Ten new features of HTML 5
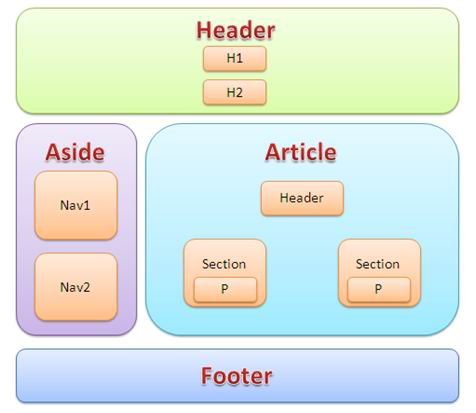
(1) Semantic tags (Semantic tags provide better page structure for pages).
Semantic tags for HTML5 include:
- <section> - Represents a paragraph or section in a document;
- Nav > - Used to build navigation;
- <article> - Represents integrated content in documents, pages, applications or websites;
- <aside> - Represents parts that are related to and different from the main content of the page.
- <hgroup> - The title of a paragraph or section;
- Header > - Header of the page;
- Footer > - Footer of the page;
- < time > - denotes date and time;
- <mark> - Text that needs to be highlighted in the document.
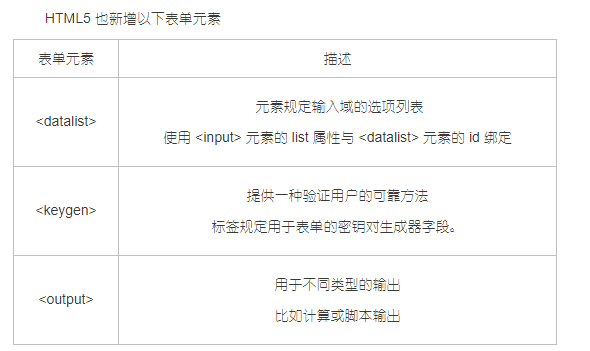
(2) Enhanced forms
New form attributes in HTML5
- The placehoder attribute, a short prompt, is displayed on the input field before the user enters the value. That is, our common input box default prompt disappears after user input.
- Required is a boolean attribute. Input fields required to be filled in cannot be empty
- The pattern attribute describes a regular expression used to validate the value of the < input > element.
- The min and max attributes set the minimum and maximum values of the elements.
- The step attribute specifies a legal number interval for the input field.
- The height and width attributes are used for the image height and width of the < input > tag of the image type.
- The autofocus attribute is a boolean attribute. Provides that when a page is loaded, the domain automatically gets the focus.
- The multiple attribute is a boolean attribute. Provides that multiple values can be selected in the < input > element.
(3) Video and audio
Video playback: <video src="><video>
Audio playback: <audio src="></audio>
(4) Canvas Drawing
<canvas width="1000" height="1000"></canvas>
js content
var canvas = document.getElementsByTagName("canvas")[0];
var context = canvas.getContext("2d");
Path writing is a common way of writing
// 1. Start a path
// 2. What is the specific path?
// 3. End paths (optional, add them to form a closed, no add means end at any time) are commonly used in point rendering.
// 4. Setting attributes (colors) is OK as long as they are set before drawing, whatever step you take, but before redrawing.
// 5. Drawing (fill () stroke ())
context.beginPath(); //Start a path
context.rect(10,10,100,100);
context.closePath();
context.fillStyle = "#f00";
context.fill()

context.beginPath();
context.moveTo(340,10);
context.lineTo(440,10);
context.lineTo(440,110);
context.lineTo(340,110);
context.lineTo(340,10);
// context.closePath();
context.strokeStyle = "#0f0";
context.lineWidth = "10"
context.stroke()
context.beginPath();
context.moveTo(450,10);
context.lineTo(550,10);
context.lineTo(550,110);
// context.lineTo(450,110);
context.fillStyle = "#00f";
context.fill() //Solid drawing closes automatically

