opening
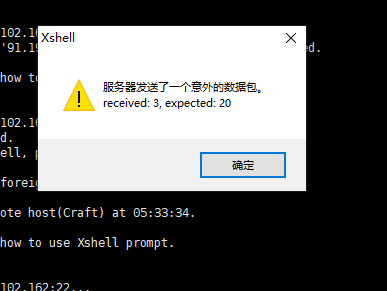
Compatibility between sshd and xhsell
 rails c
rails c
Using commands in background terminals
echo "KexAlgorithms curve25519-sha256@libssh.org,ecdh-sha2-nistp256,ecdh-sha2-nistp384,ecdh-sha2-nistp521,diffie-hellman-group14-sha1" >> /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Then restart the sshd service or reload the service configuration file
systemctl reload sshd or systemctl restart sshd
Re use the Xshell connection, successful
1, System command
shutdown
shutdown [option] time close -c Cancels the previous shutdown command -h Shut down now.Turn it off now 20:20 Timed shutdown -r restart
reboot restart
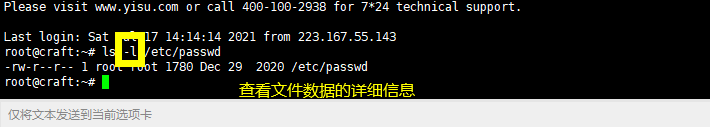
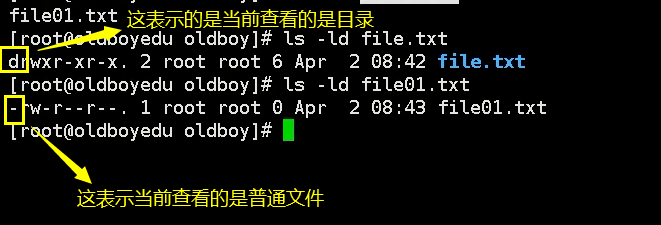
ls
ls [option] [file] Display directory file information ls -a all,View all files,Include hidden files ls -d View directory properties ls -l long,View details ls -h Show easy to read file sizes ls -i View the of the file i node
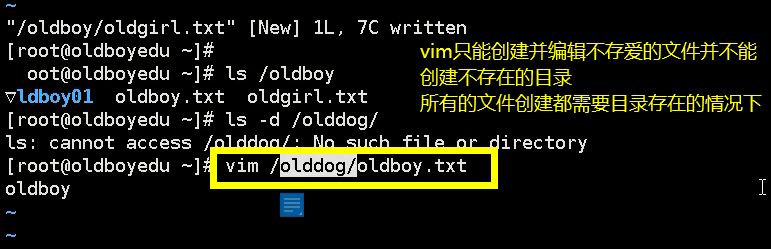
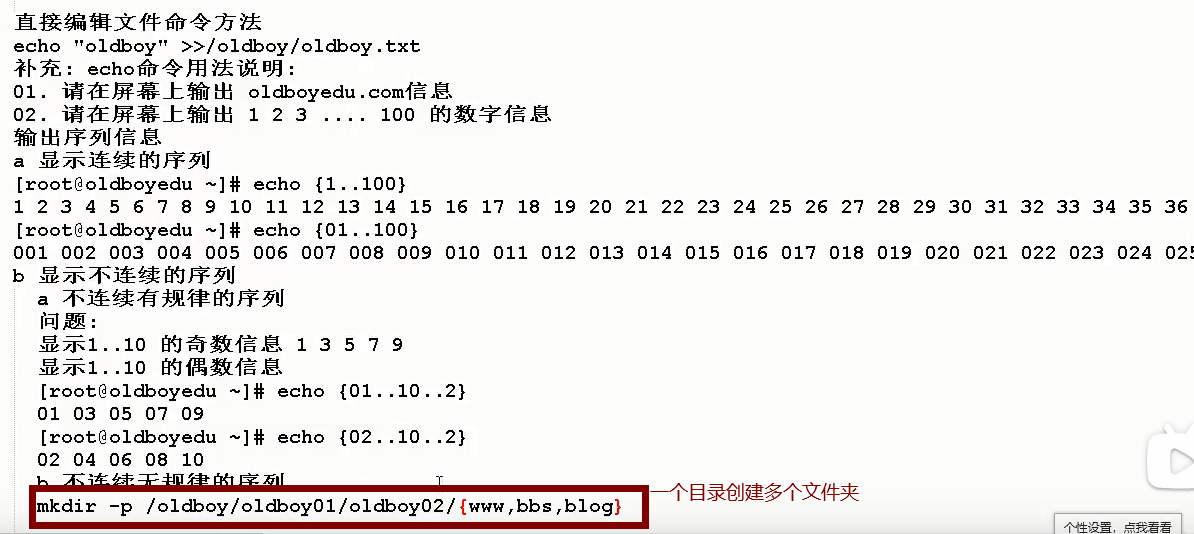
mkdir
mkdir [option] Directory name Create a blank directory mkdir -p a/b/c Create directory recursively
cd
cd [Directory name] Switch working path cd - Switch to previous directory cd ~ Switch to home directory cd ~username Switch to username Home directory
pwd
pwd Displays the current working directory of the user
touch
touch [option] [file...] Create a blank file or set the file time touch -a Modify file read time(atime) touch -m Modify file modification time(mtime) touch -d "2019-09-01" file name Simultaneous modification atime and mtime
vim/echo
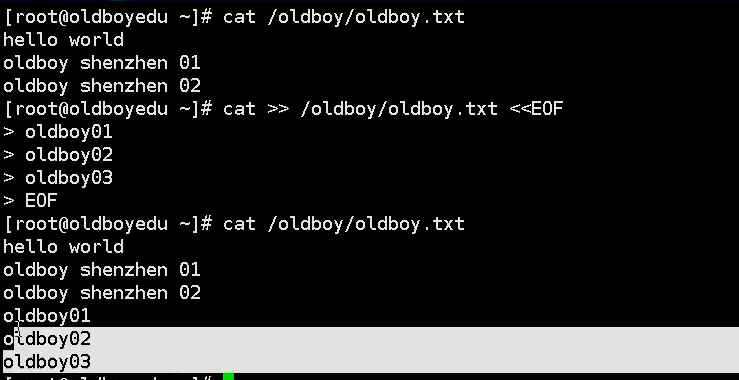
vim [Edited file path] echo "[Edit file content]" >> Target path [>> Indicates append if yes > Then the previous content will be deleted]
>Implementation principle: empty the contents of the original file first and add new information
>>Execution principle: the contents of the original file will not be overwritten, but new information will be added to the last line of the original file
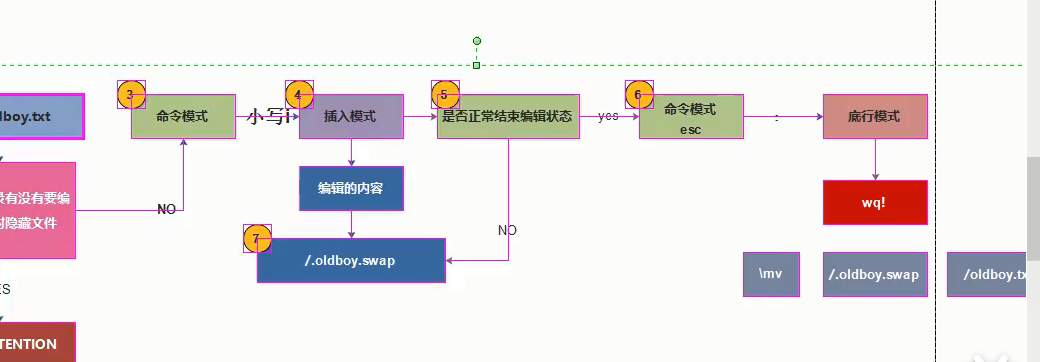
Connection interrupted while editing [Temporary documents]
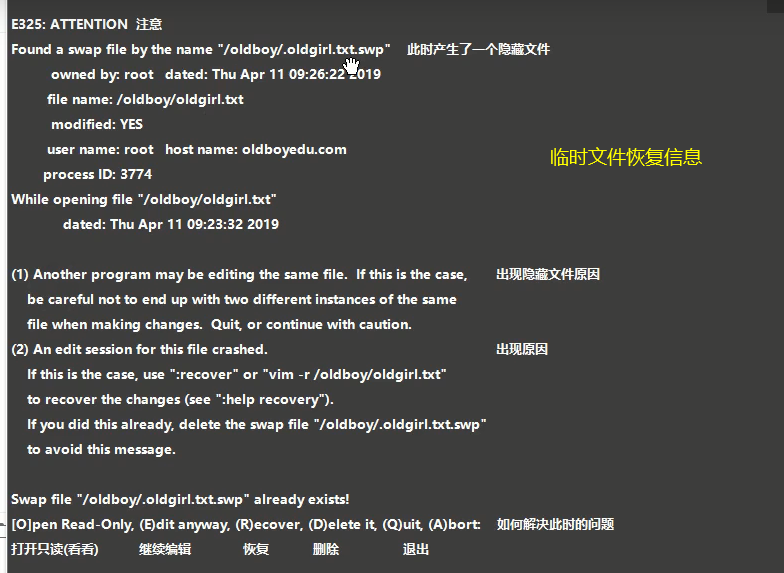
principle
Whenever you edit, a temporary file will be generated


