Stm32 cubemax (IX) -- Ultrasonic Ranging Using acquisition interrupt
preface
Because we want to realize Kalman filter, we first write about ultrasound this time and review the input acquisition interrupt by the way.
1, Principle of ultrasonic module
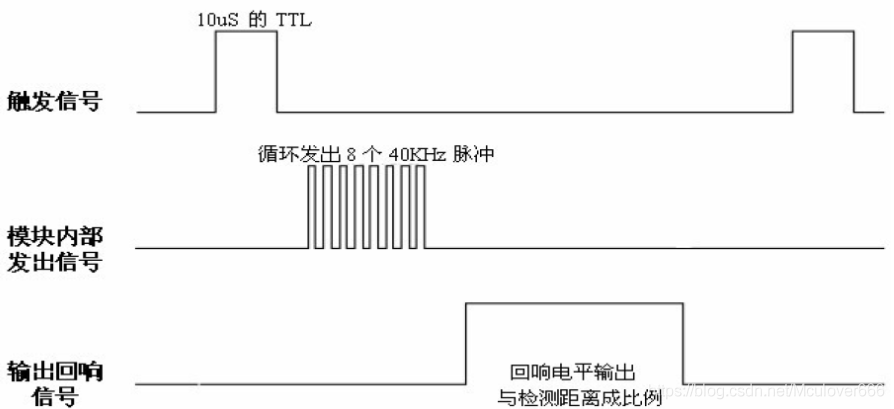
Anyone who has searched the ultrasonic module on the Internet is no stranger to this figure. In short, he wants to get the ultrasonic data, including the following steps.
1. Send trigger signal greater than 10us.
2. Detect the high level generated when the ultrasonic signal is sent.
3. Detect the low level generated when the ultrasonic receives the signal
We get the distance information through the latter two steps, that is, to detect the time of high level generated by ultrasonic wave. The function of input capture is to capture the duration of high level or low level
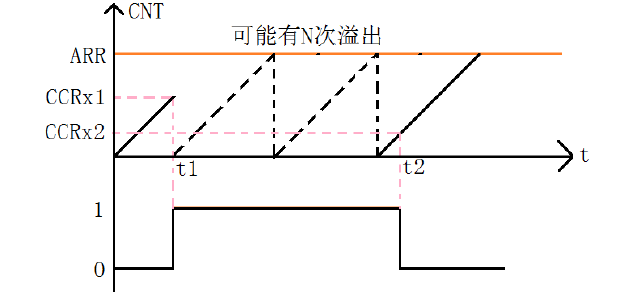
Our programming is based on the above figure.
2, Cubmax configuration
1. Configure timer input capture
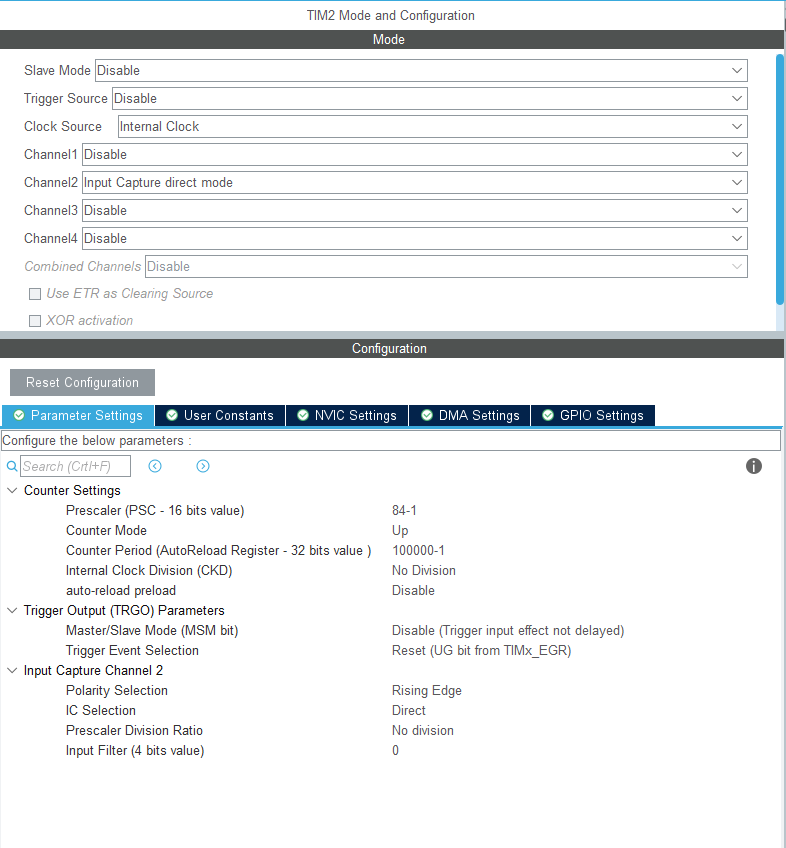
The experimental board is F407, and the frequency division coefficient is 84-1, then the counting accuracy reaches 1us. 100000 is the upper overflow limit
----------------------—
2. Configure trigger pin
This pin is used to generate a high level of 20us to trigger ultrasound.
