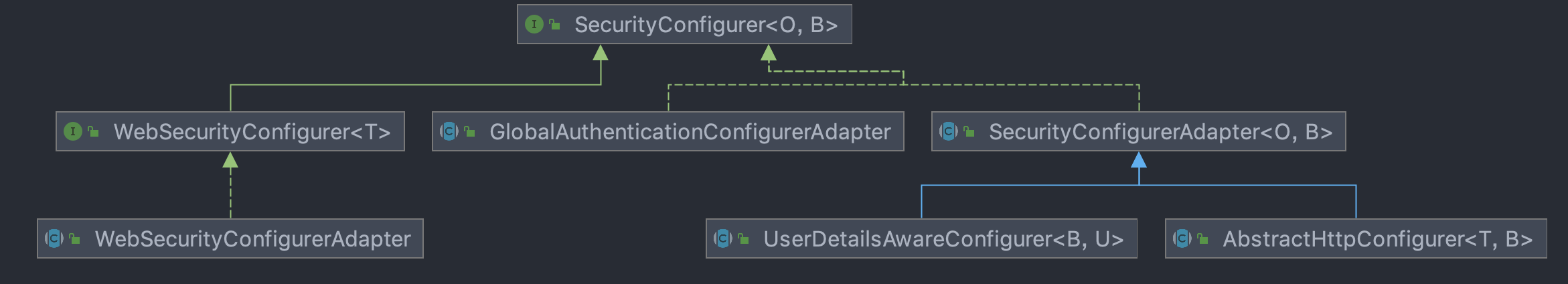
There are many implementation classes of SecurityConfigurer, mainly including the following common implementation classes:
SecurityConfigurer
public interface SecurityConfigurer<O, B extends SecurityBuilder<O>> {
// Used to complete the initialization of configuration classes, such as the initialization of SecurityBuilder
void init(B builder) throws Exception;
// Configure the configuration class, such as SecurityBuilder
void configure(B builder) throws Exception;
}
There are many subclasses of SecurityConfigurer, because each filter has its own corresponding xxxConfigurer. Here are some key:
SecurityConfigurerAdapter
public abstract class SecurityConfigurerAdapter<O, B extends SecurityBuilder<O>> implements SecurityConfigurer<O, B> {
// Each configuration class is provided with a SecurityBuilder object, which can be used to build specific configuration objects in the future
private B securityBuilder;
private CompositeObjectPostProcessor objectPostProcessor = new CompositeObjectPostProcessor();
@Override
public void init(B builder) throws Exception {
}
@Override
public void configure(B builder) throws Exception {
}
// Return the SecurityBuilder object through the and method, which is convenient for chain configuration of different configuration classes
public B and() {
return getBuilder();
}
protected final B getBuilder() {
Assert.state(this.securityBuilder != null, "securityBuilder cannot be null");
return this.securityBuilder;
}
protected <T> T postProcess(T object) {
return (T) this.objectPostProcessor.postProcess(object);
}
public void addObjectPostProcessor(ObjectPostProcessor<?> objectPostProcessor) {
this.objectPostProcessor.addObjectPostProcessor(objectPostProcessor);
}
public void setBuilder(B builder) {
this.securityBuilder = builder;
}
// Internal class, which is a composite object post processor
private static final class CompositeObjectPostProcessor implements ObjectPostProcessor<Object> {
private List<ObjectPostProcessor<?>> postProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
public Object postProcess(Object object) {
for (ObjectPostProcessor opp : this.postProcessors) {
Class<?> oppClass = opp.getClass();
Class<?> oppType = GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(oppClass, ObjectPostProcessor.class);
if (oppType == null || oppType.isAssignableFrom(object.getClass())) {
object = opp.postProcess(object);
}
}
return object;
}
// Add a new ObjectPostProcessor instance to the composite object postprocessor
private boolean addObjectPostProcessor(ObjectPostProcessor<?> objectPostProcessor) {
boolean result = this.postProcessors.add(objectPostProcessor);
this.postProcessors.sort(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE);
return result;
}
}
}
UserDetailsAwareConfigurer
The subclass of userdetailsaawareconfigurer is mainly responsible for configuring components related to user authentication, such as UserDetailsService. Userdetailsaawareconfigurer provides an abstract method to obtain UserDetailsService, and the specific implementation is in its subclass.
