1. Introduction to swagger
Back end era:
- The front end can only manage static pages; HTML = = > back end. Template engine JSP = = > the back end is the main force
Era of front and rear end separation:
At present, the more popular framework is Vue + SpringBoot
- Front end - > front end control layer, view layer
- Backend - > backend control layer, service layer and data access layer
- The front and back end interact through API
- The front and rear ends are relatively independent and loosely coupled
- Fake front-end data, json can run without back-end
How the front and back end interact = = > API
-
The front and rear ends are relatively independent and loosely coupled;
-
The front and back end can even be deployed on different servers;
But there is a problem:
- The front and rear ends are assembled for joint commissioning, and the front-end personnel and back-end personnel cannot communicate and negotiate in time
resolvent:
- First, formulate the schema [outline of the plan] and update the latest API in real time to reduce the risk of integration
- Early years: develop word plan documents;
- Front and rear end separation:
- Front end test and back-end interface; postman
- The back-end provides an interface, which needs to update the latest messages and changes in real time
So in order to solve these writing problems, our Swagger ~ ~
Swagger
- It is known as the most popular API framework in the world;
- RestFul Api document online automatic generation tool = > API document and API definition are updated synchronously
- Run directly and test APi interface online;
- Support multiple languages (Java, ohp)
Official documents: https://swagger.io/
SpringBoot integration swagger
1. Create a new project (springboot WEB)
1. Select web dependency
2. Import related dependencies
Using Swagger in the project requires springfox and two jar packages;
-
Springfox-swagger2
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.springfox/springfox-swagger2 **Springfox-swagger2** --> <dependency> <groupId>io.springfox</groupId> <artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId> <version>3.0.0</version> </dependency> -
springfox-swagger-ui
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.springfox/springfox-swagger-ui --> <dependency> <groupId>io.springfox</groupId> <artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId> <version>3.0.0</version> </dependency>
3. Write HelloController and test whether it is successful
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String Hello(){
return "hello";
}
}
Tested questions
2. Configure Swagger
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2 //Open swagger2. Note: 222222!!!!
public class SwaggerConfig {
}
3. Test run:
At this time, I found the following error during the test run!!!
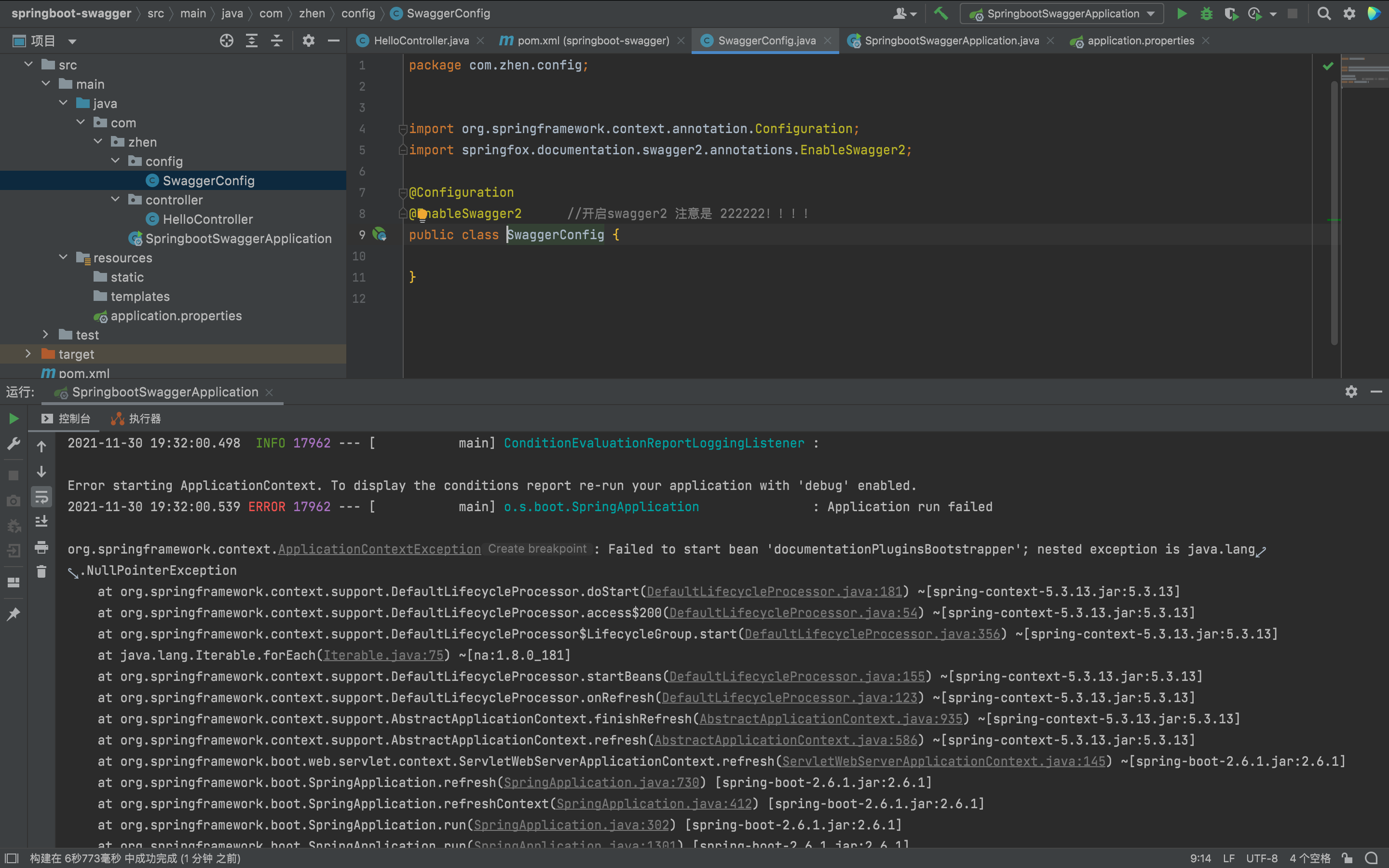
0S boot. Springapplication Application run failed
springboot can't run
Solution: after consulting many materials, I found that what I wrote was OK. It's a version problem. It was found that the springboot was downgraded to 2.5.2.....
