1. Pre order printing node
[problem description] the algorithm is designed to print the leaf nodes of the binary tree in the way of preorder traversal.
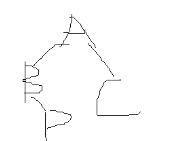
[input form] a line of string, which is the preorder traversal sequence of the extended binary tree, which is used to construct the binary tree.
[output form] the pre order leaf traversal sequence of binary tree (separated by spaces).
[sample input] AB#D##C##
[sample output]
D C
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string str;
getline(cin, str);
int i = 0;
while (str[i] != '\0') {
if(str[i]!='#'){
if (str[i + 1] == '#' && str[i + 2] == '#') {
cout << str[i] << " ";
}
}
i++;
}
}
2. Find the number of nodes of the binary tree
[problem description] design an algorithm to find the number of nodes of the binary tree.
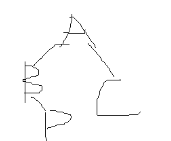
[input form] a line of string, which is the preorder traversal sequence of the extended binary tree, which is used to construct the binary tree.
[output form] number of nodes in binary tree.
[sample input] AB#D##C##
[sample output]
4
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string str;
getline(cin, str);
int i = 0;
int count = 0;
while (str[i] != '\0') {
if (str[i] != '#') {
count++;
}
i++;
}
cout << count;
}3. Find the depth of binary tree
[problem description] design algorithm to find the depth of binary tree.
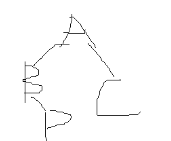
[input form] a line of string, which is the preorder traversal sequence of the extended binary tree, which is used to construct the binary tree.
[output form] depth of binary tree.
[sample input] AB#D##C##
[sample output]
3
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct BiNode {
char data;
BiNode* Lchild;
BiNode* Rchild;
};
class BiTree {
public:
BiTree() {root = Creat();}
~BiTree() {Release(root);}
int Depth() {return Depth(root);}
private:
BiNode* Creat();
void Release(BiNode* bt);
int Depth(BiNode* bt);
BiNode* root;
};
BiNode* BiTree::Creat() {
BiNode* bt;
char ch = getchar();
if (ch == '#')bt = nullptr;
else {
bt = new BiNode;
bt->data = ch;
bt->Lchild = Creat();
bt->Rchild = Creat();
}
return bt;
}
void BiTree::Release(BiNode* bt) {
if (bt == NULL)return;
else {
Release(bt->Lchild);
Release(bt->Rchild);
delete bt;
}
}
int BiTree::Depth(BiNode* bt) {
int i = 0, j = 0;
if (bt == NULL)return 0;
else {
i = Depth(bt->Lchild);
j = Depth(bt->Rchild);
}
if (i >= j) {
return i + 1;
}
else{
return j + 1;
}
}
int main() {
BiTree t;
cout << t.Depth();
return 0;
}
4. Under the binary linked list storage structure, find the parent node of node x
[problem description] take the binary linked list as the storage structure, write an algorithm to find the parents of node x in the binary tree.
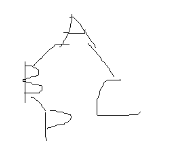
[input form] two lines. The first line is the preorder traversal sequence of the extended binary tree, and the second line is the node x to be queried
[output form] if node x has parents, output the value of their parents; Otherwise, output "NO".