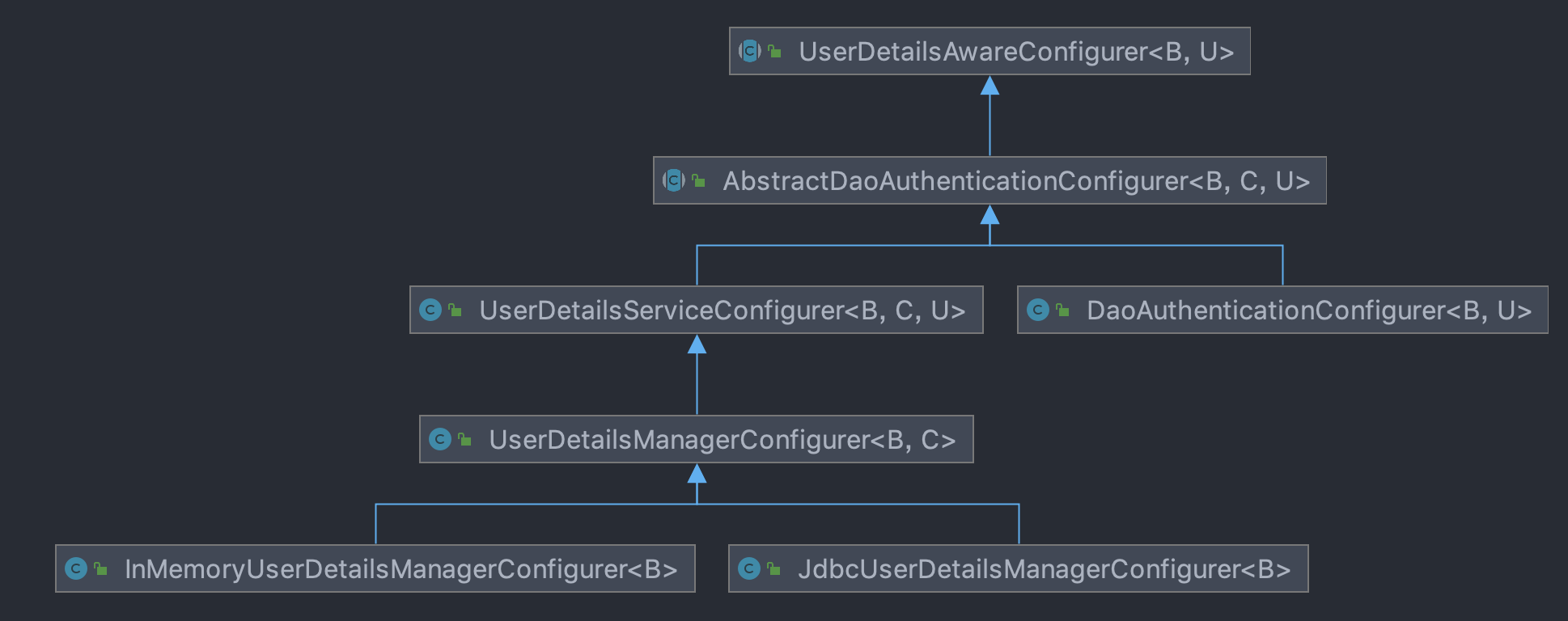
- Abstractdaoauthenticationconfigurator: completes the configuration of DaoAuthenticationProvider.
- UserDetailsServiceConfigurer: completes the configuration of UserDetailsService.
- UserDetailsManagerConfigurer: use UserDetailsManager to build user objects and complete the filling of AuthenticationManagerBuilder.
- JdbcUserDetailsManagerConfigurer: configure the JdbcUserDetailsManager and populate it into the AuthenticationManagerBuilder.
- InMemoryUserDetailsManagerConfigurer: configure InMemoryUserDetailsManager.
- Daoauthenticationconfigurator: completes the configuration of DaoAuthenticationProvider.
AbstractHttpConfigurer
Abstracthttpconfigurator is mainly used to add a convenient parent class to the configuration class used in HttpSecurity and extract common operations.
public abstract class AbstractHttpConfigurer<T extends AbstractHttpConfigurer<T, B>, B extends HttpSecurityBuilder<B>>
extends SecurityConfigurerAdapter<DefaultSecurityFilterChain, B> {
// It means disabling a configuration. In essence, it means removing a configuration class from the configurers collection of the builder, so that the configuration class will not exist when it is built in the future,
// Then the corresponding function does not exist
public B disable() {
getBuilder().removeConfigurer(getClass());
return getBuilder();
}
// It means adding an object post processor to an object. Since the return value of this method is the current object, this method can be used in chain configuration
public T withObjectPostProcessor(ObjectPostProcessor<?> objectPostProcessor) {
addObjectPostProcessor(objectPostProcessor);
return (T) this;
}
}
Abstracthttpconfigurator has many implementation classes, which are basically used to configure various filters:
| Configuration class name | effect |
|---|---|
| HttpBasicConfigurer | Configure the http basic authentication filter |
| LogoutConfigurer | Configure logout filter LogoutFilter |
| RequestCacheConfigurer | Configure request cache filter requestcachewarefilter |
| RememberMeConfigurer | Configure remember me login filterrembermeauthenticationfilter |
| ServletApiConfigurer | Configure the wrapper original request filter securitycontextholderawarerequesfilter |
| DefaultLoginPageConfigurer | Configure the filter DefaultLoginPageGeneratingFilter that provides the default login page and the filter DefaultLogoutPageGeneratingFilter that provides the default logout page |
| SessionManagementConfigurer | Configure session management filters SessionManagementFilter and ConcurrentSessionFilter |
| PortMapperConfigurer | Configure a shared PortMapper instance to determine the port when redirecting between HTTP and HTTPS |
| ExceptionHandlingConfigurer | Configure exception handling filter ExceptionTranslationFilter |
| HeadersConfigurer | Configure security related response header information |
| CsrfConfigurer | Configure CsrfFilter to prevent CSRF attack |
| OAuth2ClientConfigurer | Configure OAuth2 related filters OAuth2AuthorizationRequestRedirectFilter and OAuth2AuthorizationCodeGrantFilter |
| ImplicitGrantConfigurer | Configure the filter for OAuth2 authentication request redirection OAuth2AuthorizationRequestRedirectFilter |
| AnonymousConfigurer | Configure anonymous authenticationfilter |
| JeeConfigurer | Configure J2EE identity pre verification filter |
