1, Cache agent
As an application layer proxy service software, Squid mainly provides cache acceleration and application layer filtering control functions.
① Working mechanism of agency
When a client requests a Web page through a proxy, the specified proxy server will first check its own cache. If there are pages needed by the client in the cache, the contents of the pages in the cache are directly fed back to the client. If there is no page to be accessed by the client in the cache, the proxy server sends an access request to the Internet. After obtaining the returned Web page, the Web page data is saved in the cache and sent to the client,
- The cache acceleration objects of HTTP proxy are mainly static Web elements such as text and image.
- After using the caching mechanism, when clients access the same Web element at different times, or different clients access the same Web element, the results can be obtained directly from the cache of the proxy server.
- This greatly reduces the process of submitting repeated Web requests to the Internet and improves the Web access response speed of the client.
- Because the Web access request of the client is actually completed by the proxy server, it can hide the user's real IP address and play a certain protective role.
- On the other hand, the proxy server acts as a "broker", which can filter and control the target to be accessed, the address of the client, the access time period, etc.
② Basic types of agents
According to different implementation methods, proxy services can be divided into traditional proxy and transparent proxy.
- Traditional proxy: that is, ordinary proxy service. First, you must manually set the address and port of the proxy server in the client's browser, QQ chat tool, download software and other programs, and then you can use the proxy to access the network. For web browsers, the domain name resolution request when accessing the website will also be sent to the designated proxy server
- Transparent proxy: it provides the same functions and services as the traditional proxy. The difference is that the client does not need to specify the address and port of the proxy server, but redirects Web access through the default route and firewall policy, which is still handed over to the proxy server. The redirection process is "transparent" to the client. Users do not even know that they are using the proxy service, so it is called transparent proxy. When using transparent proxy, the domain name resolution request when the Web browser accesses the website will be sent to the DNS server first.
🐎 In practical applications, * * traditional agents are common in the Internet environment, * * if you use agents for QQ programs, you can hide the real IP address of the machine, and if you use multiple agents for download tools, you can avoid the concurrent connection restrictions of the server.
🐎 Transparent agents are more common in LAN environment. For example, after enabling transparent agents in Linux gateway, LAN hosts can enjoy better Internet speed without additional settings.
2, Pre configuration of Squid proxy server
1. Compile and install Squid
Installation dependent environment
yum -y install gcc gcc-c++ make
