catalogue
1, spring environment modification
2, Bean object underlying implementation (rough)
1, spring environment modification
1. Modify the version number and delete redundant services
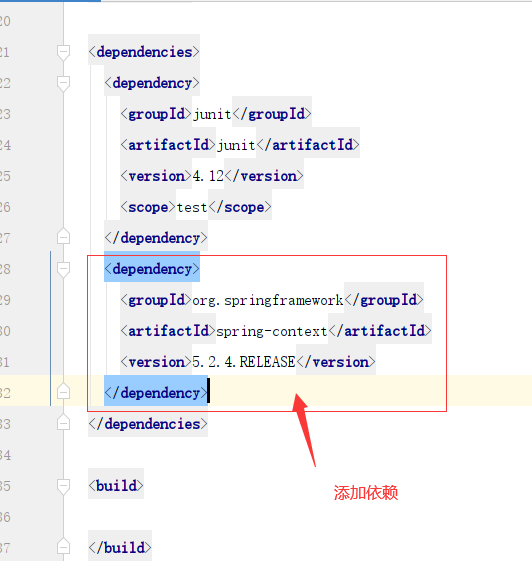
2. Add dependency
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.2.4.RELEASE</version> </dependency>
3. Check whether it is successful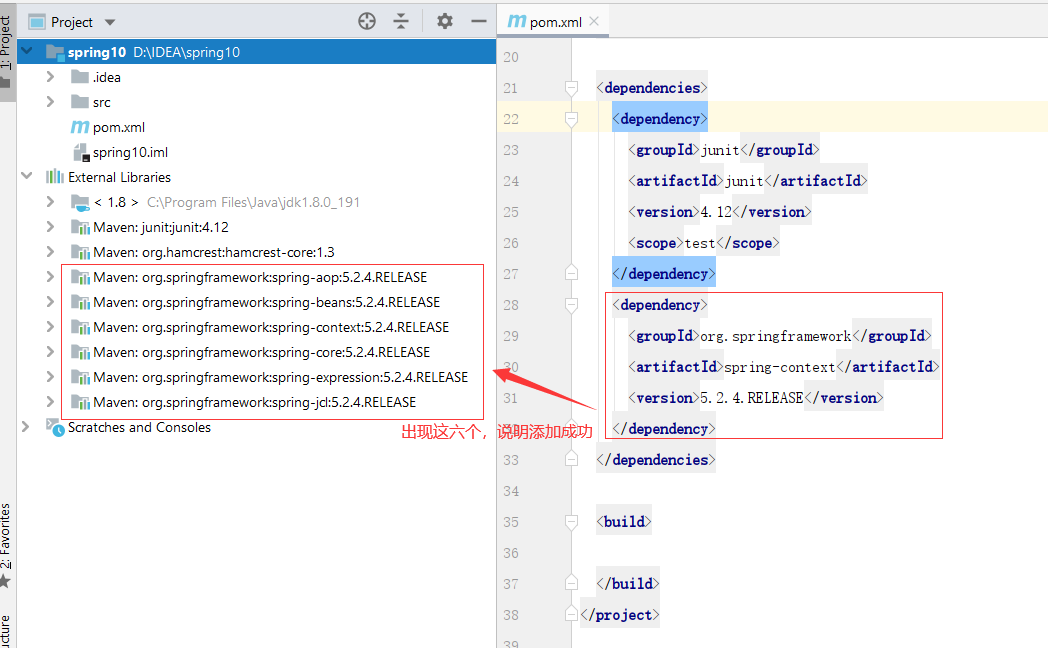
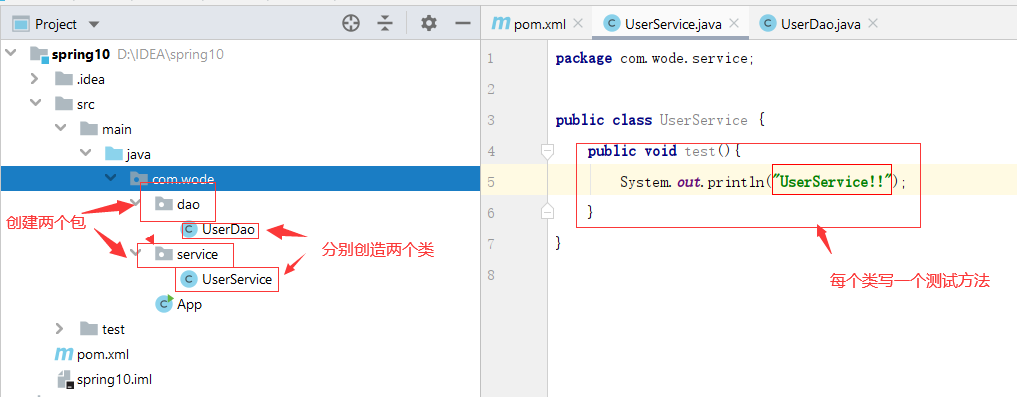
4. Writing classes and test methods
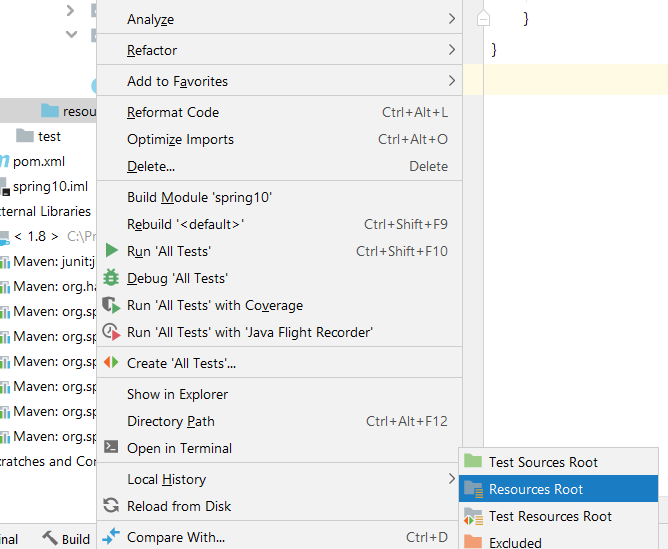
5. Create resource directory

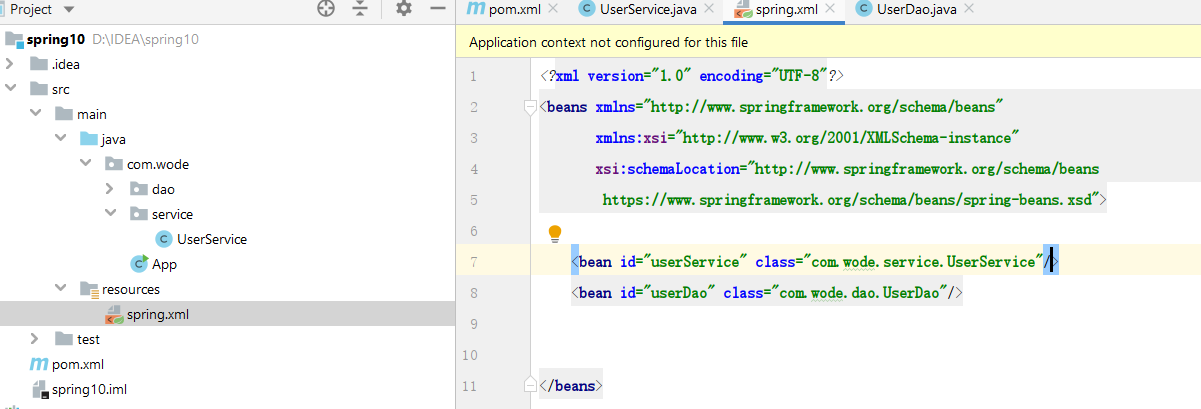 6. Create XXXX XML file, name customization, adding specification and bean
6. Create XXXX XML file, name customization, adding specification and bean
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userService" class="com.wode.service.UserService"/>
<bean id="userDao" class="com.wode.dao.UserDao"/>
</beans> 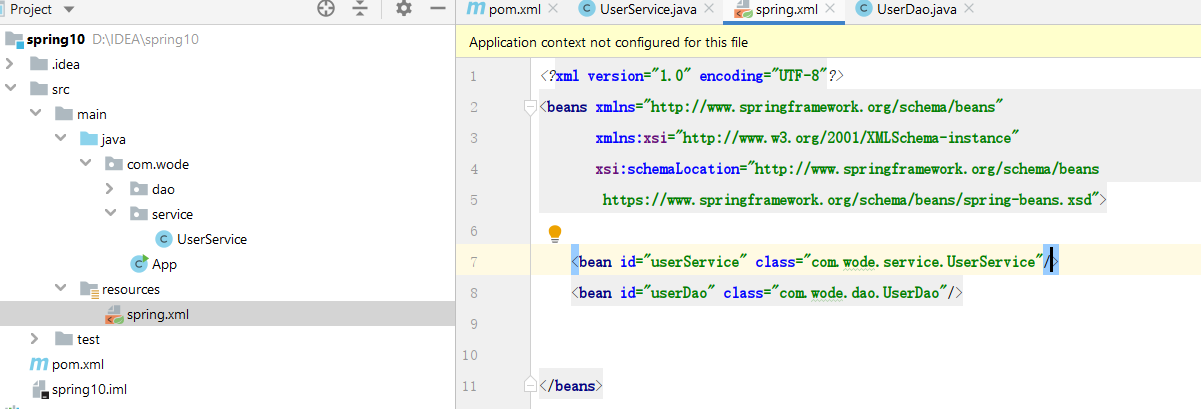
