Introduction to SpringBoot

Microservices

Environmental constraints

maven settings - the jdk-1.8 version is used by default to compile and run the project

<profile>
<id>jdk-1.8</id>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
<jdk>1.8</jdk>
</activation>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
<maven.compiler.compilerVersion>1.8</maven.compiler.compilerVersion>
</properties>
</profile>
SpringBoot's hello world entry case

1. Create maven project
2. Import springBoot dependencies
<!--Import a parent project-->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<!--add to starter-web Module dependency-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
3. Write the main program and start the springboot application
package com;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
//To mark a main program class, indicating that this is a springBoot application
@SpringBootApplication
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//The spring application starts
SpringApplication.run(Hello.class,args);
}
}
4. Write relevant controller s and service s
package com.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello()
{
return "hello world";
}
}
5. Run the main program test
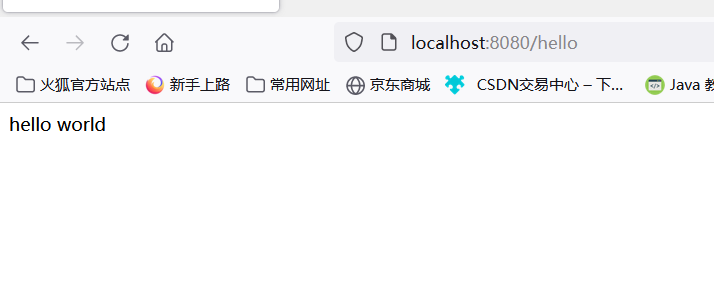
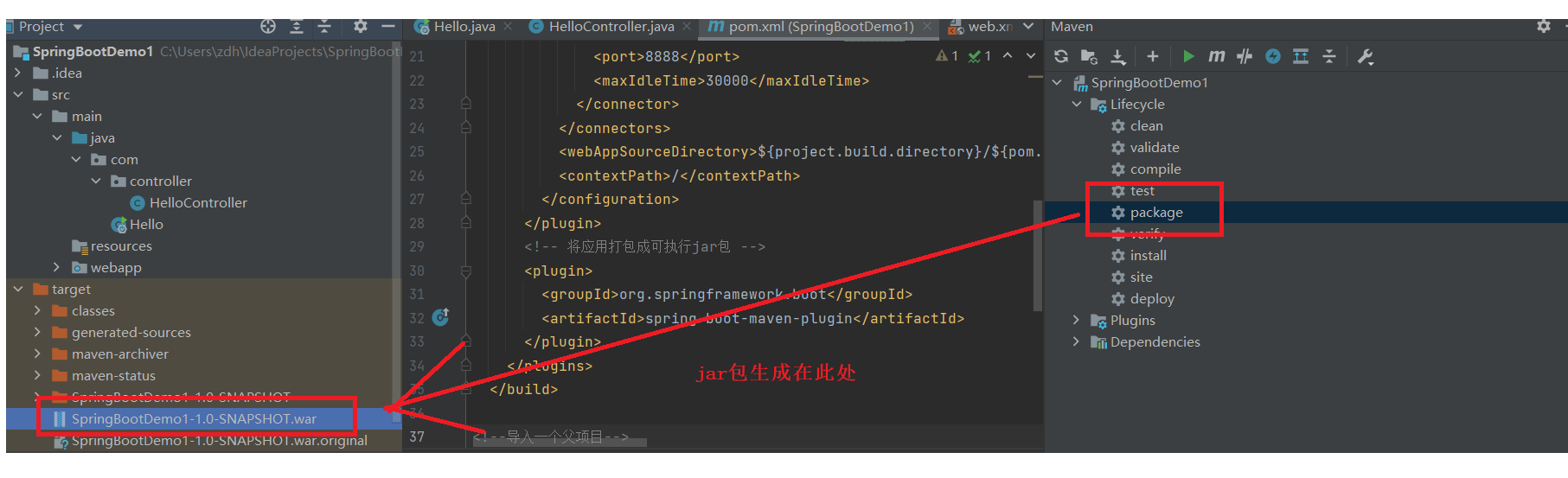
6. Deploy, package the project into an executable jar package, and install the plug-in
<!-- Package the application into executable jar package -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
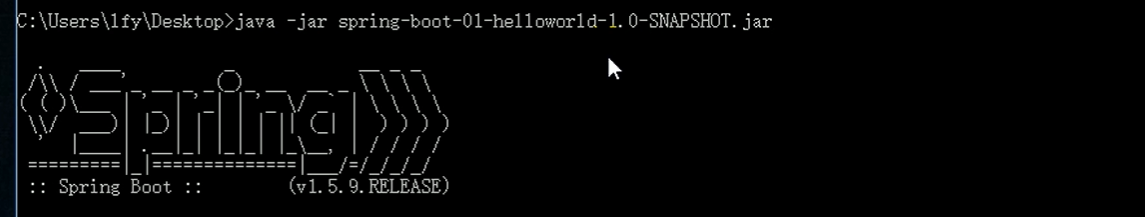
The command line uses the Java jar command to execute the jar package. Remember to go to the directory corresponding to the current jar package and go to the corresponding directory through the cd directory path –
Hello World exploration
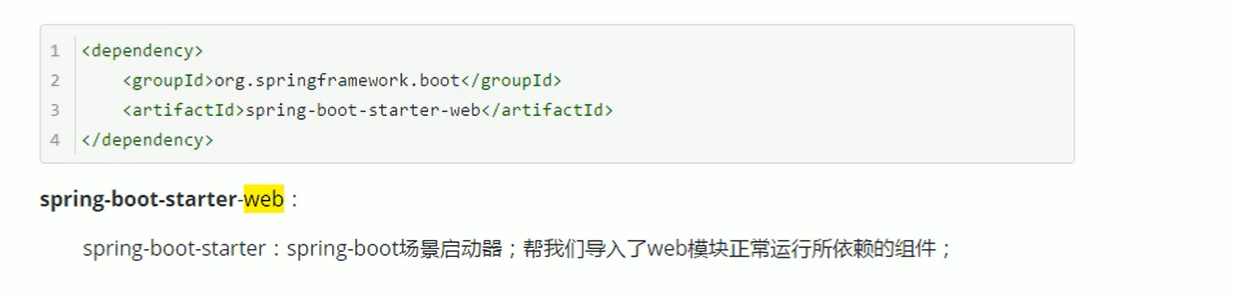
POM file
Parent item (parent dependency)


starter

Main program class (entry class)
//To mark a main program class, indicating that this is a springBoot application
@SpringBootApplication
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//The spring application starts
SpringApplication.run(Hello.class,args);
}
}