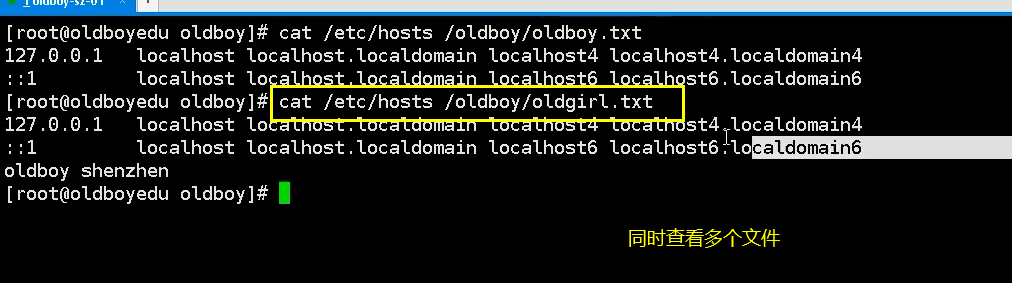
cat
cp [option] Source file 1,2,3 Target file Copy files or directories cp -p Preserve the properties of the original file cp -d If the object is a linked file,Preserve properties of linked files cp -r Recursive replication(For directory) cp -i If the target file exists,Then ask whether to overwrite cp -a amount to-pdr -r Recursive creation in cp Add before \ The overwrite confirmation message will not be displayed

rm
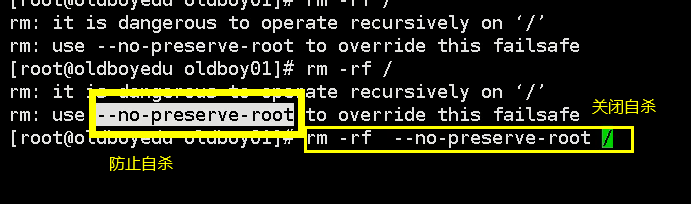
rm [option] file Delete file or directory rm -f file Force delete,No confirmation message is displayed rm -r Directory name Delete directories and files in directories rmdir Directory name [remove empty directories]
force force recursive recursion
mv
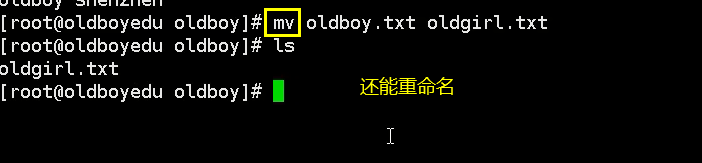
mv [options] [source file] [destination path | destination file name] cut file or rename file