| ChannelSecurityConfigurer | Configure request protocol processing filter ChannelProcessingFilter |
| CorsConfigurer | Configure CorsFilter to handle cross domain filters |
| SecurityContextConfigurer | Configure the filter for login information storage and recovery SecurityContextPersistenceFilter |
| OAuth2ResourceServerConfigurer | Configure OAuth2 identity request authentication filter BearerTokenAuthenticationFilter |
| AbstractAuthenticationFilterConfigurer | Parent of authentication configuration class |
| FormLoginConfigurer | Configure the authentication filter UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter and the filter DefaultLoginPageGeneratingFilter of the default login page |
| OAuth2LoginConfigurer | Configure the OAuth2 authentication request redirection filter OAuth2AuthorizationRequestRedirectFilter and the processing third-party callback filter OAuth2LoginAuthenticationFilter |
| OpenIDLoginConfigurer | Configure OpenID authentication filter |
| Saml2LoginConfigurer | Configure saml2 0 authentication filters Saml2WebSsoAuthenticationFilter and Saml2WebSsoAuthenticationRequestFilter |
| X509Configurer | Configure X509 authentication filter |
| AbstractInterceptUrlConfigurer | Parent class of interceptor configuration class |
| UrlAuthorizationConfigurer | Configure the URL based authority authentication interceptor FilterSecurityInterceptor |
| ExpressionUrlAuthorizationConfigurer | Configure the URL authority authentication interceptor FilterSecurityInterceptor based on the SpEL expression |
GlobalAuthenticationConfigurerAdapter
It is mainly used to configure global AuthenticationManagerBuilder. In the AuthenticationConfiguration class, the bean provided by GlobalAuthenticationConfigurerAdapter will be automatically used to configure global AuthenticationManagerBuilder.
By default, ProviderManager has a parent, which is built through the global AuthenticationManagerBuilder here.
GlobalAuthenticationConfigurerAdapter has four different subclasses:
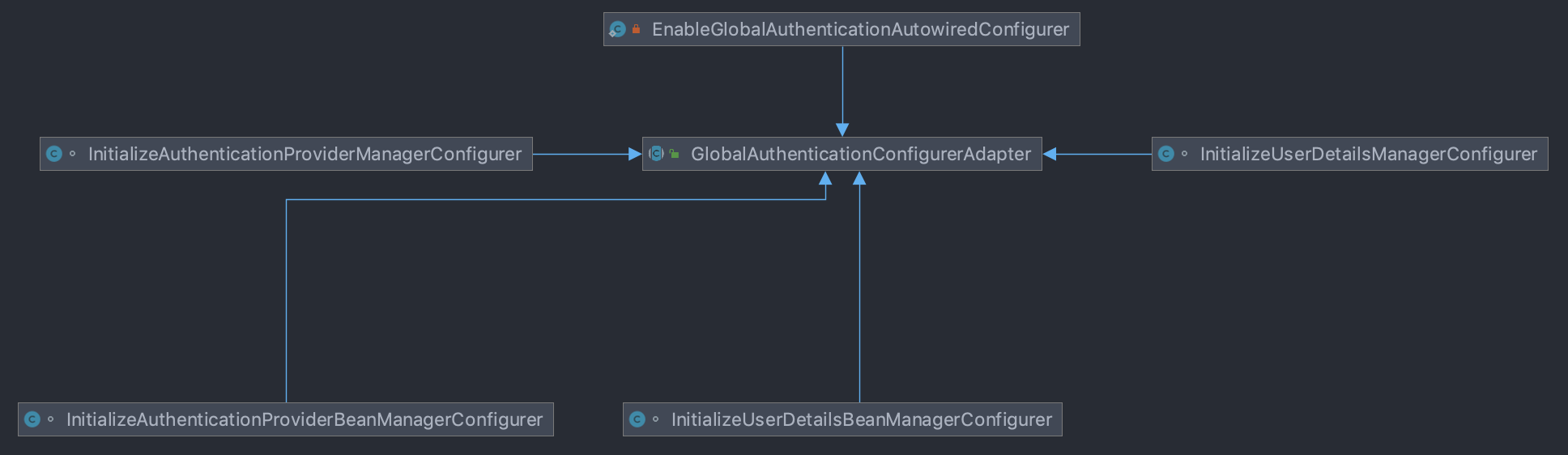
- InitializeAuthenticationProviderBeanManagerConfigurer: initializes the global AuthenticationProvider object.
- Initializeauthenticationprovidermanagerconfigurator: configure the global AuthenticationProvider object. The configuration process is to find the AuthenticationProvider from the spring container and set it to the global AuthenticationManagerBuilder object.
- Initializeuserdetailsbeanmanagerconfigurator: initializes the global UserDetailsService object.
- InitializeUserDetailsManagerConfigurer: configure the global UserDetailsService object. The configuration process is to find the UserDetailsService from the spring container and set it to the global AuthenticationManagerBuilder object.
- EnableGlobalAuthenticationAutowiredConfigurer: loads bean s marked by the @ EnableGlobalAuthentication annotation from the spring container.
WebSecurityConfigurer
This is an empty interface defined by WebSecurity. Only one implementation class is WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter. In most cases, developers implement custom configuration of WebSecurity by inheriting WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter.
WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
It is convenient to create the base class of WebSecurityConfigurer instance. Developers can customize HttpSecurity and WebSecurity by overriding the methods in it.
