Ubuntu+Nginx+uWSGI+DJango+python3 deployment
technological process
-
Client requests service resources
-
As a direct external service interface, nginx will unpack and analyze the http request sent by the client,
-
If it is a static file request, return the requested resource according to the static file directory configured by nginx,
-
If it is a dynamic request, nginx will pass the request to uWSGI through the configuration file;
-
-
uWSGI processes the received packet and forwards it to wsgi,
-
wsgi calls a file or function of django project according to the request. After processing, django will give the return value to wsgi,
-
wsgi packages the returned value and forwards it to uWSGI,
-
uWSGI will forward it to nginx after receiving it, and nginx will finally return the return value to the client (such as browser).
*Note: the transfer of information between different components involves the conversion of data format and protocol
The first level of nginx is not necessary. uwsgi can complete the whole process of interacting with the browser;
Why use nginx with uwsgi
-
nginx provides more secure service guarantee
-
Provide reverse proxy, load balancing and other functions
-
uWSGI itself is an intranet interface, and it may not be enough to open multiple work and processes. nginx can agent multiple uWSGI to complete uWSGI load balancing;
-
-
Strong processing ability for static files
-
django's ability to handle static files is not very good when debug=False, but it is more efficient to use nginx.
-
uWSGI
WSGI protocol: specification of communication between web server and web application
The web server accepts the request from the client and sends it to the web application
uWSGI: a python web server or Server/Gateway
Uwsgi protocol is a protocol owned by uwsgi server. It is used to define the type of transmission information. It is two things compared with WSGI.
-
uWSGI can perform multi-threaded scheduling and process monitoring
-
Provide complete request log processing
-
runserver performance is poor
install
sudo apt-get install python3-dev #Install this first to make pip3 install uwsgi success sudo apt-get install python3-pip sudo sudo pip3 install uwsgi
test
Create a new python file: test_for_uwsgi.py
def application(env, start_response): start_response('200 OK', [('Content-Type','text/html')]) return [b"Hello uwsgin xlf----!"]
Execute command
uwsgi --http-socket :8088 --wsgi-file test_for_uwsgi.py
Open the browser and visit: local IP:8088
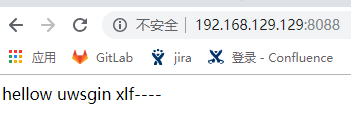
File configuration
Add uwsgi.com under the project folder of DJango INI file
input
[uwsgi] #use http Access port http = :8080 #use nginx Port to communicate with socket = :8000 #django catalogue chdir = /home/ubuntu/PycharmProjects/DRF/MyDRF/ #Django Under item wsgi.py File path module = MyDRF.wsgi # Locate through module wsgi file # Specific documents can also be used #wsgi-file = /home/ubuntu/PycharmProjects/DRF/MyDRF/MyDRF/wsgi.py master = true # Main process #Number of processes processes = 4 vacuum = true
function
uwsgi --ini Project path/uwsgi.ini
Open the browser and access: local IP:8080/Django interface path
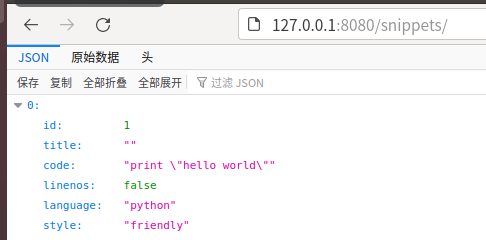
As described above, the access was successful
(if the virtual machine acts as a server and uses uwsgi to start execution, you can also open the browser on the local machine to access it.)
Nginx
-
Reverse proxy, web server, load balancing
-
Basic command
-
sudo nginx startup
-
sudo nginx -s stop (or use kill - 9 nginx)
-
sudo nginx -s quit exit
-
sudo nginx -s reopen reopen
-
sudo nginx -s reload overload
-
-
Key configuration module
-
events configuration domain: network connection related configuration (I/O module)
-
server configuration domain: configuration of related service nodes
-
location
-
http configuration domain
-
upstream configuration domain: reverse proxy configuration domain
-
-
Hierarchical relationship
events { .... } http { ... upstream { ... } server { ... location { ... } } }
install
sudo apt-get install nginx
test
nginx -v # see nginx edition nginx -t # see nginx Configuration path # implement sudo nginx
Open the browser and visit: 127.0.0.1:80
As described above, nginx is successfully opened
to configure
Enter / etc / nginx / sites enabled to create * * conf file, such as project name conf, enter the following in the file
server { listen 8099; # Browser access nginx Port of server_name localhost; # Browser access nginx Domain name or IP address # Specify project path uwsgi location / { include uwsgi_params; uwsgi_connect_timeout 30; uwsgi_pass 127.0.0.1:8000; # relation uwsgi Port, to and uwsgi In configuration socket Port consistency } # Specify static file path location /static/ { alias /home/ubuntu/PycharmProjects/DRF/MyDRF/static/; # Static file path of the project } }
Static file path of the project
In the project directory, click settings Add the following configuration to the PY file
# Static file configuration STATIC_URL = '/static/' STATIC_ROOT = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, "static") # Upload file configuration MEDIA_URL = '/media/' MEDIA_ROOT = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'media')
In URLs Add url to py file
from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path from django.conf.urls import re_path, include from django.views.static import serve from MyDRF.settings import MEDIA_ROOT,STATIC_ROOT urlpatterns = [ ... re_path(r'^media/(?P<path>.*)', serve, {'document_root': MEDIA_ROOT}), re_path(r'^static/(?P<path>.*)$', serve, {'document_root': STATIC_ROOT}), ]
Execute command
python manage.py collectstatic
Under the project path, a static folder will be generated to store static files
implement
The UWSO application has been started at this time
Execute command
sudo nginx
Open the browser to access the configured address: server IP address: 8099/Django interface path
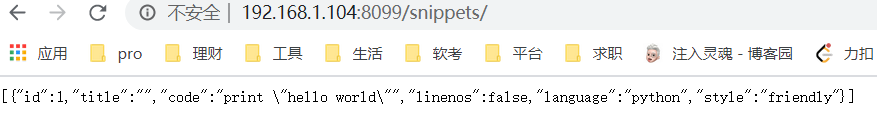
The above display indicates that the configuration is successful