Everyone knows my style and likes to bring stories into technical learning.
But... How can I bring in the source code with a story?
With my universal story template, Xiao Ming's treasure exploration journey.
That day, Xiao Ming came to the kingdom of Mybatis. He asked the old man at the gate that the gate was written iBatis. How could it be changed to Mybatis.
The old man replied: Oh, originally, it was iBatis, but now it has changed its name to Mybatis.
Xiao Ming scratched his head. The old man answered the question, but he didn't seem to answer.
Anyway, I know. Now it's Mybatis.
Xiao Ming knows that there is a magical thing in Mybatis Kingdom, called Mapper agent.
Due to his persistence in this object, Xiao Ming takes his weapon (IntelliJ IDEA) into the city to find out.
1, Curiosity
Curiosity is one of the essential factors driving our human development. It is said that Curiosity Kills cats. This sentence is not tenable in the field of technology. As a technician, we must be curious about things (I am talking about things in the field of technology. Don't be surprised by Uncle te's service, just go to Uncle TE)
You usually use Mybatis. Isn't there anything that makes you curious?
You create a Mapper interface and then write a Mapper.xml
Finally, you can add, delete, modify and query directly using Mapper interface.
Firstly, it is an interface. Secondly, how does it know what operations to perform?
I don't know whether you are curious or not. Anyway, I am very curious. It is because of this curiosity that I came to this adventure.
2, A rugged road
I've leveled the road for you. Curious students can follow my footprints. Maybe you can find a lot of wonderful things.
First of all, there must be a children's country. No, there must be a Mybatis kingdom.
pom.xml
After adding maven dependencies, remember to reload the project and ask him to download the corresponding jar package to the local warehouse.
<dependencies>
<!--Mybatis-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.4.5</version>
</dependency>
<!--mysql drive-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.47</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
mybatis-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="TestMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
TestMapper.java
package dao;
import entity.TestEntity;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author Day and night programming of Muzi
*/
public interface TestMapper {
List<TestEntity> list();
}
TestEntity.java
package entity;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
/**
* @author Day and night programming of Muzi
*/
public class TestEntity {
private Long id;
private String name;
private BigDecimal salary;
// getter setter
}
TestMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="dao.TestMapper">
<!--Query all data-->
<select id="list" resultType="entity.TestEntity">
select * from test
</select>
</mapper>
Test.java
import dao.TestMapper;
import entity.TestEntity;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author Day and night programming of Muzi
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1. mybatis configuration file
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
// 2. Get input stream
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 3. Create SqlSessionFactory factory. Mapper's dynamic proxy operation will be performed
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
// 4. Create SqlSession
try (SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
// 5. Obtain Mapper through sesson. This Mapper will program the proxy Mapper of Mybatis
TestMapper mapper = session.getMapper(TestMapper.class);
// 6. Call method
List<TestEntity> list = mapper.list();
System.out.println(list);
}
}
}
After my exploration, the main logic is completed in the third step. How do you say that? Steal heaven and change the day.
We wrote in the previous article: reflection, dynamic agent, factory mode
Here we use these 2 technologies to package our Mapper. You think you use your own Mapper, but what you think is right? It's wrong.
1. SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); 2. XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties); 3. super(new Configuration()); One attribute is: protected final MapperRegistry mapperRegistry = new MapperRegistry(this);
A simple class diagram is drawn. In fact, a MapperRegistry is created when reading the configuration file
The MapperRegistry is where the treasure (the proxy of the interface Mapper we wrote) is stored.