Two AuthenticationManagerBuilder objects are declared in WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter to build the AuthenticationManager:
// Responsible for building local authentication manager private AuthenticationManagerBuilder authenticationBuilder; // Responsible for building the global authentication manager private AuthenticationManagerBuilder localConfigureAuthenticationBldr;
The local AuthenticationManager is bound to each HttpSecurity object, while the global AuthenticationManager object is the parent of all local authenticationmanagers.
It should be noted that localConfigureAuthenticationBldr is not always useful. If the developer does not override the configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder) method, the global AuthenticationManager object is provided by the getAuthenticationManager method in the AuthenticationConfiguration class. If the user overrides the configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder) method, Then the global authentication manager is built by localConfigureAuthenticationBldr.
The initialization method of WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter class is as follows:
public abstract class WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter implements WebSecurityConfigurer<WebSecurity> {
@Override
public void init(WebSecurity web) throws Exception {
// Get an HttpSecurity instance
HttpSecurity http = getHttp();
// Add to WebSecurity
web.addSecurityFilterChainBuilder(http).postBuildAction(() -> {
FilterSecurityInterceptor securityInterceptor = http.getSharedObject(FilterSecurityInterceptor.class);
web.securityInterceptor(securityInterceptor);
});
}
protected final HttpSecurity getHttp() throws Exception {
// If it has been initialized, return directly
if (this.http != null) {
return this.http;
}
// Set the event publisher for localConfigureAuthenticationBldr
AuthenticationEventPublisher eventPublisher = getAuthenticationEventPublisher();
this.localConfigureAuthenticationBldr.authenticationEventPublisher(eventPublisher);
// Gets the global AuthenticationManager object
AuthenticationManager authenticationManager = authenticationManager();
this.authenticationBuilder.parentAuthenticationManager(authenticationManager);
Map<Class<?>, Object> sharedObjects = createSharedObjects();
// Create HttpSecurity instance
this.http = new HttpSecurity(this.objectPostProcessor, this.authenticationBuilder, sharedObjects);
if (!this.disableDefaults) {
// Apply default configuration
applyDefaultConfiguration(this.http);
ClassLoader classLoader = this.context.getClassLoader();
List<AbstractHttpConfigurer> defaultHttpConfigurers = SpringFactoriesLoader
.loadFactories(AbstractHttpConfigurer.class, classLoader);
for (AbstractHttpConfigurer configurer : defaultHttpConfigurers) {
this.http.apply(configurer);
}
}
// Make extended configuration
configure(this.http);
return this.http;
}
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests((requests) -> requests.anyRequest().authenticated());
http.formLogin();
http.httpBasic();
}
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
this.disableLocalConfigureAuthenticationBldr = true;
}
protected AuthenticationManager authenticationManager() throws Exception {
if (!this.authenticationManagerInitialized) {
configure(this.localConfigureAuthenticationBldr);
if (this.disableLocalConfigureAuthenticationBldr) {
this.authenticationManager = this.authenticationConfiguration.getAuthenticationManager();
}
else {
// If the developer rewrites the configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder) method,
// The disableLocalConfigureAuthenticationBldr variable is always false
this.authenticationManager = this.localConfigureAuthenticationBldr.build();
}
this.authenticationManagerInitialized = true;
}
return this.authenticationManager;
}
}
4.1.6 initialization process analysis
Use spring security in spring boot. Initialization starts from the automatic configuration class of spring security:
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnClass(DefaultAuthenticationEventPublisher.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(SecurityProperties.class)
// Import three configuration classes
@Import({ SpringBootWebSecurityConfiguration.class, WebSecurityEnablerConfiguration.class,
SecurityDataConfiguration.class })
public class SecurityAutoConfiguration {
// Define the default event publisher
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(AuthenticationEventPublisher.class)
public DefaultAuthenticationEventPublisher authenticationEventPublisher(ApplicationEventPublisher publisher) {
return new DefaultAuthenticationEventPublisher(publisher);
}
}
- Springboot websecurityconfiguration: imports the default configuration of web security. If the developer specifies his own WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter or SecurityFilterChain, this will become invalid.
- SecurityDataConfiguration: it mainly provides a SecurityEvaluationContextExtension instance to provide data query for authenticated users through spiel.
- Websecurity enablerconfiguration: focus of analysis.
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = BeanIds.SPRING_SECURITY_FILTER_CHAIN)
@ConditionalOnClass(EnableWebSecurity.class)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = ConditionalOnWebApplication.Type.SERVLET)
@EnableWebSecurity // Introduce the key configuration class WebSecurityConfiguration
class WebSecurityEnablerConfiguration {
}
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Documented
@Import({ WebSecurityConfiguration.class, SpringWebMvcImportSelector.class, OAuth2ImportSelector.class,
HttpSecurityConfiguration.class })
@EnableGlobalAuthentication
@Configuration
public @interface EnableWebSecurity {
/**
* Controls debugging support for Spring Security. Default is false.
* @return if true, enables debug support with Spring Security
*/
boolean debug() default false;
}
- WebSecurityConfiguration: used to configure websecurity (focus analysis).
- Spring webmvcimportselector: judge whether spring MVC exists in the current environment. If so, introduce relevant configurations.
- OAuth2ImportSelector: judge whether OAuth2 exists in the current environment. If so, introduce relevant configurations.
