catalogue
1, Course design topic and content
3, Program source code and specific notes
two studentNode type definition
three studentList type definition
(5) Other function definitions
1.initialize function definition
2. Definition of enter function
3. Definition of display function
6. Definition of sort function
7. Definition of write function
8. Definition of read function
1, Course design topic and content
Program name: student achievement management system
Functional requirements: input student scores, modify student scores, count the total and average scores of each student, sort according to the average scores of students, query student scores, and output student transcripts. Be able to save students' grades and read and write files. The interface is simple and easy to operate.
2, Main design ideas
The linked list is used as a data structure to store student scores and other information, and then a pile of functions are written around the linked list to realize a pile of functions
At the beginning of the program, the file data will be read to the linked list, and at the end, the information in the updated linked list will be rewritten to the file to save the data
3, Program source code and specific notes
(1) Preprocessing instruction
< stdlib. H > is imported because malloc function and free function are used
< string. H > is imported because the strcmp function is used
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #define NAME_LEN 10 #define FILE_NAME "student grade. txt"
(2) Type definition
1.student type definition
A student variable represents a set of student information
typedef struct {
char name[NAME_LEN + 1];//full name
int number; //Student number
int chinese; //chinese
int math; //mathematics
int english; //English
int average; //average
int sum; //Total score
} student; //Used to store information about individual studentstwo studentNode type definition
A studentNode variable represents a student node
typedef struct node {
student stu; //Data field to store student information
struct node *next; //Pointer field, pointing to the next node
} studentNode; //Student nodethree studentList type definition
A studentList variable represents a student linked list
typedef struct {
studentNode *head; //Head pointer
studentNode *tail; //Tail pointer
int count; //Total number of student nodes
} studentList; //Student list(3) Function prototype
void initialize(studentList *L);//Initialize the list, create the header node void enter(studentList *L); //Enter linked list void display(studentList *L); //Output linked list void find(studentList *L); //Find a node void modify(studentList *L); //Modify a node void sort(studentList *L); //Rebuild the table in descending order and output void write(studentList *L); //Write files to free up space while writing void read(studentList *L); //Read files and create tables while reading
(4) main function definition
At the beginning, a linked list will be created and initialized, and then the information of the file will be read into the linked list
Interact with users through an infinite loop with a switch inside
At the end, the information in the linked list will be written to the file, and then the linked list will be destroyed
int main() {
//Interactive interface
printf(" **************Student achievement management system**************\n");
printf(" * 1.Enter new student grades *\n");
printf(" * 2.Modify student grades by name *\n");
printf(" * 3.Query student scores by name *\n");
printf(" * 4.Output the results of all students *\n");
printf(" * 5.Output student scores by average *\n");
printf(" * 6.Exit student achievement management system *\n");
printf(" ********************************************\n");
printf(" \n");
//Create student linked list
studentList *L = (studentList *)malloc(sizeof(studentList));
//Initialize student linked list
initialize(L);
//Read data from file to linked list
read(L);
//The interactive interface is written with an infinite loop and a switch
