1. SpringBoot features
1.1. Dependency management
- Dependency management for parent project
Dependency management
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
His parent project
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
Almost all dependent version numbers commonly used in development are declared, and the automatic version arbitration mechanism
- Develop and import starter scenario launcher
1,See a lot spring-boot-starter-* : *Just some kind of scene 2,Just introduce starter,We will automatically introduce all the dependencies required for this scenario 3,SpringBoot All supported scenarios https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/using-spring-boot.html#using-boot-starter 4,See *-spring-boot-starter: The third party provides us with a scenario launcher to simplify development. 5,The lowest level dependency of all scenario initiators <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version> <scope>compile</scope> </dependency>
- No need to pay attention to the version number, automatic version arbitration
1,By default, no version can be written when importing dependencies 2,Introducing non version arbitrations jar,To write the version number.
- You can modify the default version number
1,see spring-boot-dependencies It specifies the current dependent version key.
2,Rewrite the configuration in the current project
<properties>
<mysql.version>5.1.43</mysql.version>
</properties>
1.2. Automatic configuration
- Automatically configure Tomcat
- Introduce Tomcat dependency.
- Configure Tomcat
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
- Automatically configure spring MVC
- Introducing a full set of spring MVC components
- Automatically configure common spring MVC components (functions)
- Automatically configure common Web functions, such as character coding
- SpringBoot helped us configure all the common scenarios for web development
- Default package structure
- The components in the package where the main program is located and all its sub packages will be scanned by default
- No previous package scan configuration is required
- To change the scanning path, @ SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages = "com.atguigu")
Or @ ComponentScan specifies the scan path
@SpringBootApplication
Equivalent to
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan("com.atguigu.boot")
- Various configurations have default values
- The default configuration is ultimately mapped to a class, such as MultipartProperties
- The value of the configuration file will eventually be bound to each class, which will create objects in the container
- Load all auto configuration items on demand
- Very many starter s
- What scenarios are introduced and the automatic configuration of this scenario will be enabled
- All spring boot autoconfigure functions are in the spring boot autoconfigure package
- ...
2. Container function
2.1. Component addition
1,@Configuration
- Basic use
- Full mode and Lite mode
- Example
- Best practice
- There is no dependency between configuration class components. Use Lite mode to accelerate the container startup process and reduce judgment
- There are dependencies between configuration class components, and the method will be called to obtain the previous single instance component in Full mode
#############################Configuration Use example######################################################
/**
* 1,The @ Bean annotation is used in the configuration class to register components for the container on the method. By default, it is also single instance
* 2,The configuration class itself is also a component
* 3,proxyBeanMethods: Method of proxy bean
* Full(proxyBeanMethods = true),[How many times each @ Bean method is called and the returned component is single instance]
* Lite(proxyBeanMethods = false)[How many times is each @ Bean method called and the returned component is newly created]
* Component dependencies must use the Full mode default. Other default Lite modes
*
*
*
*/
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) //Tell SpringBoot that this is a configuration class = = configuration file
public class MyConfig {
/**
* Full:No matter how many external calls are made to the component registration method in the configuration class, the single instance object in the previous registration container is obtained
* @return
*/
@Bean //Add components to the container. Take the method name as the id of the component. The return type is the component type. The returned value is the instance of the component in the container
public User user01(){
User zhangsan = new User("zhangsan", 18);
//The user component depends on the Pet component
zhangsan.setPet(tomcatPet());
return zhangsan;
}
@Bean("tom")
public Pet tomcatPet(){
return new Pet("tomcat");
}
}
################################@Configuration The test code is as follows########################################
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan("com.atguigu.boot")
public class MainApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. Return to our IOC container
ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class, args);
//2. View the components in the container
String[] names = run.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : names) {
System.out.println(name);
}
//3. Get component from container
Pet tom01 = run.getBean("tom", Pet.class);
Pet tom02 = run.getBean("tom", Pet.class);
System.out.println("Components:"+(tom01 == tom02));
//4,com.atguigu.boot.config.MyConfig$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$51f1e1ca@1654a892
MyConfig bean = run.getBean(MyConfig.class);
System.out.println(bean);
//If the @ Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = true) proxy object calls the method. SpringBoot always checks whether the component is in the container.