#Transfer the installation package to the / opt directory and unzip it
cd /opt
tar zxvf squid-3.5.27.tar.gz cd squid-3.5.27/ ./configure \ --prefix=/usr/local/squid \ --sysconfdir=/etc/ \ --enable-arp-acl \ --enable-linux-netfilter \ --enable-linux-tproxy \ --enable-async-io=100 \ --enable-err-language="Simplify_Chinese" \ --enable-underscore \ --enable-poll \ --enable-gnuregex

---------------------------------------------------------- ./configure \ --prefix=/usr/local/squid \ #Installation directory --sysconfdir=/etc/ \ #Separately, modify the configuration file to the / etc directory --enable-arp-acl \ #The MAC address can be set in the ACL for management to prevent IP spoofing --enable-linux-netfilter \ #Using kernel filtering --enable-linux-tproxy \ #Support transparent mode --enable-async-io=100 \ #Asynchronous I/O to improve storage performance. The value can be modified --enable-err-language="Simplify_Chinese" \ #Display language of error message --enable-underscore \ #Allow underscores in URL s --enable-poll \ #Use Poll() mode to improve performance --enable-gnuregex #Using GNU regular expressions ---------------------------------------------------------
Compile and install
make && make install
#Create linked files and optimize paths
ln -s /usr/local/squid/sbin/* /usr/local/sbin #Create linked files and optimize paths

**#Create program users, groups** useradd -M -s /sbin/nologin squid **#Change directory ownership** chown -R squid:squid /usr/local/squid/var/
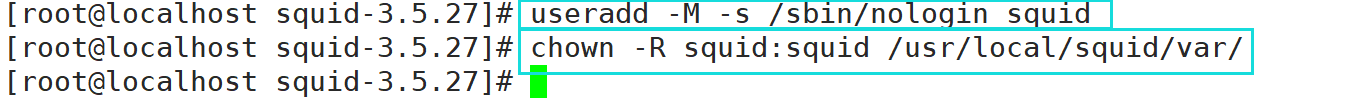
2. Modify Squid's configuration file
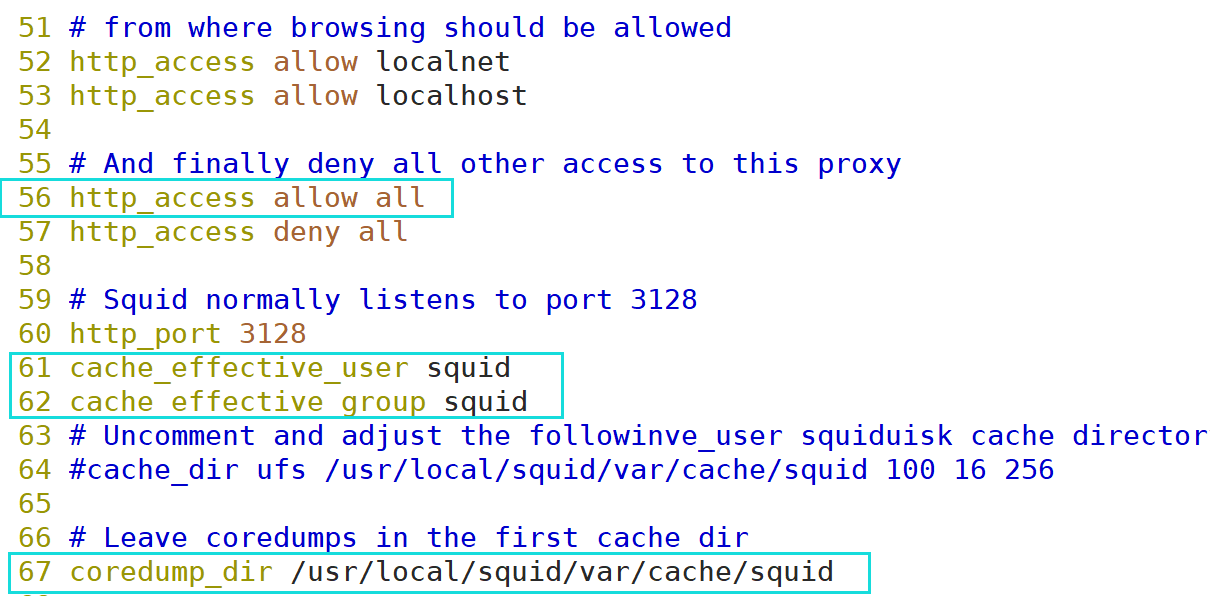
vim /etc/squid.conf ----56 that 's ok--insert------ http_access allow all #Put on HTTP_ Before access deny all, any client is allowed to use the proxy service to control the top-down matching of rules http_access deny all http_port 3128 #Used to specify the address and port that the proxy service listens to (the default port number is 3128) ----61 that 's ok--insert------ cache_effective_user squid #Add, specify the program user, which is used to set the account of initialization and runtime cache. Otherwise, the startup will not succeed cache_effective_group squid #Add, specify account basic group coredump_dir /usr/local/squid/var/cache/squid #Specify cache file directory #Check configuration file squid -k parse #Initialize cache directory squid -zX #service squid start squid #Confirm that squid service is in normal listening state netstat -napt | grep squid

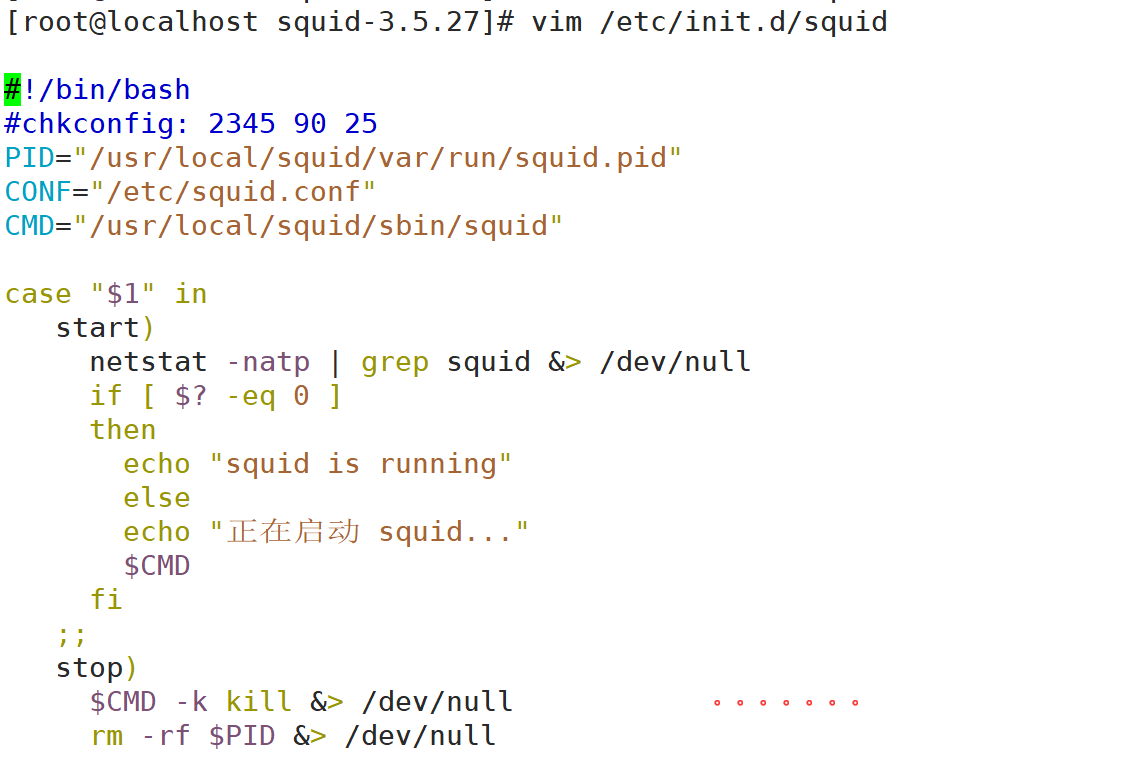
3. Write Squid service script
vim /etc/init.d/squid
#!/bin/bash
#chkconfig: 2345 90 25
PID="/usr/local/squid/var/run/squid.pid"
CONF="/etc/squid.conf"
CMD="/usr/local/squid/sbin/squid"
case "$1" in
start)
netstat -natp | grep squid &> /dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ]
then
echo "squid is running"
else
echo "Starting squid..."
$CMD
fi
;;
stop)
$CMD -k kill &> /dev/null
rm -rf $PID &> /dev/null
;;
status)
[ -f $PID ] &> /dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ]
then
netstat -natp | grep squid
else
echo "squid is not running"
fi
;;
restart)
$0 stop &> /dev/null
echo "Closing squid..."
$0 start &> /dev/null
echo "Starting squid..."
