From: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_29350001/article/details/81558649
I. Clock system block diagram
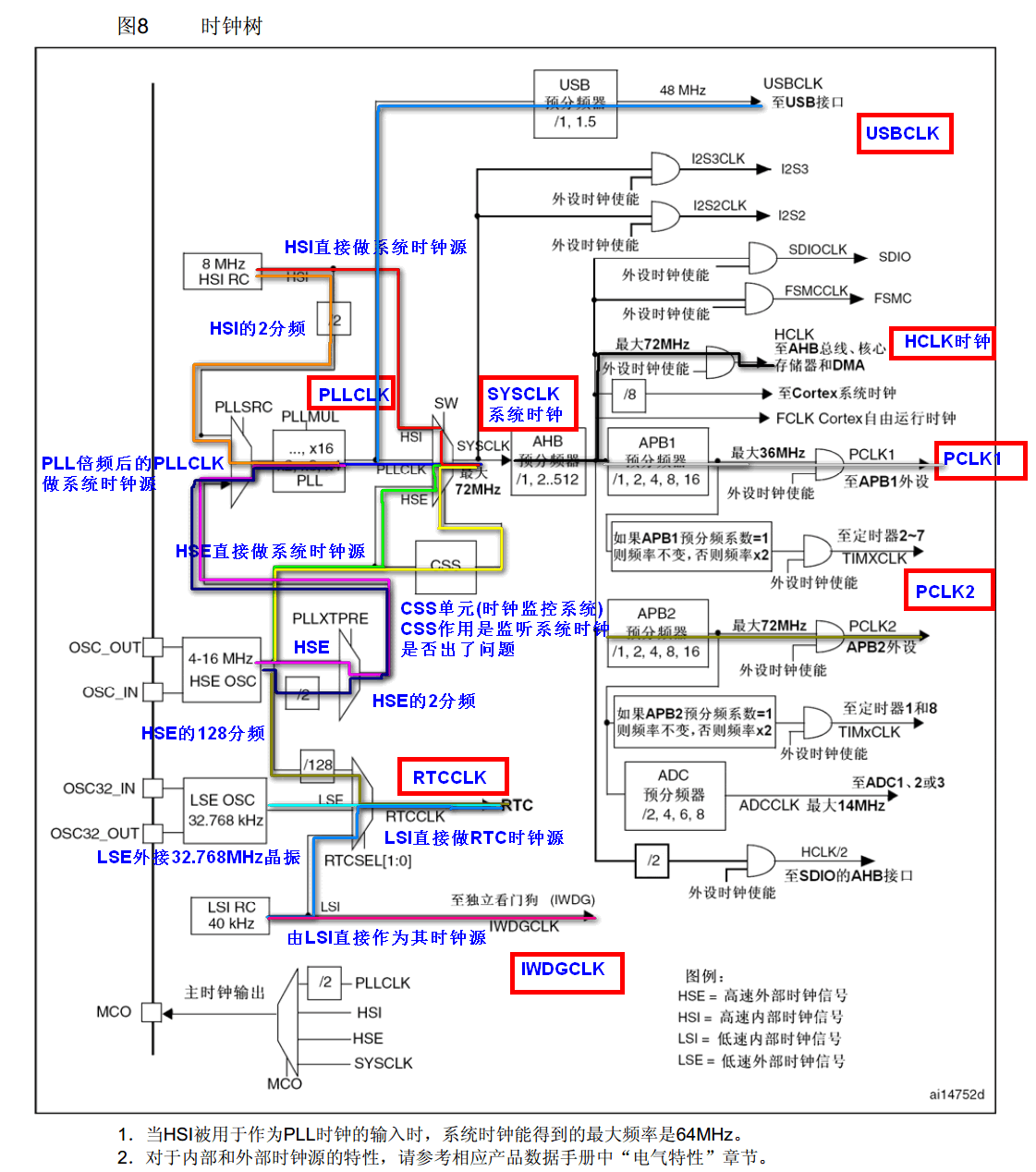
II. Clock System
- STM32 has five clock sources: HSI, HSE, LSI, LSE, PLL.
(1) HSI is a high-speed internal clock, RC oscillator, with a frequency of 8MHz and low accuracy.
