IOC usage
IOC introduction:
IOC container is provided in spring
IOC(Inversion Of Control)
Object creation is left to the external container. This is control inversion
spring uses control inversion to realize the use of objects in different programs
The necessity of container existence is to manage objects
Object creation is left to the external container. This is control inversion
spring uses control inversion to realize the use of objects in different programs
Control inversion solves the problem of object processing and gives the object to the container for creation
Dependency injection (DI): dependency injection
The dependency problem between objects is dependency injection AOP - > di
Spring uses dependency injection to implement dependencies between objects
After the object is created, the relationship processing of the object is dependency injection
Regardless of the creation of objects, the dependencies between objects, the time of object creation and the number of objects created, you can configure the object information on the IOC container of spring
Use steps:
1. Integration dependency:
<!--spring Core dependency-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>4.1.7.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId>
<version>4.1.7.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>4.1.7.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-expression</artifactId>
<version>4.1.7.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--log4j-->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
2.Spring configuration file (Applicationcontext.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd">
3. Create entity class (User)
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
}
4. Submit the entity class to container management
<bean id="user" class="com.liangcheng.bean.User" scope="singleton">
5. Get the User object through the container
//Get the IOC container by reading the spring configuration file under the classpath path path
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Applicationcontext.xml");
User user =(User) applicationContext.getBean("user");
// Book book = (Book) applicationContext.getBean("book");
// book.setId(1);
System.out.println(user);
Spring instantiation and dependency injection of beans
xml based configuration form
set form
Entity class attribute construction set method
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
The configuration information in the container is as follows:
<bean id="user" class="com.liangcheng.bean.User" scope="singleton">
<property name="id" value="123" />
<property name="name" value="Zhang San"/>
</bean>
Dependency injection in set mode: assign values using the property tag
Parameter constructor mode
The user class must provide a parameter constructor
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
/**
* Parameterized constructor
*/
public User(Integer id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
The configuration of the container is as follows:
<!--Dependency injection: parameterized constructor-->
<bean id="user3" class="com.tulun.bean.User">
<!--
Injection properties
name Property: the property name of the given class
value Attribute: assign a value to the specified attribute name, and directly obtain String Value of type
ref Attribute: assign a value to the specified attribute. The specified object is a container managed object
-->
<constructor-arg name="id" value="1" />
<constructor-arg name="name" value="graph theory"/>
<constructor-arg name="book" ref="book"/>
</bean>
When dependency injection is completed through the parameterized constructor, the constructor Arg tag is used for attribute assignment
Non basic data type injection:
Include custom types
Whether a user-defined type is a set method or a parameterized construction, note that ref is used when assigning a value to a user-defined type
<bean id="user3" class="com.tulun.bean.User">
<constructor-arg name="book" ref="book"/>
</bean>
Injection Set types: array, Set, List, Map and other formal sets can be injected
The following tags exist in the processing set:
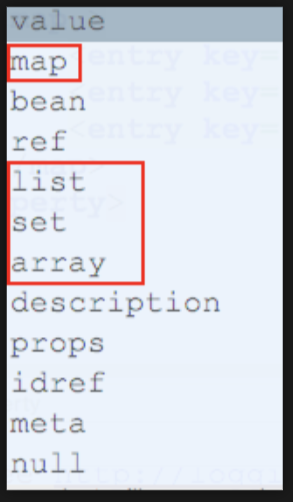
Take map type as an example
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Map<String ,String> map; //map type attribute
Configuration in container
<!--map Collection type-->
<bean id="user5" class="com.tulun.bean.User">
<!--Attribute injection-->
<property name="id" value="3"/>
<property name="name" value="Basic class 1"/>
<property name="map" >
<
<map >
<entry key="1" value="11"></entry>
<entry key="2" value="22"></entry>
<entry key="3" value="33"></entry>
</map>
</property>
</bean>
Annotation based form
Annotation based form is simpler and faster than xml
New constraints are introduced into the configuration file and annotation scanning is developed
Configure annotation scanning
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd">
<!--Enable scan annotation: classes under the specified package path will be scanned to the methods and properties of the class-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.liangcheng.bean"/>
<!--Scan only annotations for attributes in the class (not recommended)-->
<!--<context:annotation-config></context:annotation-config>-->
</beans>
Add annotation on entity class
@Component(value = "user")
public class User {
@Value("101")
private Integer id;
@Value("Li Si")
private String name;
@Autowired
private Book book;
public Book getBook(){
return book;
}
Class annotation
@Component: general annotation
@Repository: annotate DAO layer implementation classes
@Service: label the service layer and business logic layer
@Controller: label the implementation class of controller