- HttpSecurityConfiguration: exposes the configuration of HttpSecuritybean.
In addition, there is a @ EnableGlobalAuthentication annotation to enable global configuration:
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Documented
@Import(AuthenticationConfiguration.class) // Import configuration class AuthenticationConfiguration
@Configuration
public @interface EnableGlobalAuthentication {
}
WebSecurityConfiguration
The main purpose is to build the spring security filter chain proxy object FilterChainProxy. In WebSecurity configuration, the WebSecurity object will be built first, and then it will be used to build FilterChainProxy.
Let's first look at the attributes defined therein:
// By implementing the ImportAware interface, you can easily obtain the attribute value in @ EnableWebSecurity, such as debug
// By implementing the BeanClassLoaderAware interface, you can easily obtain the ClassLoader object
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class WebSecurityConfiguration implements ImportAware, BeanClassLoaderAware {
// WebSecurity object to build
private WebSecurity webSecurity;
private Boolean debugEnabled;
// All configuration classes are saved, that is, WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter object. A WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter object can create an HttpSecurity,
// Then a filter chain is constructed, and multiple filter chains can be constructed by multiple WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter objects
private List<SecurityConfigurer<Filter, WebSecurity>> webSecurityConfigurers;
private ClassLoader beanClassLoader;
// Object post processor. Note that this object is injected directly from the spring container
@Autowired(required = false)
private ObjectPostProcessor<Object> objectObjectPostProcessor;
}
setFilterChainProxySecurityConfigurer is mainly used to build a WebSecurity object and load all configuration class objects:
/**
* Set the instance of < securityconfigurer < filterchainproxy, websecuritybuilder > used to create web configuration.
*/
@Autowired(required = false)
public void setFilterChainProxySecurityConfigurer(ObjectPostProcessor<Object> objectPostProcessor,
@Value("#{@autowiredWebSecurityConfigurersIgnoreParents.getWebSecurityConfigurers()}") List<SecurityConfigurer<Filter, WebSecurity>> webSecurityConfigurers)
throws Exception {
// Go to the object post processor for processing, so that the WebSecurity object can be registered in the spring container
this.webSecurity = objectPostProcessor.postProcess(new WebSecurity(objectPostProcessor));
if (this.debugEnabled != null) {
this.webSecurity.debug(this.debugEnabled);
}
// Sort all configuration classes in the collection according to the @ Order annotation of each configuration class, because a configuration class corresponds to a filter chain,
// When the request arrives, which filter chain needs to be matched first, there must be a priority problem here
webSecurityConfigurers.sort(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE);
Integer previousOrder = null;
Object previousConfig = null;
for (SecurityConfigurer<Filter, WebSecurity> config : webSecurityConfigurers) {
Integer order = AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.lookupOrder(config);
if (previousOrder != null && previousOrder.equals(order)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@Order on WebSecurityConfigurers must be unique. Order of " + order
+ " was already used on " + previousConfig + ", so it cannot be used on " + config + " too.");
}
previousOrder = order;
previousConfig = config;
}
for (SecurityConfigurer<Filter, WebSecurity> webSecurityConfigurer : webSecurityConfigurers) {
// Add the configuration class to the configurers collection in the WebSecurity parent class. In the future, traverse the collection and call the init and configure methods of the configuration class respectively
// Complete the initialization of the configuration class
this.webSecurity.apply(webSecurityConfigurer);
}
this.webSecurityConfigurers = webSecurityConfigurers;
}
@Bean
public static AutowiredWebSecurityConfigurersIgnoreParents autowiredWebSecurityConfigurersIgnoreParents(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
return new AutowiredWebSecurityConfigurersIgnoreParents(beanFactory);
}
// Get all WebSecurityConfigurer instances in the spring container, that is, various configuration classes customized by developers that inherit from WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
public List<SecurityConfigurer<Filter, WebSecurity>> getWebSecurityConfigurers() {
List<SecurityConfigurer<Filter, WebSecurity>> webSecurityConfigurers = new ArrayList<>();
Map<String, WebSecurityConfigurer> beansOfType = this.beanFactory.getBeansOfType(WebSecurityConfigurer.class);
for (Entry<String, WebSecurityConfigurer> entry : beansOfType.entrySet()) {
webSecurityConfigurers.add(entry.getValue());
}
return webSecurityConfigurers;
}
// Create spring security filter chain
@Bean(name = AbstractSecurityWebApplicationInitializer.DEFAULT_FILTER_NAME)
public Filter springSecurityFilterChain() throws Exception {
boolean hasConfigurers = this.webSecurityConfigurers != null && !this.webSecurityConfigurers.isEmpty();
boolean hasFilterChain = !this.securityFilterChains.isEmpty();
// If there is no configuration class and no filter chain, an anonymous WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter object is created immediately and registered in the spring container
if (!hasConfigurers && !hasFilterChain) {
WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter adapter = this.objectObjectPostProcessor
.postProcess(new WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter() {
});
this.webSecurity.apply(adapter);
}
// securityFilterChains is configured by importing SpringBootWebSecurityConfiguration into SecurityAutoConfiguration
for (SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain : this.securityFilterChains) {
this.webSecurity.addSecurityFilterChainBuilder(() -> securityFilterChain);
for (Filter filter : securityFilterChain.getFilters()) {
if (filter instanceof FilterSecurityInterceptor) {
this.webSecurity.securityInterceptor((FilterSecurityInterceptor) filter);
break;
}
}
}
for (WebSecurityCustomizer customizer : this.webSecurityCustomizers) {
customizer.customize(this.webSecurity);
}
// Call the build method to build
return this.webSecurity.build();
}
After the build method of WebSecurity object is executed, all configuration classes, namely WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter instances, will be built first. In the init method of WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter, the construction of HttpSecurity will be completed. In the construction process of HttpSecurity, the construction of local AuthenticationManager objects and each specific filter will be completed.