while (1) {
int code;
printf("Please enter the number corresponding to the operation you want to perform: ");
scanf("%d", &code);
switch (code) {
case 1:
enter(L);
break;
case 2:
modify(L);
break;
case 3:
find(L);
break;
case 4:
display(L);
break;
case 5:
sort(L);
break;
case 6:
write(L);
free(L->head); //The header node is destroyed
free(L); //The linked list was destroyed
return 0;
default:
printf("%d Is an invalid number, please re-enter!\n\n", code);
break;
}
}
return 0;
}(5) Other function definitions
1.initialize function definition
Receive a linked list pointer as a parameter
Create a head node without storing any information, and let the head and tail pointers of the linked list point to it
The initial length of the linked list is set to 0
void initialize(studentList *L) {
//Create header node
studentNode *s = (studentNode *)malloc(sizeof(studentNode));
s->next = NULL;
//Initialize linked list:
//The head and tail pointers refer to the head node, and the initial length is zero
L->head = s;
L->tail = s;
L->count = 0;
}2. Definition of enter function
Receive a linked list pointer as a parameter
Let the user type information coexist in the new node
Insert the new node into the linked list
void enter(studentList *L) {
//Create a new node
studentNode *s = (studentNode *)malloc(sizeof(studentNode));
//Type information into the new node
printf("Please enter student name:");
scanf("%s", s->stu.name);
printf("Please enter student ID:");
scanf("%d", &s->stu.number);
printf("Please enter your language score:");
scanf("%d", &s->stu.chinese);
printf("Please enter your math score:");
scanf("%d", &s->stu.math);
printf("Please enter your English score:");
scanf("%d", &s->stu.english);
s->stu.sum = s->stu.chinese + s->stu.math + s->stu.english;
s->stu.average = s->stu.sum / 3;
//If the linked list is empty, point the tail pointer to the new node
if (L->head == L->tail) {
L->tail = s;
}
//Insert the new node into the head of the linked list (head insertion method)
s->next = L->head->next;
L->head->next = s;
L->count++;
//Output interactive information
printf("Information entered successfully!\n\n");
}3. Definition of display function
Traversing the linked list output is finished
void display(studentList *L) {
printf("share%d Group student data:\n", L->count);
printf("full name\t\t Student number\t\t chinese\t\t mathematics\t\t English\t\t Total score\t\t average\n");
//Create a node pointer to the head node
studentNode *p;
p = L->head;
//Traversal list output
while (p->next) {
p = p->next;
printf("%s", p->stu.name);
printf("\t\t%d", p->stu.number);
printf("\t\t%d", p->stu.chinese);
printf("\t\t%d", p->stu.math);
printf("\t\t%d", p->stu.english);
printf("\t\t%d", p->stu.sum);
printf("\t\t%d", p->stu.average);
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}4.find function definition
void find(studentList *L) {
//Let the user enter the student to find
printf("Please enter student name:");
char name[NAME_LEN + 1];
scanf("%s", name);
//Traverse the linked list and compare names
studentNode *p = L->head->next;
while (p) {
//If it matches, output and end the function
if (strcmp(p->stu.name, name) == 0) {
printf("full name\t\t Student number\t\t chinese\t\t mathematics\t\t English\t\t Total score\t\t average\n");
printf("%s", p->stu.name);
printf("\t\t%d", p->stu.number);
printf("\t\t%d", p->stu.chinese);
printf("\t\t%d", p->stu.math);
printf("\t\t%d", p->stu.english);
printf("\t\t%d", p->stu.sum);
printf("\t\t%d", p->stu.average);
printf("\n\n");
return;
}
//If the name doesn't match, it's next
p = p->next;
}
//I didn't find the name in the traversal
printf("I didn't find this%s Information!\n\n", name);
}5.modify function definition
void modify(studentList *L) {
//Let the user enter the student to modify
printf("Please enter student name:");
char name[NAME_LEN + 1];
scanf("%s", name);
//Traverse the linked list and compare names
studentNode *p = L->head->next;
