catalogue
1. Create the working directory structure and modify it to yml file.
2. Unified web return object R type.
4. Create a custom exception class:
5. Streamline the exception message returned to the front end:
6. Database and tomcat server configuration:
3. Configure radios (for long and short tokens);
4. Configure MongoDB database:
5. Configure MyBatis (add plug-ins before use)
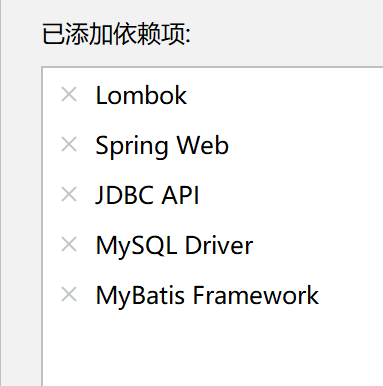
When creating a project, check three items about database, one lombok tool and spring web. Save the dependence of importing database in the later stage
1. Create the working directory structure and modify it to yml file.
1. The controller class writes the web method, and the form is the object type received in the web method.
2. Dao in db is an interface for defining methods. pojp is a model generated based on ORM
1. The log is configured to be displayed only with warnings, and the time is formatted:
logging:
level:
root: info
com.example.mineemos.db.dao: warn Make the log under this file only print out the data of warning type
partten:
console: "%d{HH:mm:ss} %-5level %msg%n" Format time
2. Unified web return object R type.
1. The Http status code that needs to be imported depends on.
2. Class R inherits the HashMap class.
<!--to R Object returned Http Status code-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId>
<artifactId>httpcore</artifactId>
<version>4.4.13</version>
</dependency>import org.apache.http.HttpStatus;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class R extends HashMap<String,Object> {
//Two pieces of information are added when initializing the object
public R(){
//Some data is put in by default when creating objects
//HttpStatus is imported into the dependency
//HttpStatus.SC_OK is a constant = 200
put("code", HttpStatus.SC_OK);
put("msg","success");
}
//The chain call is implemented, and its own map set cannot be added in a chain, so write one for him
public R put(String key,Object value){
super.put(key,value);
return this;
}
//ok indicates that the request was successful
public static R ok(){
return new R();
}
public static R ok(String msg){
R r=new R();
//There is already a message method. If you write it again, it will be overwritten
r.put("msg",msg);
return r;
}
public R ok(int code,String msg){
R r=new R();
r.put("code",code).put("msg",msg);
return r;
}
public static R ok(Map<String,Object> map){
R r=new R();
r.putAll(map);
return r;
}
//Indicates that the request failed
public static R error(int code,String msg){
R r=new R();
r.put("code",code);
r.put("msg",msg);
return r;
}
public static R error(String msg){
return error(HttpStatus.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR,msg);
}
public static R error(){
return error(HttpStatus.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR,"Unknown exception, please contact the administrator");