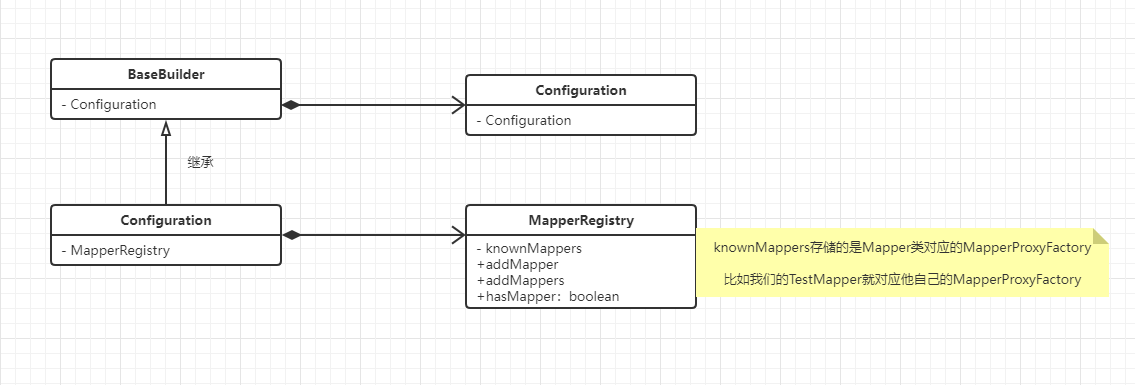
We can see when MapperRegistry comes out
Let's see when to use his addMapper method, and of course, the addMappers method
Let's focus on the addMapper method analysis. Don't be too persistent
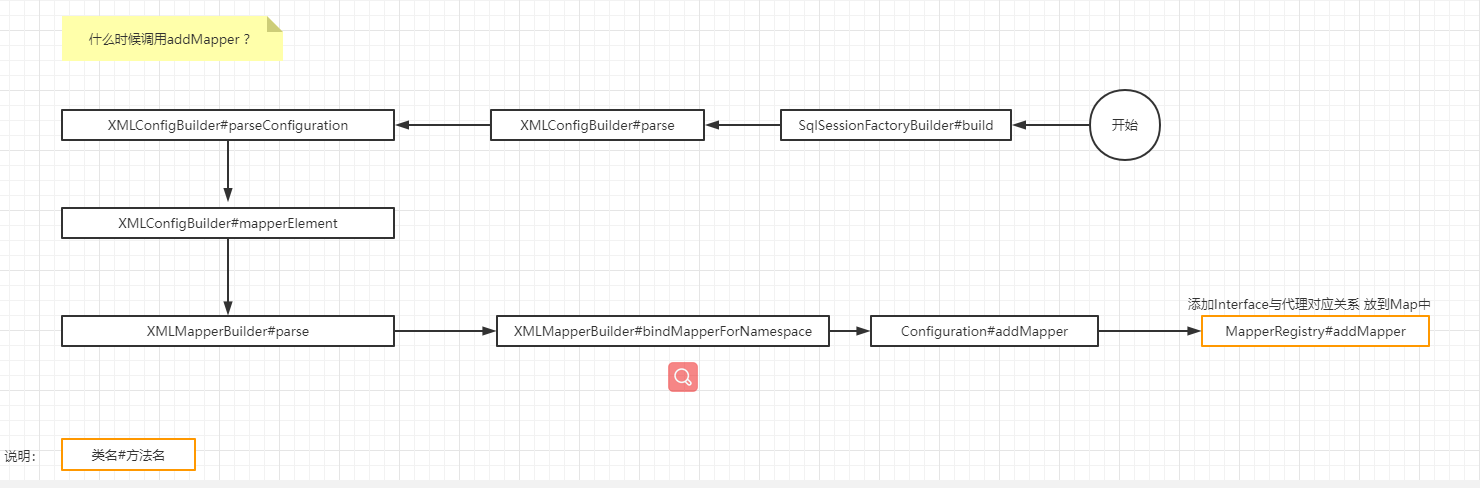
1. It has been created above parser
parser.parse()
2. You can see that the configuration file is being parsed here configuration Is the root node of our configuration file
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
3. see Mapper If so, look at this analysis mappers Other labels can be ignored first
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
// Start looping through the sub tags of mappers. Its sub tags can make mappers and package s
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
// If it's a package operation, we don't look at this
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else {
// Let's look at this to get the properties of the word tag
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
// If only resource is configured, we only see this way, because this is what we configure
// Read resources
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// Convert to XMLMapperBuilder
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
// Walk analysis
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
// If only url is configured
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {
// If only class is configured
Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
} else {
// A mapper can only have one attribute, or url, or resource, or class
// If you report this error when developing, you should configure multiple properties
// After my verification, just trust me
throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}
}
XMLMapperBuilder.java
public void parse() {
// Judge whether the file has been parsed. All parsed files are placed in a set
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// After a series of operations
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
// Put into set and mark as resolved resources
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
// Start binding Mapper and Mapper.xml
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingCacheRefs();
parsePendingStatements();
}
private void bindMapperForNamespace() {
// Get namespace dao.TestMapper
String namespace = builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace();
// If the namespace is not configured, Mapepr and Mapper.xml will not be bound
// If the namespace is empty, the preceding parsing will directly report an exception. I don't know what can go here
if (namespace != null) {
Class<?> boundType = null;
try {
// Get the class TestMapper.class corresponding to the namespace
boundType = Resources.classForName(namespace);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// If you can't find the class, forget it, because it's not necessary
// We can also refer to this method in our own business
// if class has a bala operation
// else does not operate
}
if (boundType != null) {
// First, judge whether this class has been included. In fact, it is the hasMapper of mapperRegistry called
if (!configuration.hasMapper(boundType)) {
// This is to adapt to spring. A flag is set to prevent multiple loading of this resource
// See MapperAnnotationBuilder#loadXmlResource for more information
configuration.addLoadedResource("namespace:" + namespace);
// We don't pay attention to those, we only pay attention to this
configuration.addMapper(boundType);
}
}
}
}
As we said before, look at the code, especially the source code. Don't go into the black hole. You must be clear about your purpose this time.
