Network programming
1, Overview
Network programming refers to writing programs that run on multiple devices (computers), which are connected through the network
1.1 two elements of network communication:
- Address of both parties:
-
ip
-
Port number
- Rules: protocols for network communication
-
TCP/IP
Reference model:
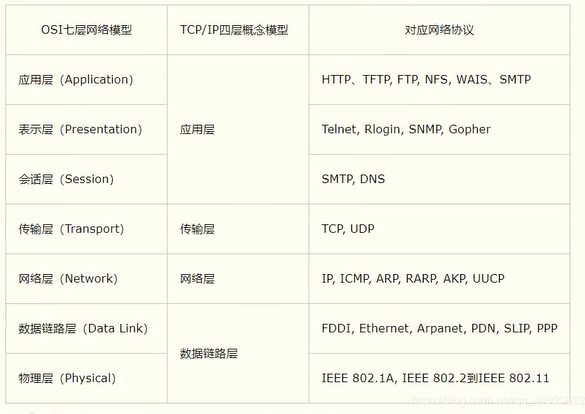
1.2 IP
ip address: inetAddress
-
Uniquely locate a computer on the network
-
127.0.0.1 == localhost (native)
-
Classification of ip addresses
-
IPv4: 127.0.0.1 4 bytes, 0-255 4.2 billion
-
IPv6: 128 bits, 8 unsigned integers
-
-
Public network (Internet) / private network (LAN)
-
Domain name: www.jd.com
InetAddress inetAddress1 = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
InetAddress inetAddress2 = InetAddress.getByName("localhost");
InetAddress inetAddress3 = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
InetAddress inetAddress4 = InetAddress.getByName("www.baidu.com");
1.3 port
The port represents the process of a program on the computer:
-
Different processes have different port numbers to distinguish software
-
Range: 0 - 65535
-
TCP/UDP : 65535*2 tcp:80 udp:80 ; Port numbers cannot conflict under the same protocol
-
Port classification:
-
Common ports: 0 ~ 1023
-
HTTP: 80
-
HTTPS: 443
-
FTP: 21
-
Telnet: 23
-
-
Program registration port: 1024 ~ 49151, assign users or register programs
-
Tomcat: 8080
-
MySQL: 3306
-
Oracle: 1521
-
-
Dynamic and private: 49152 ~ 65535
-
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException {
InetSocketAddress address1 = new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8080);
InetSocketAddress address2 = new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080);
InetSocketAddress address3 = new InetSocketAddress(InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"), 8080);
System.out.println(address1); // /127.0.0.1:8080
System.out.println(address2); // localhost/127.0.0.1:8080
System.out.println(address3); // /127.0.0.1:8080
System.out.println("--------------------------------");
System.out.println(address1.getPort()); // 8080
System.out.println(address1.getAddress()); // /127.0.0.1
System.out.println(address1.getHostName()); // 127.0.0.1
System.out.println(address1.getHostString()); // 127.0.0.1
System.out.println(address1.getClass()); //
}
1.4 communication protocol
Agreement: agreement
TCP/IP protocol cluster: it is actually a group of protocols
-
TCP: Transmission Control Protocol
-
UDP: User Datagram Protocol
-
IP: network interconnection protocol
TCP/UDP comparison:
-
TCP: call
-
Connection, stable
-
Three handshakes and four waves
-
Client, server
-
The transmission is completed, the connection is released, and the efficiency is low
-
-
UDP: send SMS
-
No connection, unstable
-
Client, server, no clear boundary (sender, receiver)
-
Ready or not, it can be sent
-
High efficiency, but packet loss may occur
-
Lack of reliability may result in loss, errors, and duplicate packets
-
DDOS: flood attack! (saturation attack)
-
1.5 TCP
TCP:(Transmission Control Protocol)
client:
-
Connect to the server Socket
-
send message
Server:
-
Establish the service port: ServerSocket
-
Waiting for the user's connection (listening): accept()
-
Receive messages from users
Client code:
Click to view the codepackage cn.com.longer.test.netWorkProgram.tcp;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
* TCP client
*/
public class TcpClientDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Socket socket = null;
OutputStream os = null;
try {
// 1. Know the address of the server: IP port number
InetAddress serverIp = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
int port = 9999;
// 2. Create a socket connection
socket = new Socket(serverIp,port);
// 3. Send message IO stream
os = socket.getOutputStream();
os.write("You ha ah, use Watson ewefef Three Dongfeng four".getBytes());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (socket != null){
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (os != null){
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
Server code:
Click to view the codepackage cn.com.longer.test.netWorkProgram.tcp;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
* TCP Server
*/
public class TcpServerDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ServerSocket serverSocket = null;
