JdbcTemplate
Jdbctemplate (concept and preparation)
1. What is a JdbcTemplate?
The Spring framework encapsulates JDBC and uses JdbcTemplate to facilitate database operation.
2. Preparation
(1) Import related jar packages
(2) Configure the database connection pool in the Spring configuration file
<!-- Database connection pool -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///user_db" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="123456" />
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
</bean>
(3) Configure the JdbcTemplate object and inject DataSource
<!--jdbcTemplate-->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<!--injection dataSource-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
(4) Create a service class, create a dao class, and inject a JDBC template object into dao
Profile open component scan
Service
@Service
public class BookService {
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
}
Dao
@Repository
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
}
JdbcTemplate operation database (add)
1. Create an entity class corresponding to the database
package com.yxm.entity;
public class Book {
private String userId;
private String username;
private String ustatus;
public String getUserId() {
return userId;
}
public void setUserId(String userId) {
this.userId = userId;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getUstatus() {
return ustatus;
}
public void setUstatus(String ustatus) {
this.ustatus = ustatus;
}
}
2. Write Service and Dao
(1) Add database in dao
(2) Call the update method in the JdbcTemplate object to implement the add operation
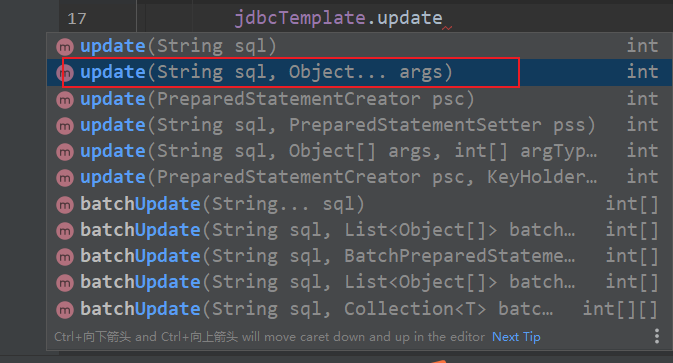
There are two parameters
⚫ First parameter: sql statement
⚫ The second parameter: variable parameter, which sets the sql statement value