It's like I click configuration.addLoadedResource("namespace:" + namespace); Here you know that it's just to make a mark for the adaptation of Spring. As for why and how to do the adaptation, you don't have to worry. Your purpose this time should be very clear. You just want to explore how Mapper proxy is represented, so don't get involved.
Configuration.java
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
mapperRegistry.addMapper(type);
}
public class MapperRegistry {
// This is a reference to Configuration, because some configurations will be used during registration
private final Configuration config;
// Finally, the treasure chest will be stored in the proxy factory here. Our last code call getMapper uses this factory to create one for us
// Proxy object: as we wrote in the previous articles, the reflection, proxy mode and factory mode fit here very well
private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>>();
public MapperRegistry(Configuration config) {
this.config = config;
}
// This method is generally called to get the proxy code
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
// If there is no factory corresponding to Mapper type, throw an exception
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
// Create a proxy object
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
// Judge whether the containsKey of hashMap exists
public <T> boolean hasMapper(Class<T> type) {
return knownMappers.containsKey(type);
}
// Register Mapper
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
// Judge whether it is an interface type. If it is not an interface type, it will not be processed
if (type.isInterface()) {
// If it already exists, no throwing exception will be added
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
// Whether the tag is loaded successfully
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
// Preemption is very important
// If it is not occupied, it may be tried to bind automatically
// If the type already exists, it will not try the judgment above. hasMapper is judging this
// I didn't quite understand it, but it doesn't matter. It's better to write like this
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<T>(type));
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
// Parse some initialization
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
// If it is not loaded successfully, it is removed from the map
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
}
Everyone who read my article yesterday knows that next, let's take a look at the matchmaker MapperProxyFactory
// The matchmaker is responsible for introducing the object and creating the factory class of our Mapper interface proxy
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {
// Class object of interface
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
// Method object and encapsulation of method object
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<Method, MapperMethod>();
// Constructor
public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
public Class<T> getMapperInterface() {
return mapperInterface;
}
public Map<Method, MapperMethod> getMethodCache() {
return methodCache;
}
//Create proxy object
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
// Create a Proxy class and return it. For this Proxy, see my previous article on dynamic Proxy
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(),
new Class[] { mapperInterface },
mapperProxy);
}
// Here is to pass in an sql session and create a Mapper interface proxy class
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
// Here you create Mapper's proxy, which implements invocationhandler (see my previous dynamic proxy articles)
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession,
mapperInterface,
methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
}
MapperProxy.java
/**
* Copyright 2009-2017 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.apache.ibatis.binding;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.lang.invoke.MethodHandles;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.ibatis.lang.UsesJava7;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.ExceptionUtil;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
// Both JKD dynamic agents need to implement InvocationHandler
// The specific proxy is done in invoke
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6424540398559729838L;
// sqlSession
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
// Interface object type TestMapper
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
// Method list in interface, etc
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache;
public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
this.methodCache = methodCache;
}
// All methods of the interface proxy object will be called here
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
// Judge whether it is the basic method toString hashCode. If so, call it directly without proxy
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {
// The method to determine whether the default is modified. If yes, it will be handled specially
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
// We usually come here
// If there is a cache, take the cached data. If there is no cache, create the data and put it into the cache
// Friends can see that Map is a magical existence. It exists everywhere
// Therefore, you must prepare relevant knowledge for the interview
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
// First judge whether there is
MapperMethod mapperMethod = methodCache.get(method);
// No,
if (mapperMethod == null) {
// establish
mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration());
// Put in cache
methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod);
}
// return
return mapperMethod;
}
}
MapperMethod.java