The following is the internal information of the @ SpringBootApplication annotation:
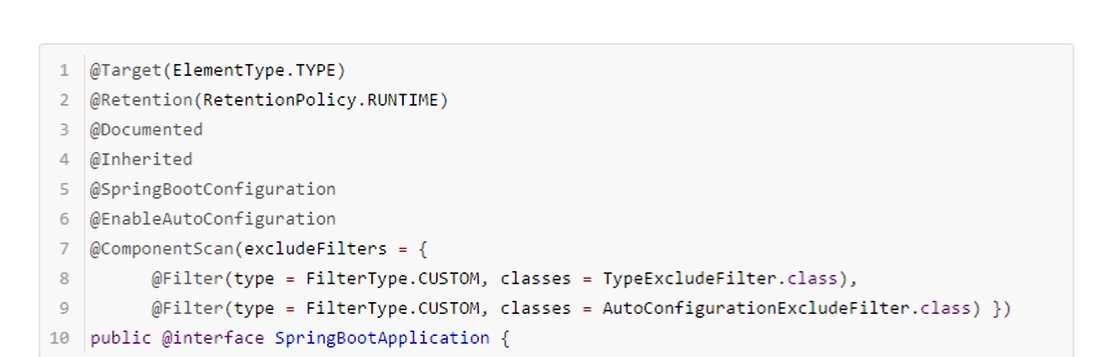
The meaning of the combined annotation is explained below:

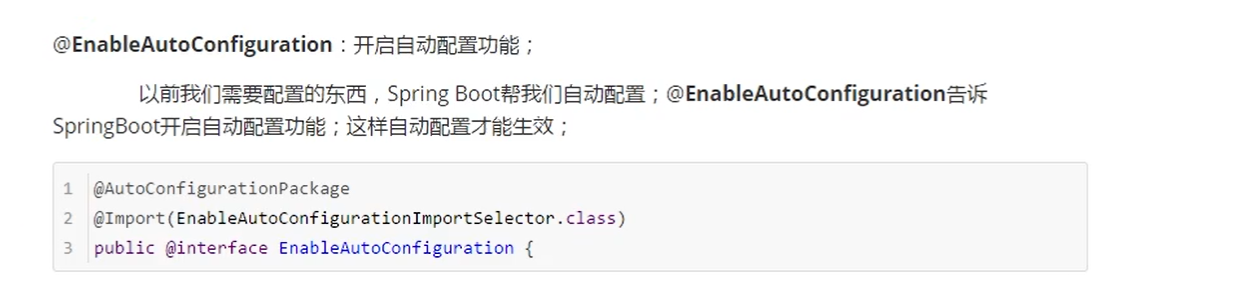
Note: the underlying principle of package scanning in springboot


The @ import annotation at the bottom will help us import many configuration classes, such as the configuration class that implements aop function and batch processing



Using Spring Initializer to quickly create a SpringBoot project

You can use @ RestController to replace @ ResponseBody and @ Controller annotations on the control class
//The data returned by all methods of this class is written directly to the browser (if the object is converted to json data)
/*@ResponseBody
@Controller*/
@RestController//Replace the above two annotations
public class helloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello()
{
return "Huyou ";
}
}
configuration file

The name of the SpringBoot global configuration file is fixed application, but the format can be properties or yml(yaml)
yaml profile

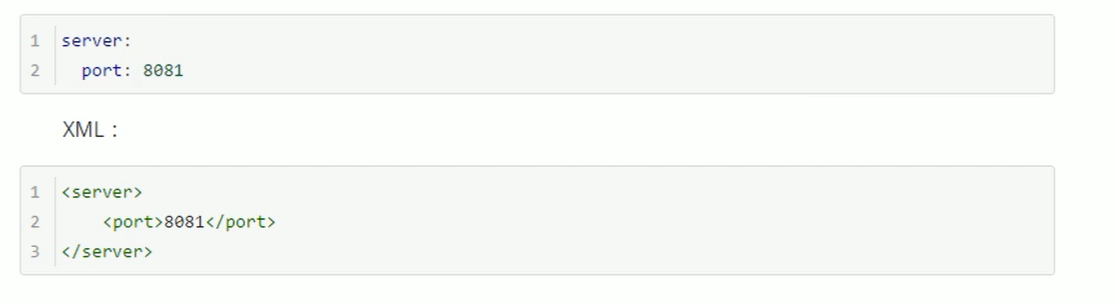
YAML basic syntax
1. Basic grammar
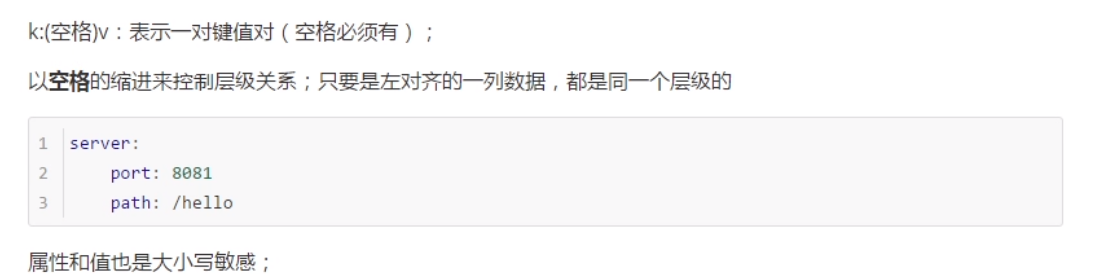
2. Writing of value
Literal: ordinary value (array, string, Boolean)

