Experimental content
1. Assuming that the sparse matrix A of n*n is represented by a triple, a program ex6-1.cpp is designed to achieve the following functions:
(1) the triples a and b of the following two sparse matrices are generated.
{ 1 0 3 0 {3 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 4 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 1 1} 0 0 0 2}
(2) triple of output a transpose matrix
(3) triple of output a+b
(4) output triple of axb
2. Design an algorithm to calculate the sum of diagonal elements of a sparse matrix represented by a triple table
3. Design an algorithm, Same (g1,g2), to judge whether two generalized g1 and g2 are the Same
code implementation
1,
exp6-1.cpp
#include<stdio.h>
#define N 4
typedef int ElemType;
#define MaxSize 100 / * maximum number of non-zero elements of matrix*/
typedef struct
{
int r;/*Line number*/
int c;/*Column number*/
ElemType d;/*Element value*/
}TupNode;/*Triple definition*/
typedef struct
{
int rows;/*Row value*/
int cols;/*Column value*/
int nums;/*Number of non-zero elements*/
TupNode data[MaxSize];
}TSMatrix;/*Storage structure of triples*/
void CreatMat(TSMatrix &t,ElemType A[N][N])/*Triple representation of non generated sparse matrix A*/
{
int i,j;
t.rows=N;t.cols=N;t.nums=0;
for(i=0;i<N;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<N;j++)
if(A[i][j]!=0)
{
t.data[t.nums].r=i;t.data[t.nums].c=j;
t.data[t.nums].d=A[i][j];
t.nums++;
}
}
}
void DispMat(TSMatrix t)/*Output triplet representation*/
{
int i;
if(t.nums<=0)
return;
printf("\t%d\t%d\n",t.rows,t.cols,t.nums);
printf("\t------------------\n");
for(i=0;i<t.nums;i++)
printf("\t%d\t%d\n",t.data[i].r,t.data[i].c,t.data[i].d);
}
void TranMat(TSMatrix t,TSMatrix &tb)/*Finding the transposition tb of the triple representation t*/
{
int p,q=0,v;/*q Is the subscript of tb.data*/
tb.rows=t.cols;tb.cols=t.rows;tb.nums=t.nums;
if(t.nums!=0)
{
for(v=0;v<t.cols;v++)/*tb.data[q]The records in are arranged in the order of field c*/
for(p=0;p<t.nums;p++)/*p Is the subscript of t.data*/
if(t.data[p].c==v)
{
tb.data[q].r=t.data[p].c;
tb.data[q].c=t.data[p].r;
tb.data[q].d=t.data[p].d;
q++;
}
}
}
int MatAdd(TSMatrix a,TSMatrix b,TSMatrix &c)
{
int i=0,j=0,k=0;
ElemType v;
if(a.rows!=b.rows ||a.cols!=b.cols)
return 0;/*Cannot add when the number of rows or columns is different*/
c.rows=a.rows;c.cols=a.cols;
while(i<a.nums && j<b.nums)/*Handle each element in a and b*/
{
if(a.data[i].r==b.data[j].r)/*When line numbers are equal*/
{
if(a.data[i].c<b.data[j].c)/*a Column number of element is less than that of element b*/
{
c.data[k].r=a.data[i].r;/*Add a element to c*/
c.data[k].c=a.data[i].c;
c.data[k].d=a.data[i].d;
k++;i++;
}
else if(a.data[i].c>b.data[j].c)/*a Column number of element is greater than that of element b*/
{
