1, Introduction to SpringBoot
Baidu Encyclopedia:
Spring Boot is a new framework provided by pivot team. It is designed to simplify the initial construction and development process of new spring applications. The framework uses a specific way to configure, so that developers no longer need to define a templated configuration. In this way, Spring Boot is committed to becoming a leader in the booming field of rapid application development.
SpringBoot benefits
- Simplify dependency
- Simplified configuration
- Simplify deployment
- Simplify monitoring
2, Build SpringBoot project
2.1 automatic generation through official website
https://start.spring.io/ Fast generation
2.2 IDEA online template generation
The SpringBoot project is automatically generated through the online template provided by IDEA
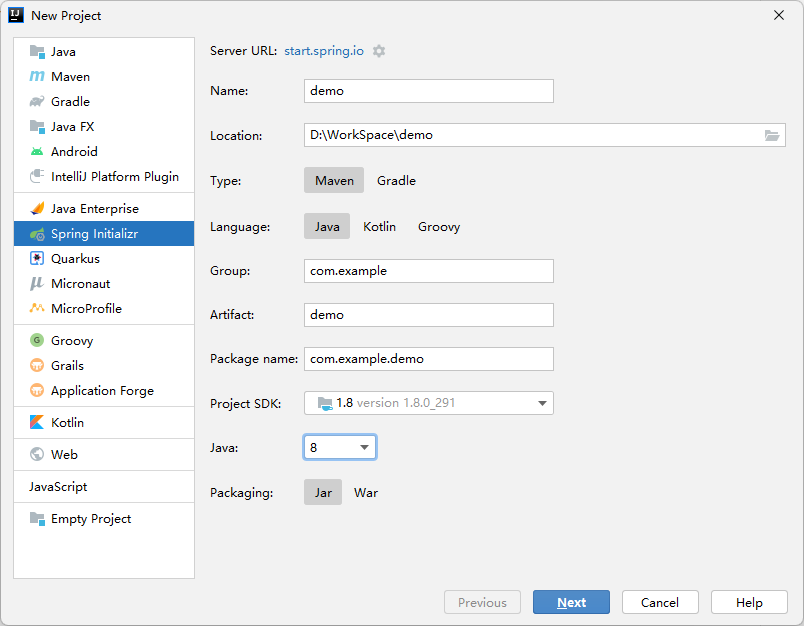
2.3 build through maven project
The second point is to build the project automatically, which is to build the project manually. Take a simple web application as an example
-
Add dependency
<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.1.15.RELEASE</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies> -
Add initiator
package com.example.springbootdemo; import org.springframework.boot.Banner; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @SpringBootApplication public class SpringBootDemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { //First startup mode //SpringApplication.run(SpringBootDemoApplication.class, args); //Second startup mode SpringApplication sa = new SpringApplication(SpringBootDemoApplication.class); //start-up sa.run(args); } }
3, Common configurations in spring boot
3.1 entry class and related notes
This is the startup class of the program. The essence of the main method is to complete the initialization of a SpringIoC container
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Initialization of Spring IoC container
ApplicationContext ac = SpringApplication.run(GpSpringbootDemo02Application.class, args);
}
}
@The SpringBootApplication annotation is a composite annotation. The specific content is
@Target({ElementType.TYPE}) // Where can annotations be written
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) // The scope of this annotation RESOURCES CLASS RUNTIME
@Documented // The annotation is extracted by the API
@Inherited // inheritable
// The above four are meta annotations provided in Java
@SpringBootConfiguration // It is essentially a Configuration annotation
@EnableAutoConfiguration // Annotation of automatic assembly
@ComponentScan( // Scanning will automatically scan the peer package (com.gupaoedu) of the class where @ SpringBootApplication is located and the beans in the sub package. In general, we recommend that the entry class be placed under the combined package of groupid + artfcatid
excludeFilters = {@Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {TypeExcludeFilter.class}
), @Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class}