[sample input] AB#D##C##
D
[sample output]
B
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct BiNode {
char data;
BiNode* Lchild;
BiNode* Rchild;
};
class BiTree {
public:
BiTree() { root = Creat(); }
~BiTree() { Release(root); }
void Search(char ch) { Search(root, ch); }
private:
BiNode* Creat();
void Release(BiNode* bt);
void Search(BiNode* bt, char ch);
BiNode* root;
};
BiNode* BiTree::Creat() {
BiNode* bt;
char ch = getchar();
if (ch == '#')bt = nullptr;
else {
bt = new BiNode;
bt->data = ch;
bt->Lchild = Creat();
bt->Rchild = Creat();
}
return bt;
}
void BiTree::Release(BiNode* bt) {
if (bt == NULL)return;
else {
Release(bt->Lchild);
Release(bt->Rchild);
delete bt;
}
}
void BiTree::Search(BiNode* bt,char ch) {
if (bt->Lchild == NULL && bt->Rchild == NULL) { return ; }
if(bt->Lchild!=NULL) {
if (bt->Lchild->data == ch) { cout << bt->data; }
else {
Search(bt->Lchild, ch);
}
}
if (bt->Rchild != NULL) {
if (bt->Rchild->data == ch) { cout << bt->data; }
else {
Search(bt->Rchild, ch);
}
}
}
int main() {
BiTree t;
char ch=getchar();
cin >> ch;
t.Search(ch);
}5. Delete the subtree with the value x as the root node
[problem description] with the binary linked list as the storage structure, delete the subtree with the value x as the root node in the binary tree.
[input form] two lines. The first line is the preorder traversal sequence of the extended binary tree, and the second line is the node x to be queried.
[output form] if node x exists, delete the subtree with value x as the root node; Otherwise, there is no operation. Finally, the middle order traversal sequence of the binary tree after the operation is output (separated by spaces). If it is an Empty binary tree, "Empty" is output.
[sample input] AB#D##C##
D
[sample output]
B A C
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct BiNode {
char data;
BiNode* Lchild;
BiNode* Rchild;
};
class BiTree {
public:
BiNode* Root() {return root;}//The return value is the root node
BiTree() {root = Create();}
~BiTree() {Release(root);}
void Release(BiNode* bt);
void Del(char x) {Del(root, x);}
void InOrder() {InOrder(root);}
private:
BiNode* root;
BiNode* Create();
void Del(BiNode* bt, char x);
void InOrder(BiNode* bt);
};
BiNode* BiTree::Create() {
BiNode* bt;
char a = getchar();
if (a == '#')bt = NULL;
else {
bt = new BiNode;
bt->data = a;
bt->Lchild = Create();
bt->Rchild = Create();
}
return bt;
}
void BiTree::Release(BiNode* bt) {
if (bt == NULL)return;
else {
Release(bt->Lchild);
Release(bt->Rchild);
delete bt;
}
}
void BiTree::Del(BiNode* bt, char ch) {
if (bt == NULL)return;
else {
if (bt->Lchild != NULL && bt->Lchild->data == ch) {
bt->Lchild = NULL;
}
if ( bt->Rchild != NULL && bt->Rchild->data == ch) {
bt->Rchild = NULL;
}
Del(bt->Lchild, ch);
Del(bt->Rchild, ch);
}
}
void BiTree::InOrder(BiNode* bt) {
if (bt == NULL) {
return;
}
else {
InOrder(bt->Lchild);
cout << bt->data << " ";
InOrder(bt->Rchild);
}
}
int main() {
BiTree t;
getchar();
char ch ;
cin >> ch;
if (t.Root()->data == ch) {//Judge whether the root node is deleted
cout << "Empty" << endl;
return 0;
}
t.Del(ch);
t.InOrder();
return 0;
}6. Preorder traversal based on sequential storage structure
[problem description] a binary tree with n nodes adopts sequential storage structure, and an algorithm is written to traverse the binary tree in sequence.
[input form] line, the binary tree traverses the sequence according to the sequence corresponding to the complete binary tree (that is, when a node has no left child or right child, add a special mark #).
[output form] preorder traversal sequence of binary tree; If it is an Empty binary tree, "Empty" is output.
[sample input] ABC#D
[sample output]
A B D C
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void preorder(int i,char s[]) {
if (s[i] == '#') return;
else {
cout << s[i]<<" ";
preorder(i * 2, s);//If the root node is 1, the left subtree is 2i and the right subtree is 2i+1
preorder(i * 2 + 1, s);
}
}
int main() {
string str;
getline(cin, str);
char s[100];
int i = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 100; j++) {
s[j] = '#';
}
while (str[i] != '\0') {
s[i + 1] = str[i];//Rounding off with subscript 0
i++;
}
preorder(1, s);
}
7. Extend sequence to construct binary tree
[problem description]
The preorder traversal sequence of an extended binary tree (the value of the virtual node is represented by "#"), constructs the binary tree, and outputs the inorder traversal sequence of the binary tree.