Socket socket =null;
InputStream is =null;
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = null;
try {
// 1. Server: I want to have an address
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9999);
// 2. Wait for the client to connect and listen
socket = serverSocket.accept();
// 3. Read the message from the client
is = socket.getInputStream();
// Pipe flow
baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1){
baos.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
System.out.println(baos.toString());
/*
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len=is.read(buffer)) != -1){
String msg = new String(buffer, 0, len);
System.out.println(msg);
}
*/
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
// Closed flow
if (baos != null){
try {
baos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (is != null){
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (socket != null){
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (serverSocket != null){
try {
serverSocket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
1.6 UDP
UDP: (User Datagram Protocol), user datagram protocol
Texting: don't connect, but you need to know each other's address!
Sender (code):
Click to view the codepackage cn.com.longer.test.netWorkProgram.udp;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.InetAddress;
/**
* UDP Sender
*/
public class UdpClientDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1. Create a socket
DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket();
// 2. Component package
String msg = "UDP Hello!!!";
InetAddress ip = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
int port = 9090;
// Who is the starting length of the packet to send
DatagramPacket datagramPacket = new DatagramPacket(msg.getBytes(), 0, msg.getBytes().length, ip, port);
// 3. Send packet
socket.send(datagramPacket);
// 4. Close the flow
socket.close();
}
}
Receiver (code):
Click to view the codepackage cn.com.longer.test.netWorkProgram.udp;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
/**
* UDP Receiver
*/
public class UdpServerDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1. Create socket and open port
DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(9090);
// 2. Receive packets
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket datagramPacket = new DatagramPacket(buffer, 0, buffer.length);
socket.receive(datagramPacket); // Blocking reception
System.out.println(datagramPacket.getAddress().getHostName());
System.out.println(datagramPacket.getData().toString());
System.out.println(new String(datagramPacket.getData(), 0, datagramPacket.getLength()));
// 3. Close the flow
socket.close();
}
}
1.7 URL
Uniform resource locator: to locate resources, locate a resource on the Internet!
DNS domain name resolution (resolve a domain name to IP): www.baidu.com com ---> https://220.181.38.149/
Protocol: / / IP address: port number / project name / resource
URLDemo:
Click to view the codepublic static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
URL url = new URL("https://space.bilibili.com/29038862/fans/follow?spm_id_from=333.1007.0.0");
System.out.println(url.getProtocol());
System.out.println(url.getHost());
System.out.println(url.getPort());
System.out.println(url.getPath());
System.out.println(url.getFile());
System.out.println(url.getQuery());
}
URLDown:
Click to view the codepackage cn.com.longer.test.netWorkProgram;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.URL;
public class UrlDown {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1. Download address
URL url = new URL("https://webfs.tx.kugou.com/202201071810/4d1be68a4efcbd709473a9d7d8f1013c/part/0/960141/G229/M0A/1A/07/xZQEAF9Iv6SAHH0xAEiEHQZqX8E377.mp3");
// 2. Connect to this resource HTTP
HttpURLConnection urlConnection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
// HttpsURLConnection urlConnection = (HttpsURLConnection) url.openConnection();
InputStream is = urlConnection.getInputStream();
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("loveOneLife.m4a");
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len=is.read(buffer)) != -1){
// Write this data
fos.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
fos.close();
is.close();
urlConnection.disconnect();
}
}