Access test: http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html ,
You can see the interface of swagger;
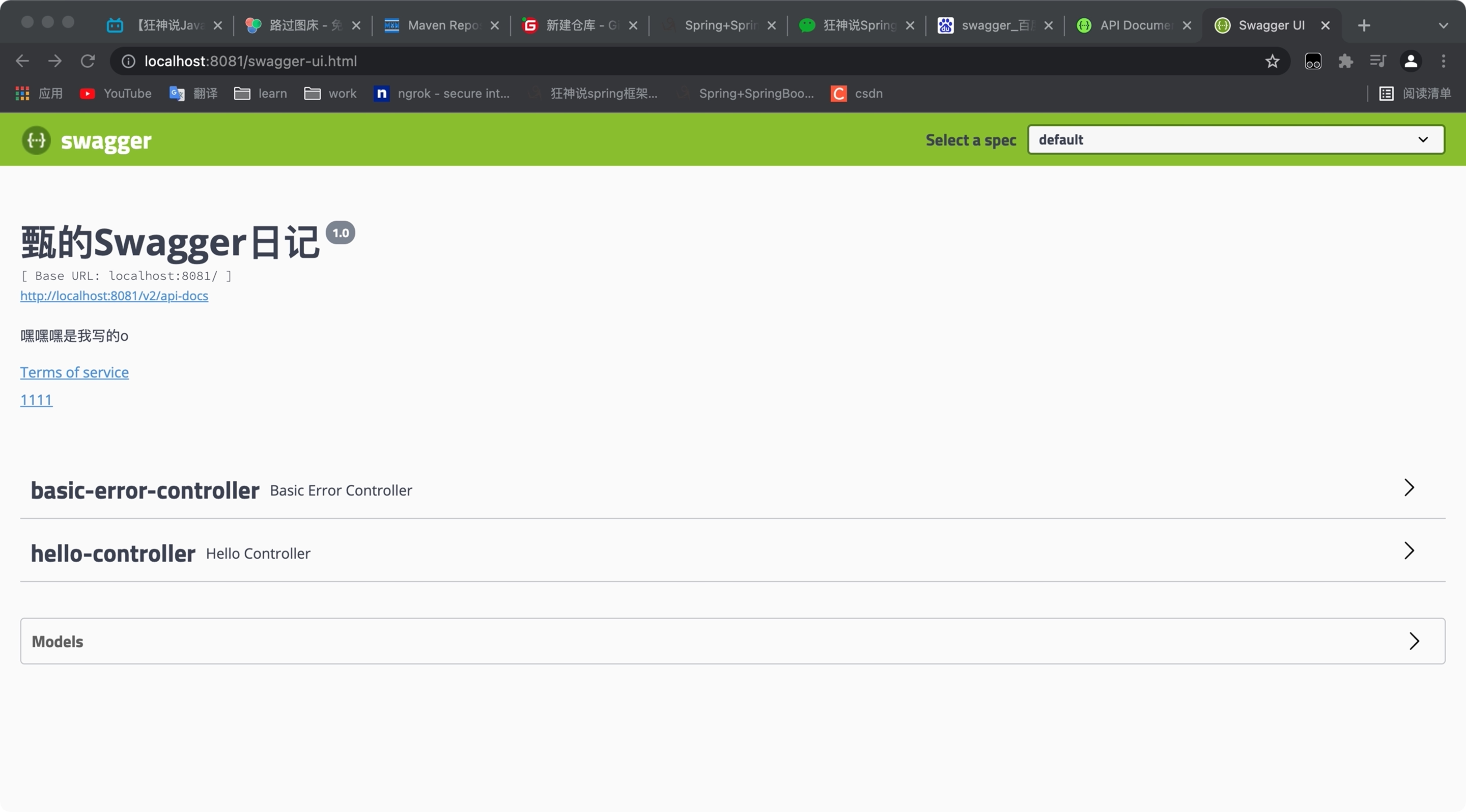
Configure Swagger
Swagger's bean instance Docket
ps . Look at the source code and find a way to be happier ~ ~ ~
Configure the document information through the apiInfo() property
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2 //Open swagger2. Note: 222222!!!!