}
}3. Configure Swagger.
See the article for details: swagger3 configuration is super simple
SpringDoc dependency;
<!--add to springDoc rely on-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-spring-boot-2-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>3.1.5</version>
</dependency>Configuration yml file
springdoc:
api-docs:
enabled: true
path: /Your own project name.html
swagger-ui:
path: /swagger-ui.html
disable-swagger-default-url: on
spring:
mvc:
pathmatch:
matching-strategy: ant_path_matcher4. Create a custom exception class:
1. Add Set and get methods. 2. Inherit RuntimeException class 3, code and message attributes
import lombok.Data;
@Data
//Exception class
public class EmosException extends RuntimeException{
private int code=500;
private String msg;
//The first two construction methods are commonly used, and the latter two are not commonly used
//Supplement the construction method of this exception class. If it is not written, there will be only one parameterless construction by default
public EmosException(String msg) {
super(msg);//Print the error message in red on the console
this.msg = msg;
}
public EmosException(String msg, int code) {
super(msg);
this.msg = msg;
this.code = code;
}
public EmosException(String msg, Throwable e) {
super(msg, e);
this.msg = msg;
}
public EmosException(String msg, int code, Throwable e) {
super(msg, e);
this.msg = msg;
this.code = code;
}
}
5. Streamline the exception message returned to the front end:
Set a configuration class to configure this simplified message, constantly if judge which class to return to, and then use the callback function res.data to display the exception message after returning to the front end
import com.example.emos.exception.EmosException;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.UnauthorizedException;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestControllerAdvice;
@Slf4j
@RestControllerAdvice//Let the system know that this is an exception handling class
//Steps: 1. Convert the exception to the corresponding type. 2. Call the get message module inside
public class ExceptionAdvice {
@ResponseBody//Return the format of the exception as json
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)//What kind of exception to handle
public String exceptionHandler(Exception e){
log.error("-----Execution exception-----"+e);//Print exception on console
//Processing backend validation failed
if(e instanceof MethodArgumentNotValidException){
//Convert exception to validation exception
MethodArgumentNotValidException exception= (MethodArgumentNotValidException) e;
//Get exception message
return exception.getBindingResult().getFieldError().getDefaultMessage();
}
//Custom exception
else if(e instanceof EmosException){