c.data[k].r=b.data[i].r;/*Add b element to c*/
c.data[k].c=b.data[i].c;
c.data[k].d=b.data[i].d;
k++;j++;
}
else /*a The column number of element is equal to the sequence number of element b*/
{
v=a.data[i].d+b.data[j].d;
if(v!=0)/*Only nodes that are not 0 will be added to c*/
{
c.data[k].r=a.data[i].r;
c.data[k].c=a.data[i].c;
c.data[k].d=v;
}
i++;j++;
}
}
else if(a.data[i].r<b.data[j].r)/*a Element's line number is less than b element's line number*/
{
c.data[k].r=b.data[i].r;/*Add b element to c*/
c.data[k].c=b.data[i].c;
c.data[k].d=b.data[i].d;
k++;i++;
}
else
{
c.data[k].r=b.data[j].r;/*Add b element to c*/
c.data[k].c=b.data[j].c;
c.data[k].d=b.data[j].d;
k++;j++;
}
c.nums=k;
}
return 1;
}
int value(TSMatrix c,int i,int j)
{
int k=0;
while(k<c.nums && (c.data[k].r!=i || c.data[k].c!=j))
k++;
if(k<c.nums)
return (c.data[k].d);
else
return 0;
}
int MatMul(TSMatrix a,TSMatrix b,TSMatrix &c)/*Seeking c=a*b*/
{
int i,j,k,p=0;
ElemType s;
if(a.cols!=b.rows)/*a Cannot multiply when the number of columns of is not equal to the number of rows of b*/
return 0;
for(i=0;i<a.rows;i++)
for(j=0;j<b.cols;j++)
{
s=0;
for(k=0;k<a.cols;k++)
s=s+value(a,i,k)*value(b,k,j);
if(s!=0)/*Generate a triple element*/
{
c.data[p].r=i;
c.data[p].c=j;
c.data[p].d=s;
p++;
}
}
c.rows=a.rows;
c.cols=b.cols;
c.nums=p;
return 1;
}
int main()
{
ElemType a1[N][N]={{1,0,3,0},{0,1,0,0},{0,0,1,0},{0,0,1,1}};
ElemType b1[N][N]={{3,0,0,0},{0,4,0,0},{0,0,1,0},{0,0,0,2}};
TSMatrix a,b,c;
CreatMat(a,a1);
CreatMat(b,b1);
printf("a Triples of:\n");DispMat(a);
printf("b Triples of:\n");DispMat(b);
printf("a Transpose to c\n");
TranMat(a,c);
printf("c Triples of:\n");DispMat(c);
printf("c=a+b\n");
MatAdd(a,b,c);
printf("c Triples of:\n");DispMat(c);
printf("c=a*b\n");
MatMul(a,b,c);
printf("c Triples of:\n");DispMat(c);
}
Screenshot of results:
2,
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define N 4
#define MaxSize 100
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct
{
int r;//Line number
int c;//Column number
ElemType d;//Element value
}TupNode;//Triple definition
typedef struct
{
int rows;//Row number
int cols;//Column number
int nums;//Number of non-zero elements
TupNode data[MaxSize];
}TSMatrix;//Triple order table definition
//Triple representation t of sparse matrix A
void CreatMat(TSMatrix &t, ElemType A[N][N])
{
int i, j;
t.rows = N;
t.cols = N;
t.nums = 0;
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
if (A[i][j] != 0)
{
t.data[t.nums].r = i;
t.data[t.nums].c = j;
t.data[t.nums].d = A[i][j];
t.nums++;
}
}
}
}
//Output triple represents t
void DispMat(TSMatrix t)
{
int i;
if (t.nums <= 0)
return;
else
printf("\t%d\t%d\t%d\n", t.rows, t.cols, t.nums);
printf("\t---------------------------\n");
for (i = 0; i < t.nums; i++)
{
printf("\t%d\t%d\t%d\n", t.data[i].r, t.data[i].c, t.data[i].d);