@Repository
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Override
public void add(Book book) {
String sql="insert into t_book values(?,?,?)";
int update = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, book.getUserId(), book.getUsername(), book.getUstatus());
System.out.println(update);
}
}
3. Testing
@Test
public void testJdbcTemplate(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
BookService bookService = context.getBean("bookService", BookService.class);
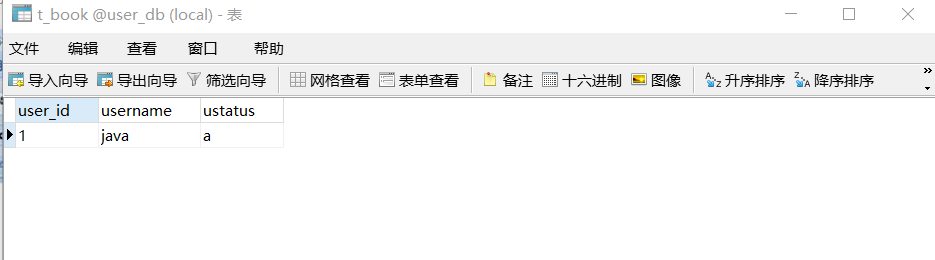
Book book = new Book();
book.setUserId("1");
book.setUsername("java");
book.setUstatus("a");
bookService.addBook(book);
}
JdbcTemplate operation database (modification and deletion)
modify
@Override
public void updateBook(Book book) {
String sql="update t_book set username=?,ustatus=? where user_id=?";
int update = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, book.getUsername(), book.getUstatus(), book.getUserId());
System.out.println(update);
}
Test class
@Test
public void testJdbcTemplate2(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
BookService bookService = context.getBean("bookService", BookService.class);
Book book = new Book();
book.setUserId("1");
book.setUsername("js");
book.setUstatus("b");
bookService.updateBook(book);
}
delete
@Override
public void deleteBook(String userId) {
String sql="delete from t_book where user_id=?";
int delete = jdbcTemplate.update(sql,userId);
System.out.println(delete);
}
Test class
@Test
public void testJdbcTemplate3(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
BookService bookService = context.getBean("bookService", BookService.class);
bookService.deleteBook("1");
}
JdbcTemplate operates the database (query returns a value)