;;
reload)
$CMD -k reconfigure
;;
check)
$CMD -k parse
;;
*)
echo "Usage: $0{start|stop|status|reload|check|restart}"
;;
esac
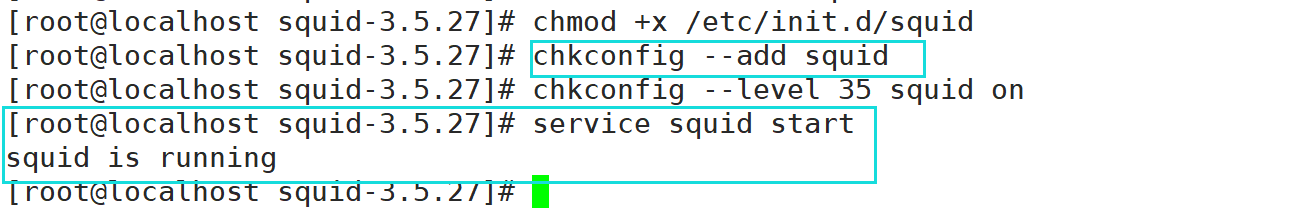
chmod +x /etc/init.d/squid chkconfig --add squid chkconfig --level 35 squid on #Specify the service startup level. 3 is the character interface and 5 is the graphical interface service squid restart #Test service
3, Experiment
Server requirements:
Squid server 192.168.17.99
web1 server 192.168.17.66
web2 server 192.168.17.33
win10 192.168.17.100
-----------------------------------Build traditional agent-----------------------------------
1. squid server
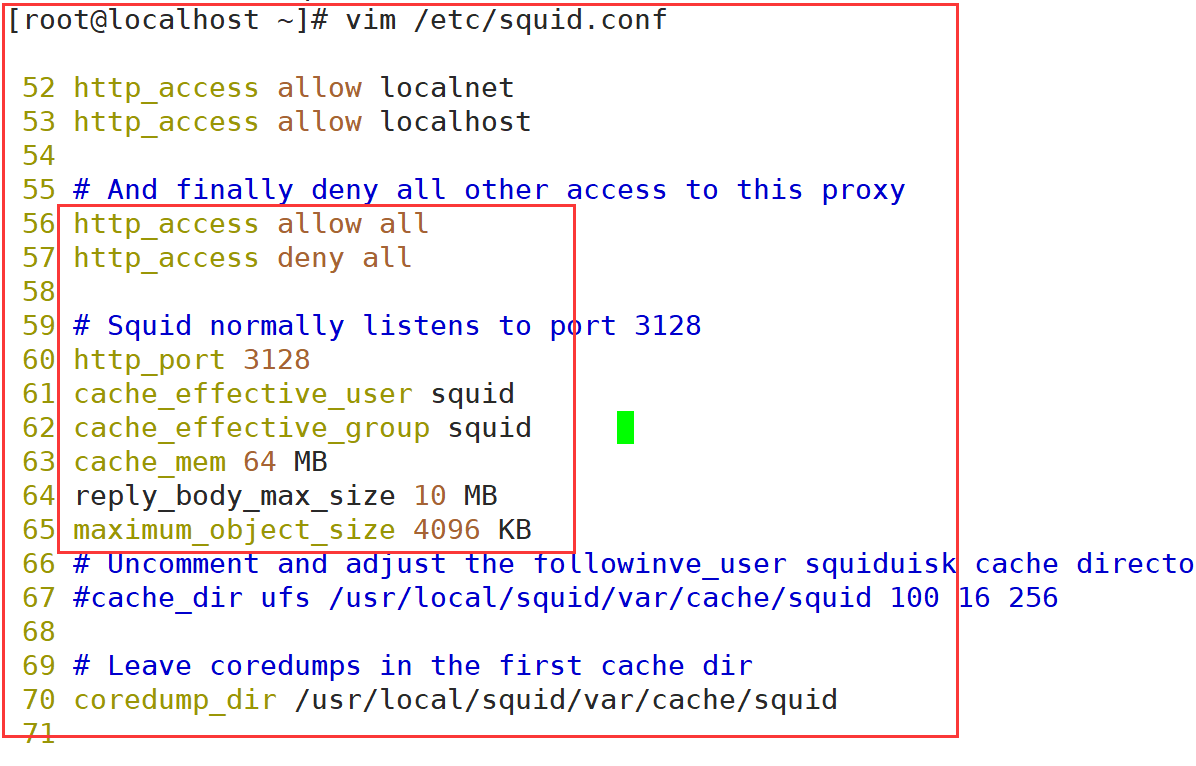
vim /etc/squid.conf http_access allow all http_access deny all http_port 3128 cache_effective_user squid cache_effective_group squid #63 line insert cache_mem 64 MB #Specify the memory space used by the cache function to maintain frequently accessed WEB objects. The capacity is preferably a multiple of 4, in MB. It is recommended to set it to 1 / 4 of the physical memory reply_body_max_size 10 MB #The maximum file size that users are allowed to download, in bytes. When downloading a Web object that exceeds the specified size, a prompt "request or access too large" will appear on the error page of the browser. The default setting is 0, which means no restriction maximum_object_size 4096 KB #The maximum object size allowed to be saved to the cache space, in kilobytes. Files exceeding the size limit will not be cached, but will be forwarded directly to the user #Modify firewall rules iptables -F iptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 3128 -j ACCEPT

2. Web1 configuration
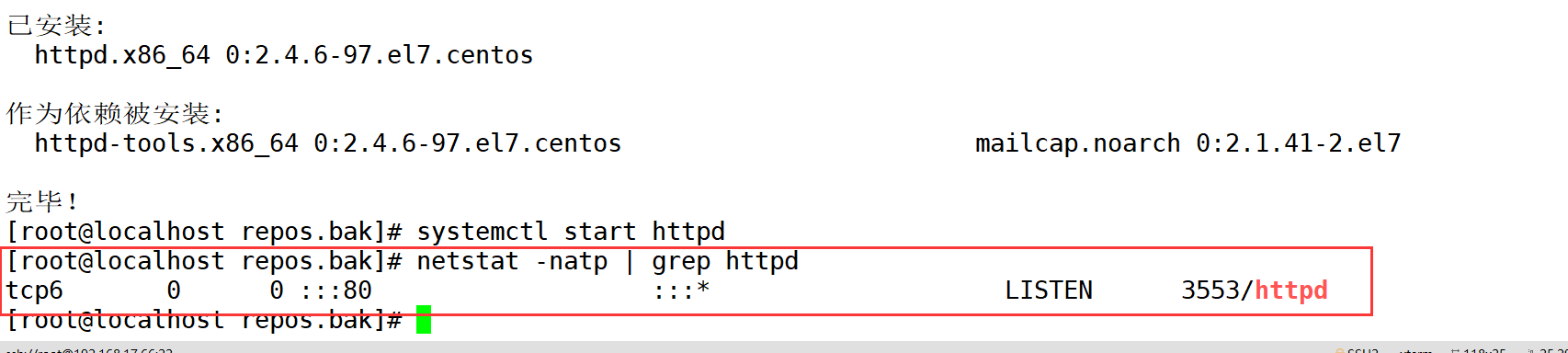
systemctl stop firewalld.service setenforce 0 yum -y install httpd systemctl start httpd netstat -natp | grep 80