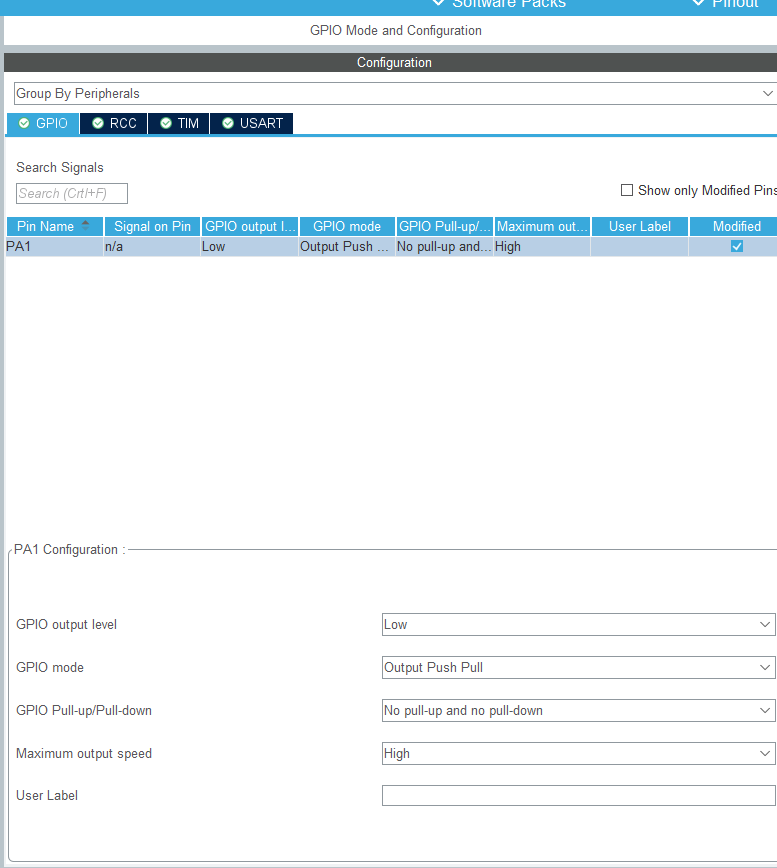
----------------------—
3. Open a 60ms timer to trigger ultrasound at a certain frequency.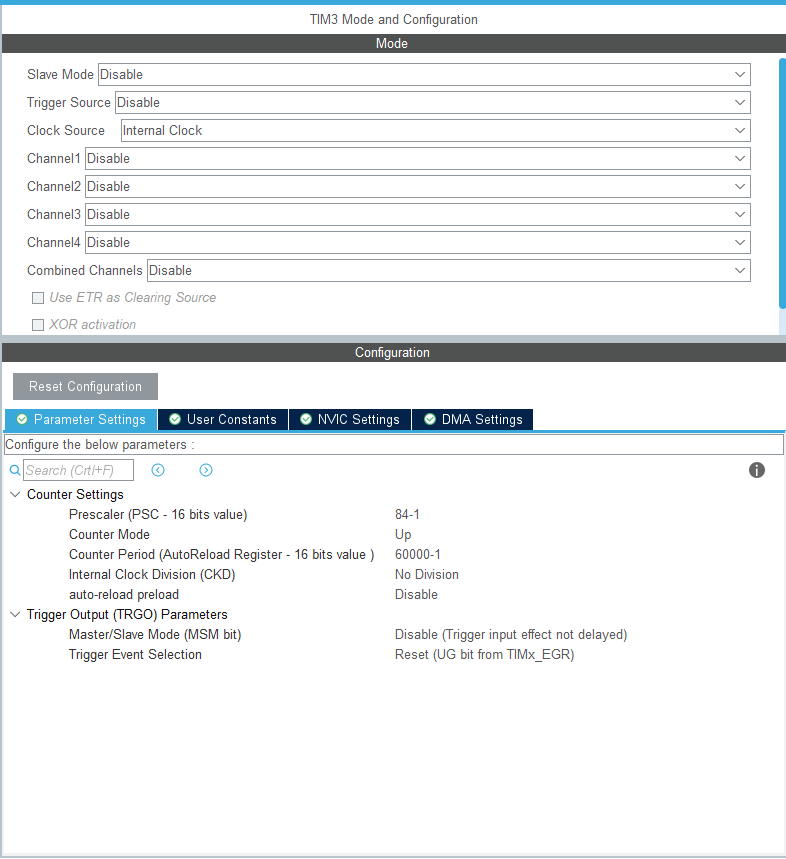
----------------------
4. Turn on the corresponding interrupt
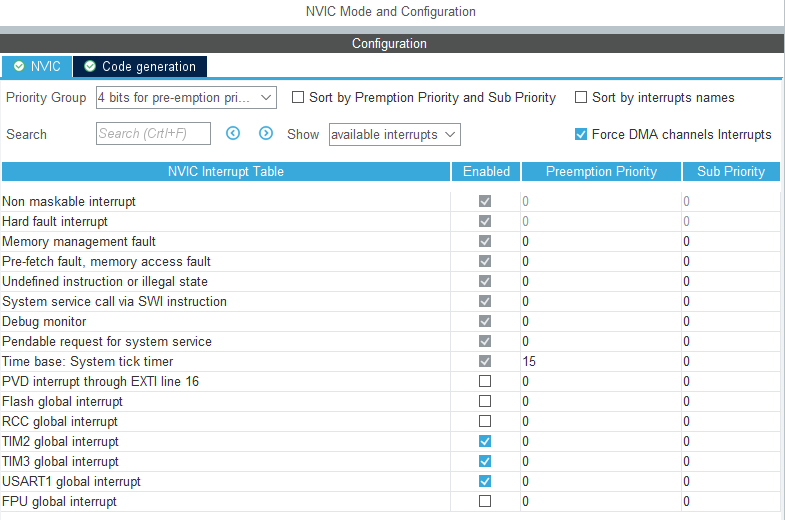
3, Code
1, As usual, we first create a structure related to ultrasonic parameters, define some parameters, and the initialization function of the structure.
#define CPU_FREQUENCY_MHZ 168 // F407 main frequency, used to write 20us delay function
#define Trig(state) HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOA,GPIO_PIN_1, (GPIO_PinState)(state)) / / trigger pin
#define RELOADVALUE 100000 // Reload value
typedef struct
{
float distance; //Calculated distance
uint8_t loop_num; //Overflow times
uint32_t rising_time; //Time to capture rising edge
uint32_t falling_time; //Time to capture falling edge
uint8_t capture_state; //Status of current capture
uint32_t time; //Calculated time
}Supersonic;
Initialization function, in main Call in C
void Supersonic_Init()
{
supersonic.distance = 0;
supersonic.rising_time = 0;
supersonic.falling_time = 0;
supersonic.capture_state = 0;
supersonic.time = 0;
supersonic.loop_num = 0;
HAL_TIM_IC_Start_IT(&htim2, TIM_CHANNEL_2); //Enable capture interrupt
HAL_TIM_Base_Start_IT(&htim3); //Open 60ms interrupt
__HAL_TIM_ENABLE_IT(&htim2,TIM_IT_UPDATE); //Enable overflow interrupt
}