EmosException exception= (EmosException) e;
return exception.getMsg();
}
//Unauthorized type
else if(e instanceof UnauthorizedException){
return "You don't have relevant authority";
}
else{
return "Backend execution exception";
}
}
}
6. Database and tomcat server configuration:
1. Configure tomcat server
server:
tomcat:
uri-encoding: UTF-8
threads:
max: 200
min-spare: 30
connection-timeout: 5000ms
port: 8080 #port
servlet:
context-path: /emos #The whole project has a prefix, which can only be accessed before routing2. Configure mySQL
To use connection pool, you must first add dependencies:
<!--Database connection pool-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.2.8</version>
</dependency>spring:
datasource:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
druid:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3307 / database name? useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username: root
password: Database password
initial-size: 8
max-active: 16
min-idle: 8
max-wait: 60000
test-while-idle: true
test-on-borrow: false
test-on-return: false3. Configure radios (for long and short tokens);
redis:
database: 0
host: localhost
port: 6379
password: abc123456
jedis:
pool:
max-active: 1000
max-wait: -1ms
max-idle: 16
min-idle: 84. Configure MongoDB database:
redis:
database: 0
host: localhost
port: 6379
password: abc123456
jedis:
pool:
max-active: 1000
max-wait: -1ms
max-idle: 16
min-idle: 85. Configure MyBatis (add plug-ins before use)
Methods are defined in Dao, interfaces written in service are also methods, and specific business logic is written in impl file of service
1. Let IDEA link to mySQL database. And add the database and all dependencies of MyBatis:
<!--Database connection pool-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.2.8</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--myBatis rely on-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2</version>
</dependency>2. Use mybatis generator to generate pojo and Dao (only use lombook)
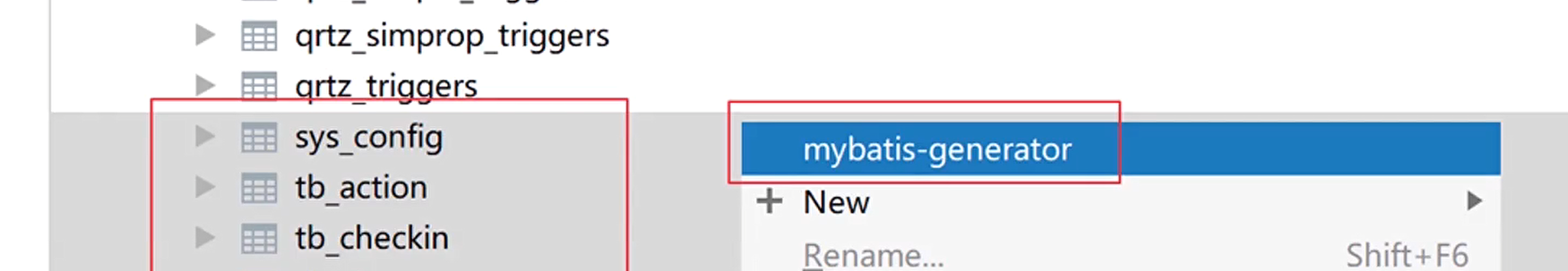
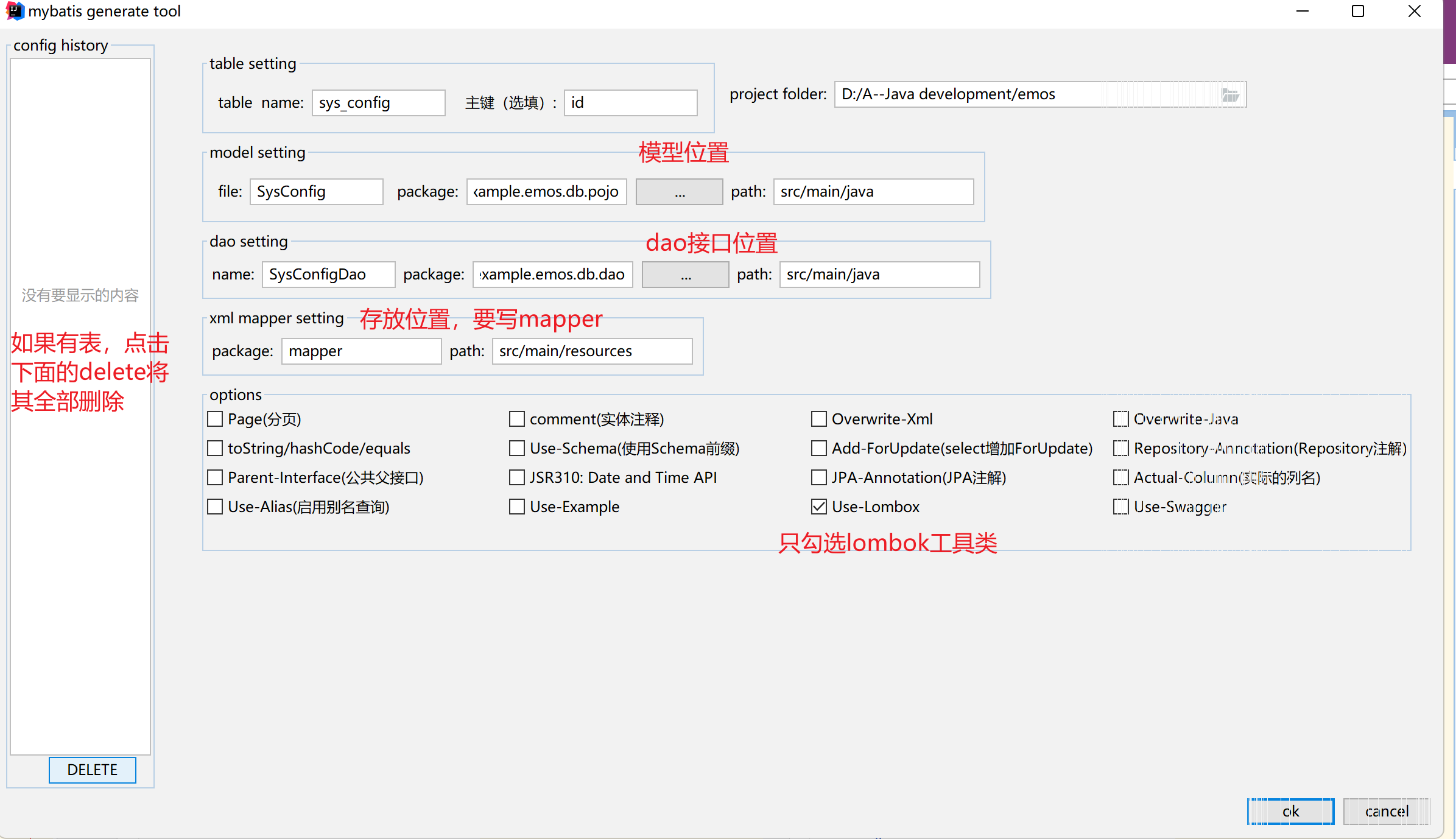
3. Add @ Mapper annotation to each Dao interface, and clear various methods in xml and Dao
4. Configure yml configuration of myBaties:
mybatis:
mapper-locations: classpath*:mapper/*.xml
type-aliases-package: com.example.mineemos.db.pojo //Path to pojo class
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl //If you want to print the SQL statement on the console, write this sentence. You don't want to delete it directly. You must delete it when the project goes online
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true //Does it support hump naming7. Configure the permissions and authentication of JWT and shiro.
To update the concise version, first look at the detailed version of another article. address