)}
)
3.2 Banner
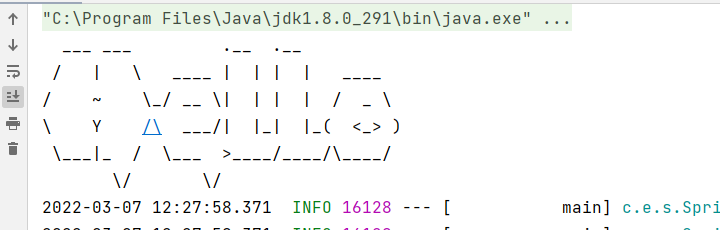
When the SpringBoot project starts, the following content will appear

This is the banner started by the program. This part can be designed freely. Just create a banner in the resources folder Txt. You can customize the banner by writing the banner icon to be displayed in the file
3.2.1 custom Banner
Custom Banner URL:
[Text to ASCII Art Generator (TAAG) (patorjk.com)](http://patorjk.com/software/taag/#p=display&f=Graffiti&t=Type Something )
For example, enter Hello in the URL
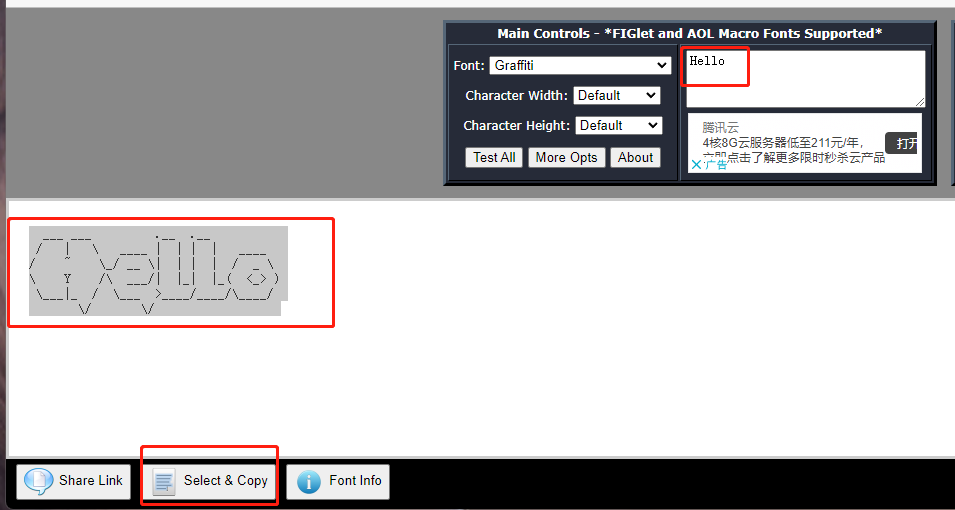
Create relevant files and enter the contents copied above
3.2.2 close the Banner
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication springApplication = new SpringApplication(SpringbootDemoApplication.class);
// To close the Banner, you need to configure it before the run method, otherwise it will not take effect
springApplication.setBannerMode(Banner.Mode.OFF);
springApplication.run(args);
}
3.3 common configurations
We are provided with two configuration files in SpringBoot
applicationContext.properties,applicationContext.yml
The functions of these two configuration files are the same, but there are some differences in writing format. Only one of them is needed in a project.
Simple example
-
Tomcat configuration modification
server.port=8082 server.servlet.context-path=/springboot
-
Chinese garbled configuration
server.tomcat.uri-encoding=UTF-8 spring.http.encoding.charset=UTF-8 spring.http.encoding.enabled=true spring.http.encoding.force=true spring.messages.encoding=UTF-8
-
Custom configuration content
# Customized configuration information user.username=zhangsan user.age=25 user.address=Nanjing, Jiangsu
Get content in entity class
//Use @ Value annotation @Value("${user.username}") private String userName; @Value("${user.age}") private Integer age; @Value("${user.address}") private String address;When importing the data in the configuration file, you need to add the following dependencies
<!--When you import the configuration file processor, you will be prompted to bind the configuration file--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency>
There is another way to output the content in the configuration file without @ Value
Use @ ConfigurationProperties annotation
package com.gupaoedu.bean; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component // Mapping of properties in the properties file and member variables in the User object @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "user") public class User { private String username; private Integer age; private String address; public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public String getAddress() { return address; } public void setAddress(String address) { this.address = address; } @Override public String toString() { return "User{" + "username='" + username + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", address='" + address + '\'' + '}'; } }