//Keep component single instance
User user = bean.user01();
User user1 = bean.user01();
System.out.println(user == user1);
User user01 = run.getBean("user01", User.class);
Pet tom = run.getBean("tom", Pet.class);
System.out.println("User's pet:"+(user01.getPet() == tom));
}
}
2,@Bean,@Component,@Controller,@Service,@Repository
Assemble objects into spring containers
3,@ComponentScan,@Import
* 4,@Import({User.class, DBHelper.class})
* Automatically create these two types of components in the container. The name of the default component is the full class name
*
*
*
*/
@Import({User.class, DBHelper.class})
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) //Tell SpringBoot that this is a configuration class = = configuration file
public class MyConfig {
}
@Import advanced usage: https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1gW411W7wy?p=8
4,@Conditional
Conditional assembly: component injection is performed when the conditions specified in conditional are met

=====================Test condition assembly==========================
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) //Tell SpringBoot that this is a configuration class = = configuration file
//@ConditionalOnBean(name = "tom")
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "tom")
public class MyConfig {
/**
* Full:No matter how many external calls are made to the component registration method in the configuration class, the single instance object in the previous registration container is obtained
* @return
*/
@Bean //Add components to the container. Take the method name as the id of the component. The return type is the component type. The returned value is the instance of the component in the container
public User user01(){
User zhangsan = new User("zhangsan", 18);
//The user component depends on the Pet component
zhangsan.setPet(tomcatPet());
return zhangsan;
}
@Bean("tom22")
public Pet tomcatPet(){
return new Pet("tomcat");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. Return to our IOC container
ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class, args);
//2. View the components in the container
String[] names = run.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : names) {
System.out.println(name);
}
boolean tom = run.containsBean("tom");
System.out.println("In container Tom Components:"+tom);
boolean user01 = run.containsBean("user01");
System.out.println("In container user01 Components:"+user01);
boolean tom22 = run.containsBean("tom22");
System.out.println("In container tom22 Components:"+tom22);
}
2.2. Importing native configuration files
1,@ImportResource
======================beans.xml=========================
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<bean id="haha" class="com.atguigu.boot.bean.User">
<property name="name" value="zhangsan"></property>
<property name="age" value="18"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="hehe" class="com.atguigu.boot.bean.Pet">
<property name="name" value="tomcat"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
@ImportResource("classpath:beans.xml")
public class MyConfig {}
======================test=================
boolean haha = run.containsBean("haha");
boolean hehe = run.containsBean("hehe");
System.out.println("haha: "+haha);//true
System.out.println("hehe: "+hehe);//true
2.3. Configure binding
How to use Java to read the contents of the properties file and package it into JavaBean s for use at any time;
public class getProperties {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
Properties pps = new Properties();
pps.load(new FileInputStream("a.properties"));
Enumeration enum1 = pps.propertyNames();//Get the name of the configuration file
while(enum1.hasMoreElements()) {
String strKey = (String) enum1.nextElement();
String strValue = pps.getProperty(strKey);
System.out.println(strKey + "=" + strValue);
//Encapsulate into JavaBean s.
}
}
}
1,@ConfigurationProperties
/**
* Only the components in the container can have the powerful functions provided by SpringBoot
*/
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mycar")
public class Car {
private String brand;
private Integer price;
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public Integer getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(Integer price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car{" +
"brand='" + brand + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}
2,@EnableConfigurationProperties + @ConfigurationProperties
3,@Component + @ConfigurationProperties
@EnableConfigurationProperties(Car.class)
//1. Enable Car configuration binding function
//2. Automatically register the Car component into the container
public class MyConfig {
}
3. Introduction to the principle of automatic configuration
3.1. Boot load automatic configuration class
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication{}
======================
1,@SpringBootConfiguration
@Configuration. Represents the current configuration class
2,@ComponentScan
Specify which Spring annotations to scan;
3,@EnableAutoConfiguration
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {}
1,@AutoConfigurationPackage
Auto configuration package? The default package rule is specified
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class) //Import a component into the container
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {}
//Use the Registrar to import a series of components into the container
//Import all components under a specified package? Under the package of MainApplication.