1. How many records are there in the query table? A certain value is returned
2. Use JdbcTemplate to query and return a value code
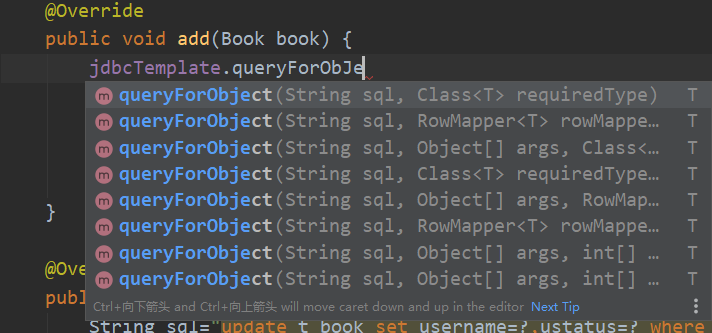
There are two parameters
⚫ First parameter: sql statement
⚫ Second parameter: return type Class
@Override
public int seleteCount() {
String sql="select count(*) from t_book";
Integer count = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, Integer.class);
return count;
}
Test class
@Test
public void testJdbcTemplate4(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
BookService bookService = context.getBean("bookService", BookService.class);
int i = bookService.seleteCount();
System.out.println(i);
}
JdbcTemplate operation database (query return object)
1. Scenario: query book details
2.JdbcTemplate implements the query return object
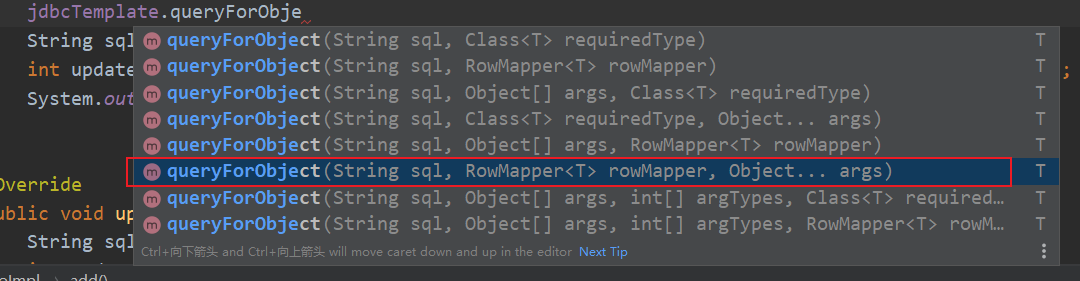
⚫ There are three parameters
⚫ First parameter: sql statement
⚫ The second parameter: RowMapper is an interface. For returning different types of data, use the implementation classes in this interface to complete data encapsulation
⚫ The third parameter: sql statement value
@Override
public Book findBookInfo(String userId) {
String sql="select * from t_book where user_id=?";
Book book = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Book>(Book.class), userId);
return book;
}
Test class
@Test
public void testJdbcTemplate5(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
BookService bookService = context.getBean("bookService", BookService.class);
Book book= bookService.findBookInfo("1");
System.out.println(book);
}
JdbcTemplate operation database (query return object)
1. Scenario: query book details
2. The jdbctemplate implements the query return set
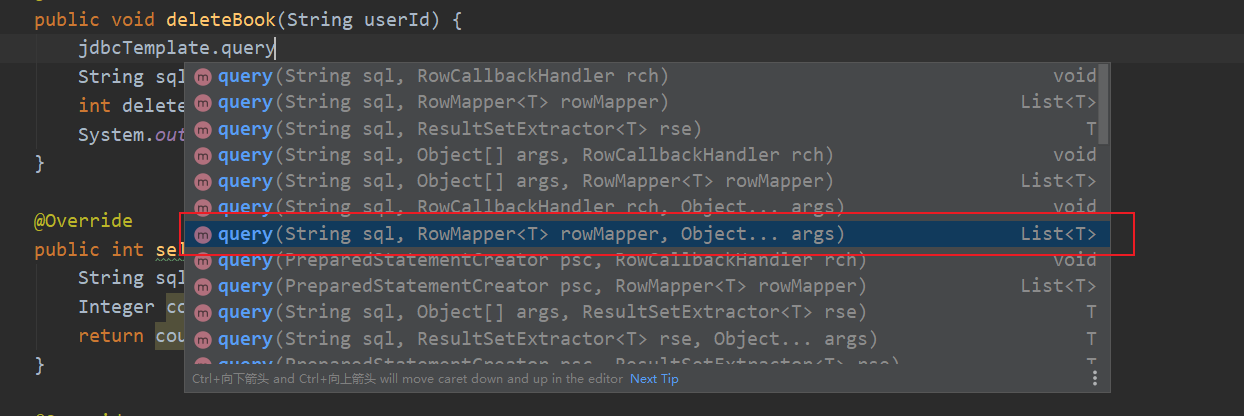