The four annotations can be universal, have the same functions and can be interchanged. Different annotations are mainly used to distinguish the annotated classes from different business layers, so as to make the logic clearer
Attribute annotation
@Value("3") / / inject common type attributes
@Resource / / injected object type
@Autowired / / injects object types. Annotation is by type by default
Dependency injection is on the properties of the class
AOP implementation
Implementation of AOP based on Aspectj configuration
In spring, the use of AOP is realized through Aspectj third-party framework, which is a special aspect oriented programming framework implemented in java language
Aspectj is not part of the spring framework. It implements AOP operations with spring
1. Introduce AOP related dependencies
In addition to spring's basic dependencies, add AOP dependencies
<!--spring AOP relevant jar-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>4.1.7.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.7.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>aopalliance</groupId>
<artifactId>aopalliance</artifactId>
<version>1.0</version>
</dependency>
2. Introduce AOP related constraints
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
</beans>
3. Business realization
public class Student {
public void addStudent(){
System.out.println("Student.addStudent");
}
}
4. Enhanced class implementation
public class DIYLog {
public void writeLog(){
System.out.println("DIYLog.writeLog");
}
}
5. Configuration object
<!--Configuration object-->
<bean id="student" class="com.liangcheng.bean.Student"/>
<bean id="log" class="com.liangcheng.config.DIYLog"/>
6. Configure AOP operation
<!--to configure AOP operation-->
<aop:config>
<!--Configuring pointcuts: Using execution expression-->
<aop:pointcut id="pointcut1" expression="execution(* com.liangcheng.bean.Student.addStudent())"/>
<!--Configuration aspect: the process of applying notifications to methods-->
<aop:aspect ref="log">
<aop:after method="writeLog" pointcut-ref="pointcut1"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
Introduction to execution function
In the process of realizing notification, the method of pointcut can be defined through the execution function
Format: execution (< access modifier >? < return type > < method name > (< parameter >) < exception >)
Review: method format: access qualifier return type method name (parameter) exception
(1) execution(* com.tulun.bean.Book.show(...)) is a method in the table class
(2) execution(* com.tulun.bean.Book. (...)) table class all methods of a class in a package
(3) execution(. (...)) indicates all
Example:
-Match all classes public method execution(public *.*(..)) -Match all class methods under the specified package execution(* com.tulun.bean.*(..)) ((excluding sub packages) - execution(* com.tulun.bean..*(..)) (Including all classes under package and sub package) -Matches all methods of the specified class execution(* com.tulun.bean.Book.*(..)) -Matches all class methods that implement a specific interface execution(* com.tulun.bean.Book+.*(..)) -Match all com Starting method execution(* com*(..))
7. Use
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Springaop.xml");
Student studdnt =(Student) applicationContext.getBean("student");
studdnt.addStudent();
Note: features surrounding notifications
/**
* Surrounding the notification, there must be a parameter of type proceed ingjoinpoint, which calls processed to execute the real implementation
*/
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("Method");
//Implement the real implementation method
joinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("Method");
}
Various notification types are configured as follows:
<!--Advance notice: aop:before-->
<aop:before method="writeLog1" pointcut-ref="pointcut1"/>
<!--Post notification: aop:after-->
<aop:after method="writeLog1" pointcut-ref="pointcut1"/>
<!--Final notice: aop:after-returning-->
<aop:after-returning method="writeLog2" pointcut-ref="pointcut1"/>
<!--Exception notification: aop:after-throwing-->
<aop:after-throwing method="around" pointcut-ref="pointcut1"/>
<!--Surround notification: aop:around-->
<aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="pointcut1"/>
AOP is implemented based on annotation
The annotation form is only for those different from the xml configuration form
6. Open the annotation operation of AOP
<!--open AOP annotation-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
7. Add notes to the enhanced class
@Aspect
public class DIYLog {
@Before(value = "execution(* com.tulun.bean.Student.addStudent(..))")
@After(value = "execution(* com.tulun.bean.Student.addStudent(..))") //Post notification
@AfterReturning //Final notice
@AfterThrowing //Exception notification
public void writeLog(){
System.out.println("DIYLog.writeLog");
}
@Around(value = "execution(* com.liangcheng.bean.Student.addStudent())")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable{
System.out.println("Before execution");
joinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("After execution");
}
}
be careful:
The annotation of AOP related operations must be on the enhanced classes and methods
Add annotation @ Aspect on enhanced class
In the enhancement class, different annotations are added to the response methods according to different enhancement types
@Around(value = "execution(* com.tulun.bean.Student.addStudent(..))") //Around Advice @Before(value = "execution(* com.tulun.bean.Student.addStudent(..))")//Before advice @After(value = "execution(* com.tulun.bean.Student.addStudent(..))") //Post notification @AfterReturning //Final notice @AfterThrowing //Exception notification