AuthenticationConfiguration
It is mainly used for global configuration and provides a global authentication manager instance.
/**
* If the developer overrides the configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder) method in the custom configuration class,
* The global AuthenticationManager object here will not take effect, but will be rewritten in most cases
*/
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
// Import the configuration class ObjectPostProcessorConfiguration, which provides a basic object postprocessor, autowirebeanfactory objectpostprocessor,
// Used to register an object into the spring container
@Import(ObjectPostProcessorConfiguration.class)
public class AuthenticationConfiguration {
/**
* Define an AuthenticationManagerBuilder instance to build the global AuthenticationManager object,
* This process will find the AuthenticationEventPublisher instance from the spring container and set it to the AuthenticationManagerBuilder object
*/
@Bean
public AuthenticationManagerBuilder authenticationManagerBuilder(ObjectPostProcessor<Object> objectPostProcessor,
ApplicationContext context) {
LazyPasswordEncoder defaultPasswordEncoder = new LazyPasswordEncoder(context);
AuthenticationEventPublisher authenticationEventPublisher = getBeanOrNull(context,
AuthenticationEventPublisher.class);
DefaultPasswordEncoderAuthenticationManagerBuilder result = new DefaultPasswordEncoderAuthenticationManagerBuilder(
objectPostProcessor, defaultPasswordEncoder);
if (authenticationEventPublisher != null) {
result.authenticationEventPublisher(authenticationEventPublisher);
}
return result;
}
@Bean
public static GlobalAuthenticationConfigurerAdapter enableGlobalAuthenticationAutowiredConfigurer(
ApplicationContext context) {
return new EnableGlobalAuthenticationAutowiredConfigurer(context);
}
@Bean
public static InitializeUserDetailsBeanManagerConfigurer initializeUserDetailsBeanManagerConfigurer(
ApplicationContext context) {
return new InitializeUserDetailsBeanManagerConfigurer(context);
}
@Bean
public static InitializeAuthenticationProviderBeanManagerConfigurer initializeAuthenticationProviderBeanManagerConfigurer(
ApplicationContext context) {
return new InitializeAuthenticationProviderBeanManagerConfigurer(context);
}
// Build a concrete AuthenticationManager object
public AuthenticationManager getAuthenticationManager() throws Exception {
if (this.authenticationManagerInitialized) {
return this.authenticationManager;
}
AuthenticationManagerBuilder authBuilder = this.applicationContext.getBean(AuthenticationManagerBuilder.class);
// AuthenticationManagerDelegator is used to prevent infinite recursion when initializing AuthenticationManager
if (this.buildingAuthenticationManager.getAndSet(true)) {
return new AuthenticationManagerDelegator(authBuilder);
}
for (GlobalAuthenticationConfigurerAdapter config : this.globalAuthConfigurers) {
authBuilder.apply(config);
}
this.authenticationManager = authBuilder.build();
if (this.authenticationManager == null) {
this.authenticationManager = getAuthenticationManagerBean();
}
this.authenticationManagerInitialized = true;
return this.authenticationManager;
}
}
4.2ObjectPostProcessor usage
All filters are created by the corresponding configuration class. After successfully creating the filter, the configuration class will call the postProcess method of the parent class. In this method, it will traverse all ObjectPostProcessor objects stored in the collection maintained by the CompositeObjectPostProcessor object, and call its postProcess method to post process the object. By default, there is only one object in the collection maintained in the CompositeObjectPostProcessor object, that is, autowirebeanfactory ObjectPostProcessor. Calling its postProcess method can register the object in the spring container.
Developers can customize ObjectPostProcessor objects and add them to the collection maintained by CompositeObjectPostProcessor. At this time, when a filter is created successfully, it will be processed by two object postprocessors.
The typical usage of objectprocessor is dynamic configuration of custom objects.
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
// After the formLogin method is called, the configuration of FormLoginConfigurer is enabled to configure the UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter. After the formLogin method is executed,
// Call the withObjectPostProcessor method to process the UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter again
.formLogin()
.withObjectPostProcessor(new ObjectPostProcessor<UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter>() {
@Override
public <O extends UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter> O postProcess(O object) {
object.setUsernameParameter("name");
object.setPasswordParameter("passwd");
object.setAuthenticationSuccessHandler((request, response, authentication) -> {
response.getWriter().write("login success");
});
return object;
}
})
.and()
.csrf().disable();
}
}
4.3 multiple user-defined methods
There are two types of AuthenticationManager in spring security, one is global and the other is local. The local AuthenticationManager is configured by HttpSecurity, while the global AuthenticationManager can not be configured. The system will provide a global AuthenticationManager object by default, or it can be configured globally by overriding the configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder) method.
When user authentication is performed, it will first be verified through the local AuthenticationManager object. If the authentication fails, its parent, that is, the global object, will be called for authentication again.