public class SwaggerConfig {
//Configure the bean instance of the dock of swagger
@Bean
public Docket docket() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo());
}
//Configure configuration information apiInfo for swagger
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
String contact = "zhen";
return new ApiInfo(
"Zhen Swagger diary",
"Hey, hey, I wrote it o",
"1.0",
"urn:tos",
contact,
"1111",
"http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0"
);
}
}
Run the test and find the in seagger[ Page changed successfully~~~
Page changed successfully~~~
Swagger configuration scan interface
1. When building a Docket, configure how to scan the interface through the select() method.
//Configure the bean instance of the dock of swagger
@Bean
public Docket docket() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select() // Configure the scanning interface through the. select() method, and RequestHandlerSelectors configure how to scan the interface
//RequestHandlerSelectors configure how interfaces are to be scanned
//basePackage specifies the package to scan
//ang scan any package
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.zhen.controller"))
}
2. Interface scanning and filtering can also be configured:
//Configure the bean instance of the dock of swagger
@Bean
public Docket docket() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select() // Configure the scanning interface through the. select() method, and RequestHandlerSelectors configure how to scan the interface
//RequestHandlerSelectors configure how interfaces are to be scanned
//basePackage specifies the package to scan
//ang scan any package
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.zhen.controller"))
//Path filter path
.paths(PathSelectors.ant("/zhen/**"))
.build();
}
3. Configure Swagger switch
-
Configure whether to enable swagger through the enable() method. If false, swagger will not be accessible in the browser
@Bean public Docket docket() { return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2) .apiInfo(apiInfo()) .enable(false) //close .select() // Configure the scanning interface through the. select() method, and RequestHandlerSelectors configure how to scan the interface //RequestHandlerSelectors configure how interfaces are to be scanned //basePackage specifies the package to scan //ang scan any package .apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.zhen.controller")) //Path filter path //.paths(PathSelectors.ant("/zhen/**")) .build(); }Test: it's really inaccessible
**I just want my Swagger to be used in a production environment and not at release**
-
Determine whether the production environment
-
Then judge through enable
//Configure the bean instance of the dock of swagger @Bean public Docket docket(Environment environment) { // Set the environment in which you want to display swagger Profiles of = Profiles.of("dev", "test"); // Judge whether you are currently in this environment // Receive this parameter through enable() to determine whether to display boolean b = environment.acceptsProfiles(of); return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2) .apiInfo(apiInfo()) .enable(false) //Enable swagger .select() // Configure the scanning interface through the. select() method, and RequestHandlerSelectors configure how to scan the interface //RequestHandlerSelectors configure how interfaces are to be scanned //basePackage specifies the package to scan //ang scan any package .apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.zhen.controller")) //Path filter path //.paths(PathSelectors.ant("/zhen/**")) .build(); }
Configure Api file grouping
-
.groupName("zhen") -
A docker can return one group and configure multiple groups. You only need to configure multiple docket s
@Bean public Docket docket1(){ return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("group1"); } @Bean public Docket docket2(){ return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("group2"); } @Bean public Docket docket3(){ return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("group3"); }
Entity class configuration
-
New entity class
@ApiModel("User entity") public class User { @ApiModelProperty("user name") public String username; @ApiModelProperty("password") public String password; } -
Write controller
@RequestMapping("/getUser") public User getUser(){ return new User(); }ps.
-
@ApiModel adds comments to the class
-
@ApiModelProperty adds comments for class properties
-
-
Common notes
Swagger annotation Brief description @Api(tags = "xxx module description") Act on module classes @ApiOperation("xxx interface description") Act on interface methods @ApiModel("xxxPOJO description") Act on model classes: such as VO and BO @ApiModelProperty(value = "xxx property description", hidden = true) It acts on class methods and attributes. Setting hidden to true can hide the attribute @ApiParam("xxx parameter description") It acts on parameters, methods and fields, similar to @ ApiModelProperty -
Configure some comments for the requested interface
@ApiOperation("Zhen Interface") @PostMapping("/zhen") @ResponseBody public String zhen(@ApiParam("user name: ")String username){ return username; }
[note]
Remember to turn off Swagger during the official release!!! For safety and memory saving ~·