}
}
bool diagonal(TSMatrix a, ElemType &sum)
{
sum = 0;
if (a.rows != a.cols)
{
printf("Not diagonal matrix\n");
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < a.nums; i++)
{
if (a.data[i].r == a.data[i].c)
sum += a.data[i].d;
}
return true;
}
int main()
{
ElemType sum,A[N][N] = { {1,0,0,0},{0,3,0,5},{0,0,5,0},{0,0,0,7} };
TSMatrix a;
CreatMat(a, A);
printf("A Three tuple\n");
DispMat(a);
diagonal(a, sum);
printf("The sum of diagonal elements is%d\n", sum);
return 0;
}
Screenshot of results: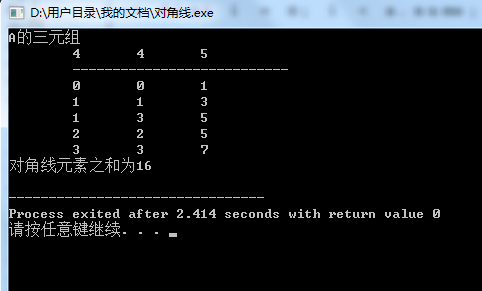
3,
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef struct lnode
{
int tag;//Node type identification
union
{
char data;
struct lnode *sublist;
}val;
struct lnode *link;//Point to next element
}GLNode;//Declaring generalized table node types
//Returns the generalized table concatenated storage structure of s represented by bracket notation
GLNode *CreateGL(const char * &s)
{
GLNode *g;
char ch = * s++;//Take a character
if (ch != '\0')//String not ended judgment
{
g = (GLNode *)malloc(sizeof(GLNode));
if (ch == '(')
{
g->tag = 1;
g->val.sublist = CreateGL(s);
}
else if (ch == ')')
g = NULL;
else if (ch == '#')
g->val.sublist = NULL;
else
{
g->tag = 0;
g->val.data = ch;
}
}
else
g = NULL;
ch = * s++;
if (g != NULL)
{
if (ch == ',')
g->link = CreateGL(s);
else
g->link = NULL;
}
return g;
}
//Output generalized table g
void DispGL(GLNode *g)
{
if (g != NULL)
{
if (g->tag == 0)
cout << g->val.data;
else
{
cout << "(";
if (g->val.sublist == NULL)
cout << "#";
else
DispGL(g->val.sublist);
cout << ")";
}
if (g->link != NULL)
{
cout << ",";
DispGL(g->link);
}
}
}
//Destroy generalized table g
void DestroyGL(GLNode * &g)
{
GLNode *g1, *g2;
g1 = g->val.sublist;
while (g1 != NULL)
{
if (g1->tag == 0)
{
g2 = g1->link;
free(g1);
g1 = g2;
}
else
{
g2 = g1->link;
DestroyGL(g1);
g1 = g2;
}
}
free(g);
}
bool Same(GLNode *g1, GLNode *g2)
{
if (g1 == NULL && g2 == NULL)
return true;
else if (g1 == NULL || g2 == NULL)
return false;
else
{
if (g1->tag == 0 && g2->tag == 0)
{
if (g1->val.data != g2->val.data)
return false;
return(Same(g1->link, g2->link));
}
else if (g1->tag == 1 && g2->tag == 1)
return(Same(g1->val.sublist, g2->val.sublist))
&Same(g1->link, g2->link);
else
return false;
}
}
int main()
{
GLNode *g1, *g2;
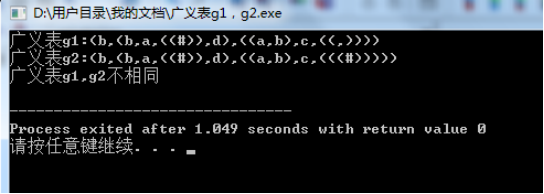
const char * str1 ="(b,(b,a,(#),d),((a,b),c,((,))))";
const char * str2= "(b,(b,a,(#),d),((a,b),c,((#))))";
g1 = CreateGL(str1);
g2 = CreateGL(str2);
cout << "Generalized table g1:";
DispGL(g1);
cout << endl;
cout << "Generalized table g2:";
DispGL(g2);
cout << endl;
if (Same(g1, g2))
{
cout << "Generalized table g1,g2 identical" << endl;
}
else
cout<< "Generalized table g1,g2 Inequality" << endl;
DestroyGL(g1);
DestroyGL(g2);
return 0;
}
Screenshot of results: