The first
3
chapter
AOP
Aspect oriented programming
AOP
brief introduction
AOP
(
Aspect Orient Programming
), aspect oriented programming. Aspect oriented programming is considered from a dynamic point of view
Sequence operation process.
AOP
The bottom layer is realized by using dynamic agent mode. Two agents are used:
JDK
Dynamic proxy for
, and
CGLIB
Dynamic proxy for
.
(
AOP
by
The abbreviation of Aspect Oriented Programming, which means: Aspect Oriented Programming, which can be dynamically programmed through runtime
Agent is a technology to realize the unified maintenance of program functions.
AOP
yes
Spring
An important part of the framework. utilize
AOP
Each part of the business logic can be isolated, so that the coupling degree between each part of the business logic can be reduced and the process can be improved
The reusability of the sequence and the efficiency of development are improved.)
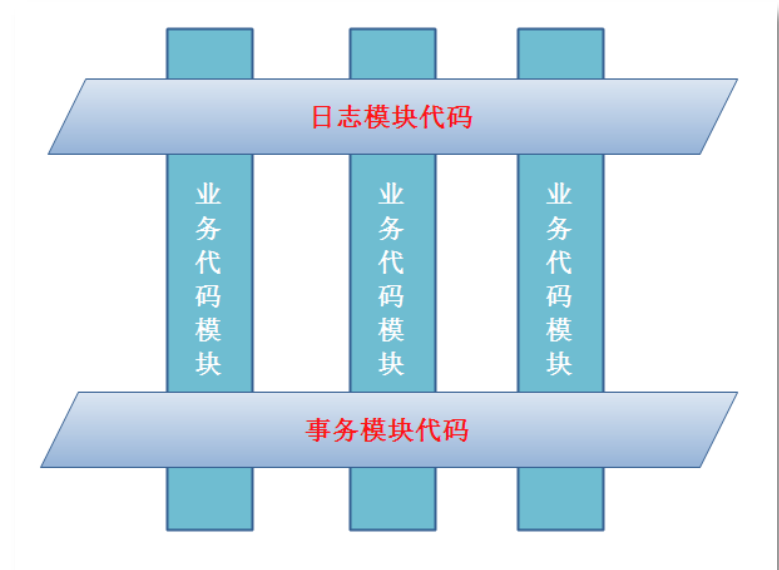
Aspect oriented programming is to encapsulate cross business logic into aspects and use
AOP
The function of the container is to weave the cut into
In the main business logic. The so-called cross business logic refers to the code that is general and irrelevant to the main business logic, such as security check
Transactions, logs, caches, etc.
If not used
AOP
, code entanglement will occur, that is, cross business logic and main business logic are mixed together. So,
It will confuse the main business logic.
For example, before and after the real transfer business logic, transfer requires permission control, logging, loading transactions and ending transactions
Business logic and other cross business logic, and these business logic are not directly related to the main business logic. However, the proportion of their code
The proportion can reach half or more of the total code. Their existence not only produces a large number of "redundant" codes, but also a large number of codes
It greatly interferes with the main business logic
---
transfer accounts.
What are the benefits of aspect oriented programming for?
1.
Reduce duplication;
2.
Focus on business;
Note: aspect oriented programming is only a supplement to object-oriented programming.
use
AOP
Reduce duplicate code and focus on business implementation:
AOP
Programming terminology
(
master
)
(
1
)Section(
Aspect
)
Aspect generally refers to cross business logic. The transaction processing and log processing in the above example can be understood as aspects. Common section
It's a notice(
Advice
). In fact, it is an enhancement of the main business logic.
(
2
)Connection point(
JoinPoint
)
Connection point refers to the specific method that can be woven by cutting. Generally, the methods in the business interface are connection points.
(
3
)Entry point(
Pointcut
)
A pointcut is a collection of one or more declared join points. Specify a set of methods through pointcuts.
Marked as
final
Methods cannot be used as join points and pointcuts. Because the final can't be modified, No
Can be enhanced.
(
4
)Target object(
Target
)
The target object is the object to be enhanced. That is, the object of the class containing the main business logic. In the above example
StudentServiceImpl
If the object of is enhanced, this class is called the target class, and this class of object is called the target object. of course,
Without enhancement, there is no goal.
(
5
)Notice(
Advice
)
The notification indicates the execution time of the section,
Advice
Also called enhancement. In the above example
MyInvocationHandler
You can manage it
It is a kind of notice. On the other hand,
The notification defines the point in time when the enhancement code cuts into the target code
, is the target
Before or after the implementation of the law. Different notification types lead to different cut in times.
The pointcut defines the location of the pointcut and notifies the time of the pointcut
.
AspectJ
yes
AOP
Implementation of
(
master
)
about
AOP
Many frameworks have implemented this programming idea.
Spring
Is one of them, which can complete the oriented
Section programming. However,
AspectJ
Also achieved
AOP
And its implementation method is simpler and more convenient to use,
It also supports annotated development. So,
Spring
Will again
AspectJ
For
AOP
The implementation of is also introduced into its own box
In the rack.
stay
Spring
Used in
AOP
When developing, it is generally used
AspectJ
Implementation of.
AspectJ
brief introduction
(
AspectJ
Is an excellent aspect oriented framework that extends
Java
Language, which provides a powerful aspect implementation.)
Official website address:
http://www.eclipse.org/aspectj/
AspetJ
yes
The open source project of Eclipse is introduced on the official website as follows:
a seamless aspect-oriented extension to the Javatm programming language
(a) based on
Java
Aspect oriented programming language for platform)
Java platform compatible
(compatible)
Java
Platform, which can be expanded seamlessly)
easy to learn and use
(easy to learn and use)
AspectJ
Notification type
(
understand
)
AspectJ
There are five types of notifications commonly used in:
(
1
)Advance notice
(
2
)Post notification
(
3
)Surround notification
(
4
)Exception notification
(
5
)Final notice
AspectJ
Pointcut expression for
(
master
)
AspectJ
A special expression is defined to specify the pointcut. The prototype of the expression is:
execution(modifiers-pattern? ret-type-pattern declaring-type-pattern?name-pattern(param-pattern) throws-pattern?)
