Uiautomator2 common API s
Pure manual output, it is recommended to collect praise, one key and three connections
github reference link:
- https://github.com/openatx/uiautomator2/tree/master/uiautomator2
-
Install ATX agent
- python -m uiautomator2 init
-
Using webitor under win
- python -m weditor
-
Enter the page by address http://192.168.124.133:17310/
-
adb_wifi is via adb tcpip mode
-
API
d(resourceId="Element positioning expression") d.implicitly_wait(Waiting time) #The unit is s d.app_stop('Specified package name') d.app_clear('Specified package name')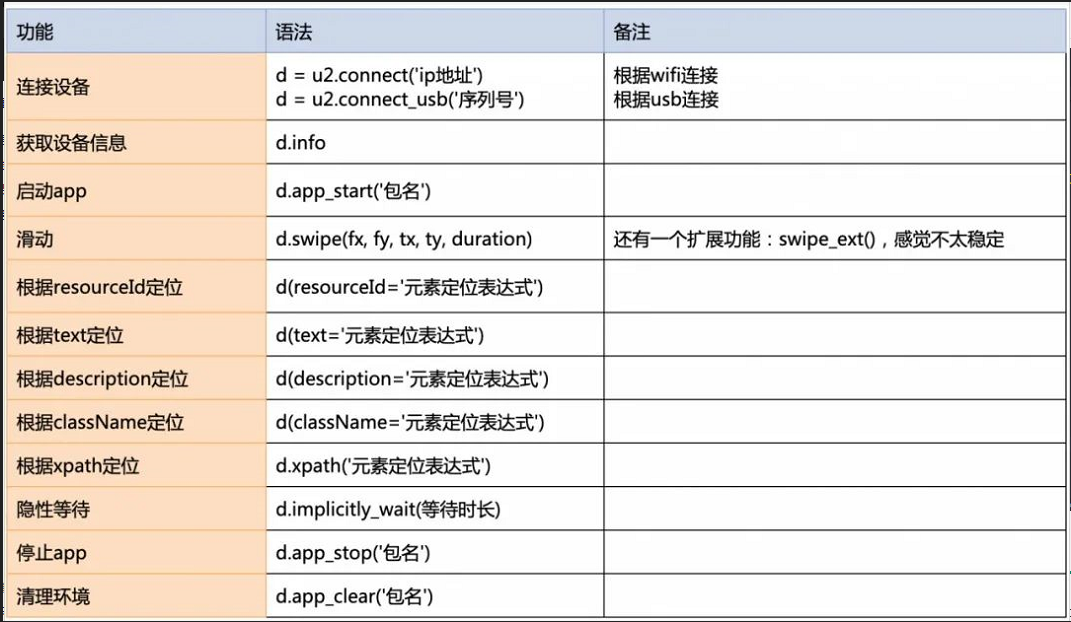
Standard APi
Wait correlation
# wait until app running
pid = d.app_wait("com.example.android") # Wait for the application to run, return pid(int)
if not pid:
print("com.example.android is not running")
else:
print("com.example.android pid is %d" % pid)
d.app_wait("com.example.android", front=True) # Waiting for the application foreground to run
d.app_wait("com.example.android", timeout=20.0) # Wait time (default: 20s)
Upload and download files
- Upload to device
# push to a folder
d.push("foo.txt", "/sdcard/")
# push and rename
d.push("foo.txt", "/sdcard/bar.txt")
# push fileobj
with open("foo.txt", 'rb') as f:
d.push(f, "/sdcard/")
# push and change file access mode
d.push("foo.sh", "/data/local/tmp/", mode=0o755)
- Download files from device
d.pull("/sdcard/tmp.txt", "tmp.txt")
# FileNotFoundError will raise if the file is not found on the device
d.pull("/sdcard/some-file-not-exists.txt", "tmp.txt")
Retrieving device information
Check and keep the device side daemon running
d.healthcheck()
Get screen size
print(d.window_size()) # device upright output example: (1080, 1920) # device horizontal output example: (1920, 1080)
Get current device information
print(d.app_current())
# Output example 1: {'activity': '.Client', 'package': 'com.netease.example', 'pid': 23710}
# Output example 2: {'activity': '.Client', 'package': 'com.netease.example'}
# Output example 3: {'activity': None, 'package': None}
Waiting activity
d.wait_activity(".ApiDemos", timeout=10) # default timeout 10.0 seconds
# Output: true of false
Get device serial number
print(d.serial) # output example: 74aAEDR428Z9
Get network ip
print(d.wlan_ip) # output example: 10.0.0.1
Get detailed device information
print(d.device_info)
## {'udid': '3578298f-b4:0b:44:e6:1f:90-OD103',
'version': '7.1.1',
'serial': '3578298f',
'brand': 'SMARTISAN',
'model': 'OD103',
'hwaddr': 'b4:0b:44:e6:1f:90',
'port': 7912,
'sdk': 25,
'agentVersion': 'dev',
'display': {'width': 1080, 'height': 1920},
'battery': {'acPowered': False,
'usbPowered': False,
'wirelessPowered': False,
'status': 3,
'health': 0,
'present': True,
'level': 99,
'scale': 100,
'voltage': 4316,
'temperature': 272,
'technology': 'Li-ion'},
'memory': {'total': 3690280, 'around': '4 GB'},
'cpu': {'cores': 8, 'hardware': 'Qualcomm Technologies, Inc MSM8953Pro'},
'presenceChangedAt': '0001-01-01T00:00:00Z',
'usingBeganAt': '0001-01-01T00:00:00Z'}
Keyboard events
Information screen on
d.screen_on() # turn on the screen d.screen_off() # turn off the screen
Get current screen status
d.info.get('screenOn') # require Android >= 4.4
Press hard / soft key
d.press("home") # press the home key, with key name
d.press("back") # press the back key, with key name
d.press(0x07, 0x02) # press keycode 0x07('0') with META ALT(0x02)
home
back
left
right
up
down
center
menu
search
enter
delete ( or del)
recent (recent apps)
volume_up
volume_down
volume_mute
camera
power
Unlock screen
d.unlock() # This is equivalent to # 1. launch activity: com.github.uiautomator.ACTION_IDENTIFY # 2. press the "home" key
Click interaction event
click
# single click d.click(x, y) # double-click d.double_click(x, y) d.double_click(x, y, 0.1) # default duration between two click is 0.1s # Long press d.long_click(x, y) d.long_click(x, y, 0.5) # long click 0.5s (default)
Sliding event
# slide
d.swipe(sx, sy, ex, ey)
d.swipe(sx, sy, ex, ey, 0.5) # swipe for 0.5s(default)
# Sliding extension function
d.swipe_ext("right") # Slide your finger to the right and choose 1 "left", "right", "up", "down" from 4
d.swipe_ext("right", scale=0.9) # The default is 0.9, and the sliding distance is 90% of the screen width
d.swipe_ext("right", box=(0, 0, 100, 100)) # Slide in the area (0,0) - > (100, 100)
# Practice has found that when sliding up or down, the success rate of sliding from the midpoint will be higher
d.swipe_ext("up", scale=0.8) # The code will vkk
# You can also use Direction as a parameter
from uiautomator2 import Direction
d.swipe_ext(Direction.FORWARD) # Page down, equivalent to d.swipe_ext("up") is just better understood
d.swipe_ext(Direction.BACKWARD) # Page up
d.swipe_ext(Direction.HORIZ_FORWARD) # Page horizontal right flip
d.swipe_ext(Direction.HORIZ_BACKWARD) # Page horizontal left flip
drag
d.drag(sx, sy, ex, ey) d.drag(sx, sy, ex, ey, 0.5) # swipe for 0.5s(default)
Positioning sliding
# swipe from point(x0, y0) to point(x1, y1) then to point(x2, y2) # time will speed 0.2s bwtween two points d.swipe_points([(x0, y0), (x1, y1), (x2, y2)], 0.2))
Touch and drag
d.touch.down(10, 10) # Analog press time.sleep(.01) # The delay between down and move can be controlled by yourself d.touch.move(15, 15) # Simulated movement d.touch.up() # Simulated lift
Screen related
# take screenshot and save to a file on the computer, require Android>=4.2.
d.screenshot("home.jpg")
# get PIL.Image formatted images. Naturally, you need pillow installed first
image = d.screenshot() # default format="pillow"
image.save("home.jpg") # or home.png. Currently, only png and jpg are supported
# get opencv formatted images. Naturally, you need numpy and cv2 installed first
import cv2
image = d.screenshot(format='opencv')
cv2.imwrite('home.jpg', image)
# get raw jpeg data
imagebin = d.screenshot(format='raw')
open("some.jpg", "wb").write(imagebin)
Transfer to storage UI hierarchy
# get the UI hierarchy dump content (unicoded). xml = d.dump_hierarchy()
Turn on notifications and quick settings
d.open_notification() d.open_quick_settings()
Selector selector
Selector is a handy mechanism to identify a specific UI object in the current window.
# Select the object with text 'Clock' and its className is 'android.widget.TextView' d(text='Clock', className='android.widget.TextView')
Selector supports below parameters. Refer to UiSelector Java doc for detailed information.
- text, textContains, textMatches, textStartsWith
- className, classNameMatches
- description, descriptionContains, descriptionMatches, descriptionStartsWith
- checkable, checked, clickable, longClickable
- scrollable, enabled,focusable, focused, selected
- packageName, packageNameMatches
- resourceId, resourceIdMatches
- index, instance
Sibling node
Child node
# get the children or grandchildren d(className="android.widget.ListView").child(text="Bluetooth")
brothers and sisters
# get siblings d(text="Google").sibling(className="android.widget.ImageView")
Children listed by text, description or example
# get the child matching the condition className="android.widget.LinearLayout"
# and also its children or grandchildren with text "Bluetooth"
d(className="android.widget.ListView", resourceId="android:id/list") \
.child_by_text("Bluetooth", className="android.widget.LinearLayout")
# get children by allowing scroll search
d(className="android.widget.ListView", resourceId="android:id/list") \
.child_by_text(
"Bluetooth",
allow_scroll_search=True,
className="android.widget.LinearLayout"
)
Comprehensive case [locating complex nodes]
Sometimes the screen may contain multiple views with the same properties, e.g. text, then you will have to use the "instance" property in the selector to pick one of qualifying instances, like below:
d(text="Add new", instance=0) # which means the first instance with text "Add new"
In addition, uiautomator2 provides a list-like API (similar to jQuery):
# get the count of views with text "Add new" on current screen
d(text="Add new").count
# same as count property
len(d(text="Add new"))
# get the instance via index
d(text="Add new")[0]
d(text="Add new")[1]
...
# iterator
for view in d(text="Add new"):
view.info # ...
U2 service start pause
import uiautomator2 as u2
import time
# Connect via wifi
d = u2.connect_wifi("192.168.1.8")
# View device information
# print(d.device_info)
# print(d.service("uiautomator").running())
# Start the uiautomator service through the start method
# d.service("uiautomator").start()
# time.sleep(2)
# print(d.service("uiautomator").running())
# Out of Service
# d.service("uiautomator").stop()
# time.sleep(2)
# print(d.service("uiautomator").running())
# Check the running status of ATX agent. If the ATX agent really stops, we can wake up the ATX agent service through connect
# print(d.agent_alive)
# View device information
print(d.device_info)
# View the resolution of the device
print(d.window_size())
# View the obtained wifi address
print(d.wlan_ip)
Get ui object status and information
Determine whether the ui exists
d(text="Settings").exists # True if exists, else False d.exists(text="Settings") # alias of above property. # advanced usage d(text="Settings").exists(timeout=3) # wait Settings appear in 3s, same as .wait(3)
Retrieve specific UI object information
d(text="Settings").info
## { u'contentDescription': u'',
u'checked': False,
u'scrollable': False,
u'text': u'Settings',
u'packageName': u'com.android.launcher',
u'selected': False,
u'enabled': True,
u'bounds': {u'top': 385,
u'right': 360,
u'bottom': 585,
u'left': 200},
u'className': u'android.widget.TextView',
u'focused': False,
u'focusable': True,
u'clickable': True,
u'chileCount': 0,
u'longClickable': True,
u'visibleBounds': {u'top': 385,
u'right': 360,
u'bottom': 585,
u'left': 200},
u'checkable': False
}
Get, set and clear text information
d(text="Settings").get_text() # get widget text
d(text="Settings").set_text("My text...") # set the text
d(text="Settings").clear_text() # clear the text
Get screen center point
x, y = d(text="Settings").center() # x, y = d(text="Settings").center(offset=(0, 0)) # left-top x, y
Screenshot
im = d(text="Settings").screenshot()
im.save("settings.jpg")
Locate element Click
# click on the center of the specific ui object d(text="Settings").click() # wait element to appear for at most 10 seconds and then click d(text="Settings").click(timeout=10) # click with offset(x_offset, y_offset) # click_x = x_offset * width + x_left_top # click_y = y_offset * height + y_left_top d(text="Settings").click(offset=(0.5, 0.5)) # Default center d(text="Settings").click(offset=(0, 0)) # click left-top d(text="Settings").click(offset=(1, 1)) # click right-bottom # click when exists in 10s, default timeout 0s clicked = d(text='Skip').click_exists(timeout=10.0) # click until element gone, return bool is_gone = d(text="Skip").click_gone(maxretry=10, interval=1.0) # maxretry default 10, interval default 1.0
Drag UI slide operation