3. Client configuration (add agent)
Google browser: set up-->senior-->system-->Open proxy settings-->Set agent #Accessing web2 IP using win10 #Viewing access log information on web2 server #Dynamically view the access log and observe the access IP tail -f /var/log/httpd/access_log
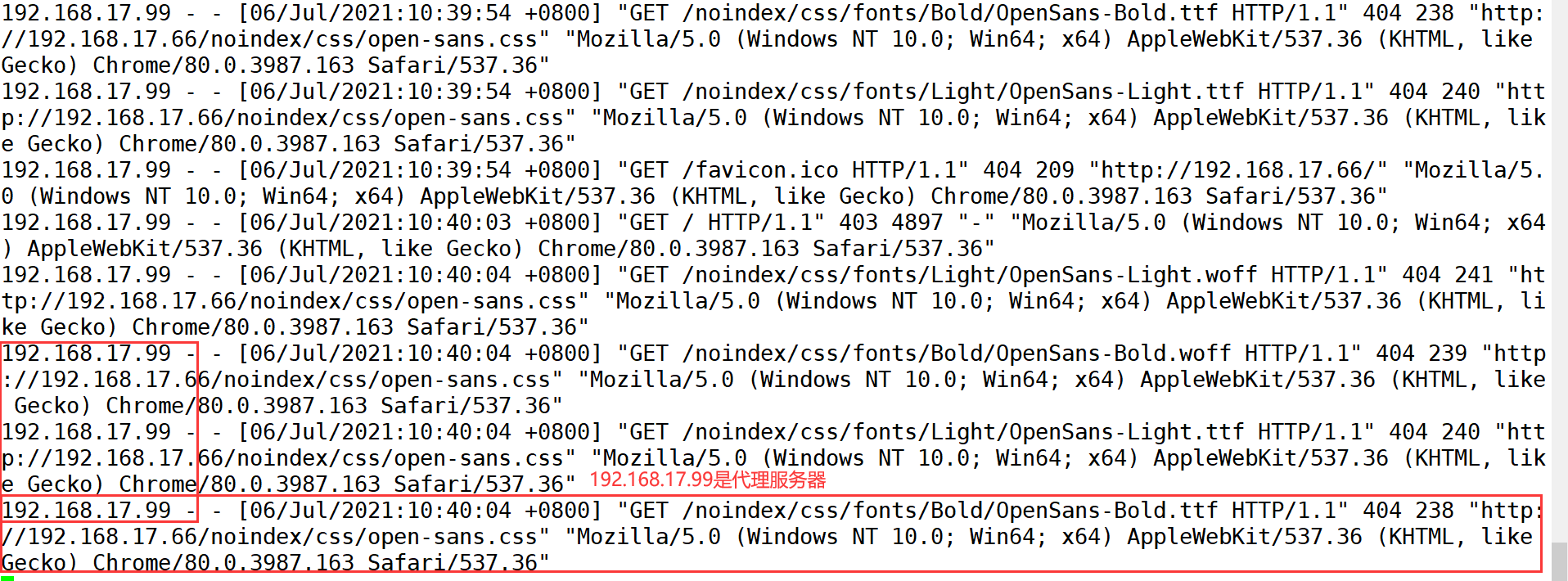
---------------------------------Transparent proxy----------------------------------------
1. Squid server configuration
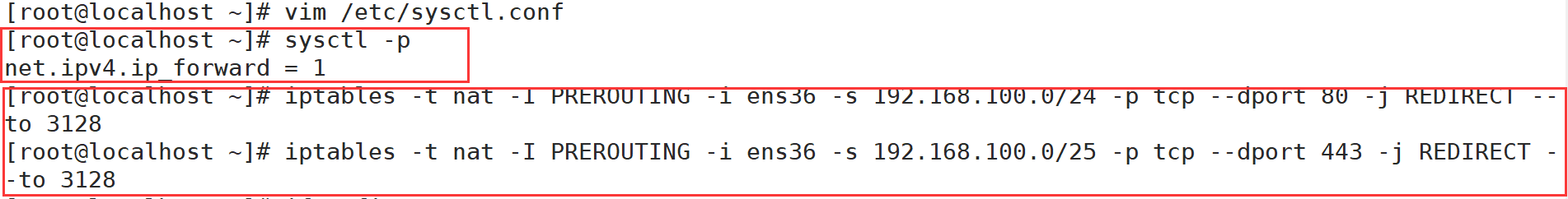
cd /etc/ sysconfig/network-scripts/ cp ifcfg-ens33 ifcfg-ens36 vim ifcfg-ens36 systemctl restart network #In line 60, modify and add the IP address that provides intranet services, and support the transparent proxy option transparent vim /etc/ squid.conf http_access allow all http_access deny all http_port 192.168.17.99:3128 transparent systemctl restart squid echo 'net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1' >> /etc/sysctl.conf sysctl -P iptables -F iptables -t nat - F #Add firewall rules (redirect traffic from 100 network segment: port 80 / 443 to port 3128) iptables -t nat -I PREROUTING -i ens36 -s 192.168.100.0/24 -p tcp --dport 80 -j REDIRECT --to 3128 iptables -t nat -I PREROUTING -i ens36 -s 192.168.100.0/24 -p tcp --dport 443 -j REDIRECT --to 3128 #To restart, you need to configure the following rules iptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 3128 -j ACCEPT
2. web1 server adds a - static route
route add -net 192.168.17.0/24 gw 12.0.0.100

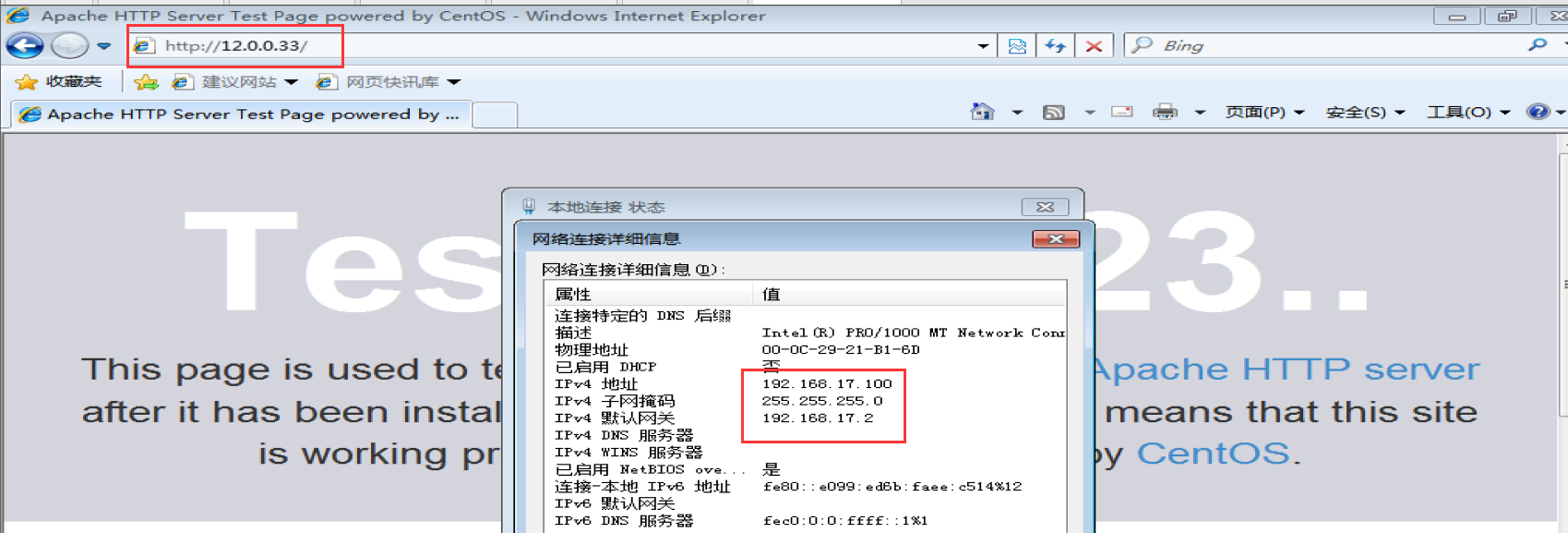
3. The client closes the proxy and modifies the win10 address to 100 network segment
#Access web1 server tail -f /var/log/httpd/access_log #It can be seen from the log content that the proxy server external network port 12.0.0.1 accesses the web server 12.0.0.12