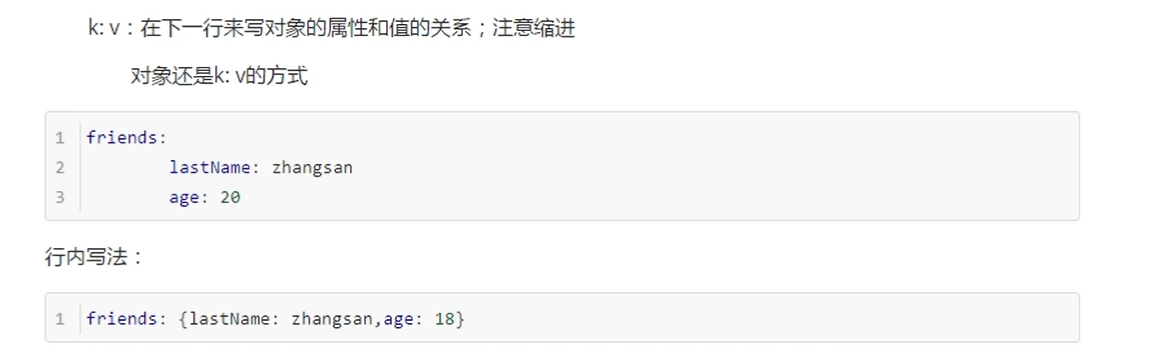
Object, map (properties and values) (key value pair)
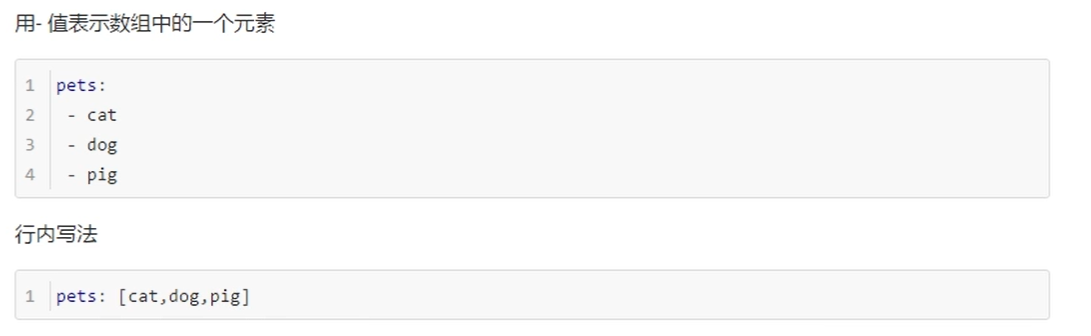
Array (List,Set)
YAML profile injection component
yaml:
server:
port: 8081
person:
name: Huyou
age: 18
boss: false
birth: 2002/1/2
maps: {k1: v1,k2: 12}
lists:
- history
- language
- mathematics
dog:
name: puppy
age: 1
Map the value of each attribute configured in the configuration file to this component;
@ConfigurationProperties: tell SpringBoot to bind all properties in this class to the relevant configuration in the configuration file
prefix = "person": which of the following attributes in the configuration file is mapped one by one
Only if this component is a component in the container can the @ ConfigurationProperties function provided in the container be used
peo class:
/*
* Map the value of each attribute configured in the configuration file to this component
* @ConfigurationProperties:Tell SpringBoot to bind all properties in this class to the relevant configuration in the configuration file
* prefix = "person":Which of the following attributes in the configuration file is mapped one by one
* Only if this component is a component in the container can the @ ConfigurationProperties function provided in the container be used
* */
@Controller
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
public class peo
{
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Boolean boss;
private Date birth;
private Map<String,Object> maps;
private List<Object> lists;
private Dog dog;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "peo{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", boss=" + boss +
", birth=" + birth +
", maps=" + maps +
", lists=" + lists +
", dog=" + dog +
'}';
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Boolean getBoss() {
return boss;
}
public void setBoss(Boolean boss) {
this.boss = boss;
}
public Date getBirth() {
return birth;
}
public void setBirth(Date birth) {
this.birth = birth;
}
public Map<String, Object> getMaps() {
return maps;
}
public void setMaps(Map<String, Object> maps) {
this.maps = maps;
}
public List<Object> getLists() {
return lists;
}
public void setLists(List<Object> lists) {
this.lists = lists;
}
public Dog getDog() {
return dog;
}
public void setDog(Dog dog) {
this.dog = dog;
}
}
Import the dependency of the configuration file processor, so that you will be prompted to bind the corresponding component to the configuration file
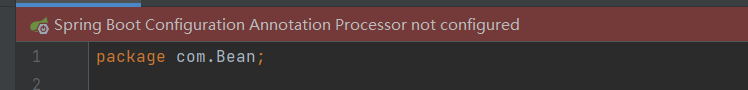
The annotation configuration processor of springboot is not found in the classpath. You need to import the dependency of the configuration file processor
<!-- When you import the configuration file processor, you will be prompted to bind the configuration file-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
Spring boot unit test just injected results
If you want to complete the injection of the corresponding class attribute, the corresponding class should provide a set method
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
class SpringBootQuickStartOneApplicationTests {
@Autowired
peo people;
@Test
void contextLoads()
{
System.out.println(people);
}
}