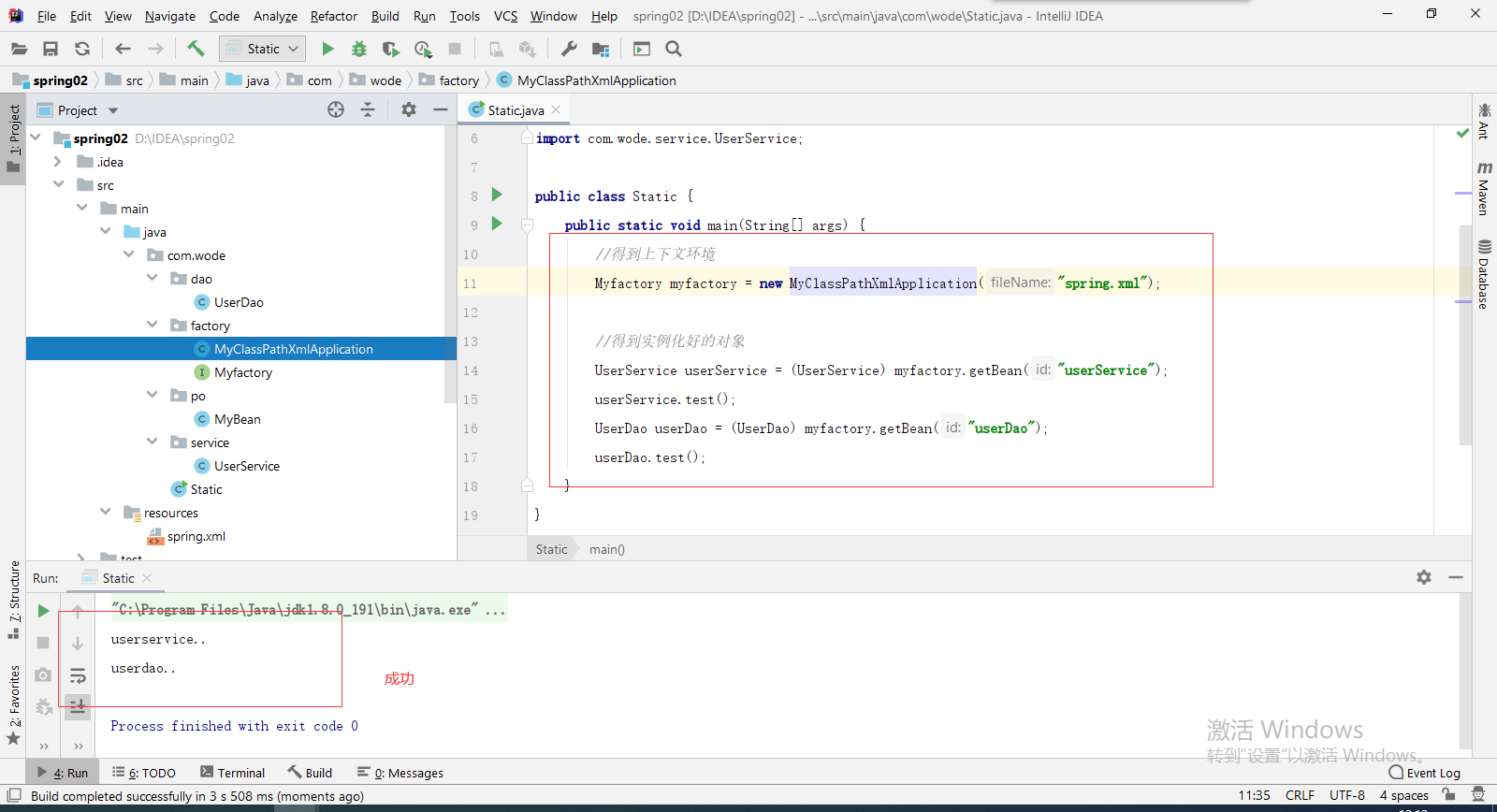
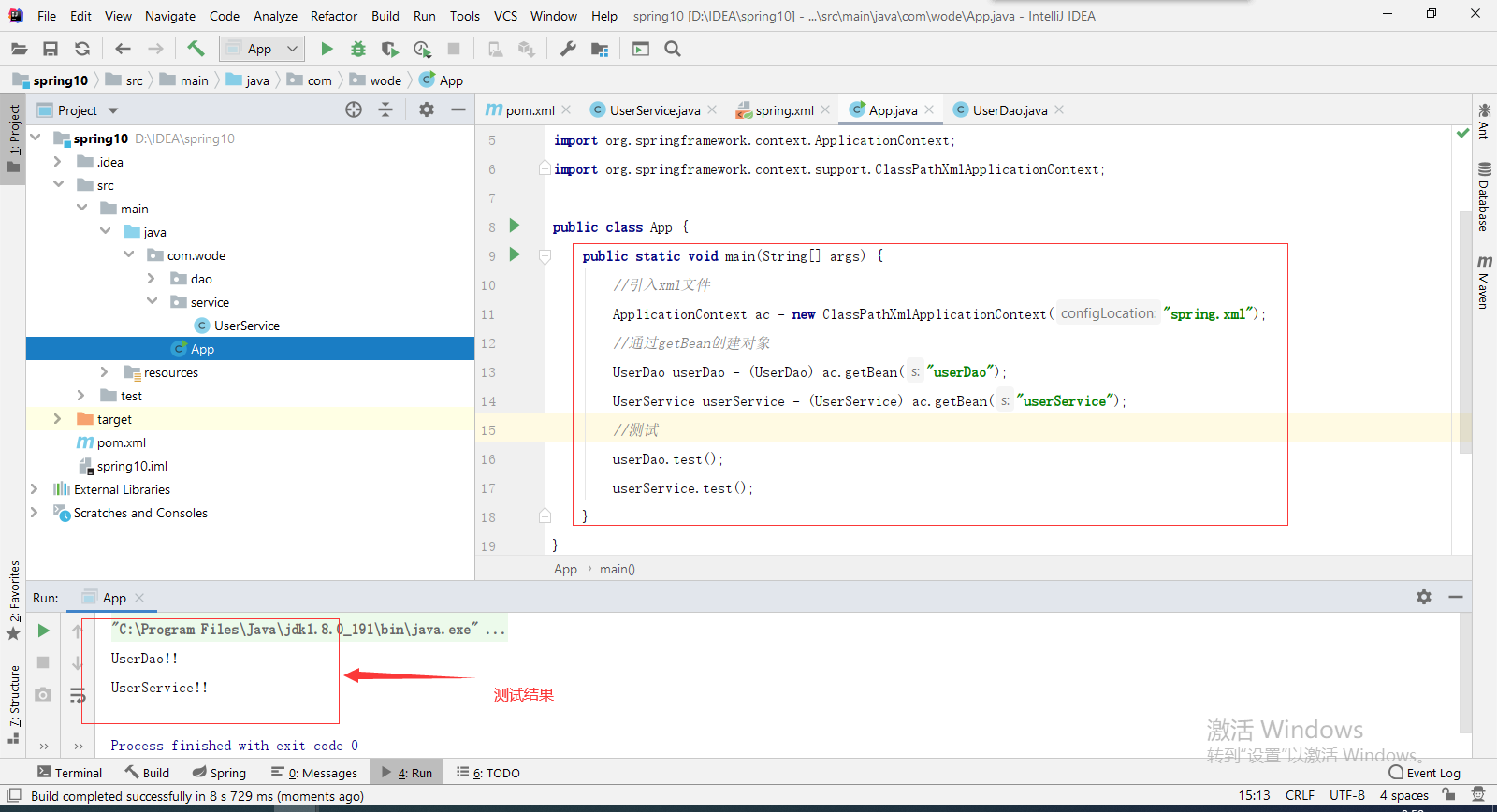
7. Write the main method and test it.
2, Bean object underlying implementation (rough)
In the past, we used to use new to create a new object, but now in order to simplify java development and reduce coupling, spring IOC came into being. It uses a bean object to solve these problems. That is, as long as an object is created, it will not "new" one in the code at any time, but complete this operation in the bean, so as to achieve the purpose of easy modification and reducing coupling. (some very rough ideas are just for easy understanding. For deeper problems, you can query relevant blog posts, etc.)
1. First, create a maven project and introduce dom4j for parsing files (handwriting parsing is very troublesome, use the jar already made). pom. Adding dom4j dependencies to XML