2, Write 20us delay function and trigger function
//Delay function, just copy it directly
void delay_us(__IO uint32_t delay)
{
int last, curr, val;
int temp;
while (delay != 0)
{
temp = delay > 900 ? 900 : delay;
last = SysTick->VAL;
curr = last - CPU_FREQUENCY_MHZ * temp;
if (curr >= 0)
{
do
{
val = SysTick->VAL;
}
while ((val < last) && (val >= curr));
}
else
{
curr += CPU_FREQUENCY_MHZ * 1000;
do
{
val = SysTick->VAL;
}
while ((val <= last) || (val > curr));
}
delay -= temp;
}
}
//High level of 20us
void Supersonic_Start()
{
Trig(0);
delay_us(20);
Trig(1);
}
3, Write input capture interrupt and update interrupt
//Override input capture interrupt
void HAL_TIM_IC_CaptureCallback(TIM_HandleTypeDef *htim)
{
if(htim->Instance == htim2.Instance)
{
if(supersonic.capture_state == 0) //If the current status is capture high
{
supersonic.rising_time = HAL_TIM_ReadCapturedValue(&htim2, TIM_CHANNEL_2); //Time of rising edge
__HAL_TIM_SET_CAPTUREPOLARITY(&htim2, TIM_CHANNEL_2,TIM_INPUTCHANNELPOLARITY_FALLING); //Start capturing low level
HAL_TIM_IC_Start_IT(&htim2, TIM_CHANNEL_2); //Reopen input capture interrupt
supersonic.capture_state = 1; //Change the status to capture low
}
else if(supersonic.capture_state == 1) //If the current status is capture low
{
supersonic.falling_time = HAL_TIM_ReadCapturedValue(&htim2, TIM_CHANNEL_2); //Time to obtain falling edge