# notes : drag can not be used for Android<4.3. # drag the UI object to a screen point (x, y), in 0.5 second d(text="Settings").drag_to(x, y, duration=0.5) # drag the UI object to (the center position of) another UI object, in 0.25 second d(text="Settings").drag_to(text="Clock", duration=0.25)
WatchContext
with d.watch_context() as ctx:
ctx.when("^immediately(download|to update)").when("cancel").click() # Click Cancel when both (install now or cancel now) and Cancel buttons appear at the same time
ctx.when("agree").click()
ctx.when("determine").click()
# The above three lines of code are executed immediately and there will be no waiting
ctx.wait_stable() # Open pop-up monitoring and wait for the interface to stabilize (no pop-up in two pop-up inspection cycles represents stability)
# Use the call function to trigger a function callback
# call supports two parameters, d and el. It does not distinguish between parameter positions. You can not pass parameters. If you pass parameter variable names, you can't write them wrong
# eg: when there are elements matching midsummer night, click the back button
ctx.when("summer night ").call(lambda d: d.press("back"))
ctx.when("determine").call(lambda el: el.click())
# Other operations
# For convenience, you can also use the default pop-up monitoring logic in the code
# The following is the current built-in default logic. You can add a group at group owner, add a new logic, or directly mention pr
# when("continue to use") click()
# when("move in control") when("Cancel") click()
# when("^ now (download update)") when("Cancel") click()
# when("consent") click()
# when("^ (OK | OK)") click()
with d.watch_context(builtin=True) as ctx:
# Increase on the existing basis
ctx.when("@tb:id/jview_view").when('//*[@ content desc = "picture"]) click()
# Other script logic
Monitoring operation
# Remove monitoring of ANR
d.watcher.remove("ANR")
# Remove all monitoring
d.watcher.remove()
# Start background monitoring
d.watcher.start()
d.watcher.start(2.0) # The default monitoring interval is 2.0s
# Force all monitoring
d.watcher.run()
# Stop monitoring
d.watcher.stop()
# Stop and remove all monitoring, commonly used for initialization
d.watcher.reset()
Global settings
d.HTTP_TIMEOUT = 60 # The default value is 60s, and the HTTP request timeout is the default # When the equipment is disconnected, the waiting time for the equipment to be online is long. It is only valid when TMQ=true. It supports waiting through the environment variable_ FOR_ DEVICE_ Timeout settings d.WAIT_FOR_DEVICE_TIMEOUT = 70
At present, most other configurations have been concentrated in d.settings, and the configuration may be increased or decreased according to the later requirements.
print(d.settings)
{'operation_delay': (0, 0),
'operation_delay_methods': ['click', 'swipe'],
'wait_timeout': 20.0,
'xpath_debug': False}
# Configure the delay of 0.5s before clicking and 1s after clicking
d.settings['operation_delay'] = (.5, 1)
# Modify the method of delayed entry into force
# Where double_click, long_click corresponds to click
d.settings['operation_delay_methods'] = ['click', 'swipe', 'drag', 'press']
d.settings['xpath_debug'] = True # Open the debugging log of xpath plug-in
d.settings['wait_timeout'] = 20.0 # Default control waiting time (native operation, waiting time of xpath plug-in)
When setting expired configurations with version upgrade, you will be prompted with Deprecated, but no exceptions will be thrown.
>>> d.settings['click_before_delay'] = 1 [W 200514 14:55:59 settings:72] d.settings[click_before_delay] deprecated: Use operation_delay instead
Input method
This method is usually used for input without knowing the control. The first step is to switch the input method, and then send the adb broadcast command. The specific methods are as follows
d.set_fastinput_ime(True) # Switch to FastInputIME input method
d.send_keys("Hello 123 abcEFG") # adb broadcast input
d.clear_text() # Clear all contents of the input box (require Android uiautomator. APK version > = 1.0.7)
d.set_fastinput_ime(False) # Switch to normal input method
d.send_action("search") # Search of analog input method
send_action description
The parameters that can be used in this function are go search send next done previous
When should I use this function?