⚫ There are three parameters
⚫ First parameter: sql statement
⚫ The second parameter: RowMapper is an interface. For returning different types of data, use the implementation classes in this interface to complete data encapsulation
⚫ The third parameter: sql statement value
@Override
public List<Book> findAllBook() {
String sql="select * from t_book";
List<Book> books= jdbcTemplate.query(sql,new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Book>(Book.class));
return books;
}
Test class
@Test
public void testJdbcTemplate6(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
BookService bookService = context.getBean("bookService", BookService.class);
List<Book> books= bookService.findAllBook();
System.out.println(books);
}
JdbcTemplate operation database (batch operation)
1. Batch operation: multiple records in the operation table
2. JdbcTemplate implements batch addition
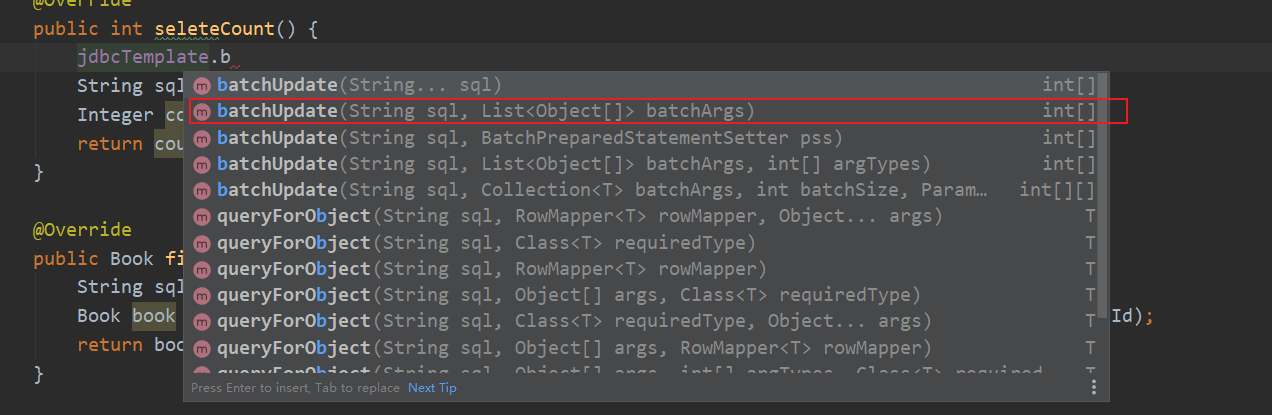
⚫ There are two parameters
⚫ First parameter: sql statement
⚫ The second parameter: List set, adding multiple record data
Batch add
@Override
public void batchAddBook(List<Object[]> batchArgs) {
String sql="insert into t_book values(?,?,?)";
int[] ints = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, batchArgs);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ints));
}
Test class
@Test
public void testJdbcTemplate7(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
BookService bookService = context.getBean("bookService", BookService.class);
List<Object[]> batchArgs=new ArrayList<>();
Object[] o1={"3","c++","a"};
Object[] o2={"4","mysql","b"};
Object[] o3={"5","vb","c"};
batchArgs.add(o1);
batchArgs.add(o2);
batchArgs.add(o3);
bookService.batchAddBook(batchArgs);
}
Batch modification
@Override
public void batchUpdateBook(List<Object[]> batchArgs) {