Shortcut
vim ctrl+a Quickly move the cursor to the beginning of the line ctrl+e Quickly move the cursor to the end of the line ctrl+Left and right direction keys Move the cursor according to an English word ctr1+w Delete a string separated by spaces as a whole(shear) ctrl+u Delete the cursor at the beginning of the line(shear) ctr1+k Delete the cursor position to the end of the line(shear) ctr1+y Paste cut content ctrl+s xshel1 Entered the locked state ctr1+q Unlock status quit Exit locked state ctr1+. Call the last command
2, linux directory structure

Write the saved path during backup
If it is specific to the file name, it is to rename the file
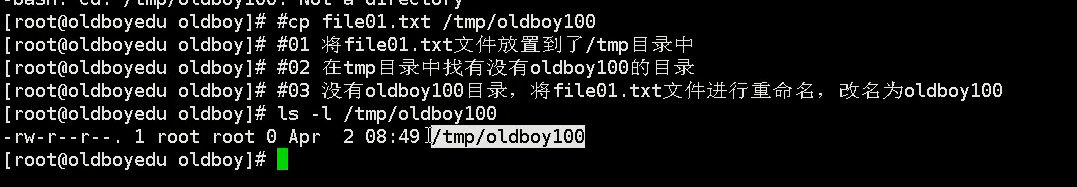
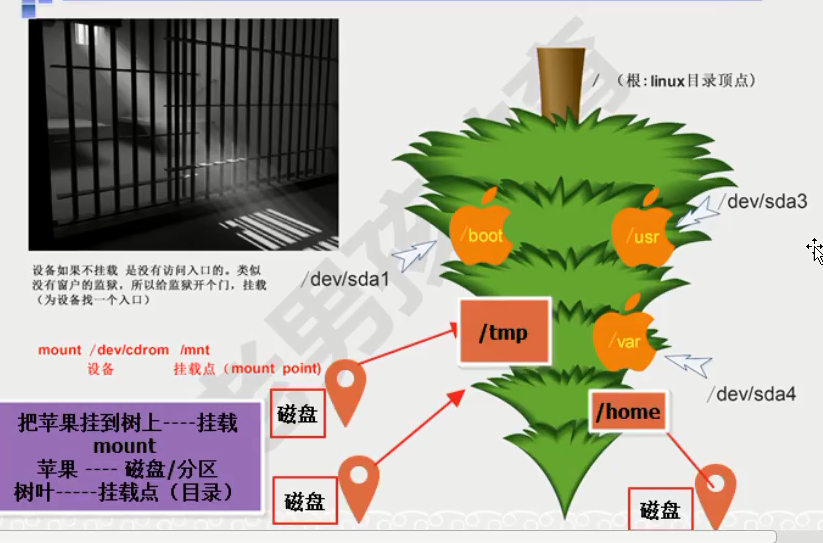
mount
stay linux Everything in the system is a file catalogue--Special documents storage device--Special documents command--Command file
dev device linux Device directory in /dev/sr0 is write-protected, mounting read- only [/dev/sr0 It is a write protected device. After mounting, the directory is in a read-only state]
System mount concept After storing data on disk, you need to establish a relationship between a directory and disk(mount ) Enter directory(Mount point)You can see the data in the disk
Practical demonstration 1 inux System mount process? First step:Have a storage device-CD drive Load the disc drive Second step:stay linux Optical drive device found in system [root@ old]# 1s - 1 /dev/cdrom 1rwxrwxrwx.1 root root 3 Mar 29 12 :02 /dev/cdrom -> sr0 Third step:You need to mount the storage device to view the information in the device Mount command syntax format: mount Mount device file information mount point(catalog information) PS:Mount point directory must exist mount /dev/cdrom /mnt
Only after you mount the storage device can you see what's inside
umount \[Mount point] Uninstall mount
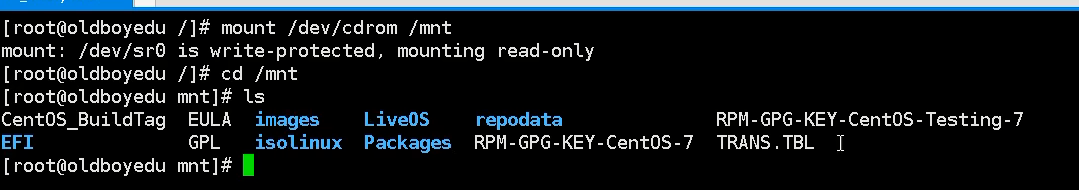
supplement
/mnt So that we can see the data stored in the disk The disk is divided into three zones /dev/sda1 Represents the first partition of the disk sas[sas Disk of interface type] a[Indicates that it is the first disk of this server] 1[Indicates the first partition of this disk] /dev/sda2 /dev/sda3 All three require a mount point to view You can't see it again until you uninstall the mount oldboy.txt [Uninstall and mount cd .. sign out mnt To the next level] Ps:When mounting,Try not to use the directory with data as the mount point, otherwise you will not see the original data