while (p) {
//If yes, let the user retype and end the function
if (strcmp(p->stu.name, name) == 0) {
printf("Please re-enter the information:\n");
printf("Please enter student ID:");
scanf("%d", &p->stu.number);
printf("Please enter your language score:");
scanf("%d", &p->stu.chinese);
printf("Please enter your math score:");
scanf("%d", &p->stu.math);
printf("Please enter your English score:");
scanf("%d", &p->stu.english);
p->stu.sum = p->stu.chinese + p->stu.math + p->stu.english;
p->stu.average = p->stu.sum / 3;
printf("Information modified successfully!\n\n");
return;
}
//If the name doesn't match, it's next
p = p->next;
}
//I didn't find the name in the traversal
printf("I didn't find this%s Information!\n\n", name);
}6. Definition of sort function
void sort(studentList *L) {
//Neither node is in fart order
if (L->count < 2) {
printf("List sorting completed!\n");
display(L);
return;
}
//Insert sort
studentNode *p, *pre, *tmp;
//p points to the second student node
p = L->head->next;
//The linked list is disconnected from the head node and the first student node
L->head->next = NULL;
//Cycle back from the first student node
while (p) {
//Save the pointer of the next node
tmp = p->next;
//Find insertion location
pre = L->head;
while (pre->next != NULL && pre->next->stu.average > p->stu.average)
pre = pre->next;
//Update tail pointer
if (pre->next == NULL) {
L->tail = p;
}
//insert
p->next = pre->next;
pre->next = p;
//Skip to next
p = tmp;
}
printf("List sorting completed!\n");
display(L);
}7. Definition of write function
This function is used to save the information in the linked list to a file and destroy all nodes (except the head node)
void write(studentList *L) {
//Open file flow
FILE *fp = fopen(FILE_NAME, "w");
if (fp == NULL) {
printf("file%s Open failed\n", FILE_NAME);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
//Output the total number of student nodes on the first line
fprintf(fp, "%d\n", L->count);
//Create a node pointer to the head node
studentNode *p;
p = L->head->next;
//Traverse the linked list and output a set of data as a row
while (p) {
fprintf(fp, "%s ", p->stu.name);
fprintf(fp, "%d ", p->stu.number);
fprintf(fp, "%d ", p->stu.chinese);
fprintf(fp, "%d ", p->stu.math);
fprintf(fp, "%d ", p->stu.english);
fprintf(fp, "%d ", p->stu.sum);
fprintf(fp, "%d ", p->stu.average);
fprintf(fp, "\n");
//Free node space after output
studentNode *next = p->next;
free(p);
p = next;
}
//Close file stream
fclose(fp);
//Interactive information
printf("Data saved! Thanks for using. Bye!\n");
}8. Definition of read function
This function is used to read the information in the file into the linked list and create nodes (except header nodes)
void read(studentList *L) {
//Open file stream
FILE *fp = fopen(FILE_NAME, "r");
if (fp == NULL) {
printf("file%s Open failed\n", FILE_NAME);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
//Read the total number of student nodes in the first row
fscanf(fp, "%d", &L->count);
//The data is read circularly, and the number of cycles is count
for (int i = 1; i <= L->count; i++) {
//Create a new node
studentNode *s = (studentNode *)malloc(sizeof(studentNode));
//Read data
fscanf(fp, "%s ", s->stu.name);
fscanf(fp, "%d ", &s->stu.number);
fscanf(fp, "%d ", &s->stu.chinese);
fscanf(fp, "%d ", &s->stu.math);
fscanf(fp, "%d ", &s->stu.english);
fscanf(fp, "%d ", &s->stu.sum);
fscanf(fp, "%d ", &s->stu.average);
//Insert the new node into the tail of the linked list (tail insertion method)
s->next = NULL;
L->tail->next = s;
L->tail = s;
}
//Close file stream
fclose(fp);
}4, Running example
Output all student scores
Enter a new set of data and close the program
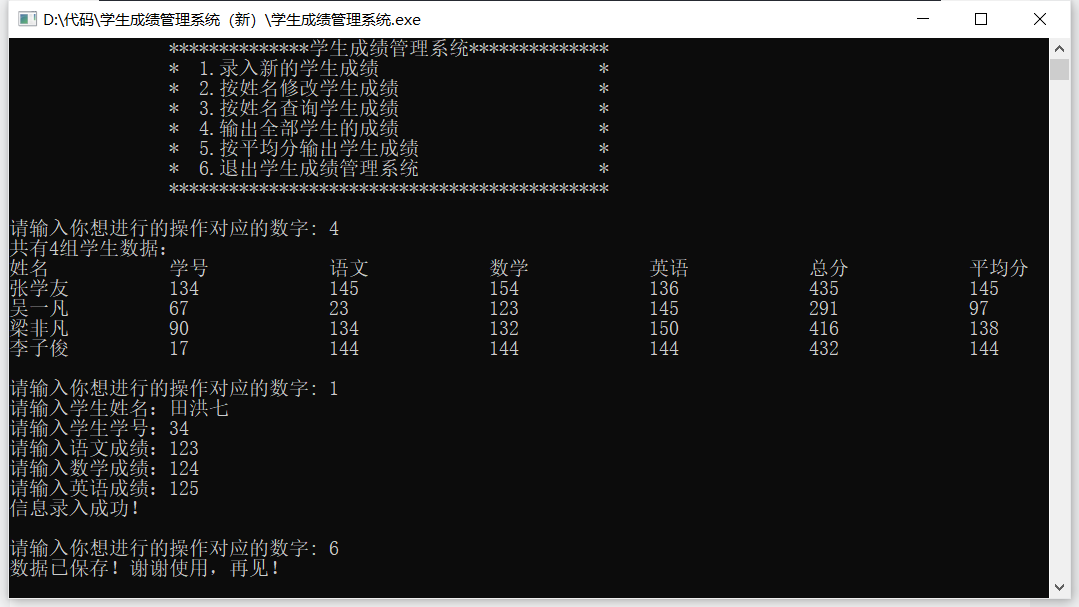
The last entered information is still there, indicating that the information is saved successfully
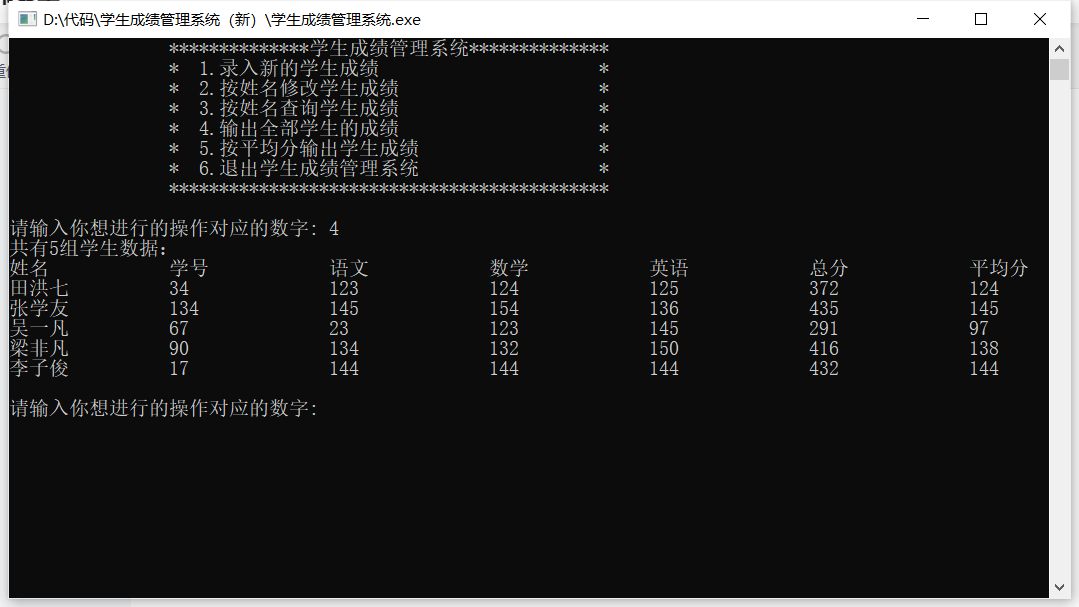
5, Precautions
The file must be in the same directory as the source code
The file name is "student grade. txt"