2,@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
1,utilize getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata);Batch import some components into the container
2,call List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes)Get all the configuration classes that need to be imported into the container
3,Using factory loading Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader);Get all the components
4,from META-INF/spring.factories Location to load a file.
By default, it scans all of our current systems META-INF/spring.factories Location file
spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.3.4.RELEASE.jar It's also in the bag META-INF/spring.factories

It's dead in the file spring-boot All configuration classes loaded in the container should be given as soon as they are started spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.3.4.RELEASE.jar/META-INF/spring.factories # Auto Configure org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch.BatchAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cassandra.CassandraAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.ConfigurationPropertiesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.LifecycleAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.MessageSourceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.couchbase.CouchbaseAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.dao.PersistenceExceptionTranslationAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ReactiveElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ReactiveElasticsearchRestClientAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jdbc.JdbcRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jpa.JpaRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.ldap.LdapRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.solr.SolrRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.r2dbc.R2dbcDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.r2dbc.R2dbcRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.r2dbc.R2dbcTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisReactiveAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.rest.RepositoryRestMvcAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.web.SpringDataWebAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRestClientAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.flyway.FlywayAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.gson.GsonAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.h2.H2ConsoleAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hateoas.HypermediaAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastJpaDependencyAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpMessageConvertersAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.codec.CodecsAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.influx.InfluxDbAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.info.ProjectInfoAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.integration.IntegrationAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JndiDataSourceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.XADataSourceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JmsAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jmx.JmxAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JndiConnectionFactoryAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.activemq.ActiveMQAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.artemis.ArtemisAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jersey.JerseyAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jooq.JooqAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jsonb.JsonbAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.kafka.KafkaAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.availability.ApplicationAvailabilityAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.embedded.EmbeddedLdapAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.LdapAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.liquibase.LiquibaseAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderValidatorAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.embedded.EmbeddedMongoAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoReactiveAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.quartz.QuartzAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.r2dbc.R2dbcAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketRequesterAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketServerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketStrategiesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.UserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityFilterAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.reactive.ReactiveSecurityAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.reactive.ReactiveUserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.rsocket.RSocketSecurityAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.saml2.Saml2RelyingPartyAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.sendgrid.SendGridAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.session.SessionAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.client.servlet.OAuth2ClientAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.client.reactive.ReactiveOAuth2ClientAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.resource.servlet.OAuth2ResourceServerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.resource.reactive.ReactiveOAuth2ResourceServerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.solr.SolrAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskSchedulingAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.TransactionAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.jta.JtaAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.validation.ValidationAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.client.RestTemplateAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.embedded.EmbeddedWebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.HttpHandlerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.ReactiveWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.WebFluxAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.error.ErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.ClientHttpConnectorAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.WebClientAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.MultipartAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.reactive.WebSocketReactiveAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketServletAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.WebServicesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.client.WebServiceTemplateAutoConfiguration
3.2. Turn on the automatic configuration item as required
Although all the automatic configurations of our 127 scenarios are loaded by default when they are started. xxxxAutoConfiguration Assembly rules according to conditions(@Conditional),It will eventually be configured on demand.
3.3. Modify the default configuration
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(MultipartResolver.class) //There are components of this type in the container
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = DispatcherServlet.MULTIPART_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME) //There is no component with this name multipartResolver in the container
public MultipartResolver multipartResolver(MultipartResolver resolver) {
//If the method labeled @ Bean passes in an object parameter, the value of this parameter will be found from the container.