tree
-a Displays all files and directories. -A use ASNI The drawing character displays the tree view instead of the drawing character ASCII Character combination. -C Add color to the list of documents and directories to distinguish various types. -d Displays the directory name instead of the contents. -D Lists when the file or directory was changed. -f Displays the full relative path name before each file or directory. -F In the execution file, directory, Socket,Symbolic connection, pipe name, each plus"*","/","=","@","|"number. -g List the group name of the file or directory. If there is no corresponding name, the group ID will be displayed. -i File or directory names are not listed in steps. -L level Limits the level of catalog display. -l If you encounter a directory that is a symbolic connection, directly list the original directory that the connection points to. -n Do not add color to the list of files and directories. -N Directly list file and directory names, including control characters. -p List the permission labels. -P<Template style> Displays only file or directory names that match the template style. -q use"?"The number replaces the control character and lists the file and directory names. -s Lists the file or directory size. -t Sort by the change time of files and directories. -u List the owner name of the file or directory. If there is no corresponding name, the user ID is displayed. -x Limit the scope to the current file system. If some subdirectories under the specified directory are stored on another file system, the subdirectories will be excluded from the search scope.
bin -> usr/bin Storage directory of commands and binary files boot System boot program+system kernel cdrom dev Device optical drive hard disk etc Store the configuration file of the system or service home Home directory of ordinary users 1ib -> usr/1ib Storage directory of library files 1ib32 - > usr/ 1ib32 1ib64 -> usr/ 1ib64 Storage directory of library files(64 Bit system) 1ibx32 -> usr/ 1ibx32 lost+found The disk and file system are damaged, and the files are temporarily stored in case of power failure media mnt Temporary mount point directory opt Third party software is installed here proc Virtual directory,Display information in memory(Process service information kernel) root root User's home directory Palace run sbin -> usr/ sbin Super command,only root Commands available to users snap srv swap. img sys Virtual directory memory information tmp Storage location of temporary documents selinux selinux And its configuration file storage location(yes root Restrictions on permissions) var Frequently changing file system log related service log files
Important file data information in directory structure
Network card profile
/etc/network/interfaces //dns resolution [dns separate profile] can be modified here
ONBOOT=yes [if it's no, it won't help to restart the service]

The modification of the configuration file requires restarting the service to take effect systemctl restart network Restart for all network cards systemctl status network . Method 2:Common usage in Enterprises ifdown eth0 && ifup eth0 Restart the specified network card
Abnormal problem:The network card configuration file is correct. The network service cannot be restarted systemctl stop NetworkManager Network management service shutdown
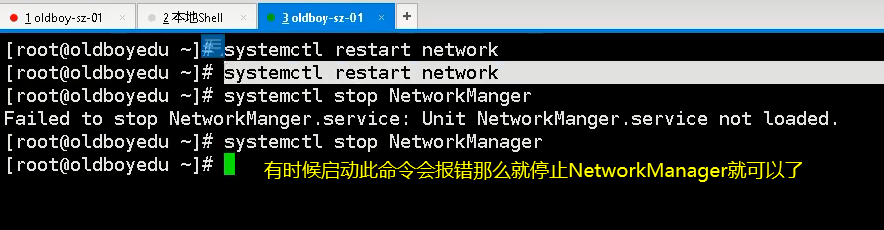
DNS resolution profile
/etc/network/interfaces //You can modify DNS resolution [network card configuration file] here to take precedence over resolv conf When restarting the service, the configuration information in the network card will be parsed first, so resolv Even if the conf is modified, the configuration information in the network card will be parsed and modified /etc/resolv.conf //DNS resolution [DNS resolution profile] can be modified here
Therefore, sometimes when the domain name cannot access the external ip, it indicates that it is the problem of the network card configuration file and DNS configuration file
Delete a line deletedelete = dd Delete multiple lines of content 3dd How to restore operation errors Lowercase letters u[undo]
root@craft:~# cat /etc/resolv.conf // DNS resolution can be modified here nameserver 8.8.8.8
The network card configuration file of ubuntu is / etc/network/interfaces
#Indicates a comment
If DNS is annotated, it can only ping ip, not domain name, because DNS cannot recognize the corresponding relationship between domain name and ip address
root@craft:~# cat /etc/network/interfaces / / DNS resolution can be modified here This file describes the network interfaces avaiblable on your system #and how too activate them.For more information ,see interfaces(5). source /etc/network/interfaces.d/* auto lo iface lo inet loopback auto eth0 iface eth0 inet static address 91.193.102.162 netmask 255.255.255.0 gateway 91.193.102.1 dns-nameservers 8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4
Remote connection exception 01.Check whether the link is unobstructed ping 10.0.0.200 Reasons for failure: a There is a problem with the physical circuit b Check network card configuration(IP Address mask gateway DNS) c Network security policy block d Is the virtual network card configured correctly(Reinitialize virtual network configuration)
Serious abnormal problems in enterprise work: Put the big trick of O & M troubleshooting: a Service reinstallation b Restart the system reboot c Reinstall the system
-l list The list displays network service information -n number Display in digital form -t tcp Network protocol -u udp Network protocol -P port Display service process information
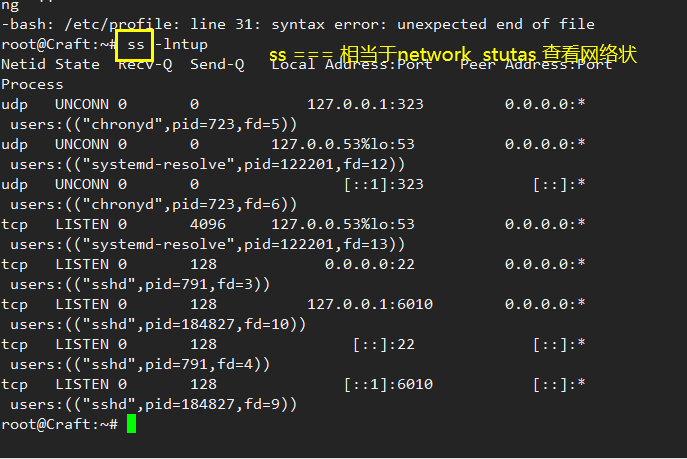
Host name profile
hostname
When you permanently modify the configuration in the system, you need to modify the configuration file Most modifications on the command line are temporary
hostname Displays the current full host name hostname [Host name to modify] Temporarily modify the host name [reboot Restore to the previous host name] /etc/hostname Permanently modify the host name
root@shepay:~# cat /etc/hostname // Permanently modify the host name yisu-60f1d4643919d