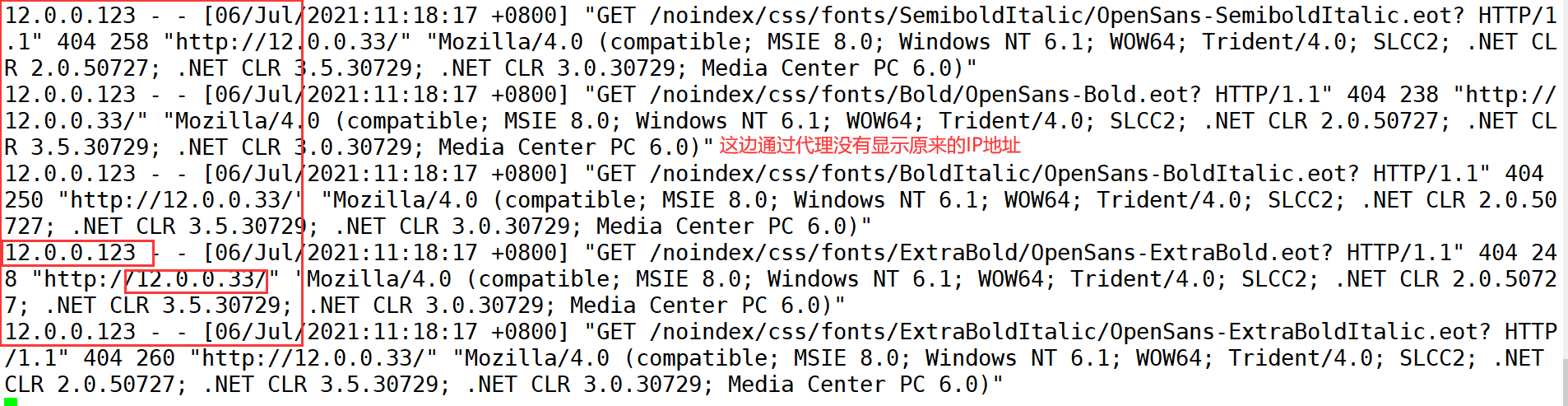
---------------------------------Reverse proxy----------------------------------------
If the requested resource is cached in the squid reverse proxy server, it will directly return the requested resource to the client. Otherwise, the reverse proxy server will request the resource from the background web server, and then return the requested response to the client. At the same time, it will also cache the response locally for use by the next requester.
Working mechanism:
🐎 Cache web page objects to reduce duplicate requests.
🐎 Internet requests are polled or weighted to intranet web servers.
🐎 Acting on the user's request, avoiding the user's direct access to the web server and improving security.
Turn on firewall and turn off local httpd systemctl stop firewalld systemctl stop httpd iptables -F iptables -t nat -F iptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 3128 -j ACCEPT
vim /etc/squid.conf ------ 60 that 's ok--modify,insert------- http_port 192.168.17.99:80 accel vhost vport cache_peer 192.168.17.66 parent 80 0 no-query originserver round-robin max_conn=30 weight=1 name=web1 cache_peer 192.168.17.133 parent 80 0 no-query originserver round-robin max_conn=30 weight=1 name=web2 cache_peer_domain web1 web2 www.kgc.com #For www.kgc.com COM, squid sends a request to port 80 of 192.168.17.66 and 192.168.17.133 http_port 80 accel vhost vport #Squid has changed from a cache to a web server reverse proxy acceleration mode. At this time, squid listens to requests on port 80 and binds to the request Vhost vport of webserver. At this time, squid does not need to forward requests. Instead, it directly needs to take data from the cache or directly request data from the bound port.