String sql = "update t_book set username=?,ustatus=? where user_id=?";
int[] ints = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, batchArgs);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ints));
}
Test class
@Test
public void testJdbcTemplate8(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
BookService bookService = context.getBean("bookService", BookService.class);
List<Object[]> batchArgs=new ArrayList<>();
Object[] o1 = {"java0909","a3","3"};
Object[] o2 = {"c++1010","b4","4"};
Object[] o3 = {"MySQL1111","c5","5"};
batchArgs.add(o1);
batchArgs.add(o2);
batchArgs.add(o3);
bookService.batchUpdate(batchArgs);
}
Batch delete
@Override
public void batchDeleteBook(List<Object[]> batchArgs) {
String sql = "delete from t_book where user_id=?";
int[] ints = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, batchArgs);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ints));
}
Test class
@Test
public void testJdbcTemplate9(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
BookService bookService = context.getBean("bookService", BookService.class);
List<Object[]> batchArgs=new ArrayList<>();
Object[] o1 = {"3"};
Object[] o2 = {"4"};
batchArgs.add(o1);
batchArgs.add(o2);
bookService.batchDelete(batchArgs);
}
Transaction operation
Transaction operation (transaction concept)
Transaction is the most basic unit of database operation. Logically, a group of operations either succeed. If one fails, all operations fail
Four characteristics of transaction (ACID)
(1) Atomicity
(2) Consistency
(3) Isolation
(4) Persistence
Transaction operation (build transaction operation environment)
1. Create database tables and add records
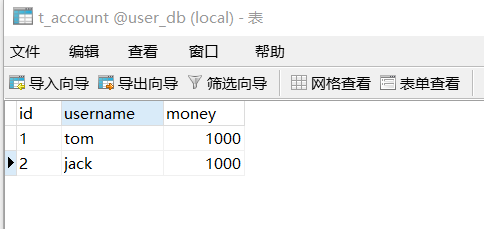