Resolve mapping address
Parse mapping file(important) hosts file:Set up locally IP Correspondence between address and host name windows Local resolution file location: C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts 1inux Local resolution file location: root@shepay:~# cat /etc/hosts 127.0.0.1 localhost 127.0.1.1 ubuntu20
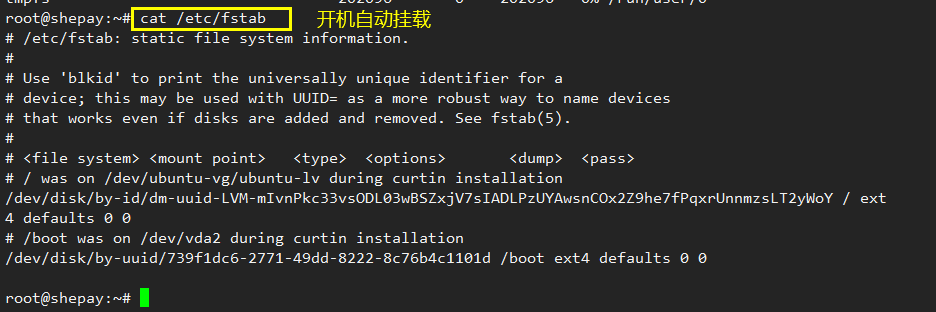
/etc/fstab Automatically mount the configuration file when the storage device is powered on
root@shepay:~# blkid -o list [view as a list] device fs_type label mount point [Mount point] UUID[Define storage device file information] --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /dev/sda2 ext4 /boot 739f1dc6-2771-49dd-8222-8c76b4c1101d /dev/sda3 LVM2_member (in use) qRakWY-n1RA-lJfE-PpYM-HL9V-InI2-m1tLg3 /dev/mapper/ubuntu--vg-ubuntu--lv ext4 / 6117b3de-c467-4f98-83ad-670b956d3f77 /dev/loop0 squashfs /snap/core18/2074 /dev/loop1 squashfs /snap/lxd/18150 /dev/loop2 squashfs /snap/core18/1944 /dev/loop3 squashfs /snap/lxd/20326 /dev/loop4 squashfs /snap/snapd/12398 /dev/loop5 squashfs /snap/snapd/10492 /dev/sda1 (not mounted)
Service bootstrap profile
Boot auto load file
root@shepay:~# ls /etc/rc.local /etc/rc.local

summary: rc.loac1 Document function 01.The content information in the file will be loaded after the system starts, 02.What is written in the document,-It must be command information [So a Trojan horse can be written directly into this file]
Operating system run level
View current run level
root@shepay:~# systemctl get-default graphical.target root@yisu-60f1d4643919d:~# runlevel N 5
poweroff.target rescue.target multi-user.target multi-user.target multi-user.target graphical.target reboot.target
Variable loading file
/etc/profile Make variable information permanent source /etc/profile Let the system reload the configuration file
Quickly switch the cursor to the tail capital G Quickly switch the cursor to the head Lowercase letters gg
Types of variables in the system: Common variable:Manual setting is required environment variable: System default variables
Variable information and alias information profile /etc/profile == /etc/bashrc effect: # System wide environment and startup programs, for 1ogin setup 01.Set environment variable information and program startup related information,?To prepare the system environment after login? # Functions and aliases go in /etc/bashrc 02.Functions can be configured(? )And alias functions are best configured in/etc/bashrc
which + command [Where is the find file command located]
The logic of command execution in the system




source Load file configuration information now letc/profile
Operating system alias settings
Variable information and alias information profile etc/profile == /etc/bashrc stay root Hide files in user's home directory.bashrc Configuring aliases in[This alias configuration takes precedence] /root/.bashrc /etc/profile == /etc/bashrc National law(Global validation) ~/.bash_ profile domestic discipline and family rules(The specified user takes effect)
How to view hidden data [rootloldboyedu ~]# ls -a explain:linux Hidden files in the system start with a dot

Sets the syntax for naming: alias Alias name='Command information

Disable alias function: 01.Cancel alias unalias rm 02.Use a crowbar \rm rf /oldboy 03.Execute commands in absolute path mode /usr/bin/rm -rf /o1dgirl
Alias persistent settings
demand:Give Way rm Command equivalence echo "command not exec"? first:to write profile file vi etc/profile alias rm=:'echo command not exec' the second:load profile File content source
summary


Operating system software installation method
Program software installation related directories
root@Craft:~# ll -d /usr/local/ drwxr-xr-x 10 root root 4096 Jul 31 2020 /usr/local//
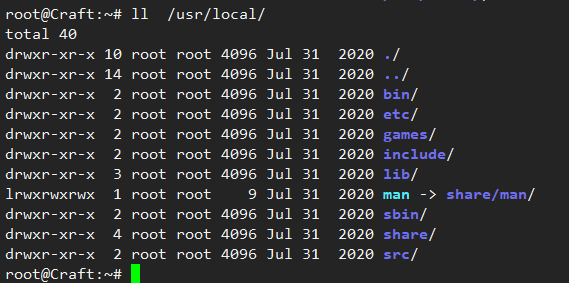
How to install software in the system(having dinner) 01.Order takeout(Cooked rice chopsticks) yum Install software Simple and fast 02,Buy semi-finished products(Quick frozen dumpling processing) rgm Install software A software installation package is required 03.Cook by yourself(Ingredients, cooking) The compilation and installation software can be adjusted flexibly
ubuntu install yum source
find /etc/apt/sources.list file This file comes with the system yum source file Then back up the file cp /etc/apt/sources.list /etc/apt/sources.list.backup
Enter the official website https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/


On the command line, enter root@Craft:/etc/apt# echo "" > sources.list.backup Empty the contents Then paste the contents of the mirror station Last update source sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade
type [command] Check whether the command is external or built-in
supplement:The system divides commands into two categories 01.External commands need to be installed 02.Built in commands all systems have built-in commands View built-in or external command methods [root@ oldboyedu ~]# type cd cd is a shell builtin [ root@ oldboyedu ~] # type mkdir mkdir is /usr /bin/mkdir

ps -ef View process kill -9 Force kill process[-9 force]