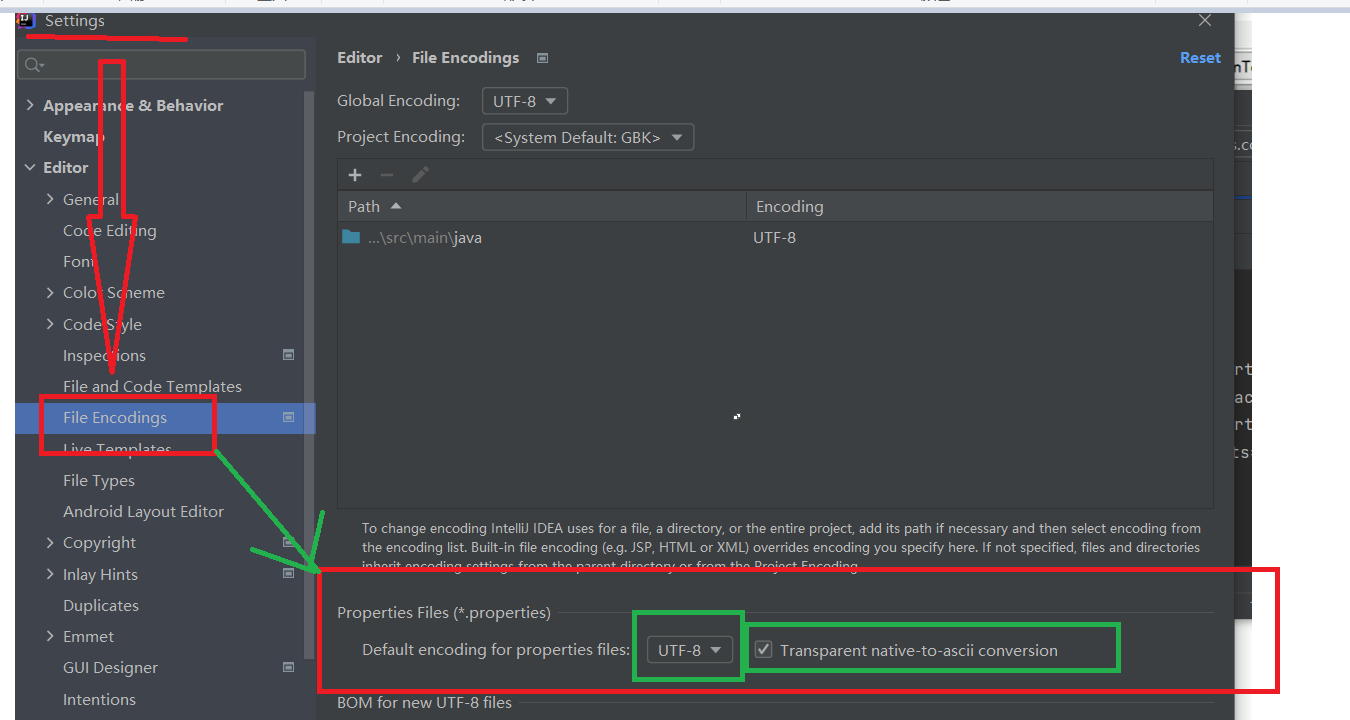
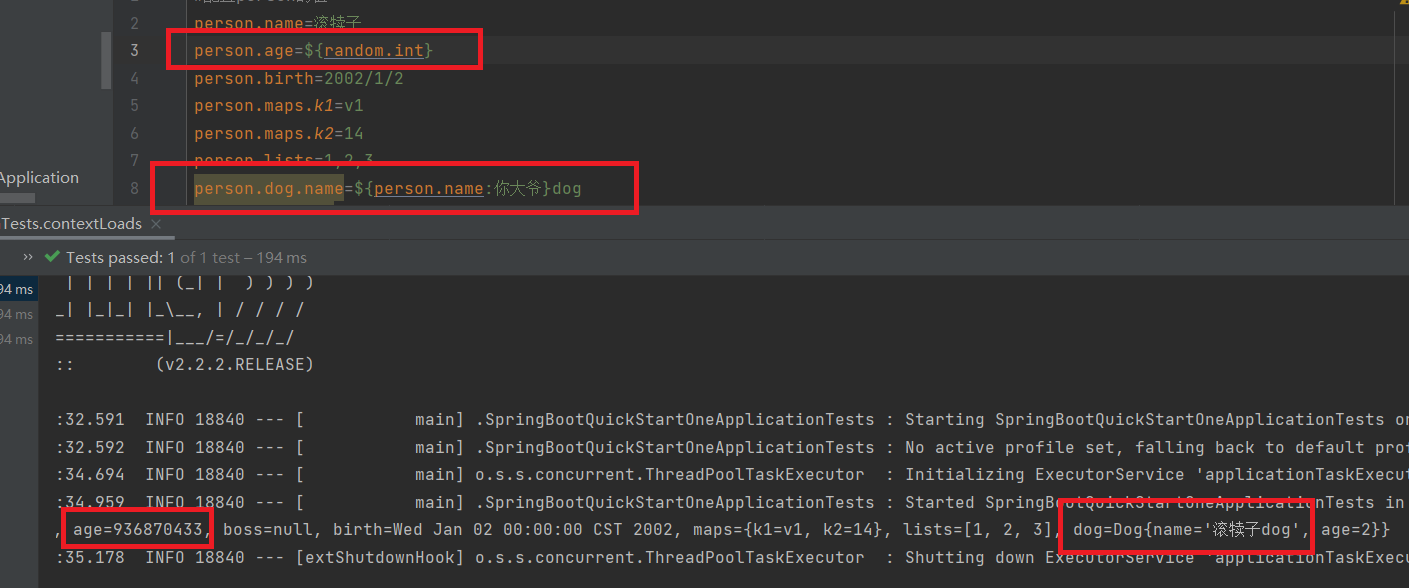
properties configuration file encoding problem
Display result: (garbled code) = = = "reason: idea uses UTF-8, while the properties file is generally ASCALL
#Configure the value of person person.name=Huyou person.age=18 person.birth=2002/1/2 person.maps.k1=v1 person.maps.k2=14 person.lists=1,2,3 person.dog.name=dog person.dog.age=2

The solution is as follows
result

The properties configuration file in the IDEA springboot project {is invalid after changing the corresponding GBK to UTF-8 and checking to ASCII} Chinese garbled code is solved at runtime
@Difference between Value annotation and @ ConfigurationProperties
@Value annotation usage demonstration:
@Controller
public class peo
{
/*
* <bean>
<property name="name" value="Literal value / ${key} get value from environment variable, configuration file / #{spel} "> < / property >
* </bean>
* */
@Value("${person.name}")
private String name;
@Value("#{11*2}")
private Integer age;
@Value("true")
private Boolean boss;

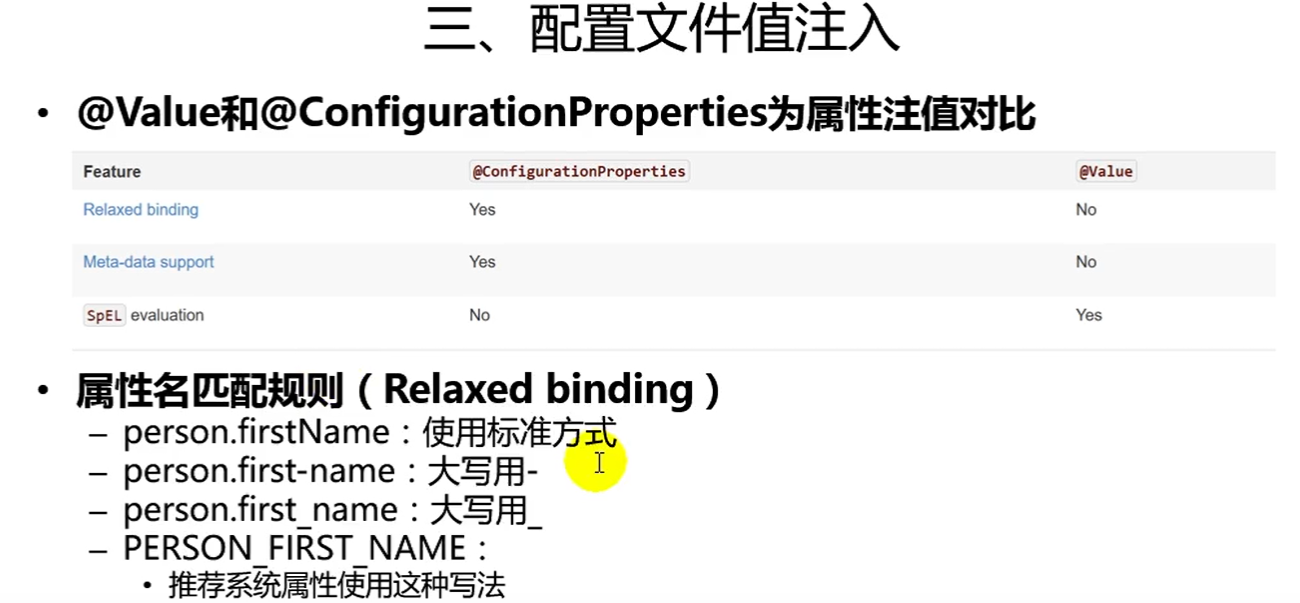
They can get values from either the configuration file yml or the properties
If we just need to get the Value in the configuration file in the business logic, we can use the @ Value annotation