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
/**
* User defined for local AuthenticationManager. It should be noted that the system will still automatically generate global users at this time.
* The user object automatically provided by the system is actually an InMemoryUserDetailsManager object registered in the spring container.
* Since the configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder) method is not overridden, this means that the global AuthenticationManager
* It is automatically generated through the AuthenticationConfiguration#getAuthenticationManager method. During the generation process,
* The corresponding UserDetailsService instance will be found from the spring container for configuration (the specific configuration is in InitializeUserDetailsManagerConfigurer)
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
InMemoryUserDetailsManager manager = new InMemoryUserDetailsManager();
manager.createUser(User.withUsername("javaboy").password("{noop}123").roles("admin").build());
http.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.permitAll()
.and()
.userDetailsService(manager)
.csrf().disable();
}
}
You can also configure the defined user to the global AuthenticationManager. Since the default global AuthenticationManager will find the UserDetailsService instance from the spring container during configuration, if you configure the user for the global AuthenticationManager, you only need to inject a UserDetailsService instance into the spring container.
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean
UserDetailsService us() {
InMemoryUserDetailsManager manager = new InMemoryUserDetailsManager();
manager.createUser(User.withUsername("A little rain in the south of the Yangtze River").password("{noop}123").roles("admin").build());
return manager;
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
InMemoryUserDetailsManager manager = new InMemoryUserDetailsManager();
manager.createUser(User.withUsername("javaboy").password("{noop}123").roles("admin").build());
http.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.permitAll()
.and()
.userDetailsService(manager)
.csrf().disable();
}
}
Of course, instead of using the default global AuthenticationManager object provided by spring security, developers can customize the global AuthenticationManager object by overriding the configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder) method:
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("javagirl").password("{noop}123").roles("admin");
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
InMemoryUserDetailsManager manager = new InMemoryUserDetailsManager();
manager.createUser(User.withUsername("javaboy").password("{noop}123").roles("admin").build());
http.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.permitAll()
.and()
.userDetailsService(manager)
.csrf().disable();
}
}
Once the configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder) method is overridden, the global AuthenticationManager object will no longer be built through the authenticationconfiguration #getauthenticationmanager method, but through the localConfigureAuthenticationBldr variable in the websecurity configureradapter, This variable is also a parameter of the overridden configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder) method.
It should be noted that once the configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder) method is overridden, the users used in the global AuthenticationManager object will be subject to the users defined in the configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder) method. At this time, if another UserDetailsService instance is injected into the spring container, the user defined in the instance will not take effect (because the AuthenticaitonConfiguration#getAuthenticationManager method has not been called).
4.4 define multiple filter chains
Multiple filter chains can exist in spring security at the same time. An instance of WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter can configure one filter chain.
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
UserDetailsService us() {
InMemoryUserDetailsManager manager = new InMemoryUserDetailsManager();
manager.createUser(User.withUsername("javaboy").password("{noop}123").roles("admin").build());
return manager;
}
@Configuration
@Order(1)
static class SecurityConfig01 extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
/**
* Since only configure(HttpSecurity http) is rewritten in SecurityConfig01, the UserDetailsService(us) registered in the spring container will be used as a local
* Authentication The user corresponding to the parent of. Therefore, if the login path is / bar/login, you can use bar/123 and javaboy/123 to log in
* @param http
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
InMemoryUserDetailsManager manager = new InMemoryUserDetailsManager();
manager.createUser(User.withUsername("bar").password("{noop}123").roles("admin").build());
http.antMatcher("/bar/**")
.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginProcessingUrl("/bar/login")
.successHandler((request, response, authentication) -> {
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
String s = new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(authentication);
response.getWriter().write(s);
})
.permitAll()
.and()
.csrf().disable()
.userDetailsService(manager);
}
}
@Configuration
@Order(2)
static class SecurityConfig02 extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
/**
* Since configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) is rewritten, the user corresponding to the parent of the local AuthenticationManager is defined in this method,
* At this time, the UserDetailsService(us) instance registered in the spring container is no longer valid for the / foo / * * filter chain. In other words, if the login path is / foo/login, you can use
* foo/123 And javagirl/123 instead of javaboy/123
* @param auth
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("javagirl").password("{noop}123").roles("admin");
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
InMemoryUserDetailsManager manager = new InMemoryUserDetailsManager();
manager.createUser(User.withUsername("foo").password("{noop}123").roles("admin").build());
http.antMatcher("/foo/**")
.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginProcessingUrl("/foo/login")
.successHandler((request, response, authentication) -> {
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
String s = new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(authentication);
response.getWriter().write(s);
})
.permitAll()
.and()
.csrf().disable()
.userDetailsService(manager);
}
}
}
It should be noted that if multiple filter chains are configured, the @ Order annotation needs to be used to mark the priority of different configurations (that is, the priority of different filter chains). The higher the number, the lower the priority. When the request arrives, it will be matched from high to low according to the priority of the filter chain.
4.5 static resource filtering
WebSecurity maintains a ignoredRequests variable, which records all requests that need to be ignored. These ignored requests will no longer pass through the spring security filter.
