Data access, startup principle analysis, custom starter
1. SpringBoot and Data Access
1,JDBC
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency>
spring: datasource: username: root password: 123456 url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.15.22:3306/jdbc driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
Effect:
The default is to use org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource as the data source.
The configuration of data source is in DataSource Properties.
Principle of automatic configuration:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc:
1. Refer to DataSource Configuration, create data source according to configuration, default use Tomcat connection pool; use spring.datasource.type to specify custom data source type;
2. SpringBoot can be supported by default.
org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource,HikariDataSource,BasicDataSource,
3. Custom Data Source Type
/** * Generic DataSource configuration. */ @ConditionalOnMissingBean(DataSource.class) @ConditionalOnProperty(name = "spring.datasource.type") static class Generic { @Bean public DataSource dataSource(DataSourceProperties properties) { //Create a data source using DataSource Builder, create a response type data source using reflection, and bind related properties return properties.initializeDataSourceBuilder().build(); } }
4,DataSourceInitializer: ApplicationListener;
Role:
Run SchemaScripts (); run table building statements;
Run DataScripts (); run sql statements that insert data;
By default, you only need to name the file as:
schema-*.sql,data-*.sql
Default rules: schema.sql, schema-all.sql;
have access to
schema:
- classpath:department.sql
Designated location
5. Operation database: automatically configure JdbcTemplate operation database
2. Integrating Druid Data Sources
Import druid data source @Configuration public class DruidConfig { @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource") @Bean public DataSource druid(){ return new DruidDataSource(); } //Configuring Druid Monitoring //1. Configuring a Servlet for the Management Background @Bean public ServletRegistrationBean statViewServlet(){ ServletRegistrationBean bean = new ServletRegistrationBean(new StatViewServlet(), "/druid/*"); Map<String,String> initParams = new HashMap<>(); initParams.put("loginUsername","admin"); initParams.put("loginPassword","123456"); initParams.put("allow","");//The default is to allow all access. initParams.put("deny","192.168.15.21"); bean.setInitParameters(initParams); return bean; } //2,Configure one web Monitored filter @Bean public FilterRegistrationBean webStatFilter(){ FilterRegistrationBean bean = new FilterRegistrationBean(); bean.setFilter(new WebStatFilter()); Map<String,String> initParams = new HashMap<>(); initParams.put("exclusions","*.js,*.css,/druid/*"); bean.setInitParameters(initParams); bean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList("/*")); return bean; } }
3. Integrating MyBatis
<dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.3.1</version> </dependency>
Steps:
1) Configuring data source related properties (see Druid in the previous section)
2) Building tables for databases
3) Creating JavaBean s
a. Annotations
//Specify that this is a mapper that operates on the database @Mapper public interface DepartmentMapper { @Select("select * from department where id=#{id}") public Department getDeptById(Integer id); @Delete("delete from department where id=#{id}") public int deleteDeptById(Integer id); @Options(useGeneratedKeys = true,keyProperty = "id") @Insert("insert into department(departmentName) values(#{departmentName})") public int insertDept(Department department); @Update("update department set departmentName=#{departmentName} where id=#{id}") public int updateDept(Department department); }
Question:
Customize the configuration rules of MyBatis; add a Configuration Customizer to the container;
@org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration public class MyBatisConfig { @Bean public ConfigurationCustomizer configurationCustomizer(){ return new ConfigurationCustomizer(){ @Override public void customize(Configuration configuration) { configuration.setMapUnderscoreToCamelCase(true); } }; } }
Use MapperScan Scan all in batches Mapper Interface; @MapperScan(value = "com.atguigu.springboot.mapper") @SpringBootApplication public class SpringBoot06DataMybatisApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringBoot06DataMybatisApplication.class, args); } }
b. Configuration file version
mybatis: config-location: classpath:mybatis/mybatis-config.xml Specify the location of the global configuration file mapper-locations: classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xml Appoint sql Location of mapping file
More use of reference
http://www.mybatis.org/spring-boot-starter/mybatis-spring-boot-autoconfigure/
4. Integrating Spring Data JPA
a. Introduction to Spring Data
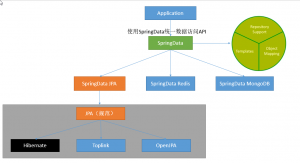
b. Integrating Spring Data JPA
JPA:ORM(Object Relational Mapping);