If we write a class to map with the configuration file, we will directly use @ ConfigurationProperties
Demonstration of whether JSR303 verification is supported
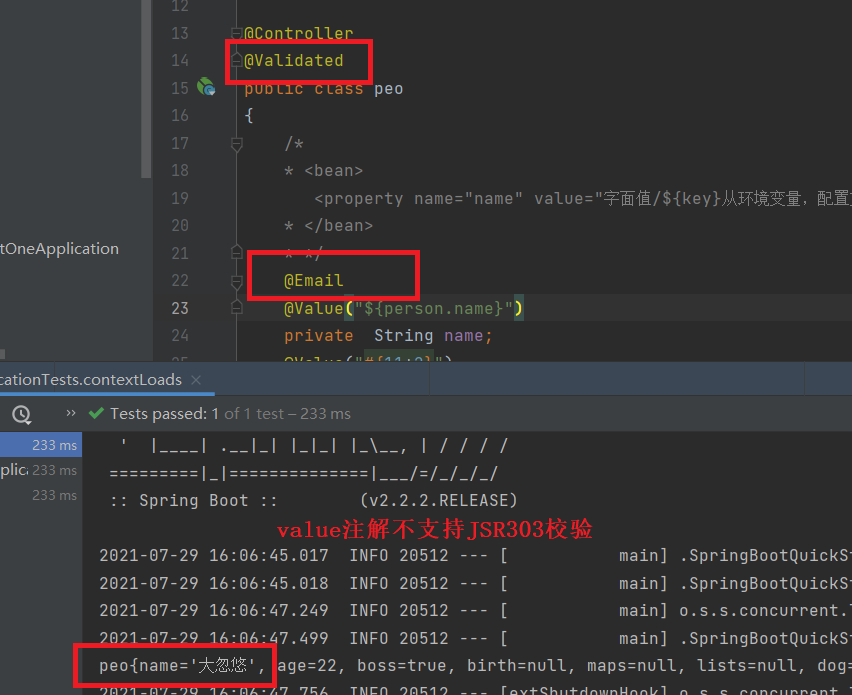

Solution to the problem that spring boot @ fail annotation interception does not take effect
Do not import packages separately. Incomplete packages may not take effect!
Directly introduce the starter of SpringBoot
<!--introduce JSR303 Verify starter-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId>
<version>RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
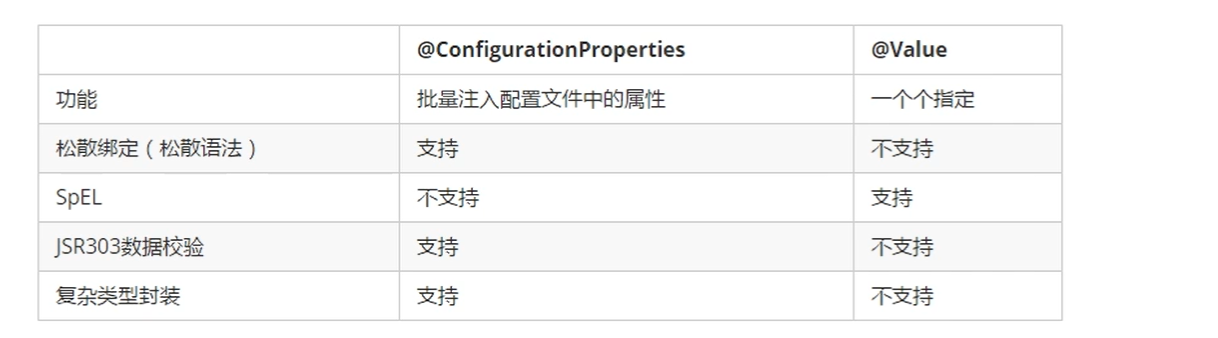
Annotation @ ConfigurationProperties and @ Value comparison, details
Annotation @ ConfigurationProperties vs. @ Value
@Get the name of the global configuration file (the default value is "application person") from the global configuration file
@PropertySource loads the specified configuration file = = = > loads peo Properties and bind to the object
@PropertySource(value={"classpath:peo.properties"})
@Controller
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
public class peo
{
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Boolean boss;
private Date birth;
private Map<String,Object> maps;
private List<Object> lists;
private Dog dog;

Pay attention to the loading order of Spring Boot configuration file, if the global configuration file properties, .yaml and PEO If the prefix matching conditions are met in properties, execute the global configuration file first
In the global configuration file properties takes precedence over yaml
PEO will only be executed if the global configuration files are not satisfied properties
@See the following two articles for details on the use of PropertySource annotation
@Use of PropertySource annotation
@PropertySource and @ ConfigurationProperties
See the following article for the loading order of Spring Boot configuration files
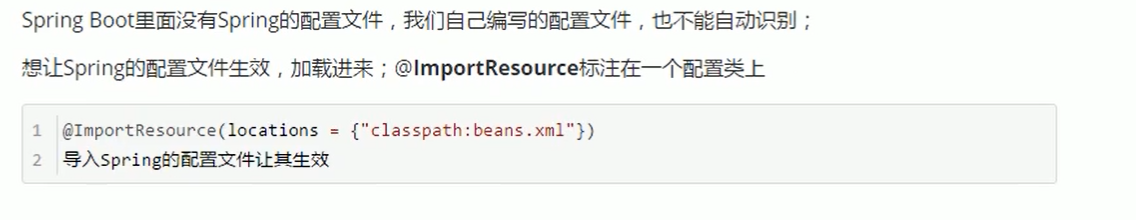
@ImportResource: import the Spring configuration file to make the content in the configuration file take effect
spring.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean class="com.Bean.pig" id="pig"/>
</beans>
springBoot unit test:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
class SpringBootQuickStartOneApplicationTests {
@Autowired
peo people;
@Autowired //Inject IOC container
ApplicationContext ioc;
@Test
void contextLoads()
{
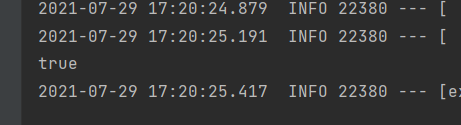
//Determine whether there is a pig in the container
boolean ret = ioc.containsBean("pig");
System.out.println(ret);
}
}
If the spring configuration file we wrote is not imported on the configuration class at this time, the result is false, that is, the corresponding Bean is not saved in the container
If yes, as follows:
@ImportResource(locations = {"classpath:spring.xml"})
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootQuickStartOneApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootQuickStartOneApplication.class, args);
}
}
SpringBoot recommends adding components to the container and using full annotation
Configuration class = = = = = Spring configuration file
@Configuration: indicates that the current class is a configuration class, replacing the previous Spring configuration file
@Bean("id name can be set here"): add the return value of the method to the container. The default id of this component in the container is the method name (not lowercase)
Configuration class:
@Configuration//Indicates that the current class is a configuration class that replaces the previous Spring configuration file
public class MyConfig
{
@Bean("pig")//Add the return value of the method to the container, and the default id of the component in the container is the method name (not lowercase)
public pig HelloPig()
{
return new pig();
}
}
Unit test class:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
class SpringBootQuickStartOneApplicationTests {
@Autowired
peo people;
@Autowired //Inject IOC container
ApplicationContext ioc;
@Test
void contextLoads()
{
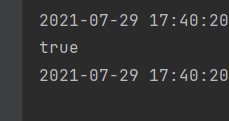
//Determine whether there is a pig in the container
boolean ret = ioc.containsBean("HelloPig");
System.out.println(ret);
}
}
Placeholder in configuration file