__HAL_TIM_SET_CAPTUREPOLARITY(&htim2, TIM_CHANNEL_2, TIM_INPUTCHANNELPOLARITY_RISING); //Return to capture high level
HAL_TIM_IC_Stop_IT(&htim2, TIM_CHANNEL_2); //Stop input capture and wait for the trigger signal to start
supersonic.time = supersonic.falling_time + supersonic.loop_num * RELOADVALUE - supersonic.rising_time;
supersonic.distance = (float)supersonic.time*340/(2*10000); //Convert to cm
//Empty status
supersonic.loop_num = 0;
supersonic.capture_state = 0;
}
}
}
//In the update interrupt, we need to deal with overflow interrupt and timer 60ms interrupt
void HAL_TIM_PeriodElapsedCallback(TIM_HandleTypeDef *htim)
{
if(htim->Instance == htim3.Instance) //60ms
{
if(supersonic.capture_state == 0) //This is the initial state
{
Supersonic_Start();
HAL_TIM_IC_Start_IT(&htim2, TIM_CHANNEL_2); //Remember to turn on capture interrupt
}
}
if(htim->Instance == htim2.Instance) //Overflow interrupt
{
if(supersonic.capture_state == 1) //At this time, it is capturing low level
{
supersonic.loop_num++;
}
}
}
----------------------—
experimental result
Here I print the measured distance value into a table.
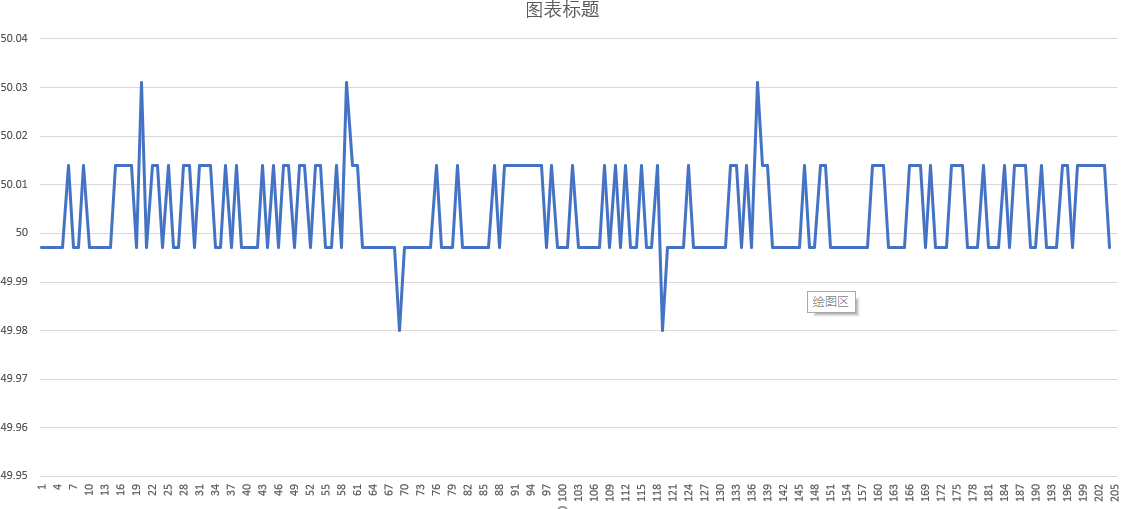
It can be seen that there is a lot of noise in the process of ultrasonic measurement, which requires us to use some filtering methods for processing.
summary
According to our results, we will use Kalman filter to process ultrasonic data to see how the results are.