1. Write an entity class (bean) and data table for mapping, and configure the mapping relationship.
//Configuring mapping relationships with JPA annotations @Entity //Tell JPA that this is an entity class (a class mapped to a data table) @Table(name = "tbl_user") //@ Table specifies which data table to correspond to; if the default table name is omitted, it is user; public class User { @Id //This is a primary key. @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)//Self increasing primary key private Integer id; @Column(name = "last_name",length = 50) //This is a column corresponding to the data table. private String lastName; @Column //Omitting the default column name is the attribute name private String email;
2. Write a Dao interface to manipulate the data table corresponding to the entity class.
//Inheriting JpaRepository to complete database operations public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User,Integer> { }
3. Basic configuration of JpaProperties
spring: jpa: hibernate: # Update or create data table structures ddl-auto: update # Console Displays SQL show-sql: true
II. Start-up Configuration Principle
Several Important Event Callback Mechanisms
Configuration in META-INF/spring.factories
ApplicationContextInitializer
SpringApplicationRunListener
Just put it in an ioc container
ApplicationRunner
CommandLineRunner
Start-up process:
1. Creating Spring Application Objects
initialize(sources); private void initialize(Object[] sources) { //Save the master configuration class if (sources != null && sources.length > 0) { this.sources.addAll(Arrays.asList(sources)); } //Judging whether a web application is currently in use this.webEnvironment = deduceWebEnvironment(); //Find all ApplicationContextInitializer s for the META-INF/spring.factories configuration from the class path; then save them setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances( ApplicationContextInitializer.class)); //Find all Application Listeners for ETA-INF/spring.factories configuration from the class path setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class)); //Find the main configuration class with main method from multiple configuration classes this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass(); }
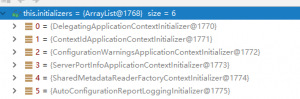
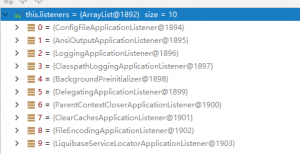
2. Running run Method
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) { StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch(); stopWatch.start(); ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null; FailureAnalyzers analyzers = null; configureHeadlessProperty(); //Get Spring Application RunListeners; META-INF/spring.factories from the classpath SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args); //Callback all methods to get Spring Application RunListener. start () listeners.starting(); try { //Encapsulating command line parameters ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments( args); //Preparation environment ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments); //Callback Spring Application RunListener. environment Prepared () when the environment is created; indicates that the environment is ready to complete Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment); //Create an Application Context; decide whether to create an ioc for the web or a normal ioc context = createApplicationContext(); analyzers = new FailureAnalyzers(context); //Prepare the context environment; save the environment in ioc; and apply Initializers (); //applyInitializers(): The initialize method for all ApplicationContextInitializer s saved before the callback //Callback the contextPrepared() of all Spring Application RunListeners; // prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner); //Callback the contextLoaded () of all Spring Application RunListeners after the prepareContext runs; //s refresh container; ioc container initialization (embedded Tomcat will be created if it is a web application); Spring annotation version //Scanning, creating, loading all components; (Configuration classes, components, automatic configuration) refreshContext(context); //Retrieve all Application Runners and CommandLineRunner s from the ioc container for callbacks //Application Runner calls back first, CommandLine Runner calls back again afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments); //All Spring Application RunListener callback finished methods listeners.finished(context, null); stopWatch.stop(); if (this.logStartupInfo) { new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass) .logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch); } //The entire SpringBoot application returns to the booted ioc container after it has been started. return context; } catch (Throwable ex) { handleRunFailure(context, listeners, analyzers, ex); throw new IllegalStateException(ex); } }
3. Event monitoring mechanism
Configuration in META-INF/spring.factories
ApplicationContextInitializer
public class HelloApplicationContextInitializer implements ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext> { @Override public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) { System.out.println("ApplicationContextInitializer...initialize..."+applicationContext); } }