[input form] preorder traversal sequence of extended binary tree
[output form] middle order traversal sequence of binary tree
[sample input] AB#D##C##
[example output] BDAC
#include<stack>
#include <cstdlib>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class DataType>
struct BiNode {
DataType data;
BiNode<DataType>* lchild, * rchild;
};
template<class DataType>
class BiTree {
public:
BiTree() { root = PreCreate(root); };
~BiTree() { Release(root); };
void InOrder() { InOrder(root); };
private:
BiNode<DataType>* root;
BiNode<DataType>* PreCreate(BiNode<DataType>* bt);
void Release(BiNode<DataType>* bt); //Sequential release
void InOrder(BiNode<DataType>* bt);
};
template<class DataType>
BiNode<DataType>* BiTree<DataType>::PreCreate(BiNode<DataType>* bt) {
char ch;
cin >> ch;
if (ch == '#') bt = nullptr;
else {
bt = new BiNode<DataType>;
bt->data = ch;
bt->lchild=PreCreate(bt->lchild);
bt->rchild=PreCreate(bt->rchild);
}
return bt;
}
template<class DataType>
void BiTree<DataType>::Release(BiNode<DataType>* bt) {
if (bt == NULL) return;
else {
Release(bt->lchild);
Release(bt->rchild);
bt = NULL;
delete bt;
}
}
template<class DataType>
void BiTree<DataType>::InOrder(BiNode<DataType>* bt) {
if (bt == NULL) return ;
else {
InOrder(bt->lchild);
cout << bt->data;
InOrder(bt->rchild);
}
}
int main()
{
BiTree<char> biTree;
biTree.InOrder();
biTree.~BiTree();
return 0;
}8. Binary tree sequence traversal sequence
[problem description] give the preorder traversal sequence of an extended binary tree (the value of the virtual node is represented by "#"), construct the binary tree, and output the sequence traversal sequence of the binary tree.
[input form] preorder traversal sequence of extended binary tree
[output form] sequence traversal sequence of binary tree
[sample input] AB#D##C##
[sample output]
#include<queue>
#include <cstdlib>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class DataType>
struct BiNode {
DataType data;
BiNode<DataType>* lchild, * rchild;
};
template<class DataType>
class BiTree {
public:
BiTree() { root = PreCreate(root); };
~BiTree() { Release(root); };
void LeverOrder();
private:
BiNode<DataType>* root;
BiNode<DataType>* PreCreate(BiNode<DataType>* bt);
void Release(BiNode<DataType>* bt); //Sequential release
};
template<class DataType>
BiNode<DataType>* BiTree<DataType>::PreCreate(BiNode<DataType>* bt) {
char ch;
cin >> ch;
if (ch == '#') bt = nullptr;
else {
bt = new BiNode<DataType>;
bt->data = ch;
bt->lchild = PreCreate(bt->lchild);
bt->rchild = PreCreate(bt->rchild);
}
return bt;
}
template<class DataType>
void BiTree<DataType>::Release(BiNode<DataType>* bt) {
if (bt == NULL) return;
else {
Release(bt->lchild);
Release(bt->rchild);
bt = NULL;
delete bt;
}
}
template<class DataType>
void BiTree<DataType>::LeverOrder() {
queue<BiNode<DataType> > Q;
if (root == NULL)return;
Q.push(*root);
while (!Q.empty()) {
BiNode<DataType> q;
q = Q.front();
Q.pop();
cout << q.data;
if (q.lchild!=NULL) {
Q.push(*q.lchild);
}
if (q.rchild!=NULL) {
Q.push(*q.rchild);
}
}
}
int main()
{
BiTree<char> biTree;
biTree.LeverOrder();
biTree.~BiTree();
return 0;
}9. Child linked list representation - find children
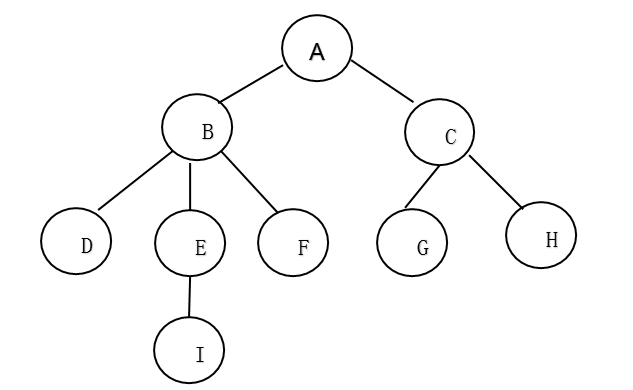
[problem description] if a tree is stored in this child linked list representation, it is now necessary to query a child of a node. If the child exists, the child information will be output; Otherwise, NO is output. For example, in the following tree, query the third child of node B, which exists and is node F; If the fourth child of node B is queried and the child does not exist, NO is output.
