Exercise 3.1: if the f function returns an unrestricted float64 value, the SVG file may output invalid polygon elements (although many SVG renderers will handle this properly). The modifier skips invalid polygons.
Exercise 3.2: experiment with rendered graphics for other functions in the math package. Can you output an egg box, moguls or a saddle pattern?
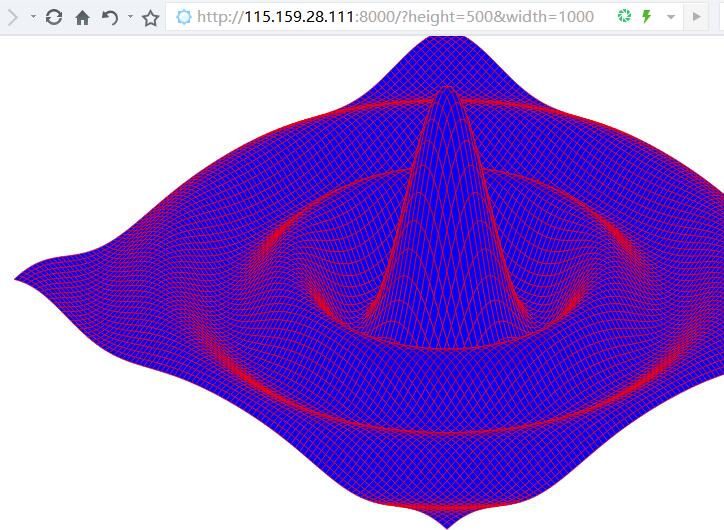
Exercise 3.3: color each polygon according to its height, so that the peak will be red (ff0000), and the valley will be blue (ff 0000ff).
Exercise 3.4: refer to the functions in the Lissajous example in section 1.7, and construct a web server to calculate the function surface and then return SVG data to the client. The server must set the content type header:
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "image/svg+xml")
(this step is not necessary in the Lissajous example, because the server uses the standard PNG image format and can automatically output the corresponding header according to the 512 bytes above.) Allows clients to request parameters such as height, width, and color through HTTP.
// Surface computes an SVG rendering of a 3-D surface function.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math"
"net/http"
"strconv"
)
var height,width float64 = 300 , 600
var cells float64= 100 // number of grid cells
var xyrange float64= 30.0 // axis ranges (-xyrange..+xyrange)
var xyscale float64= width / 2 / xyrange // pixels per x or y unit
var zscale float64= height * 0.4 // pixels per z unit
var angle float64= math.Pi / 6 // angle of x, y axes (=30°)
var sin30, cos30 = math.Sin(angle), math.Cos(angle) // sin(30°), cos(30°)
func main() {
//http services
http.HandleFunc("/",handle)
http.ListenAndServe("0.0.0.0:8000",nil)
}
func handle(w http.ResponseWriter,r *http.Request){
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "image/svg+xml")
if err := r.ParseForm();err != nil{
return
}
//var height int
//var width int
for k,v := range r.Form{
if k == "height"{
h, _ := strconv.ParseFloat(v[0],64)
if h>0 {height = h}
}
if k == "width"{
w, _ := strconv.ParseFloat(v[0],64)
if w>0 {width = w}
}
}
xyscale = width / 2 / xyrange
zscale = height * 0.4
fmt.Fprintf(w,"<svg xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg' "+
"style='stroke: #ff0000; fill: #0000ff; stroke-width: 0.7' "+
"width='%d' height='%d'>", width, height)
for i := 0; i < int(cells); i++ {
for j := 0; j < int(cells); j++ {
ax, ay := corner(i+1, j)
bx, by := corner(i, j)
cx, cy := corner(i, j+1)
dx, dy := corner(i+1, j+1)
fmt.Fprintf(w,"<polygon points='%g,%g %g,%g %g,%g %g,%g'/>\n",
ax, ay, bx, by, cx, cy, dx, dy)
}
}
fmt.Fprintf(w,"</svg>")
}
func corner(i, j int) (float64, float64) {
// Find point (x,y) at corner of cell (i,j).
x := xyrange * (float64(i)/cells - 0.5)
y := xyrange * (float64(j)/cells - 0.5)
// Compute surface height z.
z := f(x, y)
// Project (x,y,z) isometrically onto 2-D SVG canvas (sx,sy).
sx := width/2 + (x-y)*cos30*xyscale
sy := height/2 + (x+y)*sin30*xyscale - z*zscale
return sx, sy
}
func f(x, y float64) float64 {
r := math.Hypot(x, y) // distance from (0,0)
return math.Sin(r) / r
}