Array common methods interested can view the MDN document, which is very detailed Array - JavaScript | MDN https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array
https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array
Simply categorize these methods:
- Create array: array from , Array.of
- Iterators: keys, values, entries
- Copy and fill: copyWithin, fill
- Conversion method: toLocaleString, toString, valueOf
- Addition and deletion of arrays: push, pop, shift, unshift, concat,
- Sorting method: reverse, sort
- Get array index: indexof, lastIndexOf, FindIndex
- Traversal methods: forEach, filter, map, some, every, find, reduce
- Determine whether it is an array: array isArray, instanceof()
- Flattened array: flat, reduce
Next, explain one by one:
I Create array
1. Array.from
Used to convert a pseudo array structure into a true array, that is, an instance of an array
Parameter: 1 Pseudo array structure (can be any iteratable structure, including iterators, strings, etc.) 2 Mapping function
const arr = {
0: 1,
1: 2,
2: 3,
3: 4,
length: 4
}
const res = Array.from(arr, item => item ** 2) // [1, 4, 9, 16]
const strArr = Array.from('abcde') // ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']2. Array.of
It is used to convert a set of parameters into an array, in other words, put the things you pass in the array and output them
const res = Array.of(1, 2, 3123, 'a', 'c', [], {})
console.log(res); // [1, 2, 3123, 'a', 'c', Array(0), {...}]II iterator
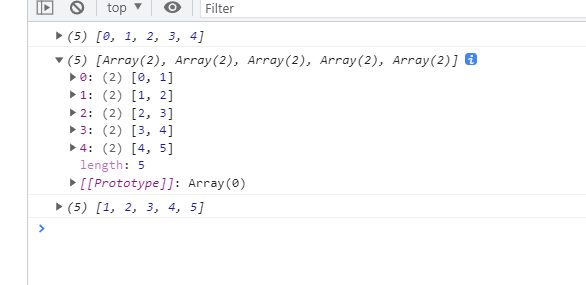
The prototype of the array exposes three methods that can access the iterator of the array. The keys method returns the iterator of the array index, the values method returns the iterator of the array element, and the entries method returns the iterator of the corresponding value of the array index, which can be accessed through array From into an array to see what it looks like
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
const keysArr = Array.from(arr.keys())
const entriessArr = Array.from(arr.entries())
const valuesArr = Array.from(arr.values())The final output is shown below
III Copy and fill
1. copyWithin replication
The concept given by MDN: this method copies a part of the array to another position in the same array and returns it without changing the length of the original array.
Parameter: 1 Copy base index (where to copy) 2 Start index (where to start replication) 3 End index (where to end)
const arr = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']
const arr2 = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']
// Explain the following operations in Vernacular: insert the first to third items in the array, excluding the third item = > b c, into the position with index 0, and change the original a b to B C
console.log(arr.copyWithin(0, 1, 3)); // ['b', 'c', 'c', 'd', 'e']
console.log(arr); // ['b', 'c', 'c', 'd', 'e']
// The copyWithin method modifies the original array
// If you do not want to modify the original array
console.log([...arr2].copyWithin(0, 1, 3)); // ['b', 'c', 'c', 'd', 'e']
console.log(arr2); // ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']1. fill
The fill method fills a value into a position in the array
Parameter: 1 Filling value: ≤ 2 Start of fill (index) 3 End of fill (index)
Explain: an empty array is created, but its length is 0, so its length is modified to fill 10 into the array. The index is 0 to 9
const arr = []
arr.length = 10
console.log(arr.fill(10, 0, 10)); // [10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10]As another example, create an array of 0-100
const arr = []
arr.length = 100
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr.fill(i + 1, i, i + 1)
}
console.log(arr); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89, 90, 91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, 99, 100]We'll talk about the rest tomorrow