package org.apache.ibatis.binding;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Flush;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.MapKey;
import org.apache.ibatis.cursor.Cursor;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.MappedStatement;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.SqlCommandType;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.MetaObject;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.ParamNameResolver;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.TypeParameterResolver;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.ResultHandler;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.RowBounds;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
import java.util.*;
// This class is powerful. This is the core class. Here we encapsulate our operations using SqlSession
public class MapperMethod {
// Type of Sql tag Insert Update Delete Select
private final SqlCommand command;
// Method parameter information, return information, etc
private final MethodSignature method;
// structure
public MapperMethod(Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) {
this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);
this.method = new MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method);
}
// Here are a series of methods encapsulating SqlSession, such as selectOne, select, insert, delete, etc
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
// Why do we often say that the three tags of Insert update delete actually have the same function
// Usually there are only semantic differences
// We can click the sqlSession source code to see that the update method is called in the end
case INSERT: {
// Processing parameters
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// Call sqlSessioninsert
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
// If it's Select, that's more
case SELECT:
// If the return type is void and there is a custom ResultHandler
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
// Return type multiline
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
// Fanhu Map
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
// Return to Cursor
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
// Return single
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
}
break;
case FLUSH:
// wipe cache
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
// This usually doesn't appear unless you're a fool, ha ha
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
// It's interesting here
// We may have encountered that if the query result is the basic type (boolean, char, byte, short, int, long, float, double), it is easy to report null exceptions
// When we write code, we must pay attention to the basic type. We must ensure that there is a return value, otherwise you will use the encapsulated type Integer Double, etc
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '"
+ command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type ("
+ method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
// Return results
return result;
}
// insert update delete return processing rowCount is the number of affected rows returned after Sqlsession execution
private Object rowCountResult(int rowCount) {
final Object result;
// If the return type is void, it will directly return null
if (method.returnsVoid()) {
result = null;
// Return type Integer int
} else if (Integer.class.equals(method.getReturnType()) || Integer.TYPE.equals(method.getReturnType())) {
result = rowCount;
// Return type Long long
} else if (Long.class.equals(method.getReturnType()) || Long.TYPE.equals(method.getReturnType())) {
result = (long)rowCount;
// Return type Boolean
} else if (Boolean.class.equals(method.getReturnType()) || Boolean.TYPE.equals(method.getReturnType())) {
result = rowCount > 0;
} else {
// Throw exceptions directly for other return types
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName() + "' has an unsupported return type: " + method.getReturnType());
}
return result;
}
// There is a custom ResuleHandler
private void executeWithResultHandler(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
MappedStatement ms = sqlSession.getConfiguration().getMappedStatement(command.getName());
//
if (void.class.equals(ms.getResultMaps().get(0).getType())) {
throw new BindingException("method " + command.getName()
+ " needs either a @ResultMap annotation, a @ResultType annotation,"
+ " or a resultType attribute in XML so a ResultHandler can be used as a parameter.");
}
//
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
//
if (method.hasRowBounds()) {
RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args);
sqlSession.select(command.getName(), param, rowBounds, method.extractResultHandler(args));
} else {
//
sqlSession.select(command.getName(), param, method.extractResultHandler(args));
}
}
// Multiple returned results
private <E> Object executeForMany(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
// Return value
List<E> result;
// Convert parameters to ParamMap
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// Whether there are paging parameters
if (method.hasRowBounds()) {
RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args);
result = sqlSession.<E>selectList(command.getName(), param, rowBounds);
} else {
// Execute the selectList of sqlSession directly
result = sqlSession.<E>selectList(command.getName(), param);
}
// class1.isAssignableFrom(class2)
// Determine whether class2 is a subclass or sub interface of class1
if (!method.getReturnType().isAssignableFrom(result.getClass())) {
// If the return type is Array, convert to Array
if (method.getReturnType().isArray()) {
return convertToArray(result);
} else {
// No, convert to declared collection
return convertToDeclaredCollection(sqlSession.getConfiguration(), result);
}
}
return result;
}
// Return to Cursor