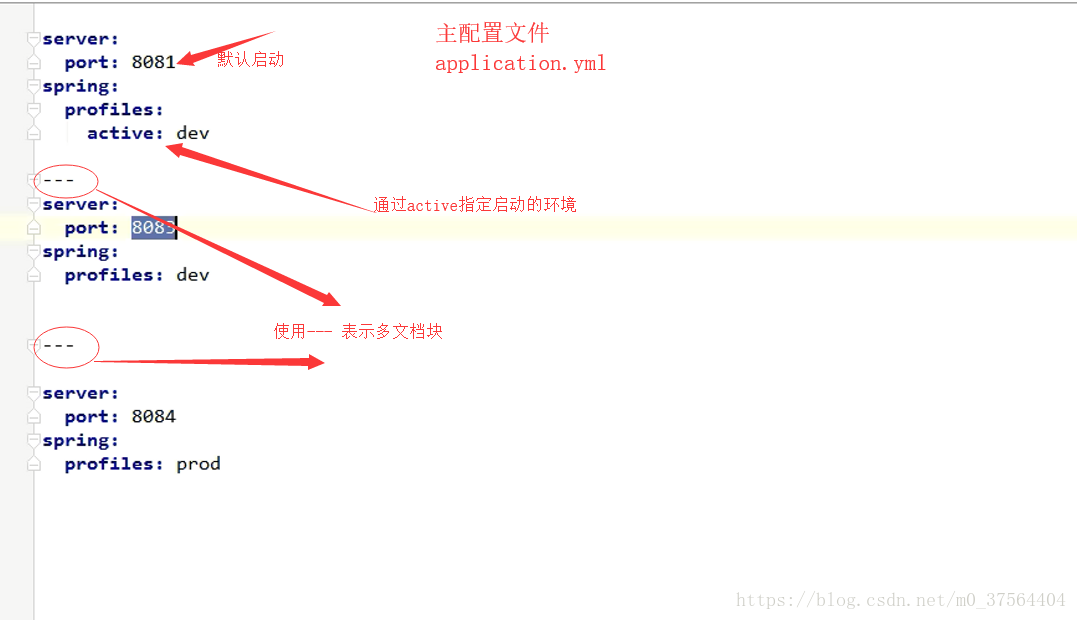
Propfile multi environment support

Multiple profile files

In application Properties main configuration file activates configuration files for different environments
SpringBoot project multi environment configuration (valid for personal testing)
In application Activate profiles for different environments in the YML master profile
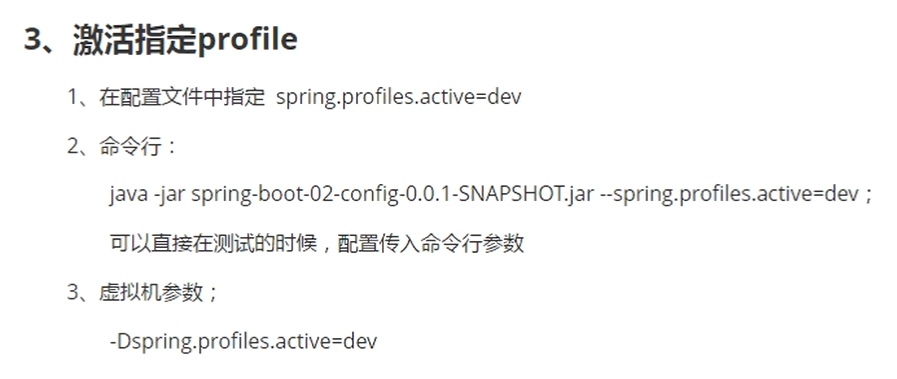
Activate by command line, type the project into jar package, and then start dos command line and use virtual machine parameters
SpringBoot configuration Profile multi environment support
Configuration file loading location


For high priority coverage and low priority coverage, it can be noted that only the same configuration item will have coverage effect. If different, it is complementary, that is, if all four places are configured, it will be accumulated.
Spring will load the main configuration file = = = > complementary configuration from these four locations
For example, if the port number is configured in the high priority configuration file and the port number and access path of the project are configured in the low priority configuration file, the high priority will only overwrite the low priority port number, and the access path will still use the low priority
server. Port = 8081 = = > configure port number
servlet. Context path = / Hello = = = > access path of configuration item
We can use spring config. Location references an external configuration file
Spring is specified in the application configuration file config. The priority of location is too low and loading is too late, resulting in the failure to load a specific configuration file. Therefore, you can increase the priority and load it into the configuration file by starting from the command line.

This only improves the priority, but still follows the complementary configuration. It is mostly used to modify some configurations after the project is packaged to overwrite the original configuration
How does springboot reference an external configuration file (spring.config.location)
Spring Boot supports a variety of external configuration methods, as shown below. The priority of loading from top to bottom is from high to low. When the content is the same, it is overwritten and not accumulated at the same time.
spring can load configurations from the following locations. The priority is from high to low. High priority configurations will overwrite low priority configurations, and all configurations will form complementary configurations
1. Command line parameters
2. JNDI attribute from java:comp/env
3. Use "spring.config.location" to change the default configuration file location
4. Java system properties (System.getProperties())
5. Operating system environment variables
6. RandomValuePropertySource configured random* Attribute value
7. Application - {profile} outside the jar package Properties or application YML (with spring.profile) configuration file
8. Application - {profile} inside the jar package Properties or application YML (with spring.profile) configuration file
9. Application.jar package Properties or application YML (without spring.profile) configuration file
10. Application.jar package Properties or application YML (without spring.profile) configuration file
11. @ PropertySource on @ Configuration annotation class
12. Via springapplication The default properties specified by setdefaultproperties



