Preface
Homology strategy: judging whether it is homologous, mainly depends on these three points, protocol, ip, port.
Homology policy is a policy that browsers restrict the access of resources from different sources for the sake of website security.
For example, under the domain name https://www.baidu.com, scripts cannot access resources from https://www.sina.com, otherwise they will be intercepted by browsers.
Two points should be noted:
1. Must be script requests, such as AJAX requests.
However, cross-domain interception does not occur in the following cases
<img src="xxx"/> <a href='xxx"> </a>
2. Cross-domain interception is that the front-end request has been sent, and when the back-end returns the response, the relevant parameters are checked to see if the back-end request is allowed to receive.
In micro-service development, a system contains multiple micro-services, and there will be cross-domain request scenarios.
This article focuses on SpringBoot's solution to cross-domain request interception.
Construction project
Here we create two web projects, web1 and web2.
The web2 project requests resources for the web1 project.
Only the key code is posted here, complete code reference GitHub
WEB2
Create a Controller to return to the html page
@Slf4j @Controller public class HomeController { @RequestMapping("/index") public String home(){ log.info("/index"); return "/home"; } }
html page home.html
A button is created here, and when pressed, the resource is requested: "http://localhost:8301/hello"
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>web2</title>
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/jquery/1.10.2/jquery.min.js">
</script>
<script>
$(function () {
$("#testBtn").click(function () {
console.log("testbtn ...");
$.get("http://localhost:8301/hello",function(data,status){
alert("data: " + data + "\n state: " + status);
});
})
})
</script>
</head>
<body>
web2
<button id="testBtn">test</button>
</body>
</html>
WEB1
@Slf4j @RestController public class Web1Controller { @RequestMapping("/hello") public String hello(){ log.info("hello "); return "hello," + new Date().toString(); } }
Two projects are configured here for different ports.
WEB1 is 8301
WEB2 is 8302
So it comes from different sources.
test
In the case that web1 has not been configured to allow cross-domain access
If you press the button, there will be an error. Display that there is no Access-Control-Allow-Origin in Header
Access to XMLHttpRequest at 'http://localhost:8301/hello' from origin 'http://localhost:8300' has been blocked by CORS policy: No 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header is present on the requested resource.
WEB1 additions allow cross-domain requests by implementing WebMvcConfigurer
@Configuration public class WebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer { @Override public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) { registry.addMapping("/hello"); } }
Re-access will return normal data.
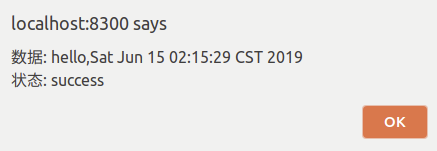
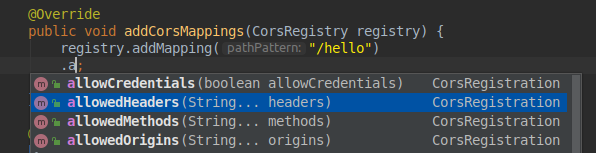
In addition to the above configurations, more detailed restrictions can be made.
For example, for the headers of the request, the method POST/GET of the request.... The source of the request is restricted.
You can also use the annotation @CrossOrigin to replace the above configuration.
@Slf4j @RestController public class Web1Controller { @CrossOrigin @RequestMapping("/hello") public String hello(){ log.info("hello "); return "hello," + new Date().toString(); } }
Annotations can be used on classes or methods, but they must be controller classes
Configuration, like the above, can also personalize methods, header s, and sources.
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface CrossOrigin { /** @deprecated */ @Deprecated String[] DEFAULT_ORIGINS = new String[]{"*"}; /** @deprecated */ @Deprecated String[] DEFAULT_ALLOWED_HEADERS = new String[]{"*"}; /** @deprecated */ @Deprecated boolean DEFAULT_ALLOW_CREDENTIALS = false; /** @deprecated */ @Deprecated long DEFAULT_MAX_AGE = 1800L; @AliasFor("origins") String[] value() default {}; @AliasFor("value") String[] origins() default {}; String[] allowedHeaders() default {}; String[] exposedHeaders() default {}; RequestMethod[] methods() default {}; String allowCredentials() default ""; long maxAge() default -1L; }