Usage scenario
In some business scenarios, after a series of actions such as initialization, restart and shutdown of the Serverlet container, some operations need to be processed, such as loading some data, initializing the cache, registering specific tasks, and so on. At this time, we can use the ApplicationListener provided by Spring to operate.
principle
ApplicationListener is an interface with only one onApplicationEvent method. The parameter of the method is ApplicationEvent. ApplicationEvent is an abstract class. As the name suggests, it is some events of Spring applications. ApplicationEvent has an abstract subclass ApplicationContextEvent. The implementation class of ApplicationContextEvent is used here. View the implementation classes of the ApplicationContextEvent document, including ContextClosedEvent, ContextRefreshedEvent, ContextStartedEvent, ContextStoppedEvent , these four are the core implementations in the spring context package:
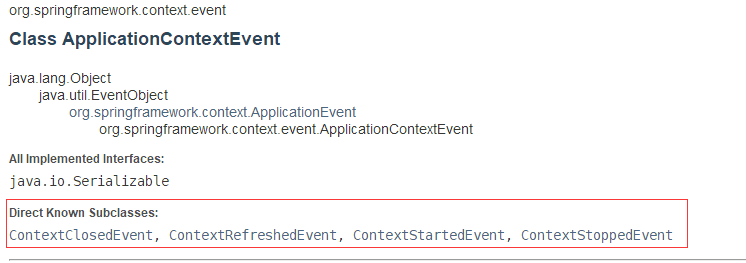
ApplicationEvent
|-ApplicationContextEvent
| - ContextClosedEvent: application shutdown event
| - ContextRefreshedEvent: apply refresh event
| - ContextStartedEvent: application startup event
| - ContextStoppedEvent: application stop event
In addition, spring boot extends two implementations:
Embeddedservlet containerinitializedevent: embedded Servlet container initialization event
ApplicationReadyEvent: spring Application startup completion event
usage
This article takes the use of Spring boot as an example. First, you need to implement the ApplicationListener interface and the onApplicationEvent method. Put the operations to be processed in onApplicationEvent for processing:
package com.example.springbootlistener.listener;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationReadyEvent;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.context.event.ContextClosedEvent;
import org.springframework.context.event.ContextRefreshedEvent;
import org.springframework.context.event.ContextStartedEvent;
import org.springframework.context.event.ContextStoppedEvent;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* <p>
* Title: AppApplicationListener
* </p>
* <p>
* Description:
* </p>
* <p>
* Copyright: Copyright (c) 2020
* </p>
* <p>
* </p>
*
* @Auther: cw
* @Date: 2021/12/31 13:23
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class AppApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
log.info("+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++");
// Container start
if (event instanceof ContextStartedEvent){
log.info("================:{}", "ContextStartedEvent");
}
// Container refresh
if (event instanceof ContextRefreshedEvent){
log.info("================:{}", "ContextRefreshedEvent");
}
// Container closed
if (event instanceof ContextClosedEvent){
log.info("================:{}", "ContextClosedEvent");
}
// Container stop
if (event instanceof ContextStoppedEvent){
log.info("================:{}", "ContextStoppedEvent");
}
// Container ready, personal understanding is to start and complete
if (event instanceof ApplicationReadyEvent){
log.info("================:{}", "ApplicationReadyEvent");
}
log.info(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>:{}\n", event.getClass().getName());
}
}
Startup operation results:
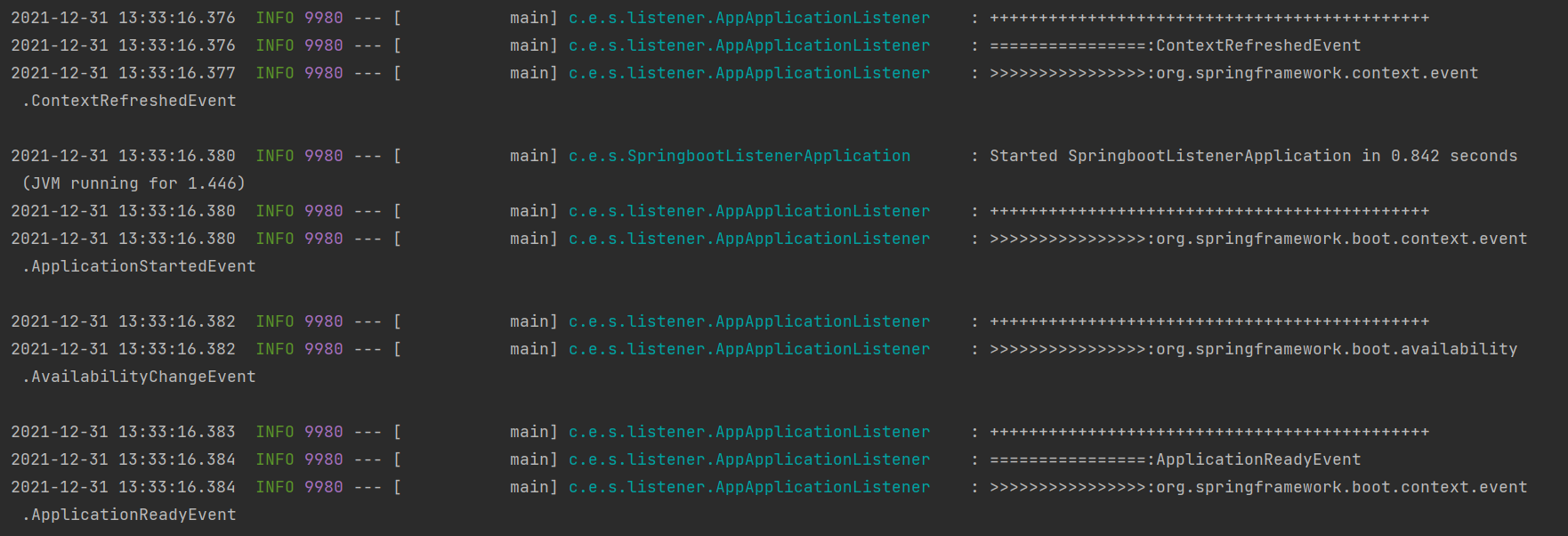
Close run result:

Secondary call problem
Spring boot is used for operation here, and there is no problem of secondary call. Using traditional ApplicationContext XML and project servlet There will be a problem of secondary call in XML configuration. The main reason is that after initializing the root container, the project servlet will be initialized The sub container corresponding to XML. What we need is to execute it only once. Then print the code of the parent container above to judge and exclude the child container. Add the following judgment before business processing:
if(contextRefreshedEvent.getApplicationContext().getParent() != null){
return;
}In this way, the initialization of other containers will be returned directly, and the corresponding business operations will be executed when the Parent container (container with null Parent) is started.
Related knowledge
In spring, the InitializingBean interface provides similar functions, but it is called only after all beans have been instantiated. Different schemes can be selected according to different business scenarios and requirements.
Code address:
https://gitee.com/yulanzhilian.com/mycroot.git https://gitee.com/yulanzhilian.com/mycroot.git
https://gitee.com/yulanzhilian.com/mycroot.git