[input form] number of tree species nodes in the first row, n; The second line is the information of each node; The third line is the number of parent-child relationship row; Enter the parent-child relationship in the next row. The first represents the parent node and the second represents the child node; The last line represents the ith child of the node elem to be queried.
[output form] if the ith child of the node elem to be queried exists, the child information is output; Otherwise, NO is output.
[sample input]
9
A B C D E F G H I
8
A B
A C
B D
B E
B F
C G
C H
E I
B 3
[sample output] F
#include<cstdlib>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct CTNode {
int child;
CTNode* next;
};
template<class DataType>
struct CBNode {
DataType data;
CTNode* firstChild;
};
template<class DataType>
class ChildLink {
public:
ChildLink(int num);
~ChildLink();
bool findChild(DataType elem, int i, DataType& value);
int findPos(DataType elem);
private:
CBNode<DataType>* arrayPtr;
int nodeNUm;
};
template<class DataType>
ChildLink<DataType>::ChildLink(int num) {
arrayPtr = new CBNode<DataType>[num + 1];
CTNode** arrayRear = new CTNode * [num + 1];//Tail insertion
nodeNUm = num;
for (int i = 1; i <= num; i++) {
DataType temp;
cin >> temp;
arrayPtr[i].data = temp;
arrayPtr[i].firstChild = NULL;
}
int row;
cin >> row;
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
DataType parent, child;
cin >> parent >> child;
int parLoc = findPos(parent);
int chiLoc = findPos(child);
if (arrayPtr[parLoc].firstChild == NULL) {//First child
arrayPtr[parLoc].firstChild = new CTNode;
arrayPtr[parLoc].firstChild->child = chiLoc;
arrayPtr[parLoc].firstChild->next = NULL;
arrayRear[parLoc] = arrayPtr[parLoc].firstChild;
}
else {
CTNode* s = new CTNode;//Tail insertion
s->child = chiLoc;
s->next = NULL;
arrayRear[parLoc]->next = s;
arrayRear[parLoc] = s;
}
}
}
template<class DataType>
ChildLink<DataType>::~ChildLink() {
CTNode* first = NULL;
for (int i = 1; i <= nodeNUm; i++) {
first = arrayPtr[i].firstChild;
while (first != NULL) {
arrayPtr[i].firstChild = first->next;
delete first;
first = arrayPtr[i].firstChild;
}
}
}
//Find the i-th child of element elem
template<class DataType>
bool ChildLink<DataType>::findChild(DataType elem, int i, DataType& value) {
int a = findPos(elem); //Find the position of elem in the array
CTNode* first = arrayPtr[a].firstChild; //Get the first child's address
int count = 1;
while (first && count < i) {
first = first->next;
count++;
}
if (first) { //Indicates the existence of the ith child
value = arrayPtr[first->child].data; //Reference variable assignment
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
template<class DataType>
int ChildLink<DataType>::findPos(DataType elem) {
for (int i = 1; i <= nodeNUm; i++)
if (arrayPtr[i].data == elem) return i;
return 0;//Search failed
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
ChildLink<char> childLink(n);
char value, elem;
int i;
cin >> elem;
cin >> i;
if (childLink.findChild(elem, i, value))
cout << value << endl;
else
cout << "NO" << endl;
childLink.~ChildLink();
return 0;
}10. Huffman tree and Huffman coding
[problem description] give n characters and the frequency of these characters, design the most economical coding scheme, and output the Huffman coding of any character. If the character does not exist, output "NO", otherwise output the corresponding Huffman code
[input form] number of characters in the first line n; Frequency of n characters in the second line (separated by commas); The third line needs to output the character sequence number encoded by Huffman.