// Circle drawing
// 1. Start a path
// 2. Route method of drawing circle
// 3. Ending a Path
// 4. Setting the properties of a circle
// 5. Start drawing
context.beginPath();
// context.arc(x,y,r, start angle, end angle [, drawing direction). boolean defaults to false, true to counterclockwise, false to clockwise])
// One original two radians, one radian is a PI (Math.PI)
// The starting angle is in the direction of three o'clock, which indicates that when the radian is zero, it is calculated clockwise.
context.arc(200,200,50,0,Math.PI,true);
context.closePath();
context.fill()

(5) SVG Drawing
What is SVG?
- SVG refers to Scalable Vector Graphics.
- SVG is used to define vector-based graphics for networks
- SVG defines graphics in XML format
- The quality of SVG image will not be lost when it is enlarged or changed in size.
- SVG is the standard of World Wide Web Alliance
<svg idth="1000" height="1000"> //To create a circle, you need to add one<circle>Label <circle cx="300" cy="150" r="140" fill="red"/> //The cx and cy attributes define the coordinates of x and y of the dots. If cx and cy are omitted, the center of the circle is set to (0, 0), and the r attribute is defined as the radius of the circle. </svg> <rect>Tags are used to create rectangles <svg width="1000" height="1000"> <rect width="400" height="200" x="20" y="20" fill="red"/> </svg>
Frequently-used SVG Graphical: (1)rectangle <rect width="100" height="50" x="400" y="350" fill="#f0f" fill-opacity="0.3" stroke="#00f" stroke-width="6" stroke-opacity=".3"></rect> (2)circular <circle r="100" cx="400" cy="300" fill="#f0f" fill-opacity="0.4" stroke="#00f" stroke-width="6" stroke-opacity=".4"></circle> (3)Ellipse <ellipse rx="100" ry="50" cx="400" cy="350" fill="#f0f" fill-opacity=".4" stroke="#00f" stroke-width="6" stroke-opacity=".4"></ellipse> (4)Straight line (no) fill only stroke) <line x1="45" y1="350" x2="450" y2="350" stroke="#f00" stroke-width="4px" stroke-opacity=".4"></line> (5)Broken line( fill Transparency must be set/stroke Must be specified manually) <polyline points="150,200 250,100 350,300 450,50" stroke="#00f" stroke-width="6" stroke-opacity=".4" fill="transparent"></polyline> (6)polygon <polygon points="100,150 100,300 400,300 400,150 250,220" fill="#f0f" fill-opacity=".4" stroke="#00f" stroke-width="6" stroke-opacity=".4"></polygon>
(7)text <text alignment-baseline="before-edge" font-size="40" fill="#f0f" stroke="#00f">Danet Technology 2018 ajgy</text> (8)image <image xlink:href="img/p3.png" x="400" y="200" width="100" height="200"></image>
(6) Geographical positioning
(7) Drag and Drop API
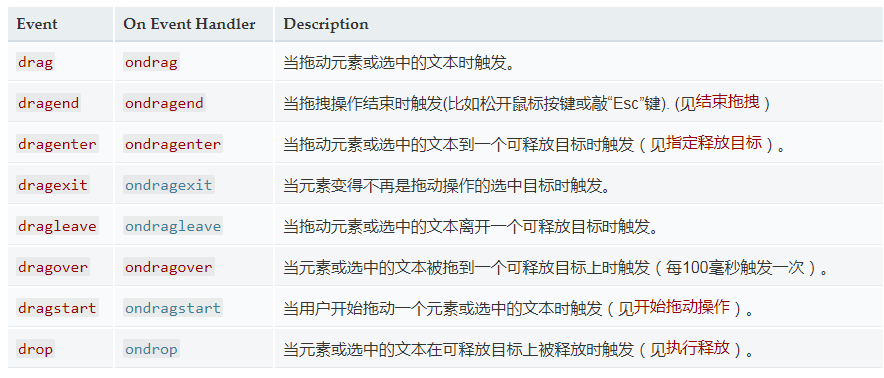
Events that may be triggered by a dragged source object:
Dragstart: dragstart
Drag: in drag
Dragend: dragend
Events that may be triggered by the dragged target:
Dragenter: dragenter
dragover: drag hover
drop: release
dragleave: drag to leave
(8) Web Worker
(9) Web Storage
(10) WebSocket