Troubleshooting

Common software installation yum install -y vim tree wget net- tools nmap bash- completion[Automatic completion]
System login prompt file
root@yisu-60f1d4643919d:~# cat /etc/motd Welcome Hacker World! effect:You can write fancy contact information to users of the operating system
echo " " >/etc/issue Empty file >/etc/issue Empty file
System important log files
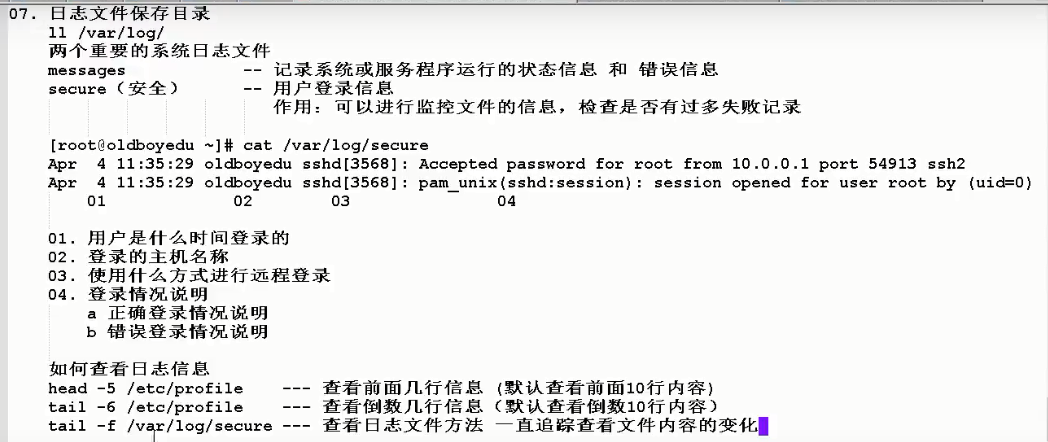
Log storage path /var/log There are two important log files [messages Centos] [syslog ubuntu=secure Centos]
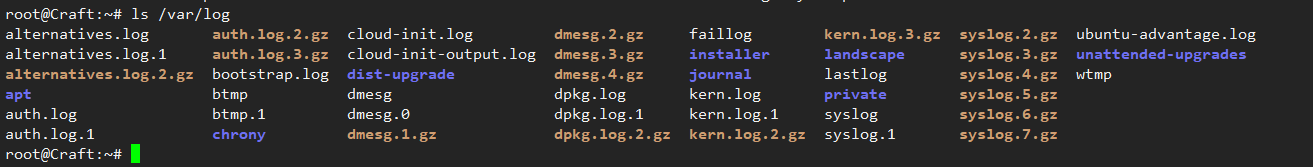
syslog records user login information
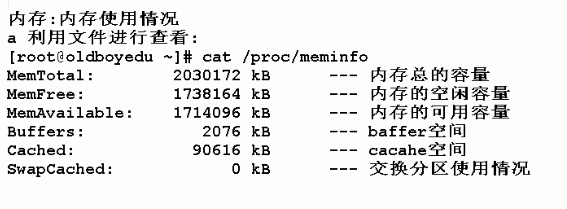
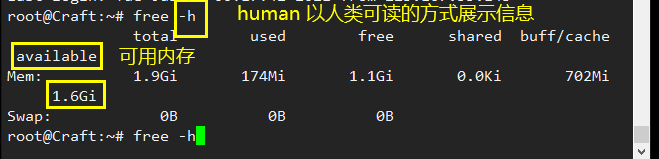
View system hardware information