The loading order of external configuration files is recommended in the following article. The above records may not be detailed enough
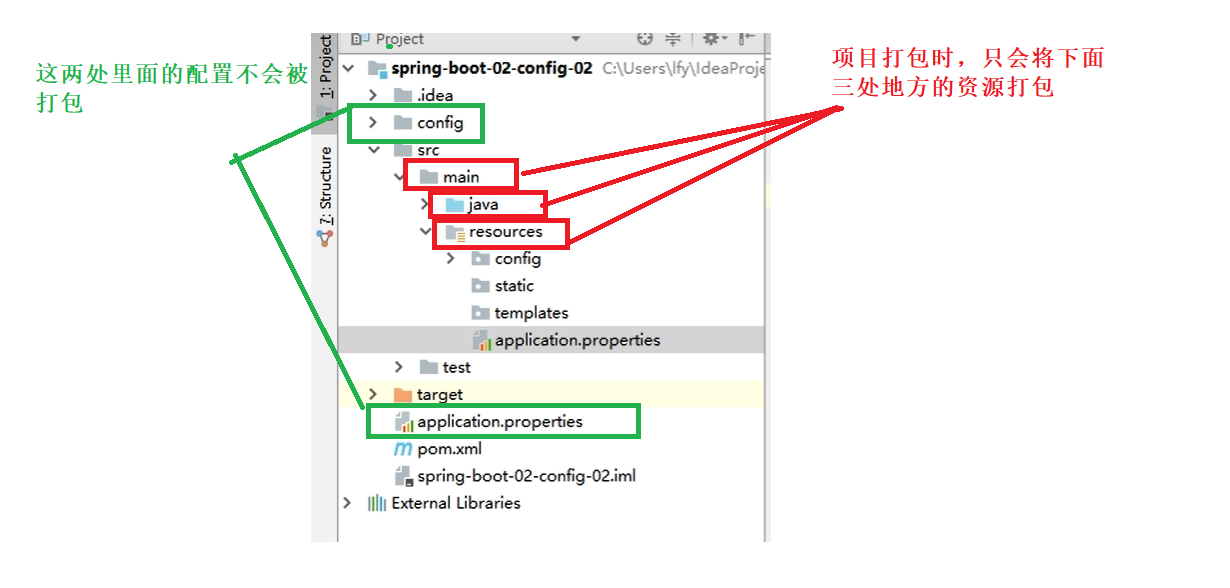
When the project is packaged, only the resources under the main,java and resources directories will be packaged
Principle of automatic configuration (key points)
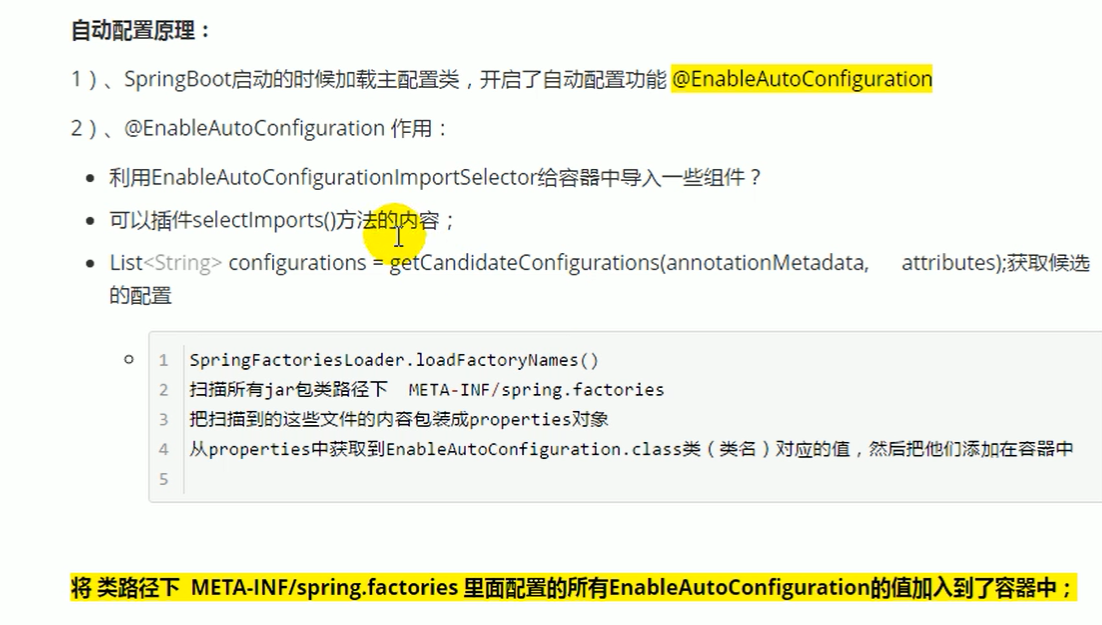
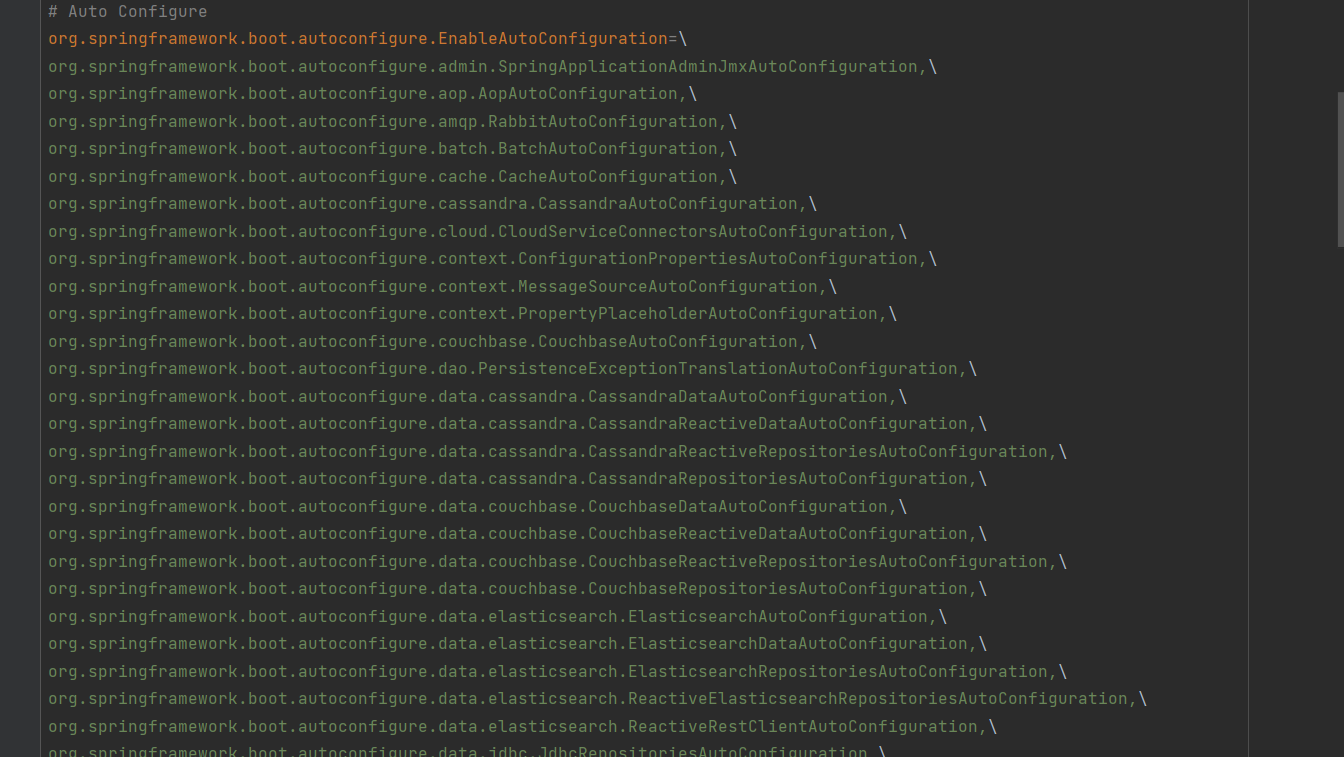