private <T> Cursor<T> executeForCursor(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Cursor<T> result;
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
if (method.hasRowBounds()) {
RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args);
result = sqlSession.<T>selectCursor(command.getName(), param, rowBounds);
} else {
result = sqlSession.<T>selectCursor(command.getName(), param);
}
return result;
}
// Convert to collection
private <E> Object convertToDeclaredCollection(Configuration config, List<E> list) {
// First create an object of the declared collection type
Object collection = config.getObjectFactory().create(method.getReturnType());
// Convert to proxy
MetaObject metaObject = config.newMetaObject(collection);
// Put all the elements in
metaObject.addAll(list);
return collection;
}
// Convert to array
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private <E> Object convertToArray(List<E> list) {
// Create array object
Class<?> arrayComponentType = method.getReturnType().getComponentType();
Object array = Array.newInstance(arrayComponentType, list.size());
// Judge whether it is the basic type array int [] long []
if (arrayComponentType.isPrimitive()) {
// If it is a base type, a conversion is required
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
//
Array.set(array, i, list.get(i));
}
return array;
} else {
// If you do not call toArray directly, convert to Array
return list.toArray((E[])array);
}
}
// Return to Map
private <K, V> Map<K, V> executeForMap(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Map<K, V> result;
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
if (method.hasRowBounds()) {
RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args);
result = sqlSession.<K, V>selectMap(command.getName(), param, method.getMapKey(), rowBounds);
} else {
result = sqlSession.<K, V>selectMap(command.getName(), param, method.getMapKey());
}
return result;
}
// Custom Map
// We can also refer to this method in our business, that is, we rewrite the get method and throw an exception if we don't get the element
public static class ParamMap<V> extends HashMap<String, V> {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2212268410512043556L;
@Override
public V get(Object key) {
if (!super.containsKey(key)) {
throw new BindingException("Parameter '" + key + "' not found. Available parameters are " + keySet());
}
return super.get(key);
}
}
}
// Encapsulates the specific actions to be performed
public static class SqlCommand {
// xml id, such as: list
private final String name;
// Insert, update, delete, etc
private final SqlCommandType type;
public SqlCommand(Configuration configuration, Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method) {
// Name list
final String methodName = method.getName();
// Class dao.TestMapper
final Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
MappedStatement ms = resolveMappedStatement(mapperInterface, methodName, declaringClass,
configuration);
if (ms == null) {
// Is there a Flush label
if (method.getAnnotation(Flush.class) != null) {
name = null;
// Set the type to Flush
type = SqlCommandType.FLUSH;
} else {
throw new BindingException("Invalid bound statement (not found): "
+ mapperInterface.getName() + "." + methodName);
}
} else {
name = ms.getId();
type = ms.getSqlCommandType();
// INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, SELECT, FLUSH exceptions are thrown directly when the type is not recognized;
if (type == SqlCommandType.UNKNOWN) {
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + name);
}
}
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public SqlCommandType getType() {
return type;
}
private MappedStatement resolveMappedStatement(Class<?> mapperInterface, String methodName,
Class<?> declaringClass, Configuration configuration) {
// statementId ==> dao.TestMapper.list
String statementId = mapperInterface.getName() + "." + methodName;
// If there is already a direct return
if (configuration.hasStatement(statementId)) {
return configuration.getMappedStatement(statementId);
} else if (mapperInterface.equals(declaringClass)) {
return null;
}
for (Class<?> superInterface : mapperInterface.getInterfaces()) {
if (declaringClass.isAssignableFrom(superInterface)) {
MappedStatement ms = resolveMappedStatement(superInterface, methodName,
declaringClass, configuration);
if (ms != null) {
return ms;
}
}
}
return null;
}
}
public static class MethodSignature {
// Return multiple results
private final boolean returnsMany;
// Return Map
private final boolean returnsMap;
// Return void
private final boolean returnsVoid;
//Return Cursor
private final boolean returnsCursor;
// Return type
private final Class<?> returnType;
// mapKey
private final String mapKey;
// The location of the resultHandler type parameter
private final Integer resultHandlerIndex;
// The location of the rowBound type parameter
private final Integer rowBoundsIndex;
// Parameter processor
private final ParamNameResolver paramNameResolver;
}
3, Nagging
The final result of the expedition was that I was blindfolded. Looking at it, I was discouraged.
This architecture is awesome, all kinds of packages, all kinds of modes, all kinds of
The most important thing is that we see that we use the proxy mode and factory mode to proxy our Mapper interface,
The interface we get through getMapper is actually a proxy object. At this time, all operations are performed through the proxy MapperProxy
The Jdk dynamic proxy by InvocationHandler is implemented
I've seen the source code for the second time, but it's still not so clear, so we don't need to master all the points at once. First, we need to master a small point, such as how to realize the Mapper interface agent through dynamic agent, and then talk about the specific contents of other agents slowly.
Welcome to the official account: Muzi's day and night programming