[output form] Huffman code of a character
[sample input]
4
2 3 4 5
2
[sample output] 01
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
struct HTNode {
int weight;
int parent, lchild, rchild;
};
class HuffmanTree {
public:
HuffmanTree(int W[], int n);
~HuffmanTree();
void Select(HTNode* HT, int len, int& i1, int& i2);
void CreatHuffmanCode();
void showHuffmanCode(int i);
private:
int nodeNum;
HTNode* HT;//Storage Huffman tree
char** HTC;//Storage Huffman coding
};
HuffmanTree::HuffmanTree(int W[], int n) {
nodeNum = n;
HT = new HTNode[2 * n - 1];
//initialization
for (int i = 0; i < 2 * nodeNum - 1; i++) {
HT[i].lchild = -1;
HT[i].rchild = -1;
HT[i].parent = -1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nodeNum; i++)
HT[i].weight = W[i];
//Huffman tree structure
for (int k = nodeNum; k < 2 * nodeNum - 1; k++) {
int i1, i2;
Select(HT, k, i1, i2);
HT[k].weight = HT[i1].weight + HT[i2].weight;
HT[i1].parent = k;
HT[i2].parent = k;
HT[k].lchild = i1;
HT[k].rchild = i2;
}
}
HuffmanTree::~HuffmanTree() {
HT = NULL;
delete HT;
HTC = NULL;
delete[]HTC;
}
void HuffmanTree::Select(HTNode* HT, int len, int& i1, int& i2) {
int min1, min2;
min1 = 9999;
min2 = 9999;
i1 = -1;//Subscript of minimum weight in node
i2 = -1;//Subscript with the lowest weight in the node
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (HT[i].parent != -1) continue;//This node has been used
if (HT[i].weight < min1) {
min1 = HT[i].weight;
i1 = i;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (HT[i].parent != -1) continue;//This node has been used
if (HT[i].weight < min2 && HT[i].weight > min1) {//Guaranteed greater than min1
min2 = HT[i].weight;
i2 = i;
}
}
}
//Encode Huffman / / creathhuffmantree
void HuffmanTree::CreatHuffmanCode()
{
//The Huffman code of each character is inversely calculated from the leaf to the root and stored in the coding table HC
int i, start, c, f;
HTC = new char* [nodeNum]; //Allocates n character encoded header pointer vectors
char* cd = new char[nodeNum]; //Allocate dynamic array space for temporarily storing codes
cd[nodeNum - 1] = '\0'; //Encoding Terminator
for (i = 0; i < nodeNum; ++i)
{ //Huffman coding character by character
start = nodeNum - 1; //start points to the last at the beginning, that is, the position of the encoding terminator
c = i;
f = HT[i].parent; //f points to the parent node of node c
while (f != -1)
{ //Backtracking from the leaf node up to the root node
--start; //Backtracking once start points forward to a position
if (HT[f].lchild == c)
cd[start] = '0'; //If node c is the left child of f, code 0 is generated
else
cd[start] = '1'; //If node c is the right child of f, code 1 is generated
c = f;
f = HT[f].parent; //Continue to backtrack up
} //Find the encoding of the ith character
HTC[i] = new char[nodeNum - start]; // Allocate space for the ith character encoding
strcpy(HTC[i], &cd[start]); //Copy the obtained code from the temporary space cd to the current line of HC
}
delete cd; //Free up temporary space
}
void HuffmanTree::showHuffmanCode(int i)
{
cout << HTC[i - 1] << endl;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
int W[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin >> W[i];
HuffmanTree huffmanTree(W, n);
huffmanTree.CreatHuffmanCode();
int i;
cin >> i;
if (i<1 || i> n)
cout << "NO" << endl;
else
huffmanTree.showHuffmanCode(i);
huffmanTree.~HuffmanTree();
return 0;
}