(2) HSE is a high-speed external clock, which can be connected with quartz/ceramic resonator or external clock source. Its frequency range is from 4MHz to 16MHz.
(3) LSI is a low-speed internal clock, RC oscillator, with a frequency of 40 kHz, providing a low-power clock.
(4) LSE is a low-speed external clock connected to 32.768 kHz quartz crystal.
(5) PLL is the frequency doubling output of PLL, and its clock input source can be HSI/2, HSE or HSE/2. Frequency doubling can be chosen as 2 to 16 times, but the maximum output frequency should not exceed 72MHz. - The system clock SYSCLK can be derived from three clock sources:
(1) HSI oscillator clock
(2) HSE oscillator clock
3. PLL Clock - STM32 can choose a clock signal to output to MCO foot (PA8), and can choose 2-frequency, HSI, HSE, or system clock for PLL output.
- Before any peripheral can be used, its corresponding clock must be enabled first.
3. RCC-related configuration registers
/**
* @brief Reset and Clock Control
*/
typedef struct
{
__IO uint32_t CR; // Enabling and Readiness Markers for HSI,HSE,CSS,PLL, etc.
__IO uint32_t CFGR; // Clock Source Selection, Frequency Division Coefficient Setting for PLL, etc.
__IO uint32_t CIR; // Clear/enable clock ready interrupt
__IO uint32_t APB2RSTR; // APB2 Line External Reset Register
__IO uint32_t APB1RSTR; // The peripheral reset register on APB1 line
__IO uint32_t AHBENR; // Clock Enablation for DMA, SDIO, etc.
__IO uint32_t APB2ENR; // APB2 Line Peripheral Clock Enablation
__IO uint32_t APB1ENR; // Peripheral Clock Enablation on APB1 Line
__IO uint32_t BDCR; // Backup Domain Control Register
__IO uint32_t CSR; // Control State Register
#ifdef STM32F10X_CL
__IO uint32_t AHBRSTR;
__IO uint32_t CFGR2;
#endif /* STM32F10X_CL */
#if defined (STM32F10X_LD_VL) || defined (STM32F10X_MD_VL) || defined (STM32F10X_HD_VL)
uint32_t RESERVED0;
__IO uint32_t CFGR2;
#endif /* STM32F10X_LD_VL || STM32F10X_MD_VL || STM32F10X_HD_VL */
} RCC_TypeDef;
IV. RCC Related Header Files and Firmware Library Resources
Where file: stm32f10x_rcc.c
Clock enabling configuration:
RCC_LSEConfig() ,RCC_HSEConfig(),
RCC_HSICmd() , RCC_LSICmd() , RCC_PLLCmd() ......
Clock Source Related Configuration:
RCC_PLLConfig (), RCC_SYSCLKConfig() ,
RCC_RTCCLKConfig() ...
Frequency division coefficient selection configuration:
RCC_HCLKConfig() , RCC_PCLK1Config() , RCC_PCLK2Config()...
Peripheral Clock Enables:
RCC_APB1PeriphClockCmd(): //Peripheral Clock Enablation on APB1 Line
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(); //APB2 Line Peripheral Clock Enablation
RCC_AHBPeriphClockCmd(); //Peripheral Clock Enablation on AHB Line
Other peripheral clock enabling
RCC_ADCCLKConfig (); RCC_RTCCLKConfig();
State parameter acquisition
RCC_GetClocksFreq();
RCC_GetSYSCLKSource();
RCC_GetFlagStatus()
RCC interrupt correlation function:
RCC_ITConfig() , RCC_GetITStatus() , RCC_ClearITPendingBit()...