System optimization operation
vi file information i ---Enter edit mode esc Exit edit mode :wq ---Save and exit :W :q :wq! ---Force save exit :q! ---forced return I Command mode-->Insert mode i ---Indicates entering the editing state from the cursor position I ---It means moving the cursor to the beginning of a line and entering the editing state o ---Under the line where the cursor is located, edit the new line O ---Above the line where the light change is located, a new line is created for editing a ---Move the cursor to the next on the right-Characters to edit A ---Move the cursor to the end of a line and enter the editing state C ---Move the cursor to the end of the line to delete the content and enter the editing state CC ---Delete the entire line and enter the editing state Only move the cursor without entering the editing state capital G Quickly switch the cursor to the tail Lowercase letters gg Quickly switch the cursor to the head. ngg n Indicates the line to move to $ Move the cursor to the end of a line 0/^ Move the cursor to the beginning of a line Command mode--Bottom row mode : I input-Some commands / Enter search status(Search down n Down in turn) ? Enter search status(towards.Search on n Up in turn) Special skills: deletedelete= =dd Delete a line(shear) 3dd Delete multiple lines of content(shear) P Paste content 3p Paste content multiple times YY Copy a line 3yy Copy multiline content How to restore operation errors Lowercase letters u undo
View system information
root@Craft:~# uname -a
Linux Craft 5.4.0-77-generic #86-Ubuntu SMP Thu Jun 17 02:35:03 UTC 2021 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
root@Craft:~# screenfetch
./+o+- root@Craft
yyyyy- -yyyyyy+ OS: Ubuntu 20.04 focal
://+//////-yyyyyyo Kernel: x86_64 Linux 5.4.0-77-generic
.++ .:/++++++/-.+sss/` Uptime: 2d 20m
.:++o: /++++++++/:--:/- Packages: 662
o:+o+:++.`..```.-/oo+++++/ Shell: bash 5.0.17
.:+o:+o/. `+sssoo+/ Resolution: No X Server
.++/+:+oo+o:` /sssooo. WM: Not Found
/+++//+:`oo+o /::--:. GTK Theme: Adwaita [GTK3]
\+/+o+++`o++o ++////. Disk: 6.0G / 21G (31%)
.++.o+++oo+:` /dddhhh. CPU: Intel Xeon E5-2680 v2 @ 2x 2.8GHz
.+.o+oo:. `oddhhhh+ GPU: Device 1234:1111 (rev 02)
\+.++o+o``-````.:ohdhhhhh+ RAM: 389MiB / 1973MiB
`:o+++ `ohhhhhhhhyo++os:
.o:`.syhhhhhhh/.oo++o`
/osyyyyyyo++ooo+++/
`````+oo+++o\:
`oo++.
root@Craft:~# linuxlogo
.-.
.-'``(|||)
,`\ \ `-`. 88 88
/ \ '``-. ` 88 88
.-. , `___: 88 88 88,888, 88 88 ,88888, 88888 88 88
(:::) : ___ 88 88 88 88 88 88 88 88 88 88 88
`-` ` , : 88 88 88 88 88 88 88 88 88 88 88
\ / ,..-` , 88 88 88 88 88 88 88 88 88 88 88
`./ / .-.` '88888' '88888' '88888' 88 88 '8888 '88888'
`-..-( )
`-`
Linux Version 5.4.0-77-generic, Compiled #86-Ubuntu SMP Thu Jun 17 02:35:03 UTC 2021
Two 2.8GHz Intel Pentium Xeon Processors, 2GB RAM, 11200 Bogomips Total
Craft