//SpringMVC multipartResolver. Prevent the file upload parser configured by some users from not conforming to the specification
// Detect if the user has created a MultipartResolver but named it incorrectly
return resolver;
}
Add a file upload parser to the container;
SpringBoot will configure all components at the bottom by default. However, if the user has configured it himself, the user's priority shall prevail
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter() {
}
Summary:
- SpringBoot loads all the autoconfiguration classes xxxxconfiguration first
- Each automatic configuration class takes effect according to conditions, and will bind the value specified in the configuration file by default. Take it from xxproperties. xxxProperties is bound to the configuration file
- The effective configuration class will assemble many components in the container
- As long as these components are in the container, they are equivalent to these functions
- Customized configuration
- Users directly replace the underlying components with @ Bean
- The user can modify the value of the configuration file obtained by this component.
Xxxxxxautoconfiguration - > component - > xxxxproperties - > get the value - > application properties
3.4 best practices
- Introduce scenario dependency
- View which are automatically configured (optional)
- After self analysis, the automatic configuration corresponding to the imported scenario generally takes effect
- debug=true in the configuration file enables the automatic configuration report. Negative \ Positive
- Need to modify
- Modify configuration items by referencing documents
- https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/appendix-application-properties.html#common-application-properties
- Analyze yourself. Which of the configuration files are bound by xxproperties.
- Custom add or replace components
- @Bean,@Component. . .
- Customizer xxxxxxcustomizer;
- ...
- Modify configuration items by referencing documents
4. Development tips
4.1,Lombok
Simplify JavaBean development
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
idea Search for installation in lombok plug-in unit
===============================simplify JavaBean development===================================
@NoArgsConstructor
//@AllArgsConstructor
@Data
@ToString
@EqualsAndHashCode
public class User {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Pet pet;
public User(String name,Integer age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
================================Simplified log development===================================
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String handle01(@RequestParam("name") String name){
log.info("The request came in....");
return "Hello, Spring Boot 2!"+"Hello:"+name;
}
}
4.2,dev-tools
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
After modifying an item or page: Ctrl+F9;
4.3. Spring Initailizr (project initialization wizard)
0. Select the development scenario we need
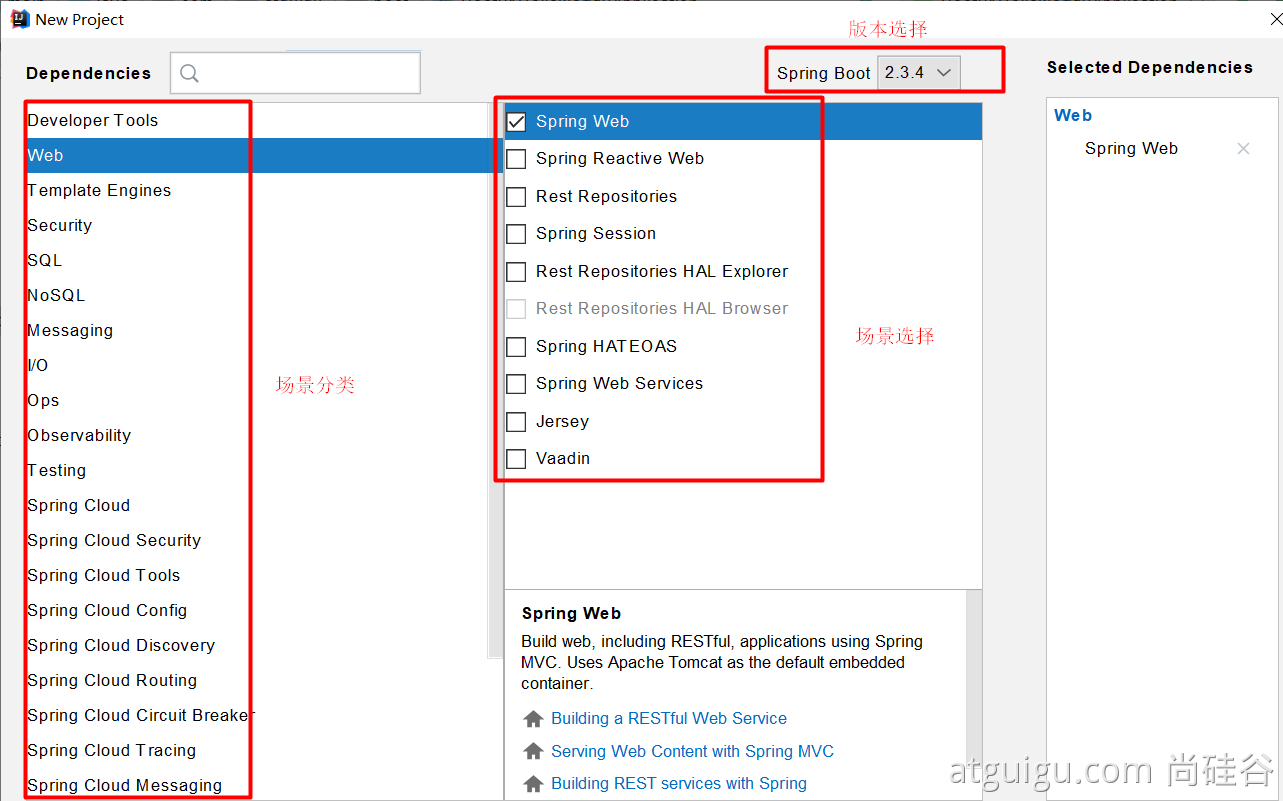
1. Automatic dependency import
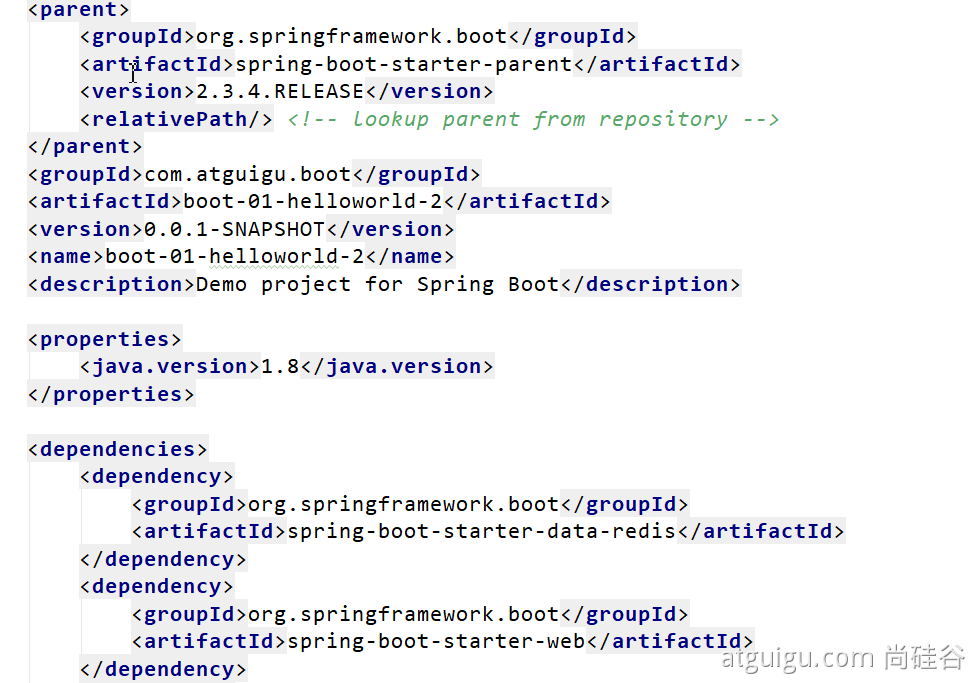
2. Automatically create project structure

3. Automatically write the main configuration class