V. System Clock Initialization
System clock initialization function: System Init ();
6. Summarize the process of system initialization function
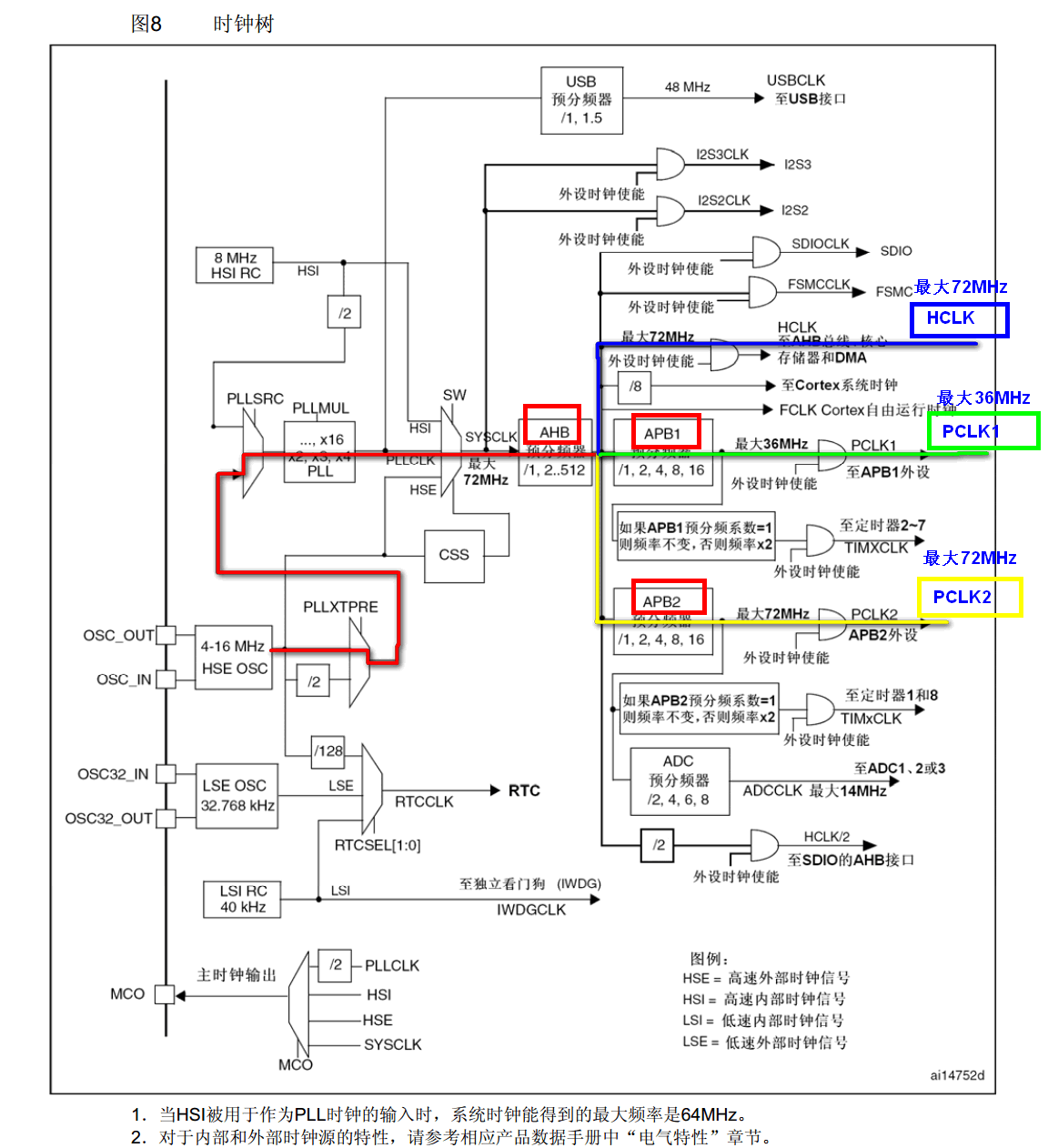
- Open HSE, wait for ready, set Flash wait operation
- Set the frequency dividing coefficients of AHB, APB1 and APB2 to determine the relationship between them and the system clock.
- Setting CFGR register to determine PLL clock source and frequency doubling coefficient (HSE external 8M*9 times = 72MHz)
- Enabling PLL to switch system clock source to PLL
Note:
** APB(Advanced Peripheral Bus),** On-Chip Peripheral Bus. Mainly used for communication between slow on-chip peripherals and ARM core
** AHB(Advanced High performance Bus),** High Performance Bus. Mainly used for high performance, high clock rate inter-module communication of the system