SpringApplicationRunListener
public class HelloSpringApplicationRunListener implements SpringApplicationRunListener { //A necessary constructor public HelloSpringApplicationRunListener(SpringApplication application, String[] args){ } @Override public void starting() { System.out.println("SpringApplicationRunListener...starting..."); } @Override public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) { Object o = environment.getSystemProperties().get("os.name"); System.out.println("SpringApplicationRunListener...environmentPrepared.."+o); } @Override public void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { System.out.println("SpringApplicationRunListener...contextPrepared..."); } @Override public void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { System.out.println("SpringApplicationRunListener...contextLoaded..."); } @Override public void finished(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) { System.out.println("SpringApplicationRunListener...finished..."); } }
Configuration (META-INF/spring.factories)
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\ com.atguigu.springboot.listener.HelloApplicationContextInitializer org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=\ com.atguigu.springboot.listener.HelloSpringApplicationRunListener
Just put it in an ioc container
ApplicationRunner
@Component public class HelloApplicationRunner implements ApplicationRunner { @Override public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception { System.out.println("ApplicationRunner...run...."); } }
CommandLineRunner
@Component public class HelloCommandLineRunner implements CommandLineRunner { @Override public void run(String... args) throws Exception { System.out.println("CommandLineRunner...run..."+ Arrays.asList(args)); } }
3. Custom starter
starter:
1. What dependencies do you need to use in this scenario?
2. How to write automatic configuration
@ Configuration // / Specifies that this class is a configuration class @ Conditional OnXXX // / Automatically configure classes to take effect if specified conditions hold @ AutoConfigureAfter//Specify the order of automatic configuration classes @ Bean // Add Components to Containers @ Configuration Properties binds related configurations with related xxxProperties classes @ Enable Configuration Properties // Enable xxProperties to be added to the container Autoconfiguration classes need to be loadable Automated configuration classes loaded on startup will be required to be configured in META-INF/spring.factories org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\
3. Mode:
The starter is only used for dependency import.
Write an automatic configuration module.
Starters rely on automatic configuration; others just need to introduce starter s.
mybatis-spring-boot-starter; custom starter name-spring-boot-starter
Steps:
1) Starter module
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.atguigu.starter</groupId> <artifactId>atguigu-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <!--starter--> <dependencies> <!--Introducing Automatic Configuration Module--> <dependency> <groupId>com.atguigu.starter</groupId> <artifactId>atguigu-spring-boot-starter-autoconfigurer</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
2) Automatic Configuration Module
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.atguigu.starter</groupId> <artifactId>atguigu-spring-boot-starter-autoconfigurer</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <name>atguigu-spring-boot-starter-autoconfigurer</name> <description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>1.5.10.RELEASE</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <!--Introduce spring-boot-starter;All starter Basic configuration--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
package com.atguigu.starter; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "atguigu.hello") public class HelloProperties { private String prefix; private String suffix; public String getPrefix() { return prefix; } public void setPrefix(String prefix) { this.prefix = prefix; } public String getSuffix() { return suffix; } public void setSuffix(String suffix) { this.suffix = suffix; } }
package com.atguigu.starter; public class HelloService { HelloProperties helloProperties; public HelloProperties getHelloProperties() { return helloProperties; } public void setHelloProperties(HelloProperties helloProperties) { this.helloProperties = helloProperties; } public String sayHellAtguigu(String name){ return helloProperties.getPrefix()+"-" +name + helloProperties.getSuffix(); } }
package com.atguigu.starter; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnWebApplication; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration @ConditionalOnWebApplication //web applications only take effect @EnableConfigurationProperties(HelloProperties.class) public class HelloServiceAutoConfiguration { @Autowired HelloProperties helloProperties; @Bean public HelloService helloService(){ HelloService service = new HelloService(); service.setHelloProperties(helloProperties); return service; } }