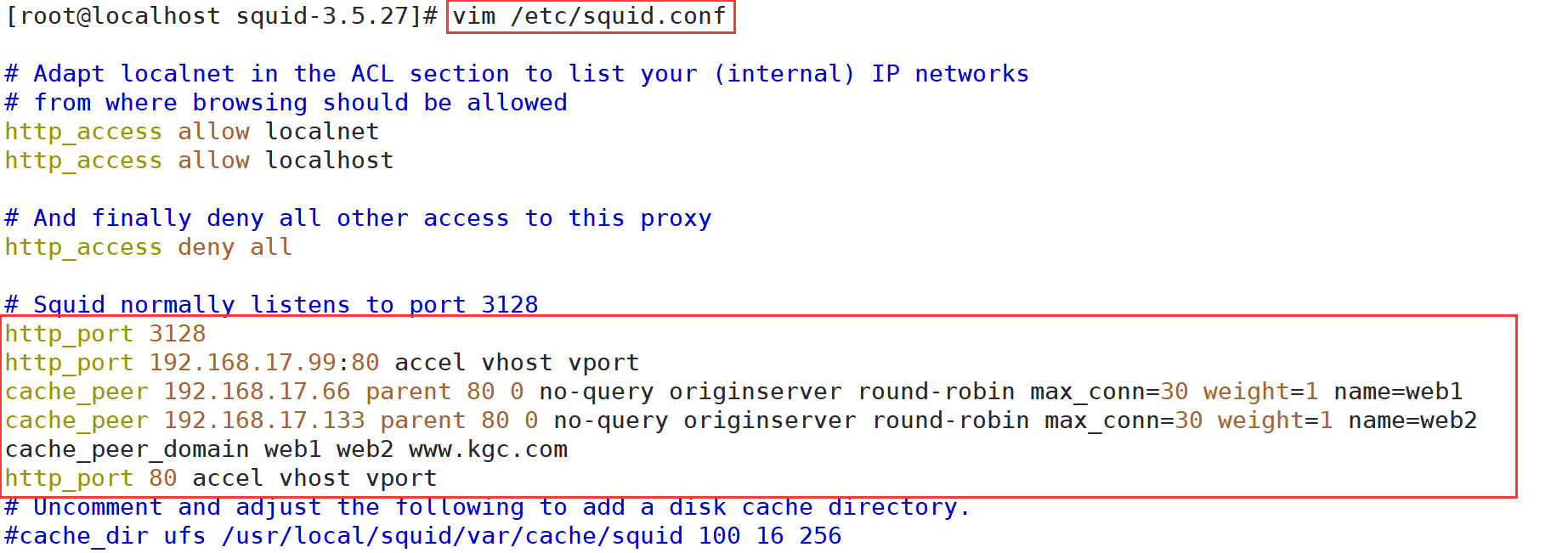
accel:Reverse proxy acceleration mode
vhost:Support domain name or host name to represent proxy node
vport:support IP And port to represent the proxy node
parent:Represents the parent node, the parent node, the parent node, the parent node, the parent node, and the parent node
80:Agent internal web Port 80 of the server
0:Not used icp,It means only one squid The server
no-query :Get data directly without query
oriainserver :Specify source server
systemctl stop httpd
service squid reload
#Back end web 2 node server settings
yum install -y httpd systemctl start httpd
#Node 1(web1):
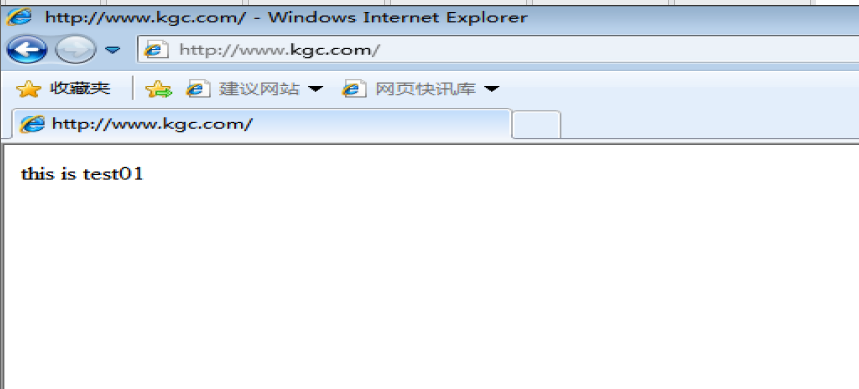
echo "this is test01" >> /var/ www / html/index.html

#Node 2(web2):
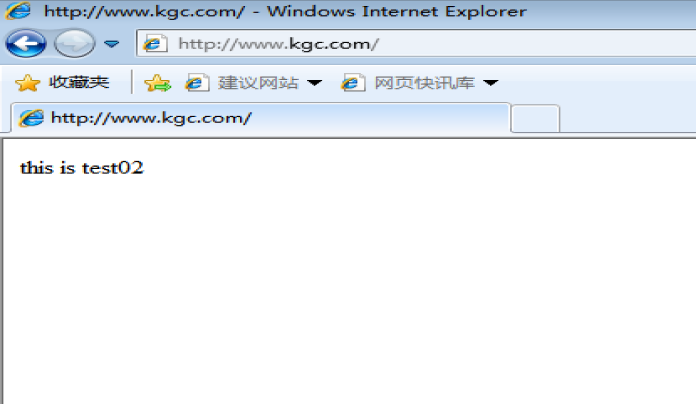
echo "this is test02" >> /var/ www / html/ index.html

#Domain name mapping configuration of the client
modify c: \windows \System32\drivers\etc\hosts File 192.168.17.99 www.kgc.com
4, Squid log analysis
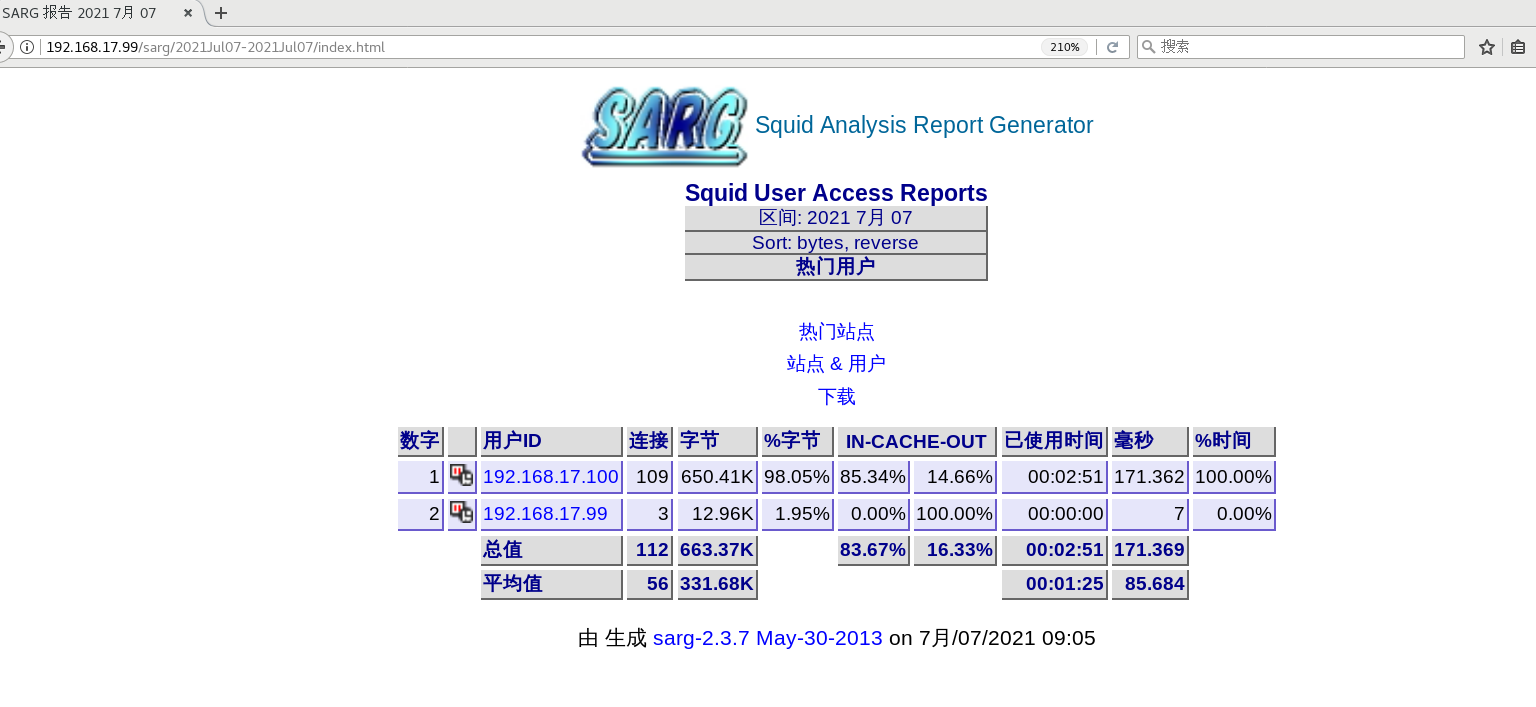
Sarg (SQUID analysis report generator) is a squid log analysis tool, which uses HTML format to list in detail the site information, time occupation information, ranking, connection times, traffic, etc. of each user accessing the Internet
#Install image processing package
yum install -y gd gd-devel pcre-devel mkdir /usr/local/sarg
#Put zxvf sarg-2.3.7 tar. Upload GZ compressed package to / opt directory
tar zxvf sarg-2.3.7.tar.gz -C /opt/ cd /opt/sarg-2.3.7 ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/sargk \ --sysconfdir=/etc/sarg \ #The configuration file directory is / usr/loca/etc by default --enable-extraprotection #Additional safety protection ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/sarg --sysconfdir=/etc/sarg --enable-extraprotection -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- make && make install
#x modify configuration file