Sometimes, after entering what is in EditText, calling press("search") or press("enter") finds no response. Send is needed at this time_ The action function is used here. Only the input method can be used IME_ACTION_CODE . send_action first sends the broadcast command to the input method operation IME_ACTION_CODE, the input method completes the subsequent communication with EditText. (I'm not sure about the principle. If you know something about it, ask the issue to tell me)
Xpath
- https://github.com/openatx/uiautomator2/blob/master/XPATH.md Common examples
# wait exists 10s
d.xpath("//android.widget.TextView").wait(10.0)
# find and click
d.xpath("//*[@ content desc = 'share'] "). click()
# check exists
if d.xpath("//android.widget.TextView[contains(@text, 'Se')]").exists:
print("exists")
# get all text-view text, attrib and center point
for elem in d.xpath("//android.widget.TextView").all():
print("Text:", elem.text)
# Dictionary eg:
# {'index': '1', 'text': '999+', 'resource-id': 'com.netease.cloudmusic:id/qb', 'package': 'com.netease.cloudmusic', 'content-desc': '', 'checkable': 'false', 'checked': 'false', 'clickable': 'false', 'enabled': 'true', 'focusable': 'false', 'focused': 'false','scrollable': 'false', 'long-clickable': 'false', 'password': 'false', 'selected': 'false', 'visible-to-user': 'true', 'bounds': '[661,1444][718,1478]'}
print("Attrib:", elem.attrib)
# Coordinate eg: (100, 200)
print("Position:", elem.center())
Simple usage of xpath
import uiautomator2 as u2
def main():
d = u2.connect()
d.app_start("com.netease.cloudmusic", stop=True)
d.xpath('//*[@ text = "private FM"]) click()
#
# Advanced usage (element positioning)
#
# @Beginning
d.xpath('@personal-fm') # Equivalent to d.xpath ('/ / * [@ resource id = "personal FM"]')
# Multiple conditional positioning, similar to AND
d.xpath('//android.widget.Button').xpath('//*[@text = "private FM"]')
d.xpath('//*[@ text = "private FM"]) Parent() # navigate to parent element
d.xpath('//*[@ text = "private FM"]) Parent ("@ Android: List") # locate the eligible parent element
U2 connect mobile phone and start / return APP
import uiautomator2 as u2
import time
#The current network environment is really a LAN
#There are no network restrictions
# The coffee shop, the school library, is in a network isolated environment
#The mobile wechat message is sent to the Tencent server, and the Tencent server is sent to your classmate's mobile phone
#To connect through mobile WIFI, you need to check the IP address of the mobile phone
d = u2.connect_wifi("192.168.1.7")
# print(d.info)
# Through the serial number of the mobile phone
# d = u2.connect_usb("4bf05af7")
# print(d.info)
#Through adb wifi, that is, adb tcpip mode, be careful not to lose the port number
# d = u2.connect_adb_wifi("192.168.1.7:5555")
#device_info to get detailed device information
# print(d.device_info)
#Start the app on the mobile phone and get the package name through aapt tool
#When appt gets the package name, it is in AAPT dump bagging XXX Apk, the package name is obtained
d.app_start("com.ss.android.ugc.aweme")
#Run for seven seconds
time.sleep(7)
#Stop shaking tiktok app
d.app_stop("com.ss.android.ugc.aweme")
Basic operation of app through U2
import uiautomator2 as u2
# Connect via wifi
d = u2.connect_wifi("192.168.1.8")
# Via app_install apk with the install method, url="xxx.apk"
# d.app_install(url="http://file.mukewang.com/apk/app/115/imooc7.3.410102001android.apk")
# Launch app
# d.app_start(package_name="cn.com.open.mooc")
# Get the information of the app currently running in the foreground
# print(d.app_current())
# d.app_stop("cn.com.open.mooc")
# Get app details
# print(d.app_info(pkg_name="cn.com.open.mooc"))
# Clear app cache
# In particular, the video data capture we will do later will produce a certain cache
# d.app_clear("cn.com.open.mooc")
# Uninstall app
# d.app_uninstall("cn.com.open.mooc")
# Get a list of all app s
# print(d.app_list())
# Get a list of all running app s
# print(d.app_list_running())
# Stop all app s
d.app_stop_all()