<dependency> <groupId>dom4j</groupId> <artifactId>dom4j</artifactId> <version>1.6</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>jaxen</groupId> <artifactId>jaxen</artifactId> <version>1.1.6</version> </dependency>
2. Write test objects UserService and UserDao and corresponding test methods,
Write XXXX XML file (spring.xml), handwritten XML (do not go to the official website to copy the specification)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans>
<bean id="userService" class="com.wode.service.UserService"/>
<bean id="userDao" class="com.wode.dao.UserDao"/>
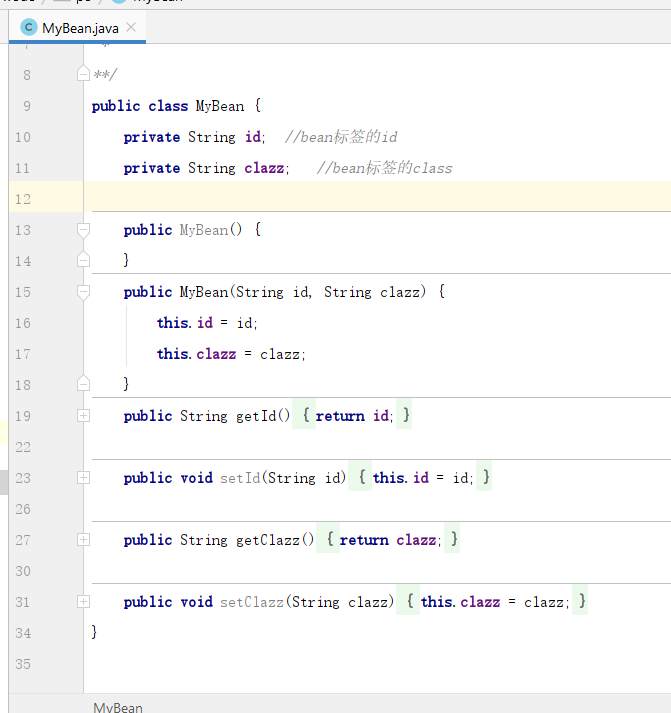
</beans>3,com. xxxx. Create a new MyBean class under po (po is a new package) to store the id and class in the bean tag
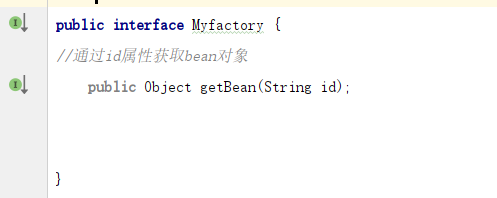
4. Create a new factory package and a factory (interface Myfactor) that produces Bean objects in the factory
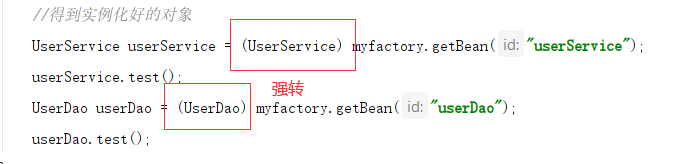