vim /etc/sarg/sarg.conf --7 that 's ok--note off access_log /usr/local/squid/var/logs/access.1og #Specify access log file --25 that 's ok--note off title "Squid User Access Reports" #Page title -- 120 that 's ok--Uncomment, modify output_dir /var/www/html/sarg #Report output directory --178 that 's ok--note off user_ip no #Display with user name --184 that 's ok--Uncomment, modify topuser_sort_field connect reverse #In top sorting, the specified connection times are arranged in descending order, and the ascending order is normal -- 190 that 's ok--Uncomment, modify user_sort_field connect reverse #For user access records, the number of connections is sorted in descending order --206 that 's ok--Uncomment, modify exclude_hosts /usr/local/sarg/noreport #Specifies files that are not included in the sorted site list --257 that 's ok--note off overwrite_report no #Overwrite logs with the same name and date --289 that 's ok--Uncomment, modify mail_utility mailq.postfix #Send mail report command --434 that 's ok--Uncomment, modify charset UTF-8 #Specifies the character set UTF-8 --518 that 's ok--note off weekdavs 0-6 #Week cycle of top ranking --525 that 's ok--note off hours 0-23 #Time period of top ranking --633 that 's ok--note off www_document_root /var/www/html #Specify page root
#Add is not included in the site file, and the added domain name will not be displayed in the sorting
touch /usr/local/sarg/noreport
sarg --help #get help #function sarg #Start a record #verification yum install httpd -y systemctl start httpd stay squid Use browser access on the server http://192.168.17.99/sarg, check the Sarg report page.

#Add scheduled tasks to perform daily report generation vim /usr/local/sarg/report.sh #/bin/bash #Get current date TODAY=$(date +%d/%m/%Y) #Get one week ago today YESTERDAY=$(date -d "1 day ago" +%d/%m/%Y) /usr/local/sarg/bin/sarg -l /usr/1ocal/squid/var/logs/access.log -o /var/www/html/sarg -z -d $YESTERDAY-$TODAY &> /dev/null exit 0 chmod +x /usr/local/sarg/report.sh crontab -e 0 0*** /usr/1ocal/sarg/report.sh
5, ACL access control
In the configuration file squid In conf, ACL access control is realized through the following two steps:
Use acl configuration items to define the conditions to be controlled; Via http_ The access configuration item allows or denies access to the defined list.