2. Create a service, build a dao, and complete the object creation and injection relationship
(1) service is injected into dao, JdbcTemplate is injected into dao, and DataSource is injected into JdbcTemplate
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
}
@Repository
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
}
@Override
public void reduceMoney() {
String sql="update t_account set money=money-? where username=?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,100,"tom");
}
@Override
public void addMoney() {
String sql="update t_account set money=money+? where username=?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,100,"jack");
}
public void accountMoney(){
userDao.reduceMoney();
userDao.addMoney();
}
Test class
@Test
public void testJdbcTemplate(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
UserService userService = context.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
userService.accountMoney();
}
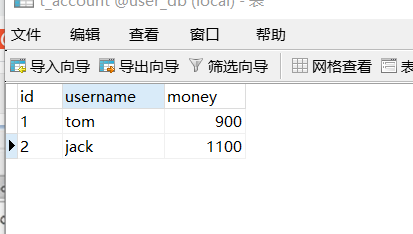
3. If the above code is executed normally, there is no problem, but if an exception occurs during code execution, there is a problem
public void accountMoney(){
userDao.reduceMoney();
//Simulation anomaly
int i=1/0;
userDao.addMoney();
}
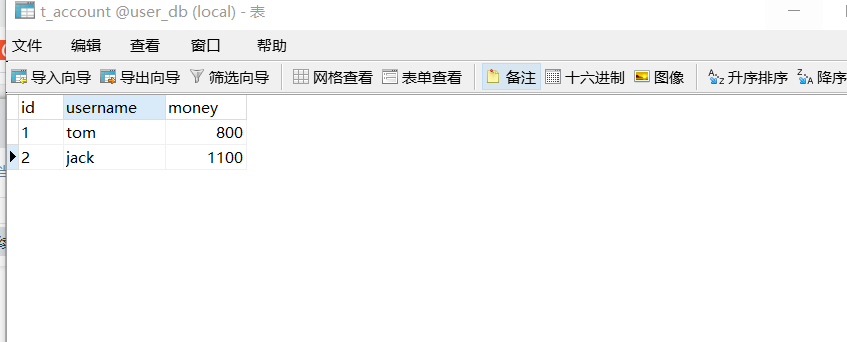
tom is less than 100, jack is not more than 100. How to use transaction resolution
4. Operation process of joining transaction
Implemented by code
public void accountMoney(){
try{
//Open transaction
userDao.reduceMoney();
//Simulation anomaly
int i=1/0;
userDao.addMoney();
}catch (Exception e){
//Transaction rollback
}
}
Transaction operation (Introduction to Spring transaction management)
1. Transactions are added to the Service layer (business logic layer) in the three-tier structure of Java EE
2. Transaction management operations in Spring