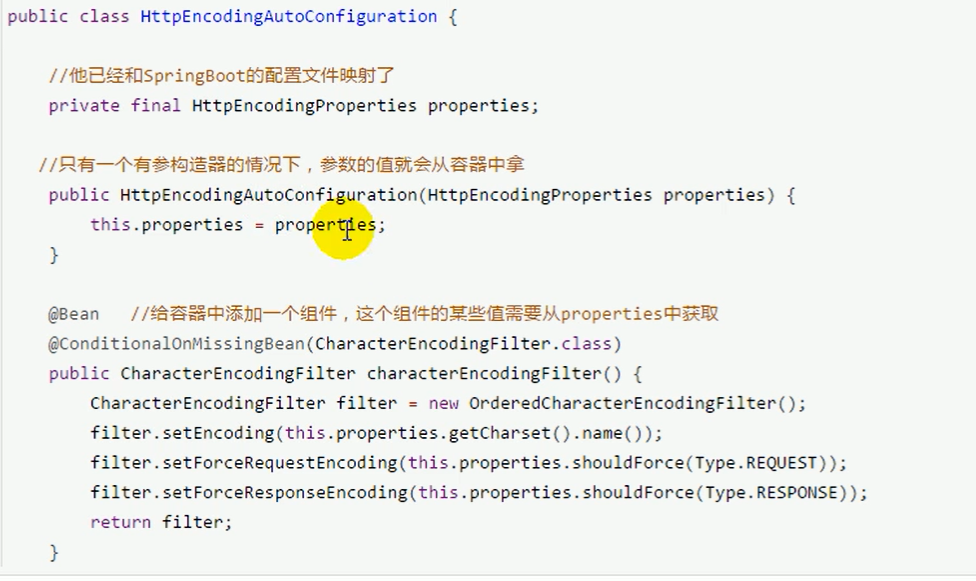

quintessence

The principle of automatic configuration and some notes involved can be explained in the following articles
The @ EnableConfigurationProperties annotation and @ Conditional annotation are involved, as well as other annotations
Comments related to @ EnableConfigurationProperties
Comments about @ EnableConfigurationProperties
Principle and implementation of SpringBoot automatic configuration
Spring boot (II): analysis of startup principle
Extension of condition annotation in automatic configuration principle

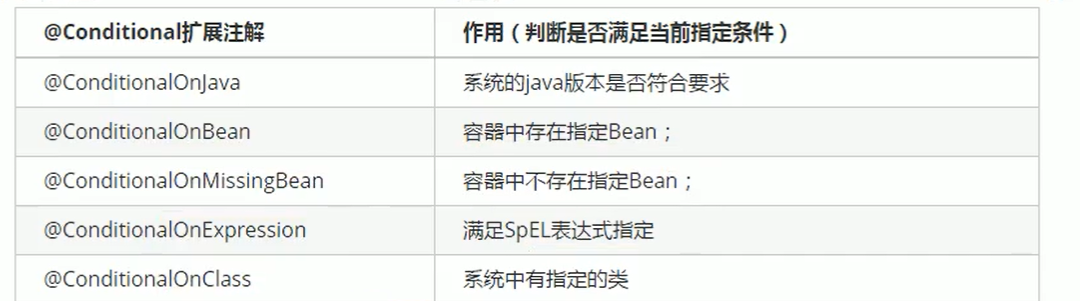
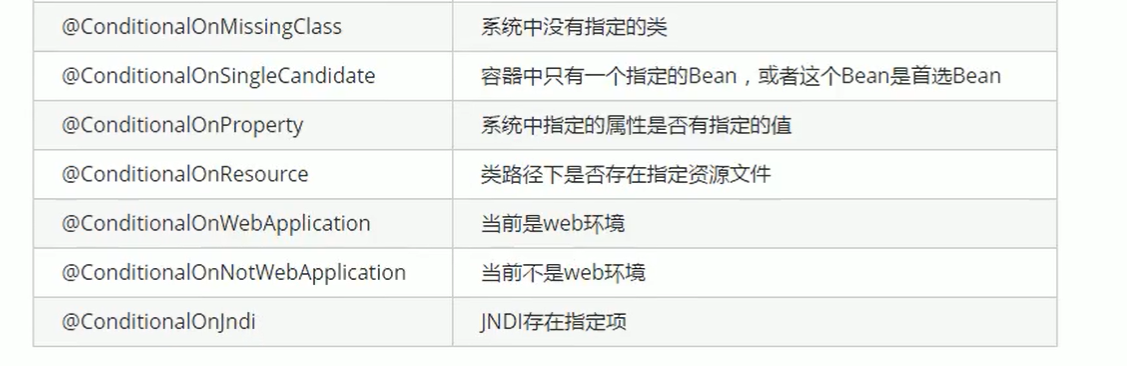
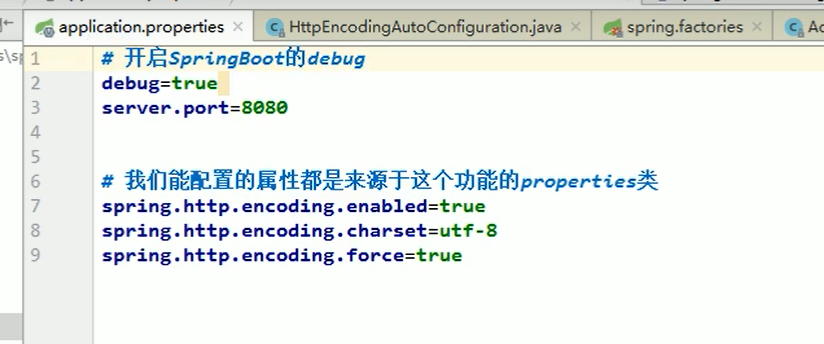
The auto configuration class will take effect only under certain conditions
Add debug=true to the configuration file to enable the debug mode of springBoot and let the console print the automatic configuration report, so that we can easily know which automatic configuration classes are effective