1. Define access control lists
Format:
acl list name list type list content
List name: custom name, which is equivalent to giving acl a name
List type: the predefined value of squid must be used to correspond to different categories of control conditions
List content: it is the specific object to be controlled. The corresponding contents of different types of lists are different. There can be multiple values (separated by spaces and the relationship of "or")
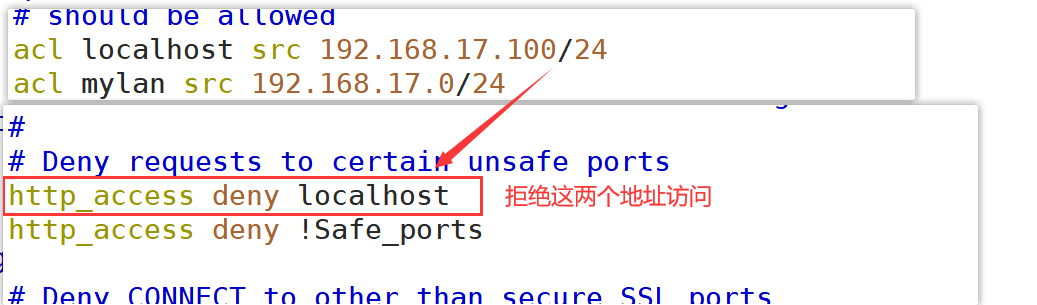
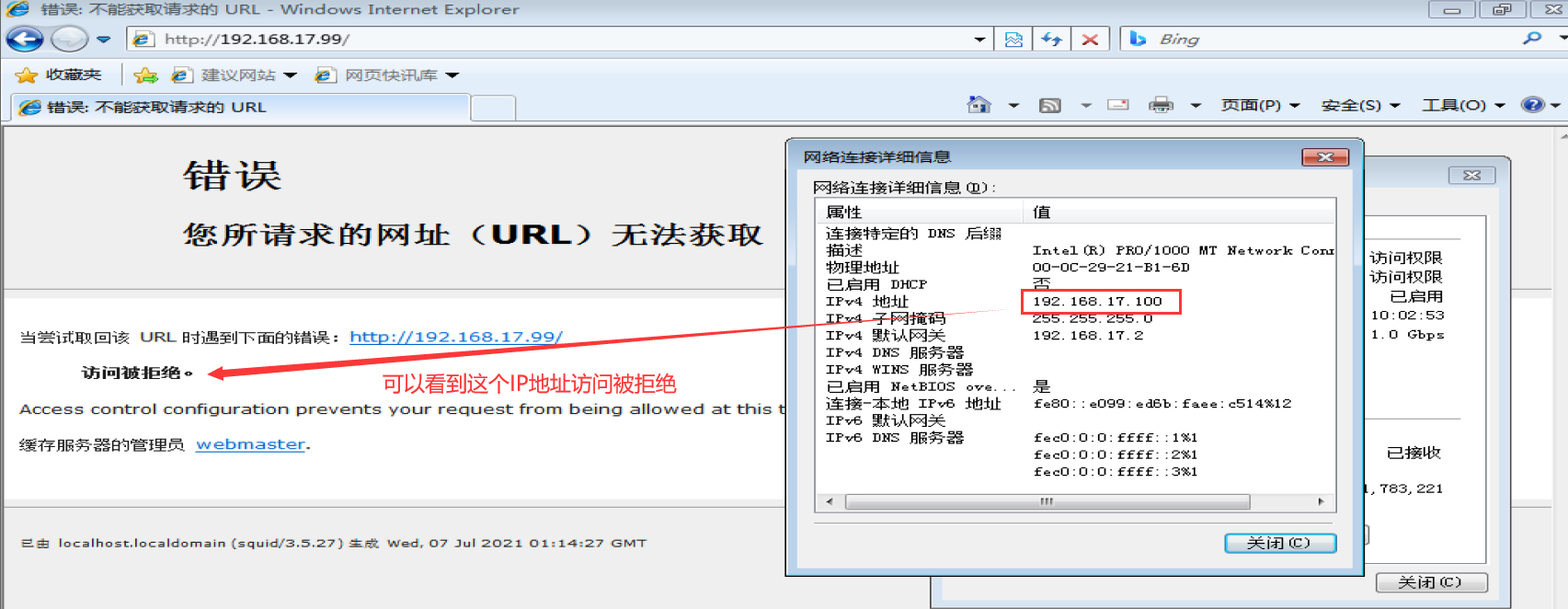
acl localhost src 192.168.17.100/24 #The source address is 192.168.184.10 acl MYLAN src 192.168.17.0/24 #Client network segment acl destinationhost dst 192.168.226.129/32 #The destination address is 192.168.184.20 acl MC20 maxconn 20 #Maximum concurrent connections 20 acl PORT port 21 #Target port 21 acl DMBLOCK dstdomain .qq.com #Target domain, matching all sites in the domain acl BURL url_regex -i ^rtsp:// ^emule:// # with rtsp://.emule:// At the beginning of the URL, - i means case is ignored acl PURL urlpath_regex -i \.mp3$ \.mp4$ \.rmvb$ #With mp3.,. mp4,. URL path at the end of rmvb acl WORKTIME time MTWHF 08:30-17:30 #The time is from 8:30 to 17:30 from Monday to Friday, "MTWHF" is the English initials of each week Article 1 insert: http_access deny host Method 2: #Start object list management mkdir /etc/squid vim /etc/squid/dest.list 192.168.226.129 #Squid server IP 192.168.226.0/24 #Any required network segment vim /etc/ squid.conf acl destinationhost dst "/etc/squid/dest.list" #Call the contents of the list in the specified file http access deny(or allow) destinationhost #Note that if it is a rejection list, it needs to be placed in http_ access allow all systemctl restart squid