Explanation:
modifiers-pattern]
Access type
ret-type-pattern
return type
declaring-type-pattern
Package name class name
name-pattern(param-pattern)
Method name
(
Parameter type and number
)
throws-pattern
Throw exception type
? Represents an optional part
The above expressions are
4
There are two parts.
execution(
Access rights
Method return value method declaration
(
parameter
)
Exception type
)
The object to be matched by the pointcut expression is the method name of the target method. So,
execution
It is obvious that
Is the signature of the method. Note that the black text in the expression indicates the parts that can be omitted, and the parts are separated by spaces. In which
To use the following symbols:

give an example:
execution(public * *(..))
The specified pointcut is: any public method.
execution(* set*(..))
Specify the pointcut as: any one with“
set"
How to start.
execution(* com.xyz.service.*.*(..))
The specified pointcut is: defined in
service
Any method of any class in the package.
execution(* com.xyz.service..*.*(..))
The specified pointcut is: defined in
service
Any method of any class in a package or sub package. “
.."
When it appears in the class name, after
The face must follow“
*
”, representing all classes under the package and sub package.
execution(* *..service.*.*(..))
Specify all packages
serivce
All methods in all classes (interfaces) under the sub package are pointcuts
AspectJ
New development environment
(
master
)
(
1
)
maven
rely on
<dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.11</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.2.5.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId> <version>5.2.5.RELEASE</version> </dependency> plug-in unit <build> <plugins> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.1</version> <configuration> <source>1.8</source> <target>1.8</target> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build>
(
2
)Introduce
AOP
constraint
In
AspectJ
realization
AOP
To import
AOP
Constraints. Used in the configuration file
AOP
Labels in constraints,
Both
AspectJ
The framework uses, not
Spring
The framework itself is being implemented
AOP
Used when.
AspectJ
about
AOP
There are two ways to implement annotation and configuration file, commonly annotation.
AspectJ
Annotation based
AOP
realization
(
master
)
AspectJ
Provides annotation for
AOP
Implementation of.
(
1
)Implementation steps
A
,
Step1
: define business interface and implementation class
package com.zsz.ba01;
public interface SomeService {
void doSome(String name,Integer age);
}
package com.zsz.ba01;
//Target class
public class SomeServiceImpl implements SomeService {
@Override
public void doSome(String name,Integer age) {
// Add a function to the doSome () method to output the execution time of the method before the execution of doSome ()
System.out.println("===Target method doSome===");
}
}
B
,
Step2
: define cut class
Class, which will be used as different notification methods to enhance functions.
package com.zsz.ba01;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @Aspect:Is an annotation in the aspectj framework.
*
* Function: indicates that the current class is a faceted class.
* Aspect classes are classes used to add functions to business methods. In this class, there are aspect function codes
* Location: above the class definition
*/
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {
/**
* Specify the parameter in the notification method: JoinPoint
* joinPoint:Business method, the business method to which the aspect function is added
*
*/
@Before(value = "execution(public void com.zsz.ba01.SomeServiceImpl.doSome(String,Integer))")
public void myBefore(JoinPoint jp){
//Gets the complete definition of the method
System.out.println("Method's signature (definition)="+jp.getSignature());
System.out.println("Name of the method"+jp.getSignature().getName());
//Gets the argument of the method
Object[] args = jp.getArgs();
for (Object arg : args){
System.out.println("parameter="+arg);
}
System.out.println("Pre notification, aspect function: output the execution time before the target method:"+new Date());
}
}
C
,
Step3
: declare target object facet class object
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--Give the object to spring Container, by spring Containers are created uniformly to manage objects-->
<!--Declare target object-->
<bean id="someService" class="com.zsz.ba01.SomeServiceImpl"></bean>
<!--Declare slice object-->
<bean id="myAspect" class="com.zsz.ba01.MyAspect"/>
</beans>
D
,
Step4
: Registration
AspectJ
Automatic proxy for
After defining the section
Aspect
Notification required after
Spring
Container, let the container generate the "target class"
+
Proxy for facet
Object. This agent is automatically generated by the container. Just in
Spring
Register a profile based on
aspectj
of
Automatic proxy generator, which will automatically scan to
@Aspect
Annotation, and weave it in according to the notification type and pointcut, and
Generate proxy.
<!--Declaring automatic proxy generators: Using aspectj Functions within the framework to create proxy objects for target objects
Creating a proxy object is implemented in memory and modifying the structure of the memory object in memory.
aspectj-autoproxy:Will put spring All target objects in the container produce proxy objects at one time.
-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
The bottom layer is made of
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
Implemented.
As can be seen from its class name, it is based on
AspectJ
Annotation adaptation automatic proxy generator.
The working principle is,
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
Found by scanning
@Aspect
Defined slice class, and then
The face class finds the target method of the target class according to the pointcut, and then finds the pointcut time by the notification type.
E
,
Step5
: the target object used in the test class
id
package com.zsz;
import com.zsz.ba01.SomeService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MyTest01 {
@Test
public void test01(){
String config="applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ac= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
//Get target object from container
SomeService someService = (SomeService) ac.getBean("someService");
//Through the object execution method of the agent, the function is enhanced when the target method is executed
//someService:com.sun.proxy.$Proxy8
System.out.println("someService:"+someService.getClass().getName());
someService.doSome("Zhao Shuzheng",20);
}
}