useradd Create user(user management ) useradd user name. passwd . Set user password command passwd user name Specify which user's password to change passwd . Modify current user password Switch user commands su-User name id Check whether the created user exists; id user name whoami Confirm user identity

Command prompt optimization


Download source optimization


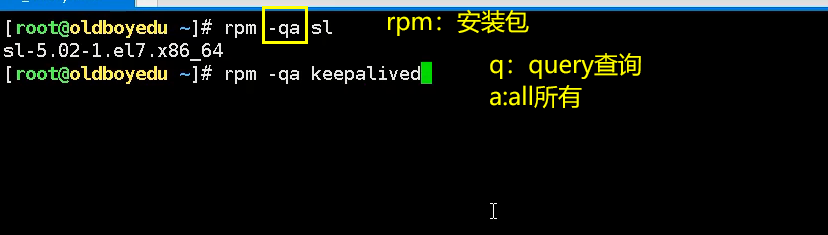

Use the absolute path when viewing. If you don't know the absolute path, use which to find it


`` backquote Give the execution result of the command in quotation marks to the command outside quotation marks for processing

firewall
If you don't turn off the firewall, some software may not work
View firewall status[ubuntu] 1.ufw status Status: inactive[close] 2.Turn on the firewall sudo ufw enable 3.Turn off firewall sudo ufw disable 4.View firewall version 3udo ufw version 5.Allow external access to this machine by default sudo ufw default allow 6.External access to the host is denied by default sudo ufw default deny 7.Allow external access to port 53 sudo ufw allow 53 8.Deny external access to port 53 sudo ufw deny 53 9.Allow a IP Address to access all ports of the machine sudo ufw allow from 192.168.0.1
selinux
Systematic selinux Service procedure selinux Service pair root User rights control Load file configuration information now /etc/profi1e / ete/ba shre ~/ .bashrc ~/ .bashrc_ prof11e
Character coding optimization
Can display Chinese Avoid garbled code
$LANG Set character encoding /etc/profile The character set in takes precedence root@Craft:~# echo $LANG en_US.UTF-8 use locale Command to view the current system code root@Craft:~# locale LANG=en_US.UTF-8 LANGUAGE= LC_CTYPE="en_US.UTF-8" LC_NUMERIC="en_US.UTF-8" LC_TIME="en_US.UTF-8" LC_COLLATE="en_US.UTF-8" LC_MONETARY="en_US.UTF-8" LC_MESSAGES="en_US.UTF-8" LC_PAPER="en_US.UTF-8" LC_NAME="en_US.UTF-8" LC_ADDRESS="en_US.UTF-8" LC_TELEPHONE="en_US.UTF-8" LC_MEASUREMENT="en_US.UTF-8" LC_IDENTIFICATION="en_US.UTF-8" LC_ALL= from /etc/default/locale Set character encoding




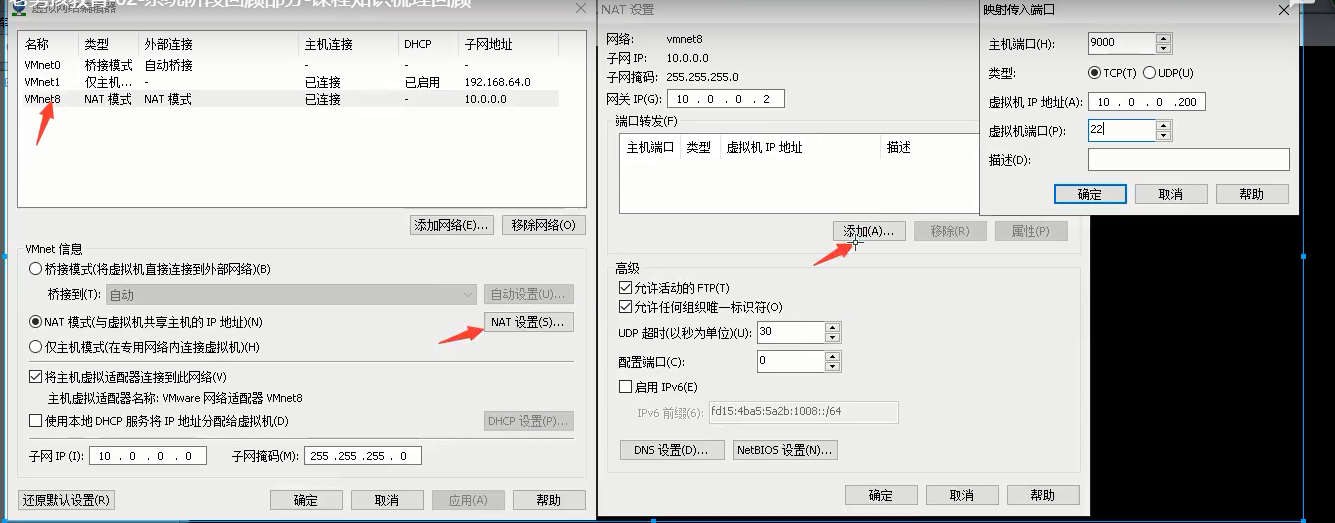
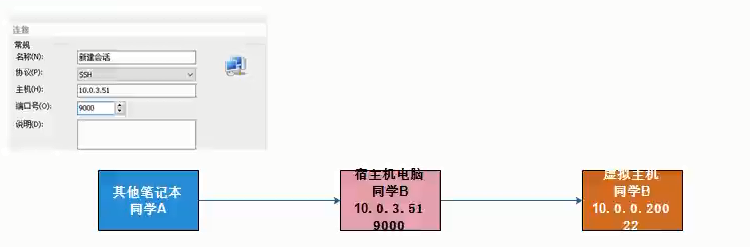
Faster remote connections
Step 1: modify the ssh service configuration file
Use set number to display the line number
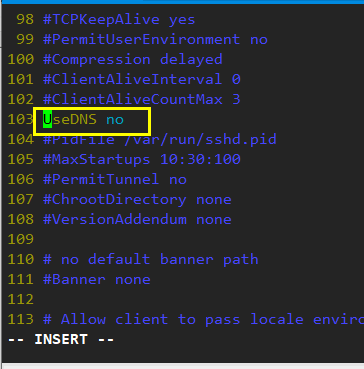

Step 2: modify the hosts file
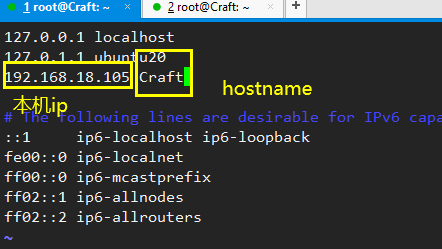
Step 3: restart ssh Remote Service
/etc/init.d/ssh restart
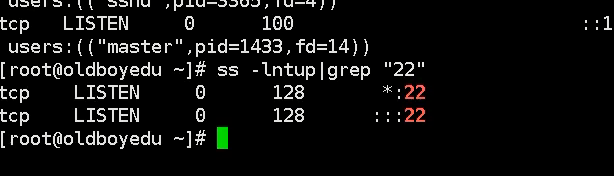
Check current ssh Opening condition: ps -e |grep ssh
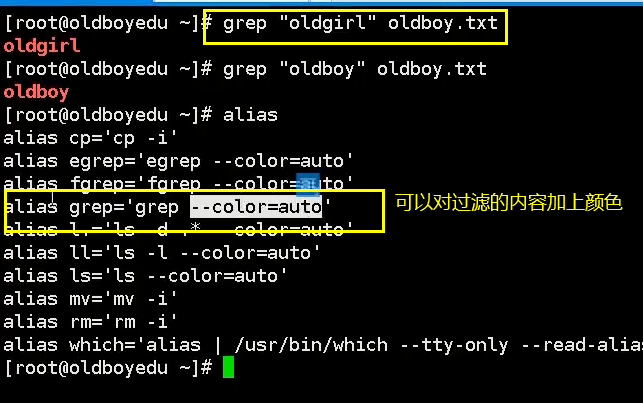
Pipe symbol filtering commands




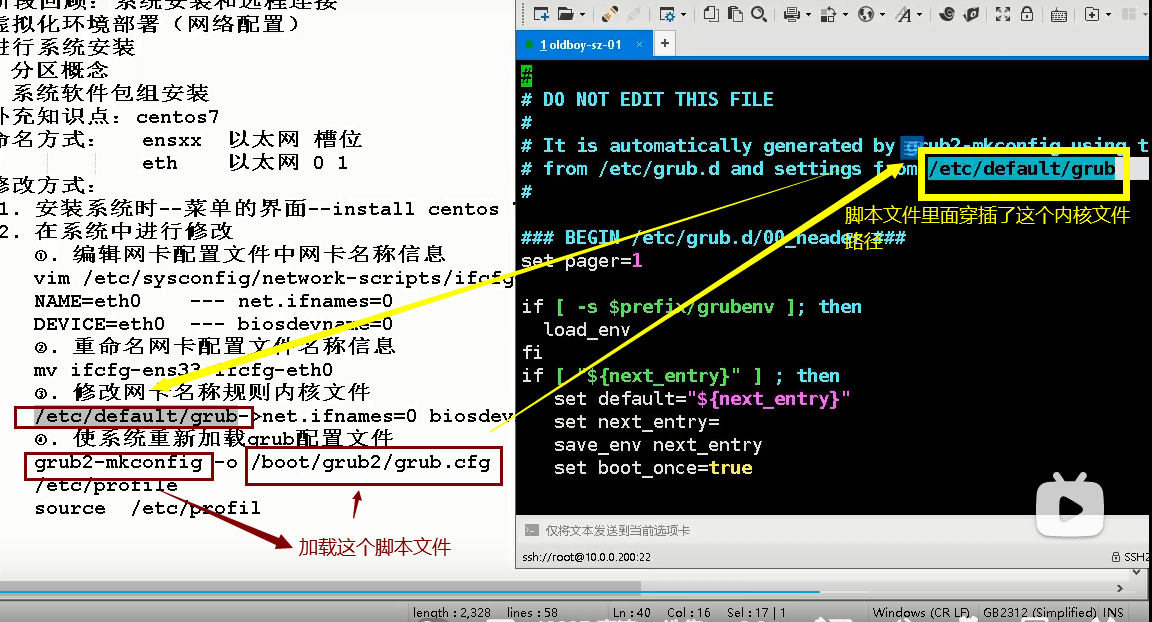
Modify network card name


View file command summary









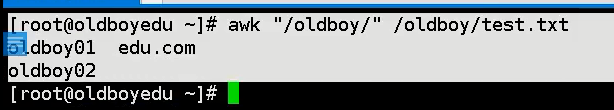
File information filtering command








sed -i To achieve real insertion