Object is the parent class of all classes (java Foundation), so the created UserService class is a subclass of object, which is equivalent to
Object object = new UserService();
When using the UserService object, it needs to be cast to the UserService class
5. Create a MyClassPathXmlApplication to inherit MyBean, which is equivalent to ApplicationContext, which also inherits BeanFactory.
Here we have created spring The getBean method that returns the object is also written in the XML file, so they need to be linked here, so you need to:
1. Write a method to parse spring XML, get the id and class in the bean tag inside. Here, use the created MyBean class to receive data, and then store the received data in list < MyBean >
2. Instantiate the object through the obtained class address and store it in the map. Then implement the getBean method.
6. First create a list < mybean > and map < string, Object >.
7. Write parselXml to parse spring XML file
dom4j is used here to parse spring XML file, parsing bean tags using xpath
private void parselXml(String fileName) {
//Get parser
SAXReader saxReader = new SAXReader();
//Find the url where the file is located
URL url = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource(fileName);
//To resolve its configuration file, return the Document object
try {
Document document = saxReader.read(url);
//Parsing tags through xpath syntax
XPath xPath = document.createXPath("beans/bean");
//Parsing the specified element through xpath
List<Element> elementList = xPath.selectNodes(document);
//Judgment element set
if(elementList!=null&&elementList.size()>0){
//Instantiation combination
beanList = new ArrayList<>();
//Traversal set
for (Element el:elementList){
//Get the id attribute value and class of the element
String id = el.attributeValue("id");
String clazz = el.attributeValue("class");
//Set the value of idclass to mybean
MyBean myBean = new MyBean(id,clazz);
//Set to collection
beanList.add(myBean);
}
}
} catch (DocumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}8. Instantiate object
private void instanceBean() {
//Determine whether the collection of bean pairs exists
if (beanList!=null&&beanList.size()>0)
//ergodic
for (MyBean bean:beanList){
try {
String id = bean.getId();
//Value (instantiated object) gets the instantiated object through the class attribute value
Object object = Class.forName(bean.getClazz()).newInstance();
//Set map
beanMap.put(id,object);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}9. Create a construction method with parameters and call the parsing and instantiation methods
public MyClassPathXmlApplication(String fileName) {
//Parsing configuration files
this.parselXml(fileName);
//Instantiate bean object
this.instanceBean();
}
10. Implement the getBean method
public Object getBean(String id) {
return beanMap.get(id);
}11. Testing