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
/**
* The ignored addresses will eventually be added to the ignoredRequests collection and finally presented in the form of filter chain (see WebSecurity#performBuild method for details). In other words, the rewritten method contains a total of five filter chains:
* configure(WebSecurity web)Four configured in and one configured in configure(HttpSecurity http) (i.e. / * *, all requests need authentication filtering)
* @param web
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void configure(WebSecurity web) throws Exception {
web.ignoring().antMatchers("/login.html", "/css/**", "/js/**", "/images/**");
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.and()
.csrf().disable();
}
}
4.6 login in JSON format
The extraction of login parameters is completed in the UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter filter. If you want to login in JSON format, you just need to define your own filter by imitating it, and then put the customized filter in the location of UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.
First, customize a LoginFilter that inherits from UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter:
public class LoginFilter extends UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter {
@Override
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException {
if (!"POST".equals(request.getMethod())) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException("Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
}
// Login in JSON format
if (MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE.equalsIgnoreCase(request.getContentType()) || MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8_VALUE.equalsIgnoreCase(request.getContentType())) {
Map userInfo = new HashMap<>();
try {
userInfo = new ObjectMapper().readValue(request.getInputStream(), Map.class);
String username = userInfo.get(getUsernameParameter()).toString();
String password = userInfo.get(getPasswordParameter()).toString();
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, password);
setDetails(request, authRequest);
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// If the login is not in JSON format, call the parent method to continue authentication
return super.attemptAuthentication(request, response);
}
}
After the definition is completed, add it to the spring security filter chain:
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("javaboy").password("{noop}123").roles("admin");
}
// Override the authenticationManagerBean method of the parent class to provide an AuthenticationManager instance and configure it to LoginFilter
@Override
@Bean
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManagerBean() throws Exception {
return super.authenticationManagerBean();
}
@Bean
LoginFilter loginFilter() throws Exception {
LoginFilter loginFilter = new LoginFilter();
loginFilter.setAuthenticationManager(authenticationManagerBean());
loginFilter.setAuthenticationSuccessHandler((request, response, authentication) -> {
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().write(new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(authentication));
});
return loginFilter;
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.and()
.csrf().disable();
// Add a custom filter at the location of UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter for processing. If it cannot be processed,
// Then call UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter through super for processing
http.addFilterAt(loginFilter(), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
}
}
There are two ways to obtain an AuthenticationManager instance:
- The first is obtained by overriding the authenticationManager method of the parent class.
- The second is obtained by overriding the authenticationManagerBean method of the parent class.
The difference between the two is that the first one obtains the global authentication manager instance, while the second one obtains the local instance. As a link in the filter chain, LoginFilter should obviously configure local instances, because if the global instance is configured to LoginFilter, the user corresponding to the local AuthenticationManager instance will become invalid.
/**
* Unable to log in with javagirl/123 because the global AuthenticationManager is specified in LoginFilter for authentication,
* So the local authentication manager fails
*/
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("javaboy").password("{noop}123").roles("admin");
}
@Override
@Bean
protected AuthenticationManager authenticationManager() throws Exception {
return super.authenticationManager();
}
@Bean
LoginFilter loginFilter() throws Exception {
LoginFilter loginFilter = new LoginFilter();
loginFilter.setAuthenticationManager(authenticationManager());
loginFilter.setAuthenticationSuccessHandler((request, response, authentication) -> {
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().write(new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(authentication));
});
return loginFilter;
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
InMemoryUserDetailsManager users = new InMemoryUserDetailsManager();
users.createUser(User.withUsername("javagirl").password("{noop}123").roles("admin").build());
http.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.and()
.csrf().disable()
.userDetailsService(users);
http.addFilterAt(loginFilter(), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
}
}
In practical application, if you need to configure an AuthenticationManager instance yourself, in most cases, it is obtained by overriding the authenticationManagerBean method.
4.7 add login verification code
public class LoginFilter extends UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter {
@Override
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException {
if (!"POST".equalsIgnoreCase(request.getMethod())) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException("Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
}
String kaptcha = request.getParameter("kaptcha");
String sessionKaptcha = (String) request.getSession().getAttribute("kaptcha");
if (StringUtils.hasLength(kaptcha) && StringUtils.hasLength(sessionKaptcha) && kaptcha.equalsIgnoreCase(sessionKaptcha)) {
return super.attemptAuthentication(request, response);
}
throw new AuthenticationServiceException("Verification code input error");
}
}
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("javaboy").password("{noop}123").roles("admin");
}
@Override
@Bean
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManagerBean() throws Exception {
return super.authenticationManagerBean();
}
@Bean
LoginFilter loginFilter() throws Exception {
LoginFilter loginFilter = new LoginFilter();
loginFilter.setFilterProcessesUrl("/doLogin"); // Equivalent to loginprocessing URL
loginFilter.setAuthenticationManager(authenticationManagerBean());
loginFilter.setAuthenticationSuccessHandler(new SimpleUrlAuthenticationSuccessHandler("/hello"));
loginFilter.setAuthenticationFailureHandler(new SimpleUrlAuthenticationFailureHandler("/mylogin.html"));
// loginFilter.setUsernameParameter("uname"); // If UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter is inherited, the relevant configuration items need to be configured on the LoginFilter instance
// loginFilter.setPasswordParameter("passwd");
return loginFilter;
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/vc.jpg").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/mylogin.html")
// . usernameParameter("uname") / / after inheriting UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter, the configuration in this place is invalid
// .passwordParameter("passwd")
.permitAll()
.and()
.csrf().disable();
http.addFilterAt(loginFilter(), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
}
}