There are two ways: programmatic transaction management and declarative transaction management (using)
3. Declarative transaction management
(1) Annotation based approach (use)
(2) xml based configuration file mode
4. For declarative transaction management in Spring, the underlying layer uses AOP principle
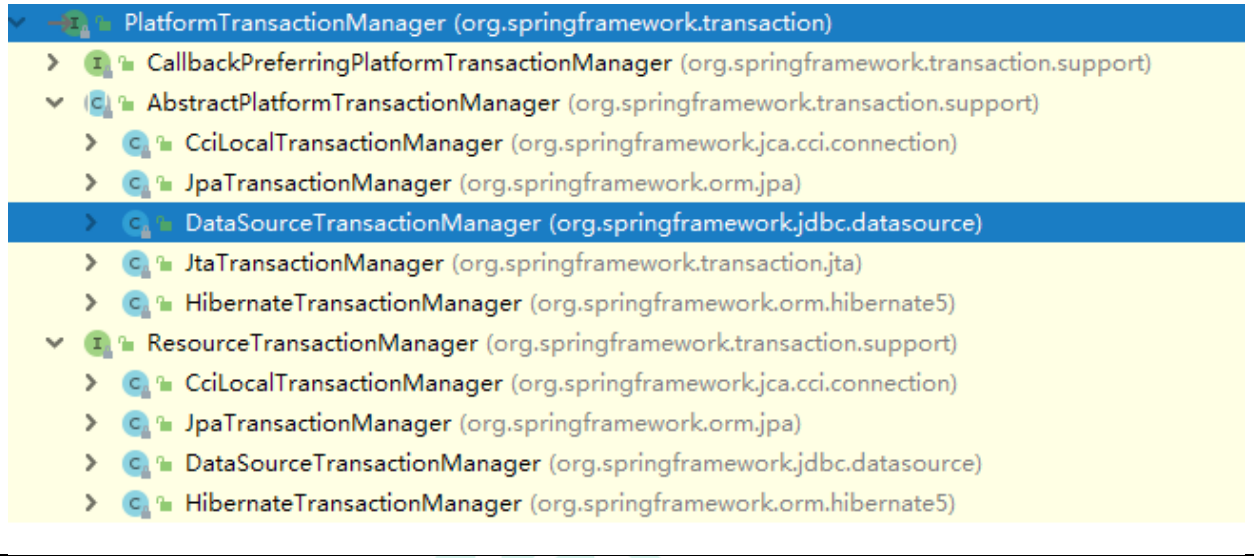
5. Spring Transaction Management API
(1) An interface is provided to represent the transaction manager. This interface provides different implementation classes for different frameworks
Transaction operations (annotated declarative transaction management)
1. Configure the transaction manager in the spring configuration file
<!--Create transaction manager-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
2. In the spring configuration file, open the transaction annotation
(1) Introducing the namespace tx into the spring configuration file
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
(2) Open transaction annotation
<!--Open transaction annotation-->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"></tx:annotation-driven>
3. Add transaction annotations on the service class (or on the methods in the service class)
(1) @ Transactional, this annotation can be added to classes or methods
(2) If you add this annotation to the class, all the methods in the class will add transactions
(3) If you add this annotation to the method, add transactions for the method
@Service
@Transactional
public class UserService {
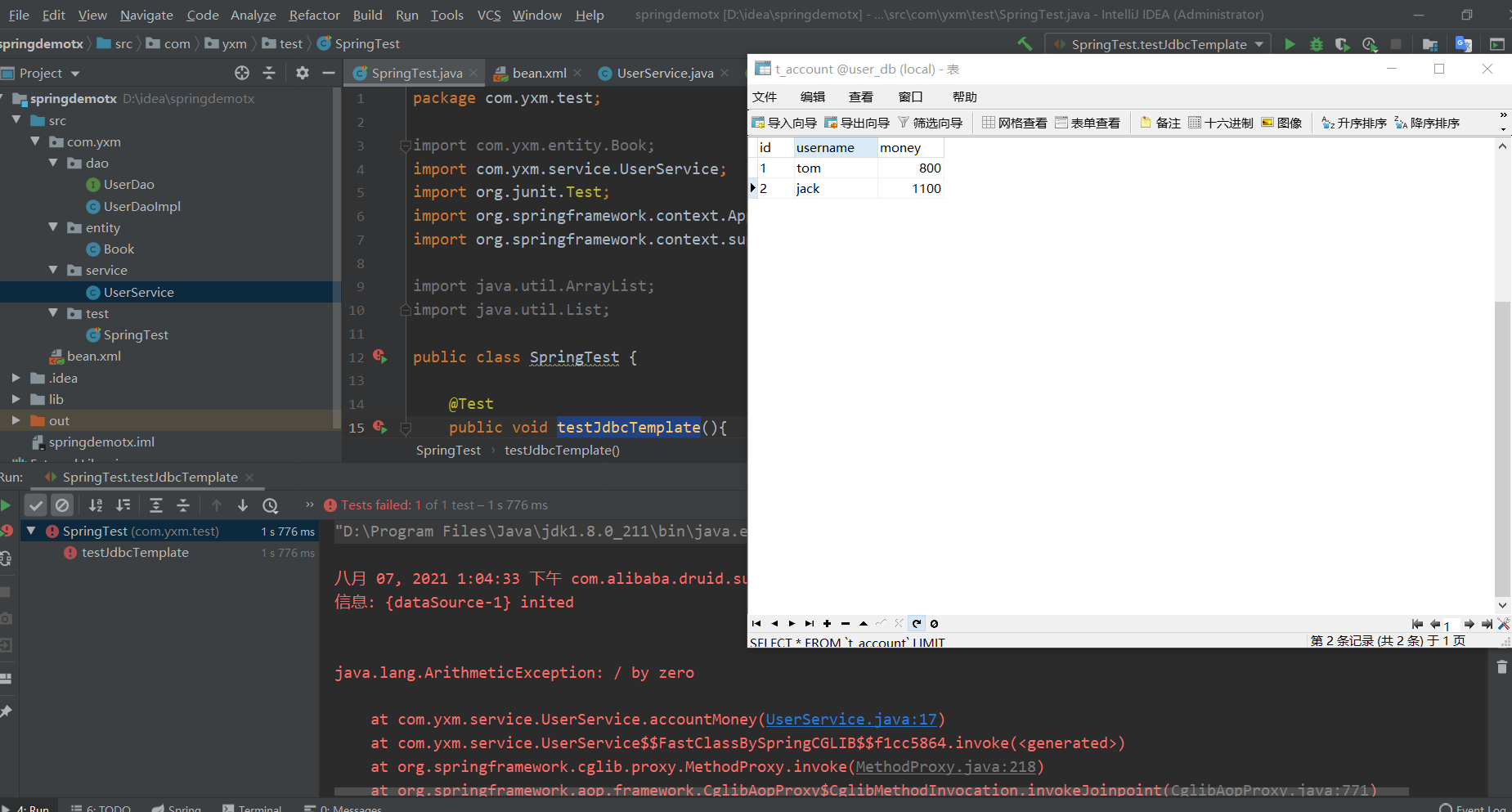
You can see that the simulated exception data will not change after adding this annotation
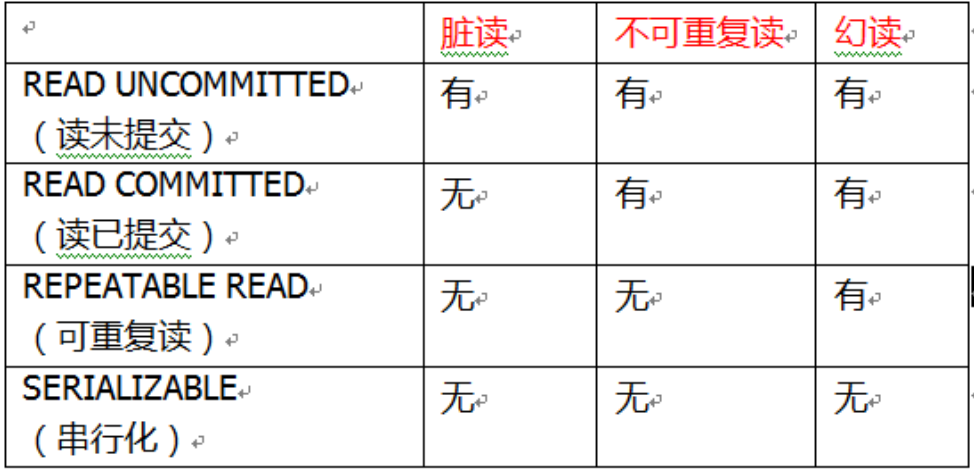
Propagation behavior of transactions
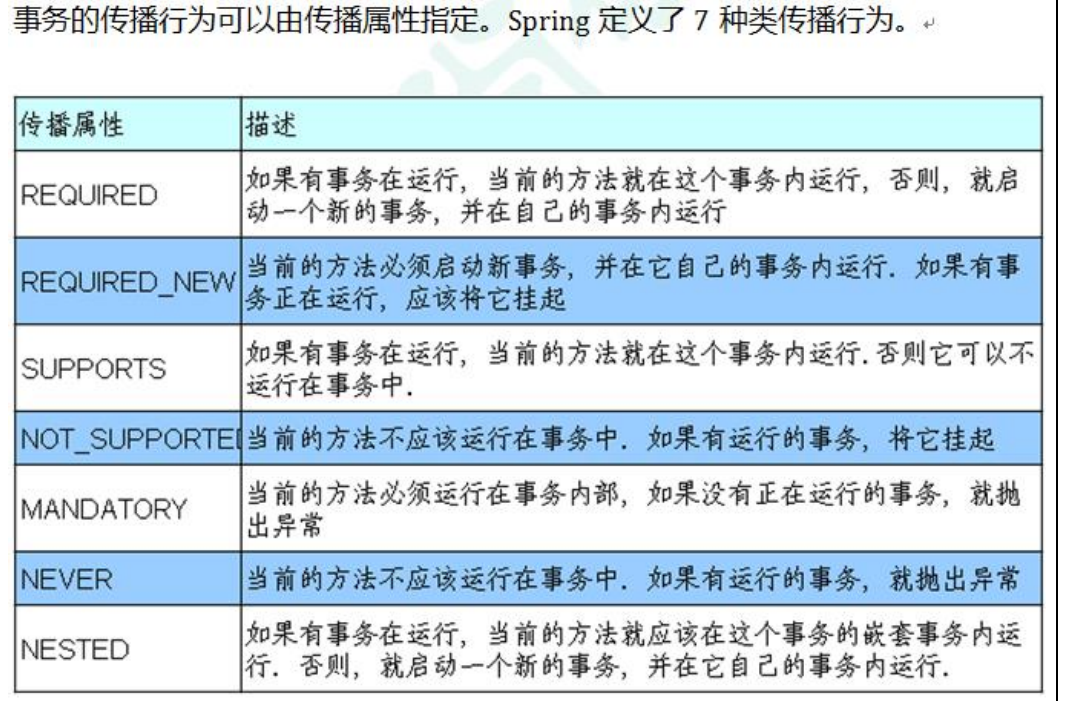
Transaction isolation level