# Uninstall all apps, uninstall all third-party apps, U2 project packages will not uninstall 'PM', 'list', 'packages',' - 3
d.app_uninstall_all()
xpath positioning
import uiautomator2 as u2
d = u2.connect_usb("4bf05af7")
# with open("phone.file", 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
# # Use this method to get the source code file of the control
# f.write(d.dump_hierarchy())
d.xpath('//*[@ text = "Bluetooth"]) click()
Coordinate positioning
import uiautomator2 as u2
d = u2.connect_usb("4bf05af7")
d.app_start("com.android.settings")
# Here, you can locate the control through coordinate points
# We can choose the actual coordinate points or locate them by percentage
d.click(0.168, 0.341)
Control timed out
import uiautomator2 as u2
d = u2.connect_usb("4bf05af7")
d.app_start("com.android.settings")
# Control does not exist, what should we do
# Control throw exception UiObjectNotFoundError not found
# d(text = "Bluetooth 1") click(timeout=5)
# click_exists: click if the control exists, and return if the control does not exist. Within the timeout time
# d(text = "Bluetooth 1") click_ exists(timeout=5)
# Before the operation, judge whether the control exists through the exists property
# Print (d) (text = "Bluetooth 1") exists)
# Print (d) (text = "Bluetooth") exists(timeout=5))
# print(d(resourceId="android:id/list").child(resourceId="oppo:id/oppo_preference").count)
for view in d(resourceId="android:id/list").child(resourceId="oppo:id/oppo_preference"):
print(view.info)
Select and manipulate the control
import uiautomator2 as u2
d = u2.connect_usb("4bf05af7")
d.app_start(package_name="com.android.settings")
# Locate the control through the resource ID and limit it through the index
# You can select multiple controls. The first control is selected by default
# d(resourceId="android:id/title")[2].click()
# Search by instance, and the value and index value are the same
# d(resourceId="android:id/title", instance=2).click()
# Qualified by multiple conditions
# d(resourceId="android:id/title", text = "Bluetooth") click()
# Get the resource ID through regular expression method and locate the control
# d(resourceIdMatches="android:id\/\w{5}", text = "Bluetooth") click()
# When using className to get control positioning, you need to pay attention to the hierarchical relationship
# d(className="android.widget.TextView")[4].click()
# d(className="android.widget.TextView", instance=4).click()
# d(classNameMatches="android\.widget\.\w{8}", text = "Bluetooth") click()
# Here is the chain positioning mode
# d(className="android.widget.ListView").child(text = "Bluetooth") click()
# d(className="android.widget.ListView").child_by_text("Bluetooth", resourceid = "Android: ID / Title") click()
# Complete chain positioning method, the code is very lengthy, we do not recommend it
# d(className="android.widget.ListView").child(resourceId="oppo:id/oppo_preference")[2].child(className="android.widget.RelativeLayout").child(resourceId="android:id/title").click()
# This method is based on many times and is not recommended
# d(resourceId="oppo:id/oppo_preference").sibling(resourceId="oppo:id/oppo_preference", instance=2).click()
Unlock Jiugong grid
import uiautomator2 as u2
d = u2.connect_usb("4bf05af7")
# Sliding unlocking operation
# Rest screen
# d.screen_off()
# Light up the screen
# d.screen_on()
# Unlock
# d.unlock()
# Get screen status
# print(d.info.get("screenOn"))
# d.unlock()
# home key
# d.press("home")
# Return key
# d.press("back")
# d.swipe_ext("left")
# d.swipe_ext("right")
# Slide unlock
# swipe_points
# Unlock the Jiugong grid interface first
# 0.224, 0.393
# (0.493, 0.395)
# (0.781, 0.396)
# (0.501, 0.551)
# (0.218, 0.705)
# (0.501, 0.703)
# (0.773, 0.703)
# duration0. It's 2.0 seconds
d.unlock()
d.swipe_points(points=[
(0.224, 0.393),
(0.493, 0.395),
(0.781, 0.396),
(0.501, 0.551),
(0.218, 0.705),
(0.501, 0.703),
(0.773, 0.703)
], duration=0.2)
d.screen_off()
Actual combat of postgraduate entrance examination Gang
import uiautomator2 as u2
class HandleKaoyanbang(object):
def __init__(self, serial="4bf05af7"):
# Currently, mobile devices are connected through usb
self.d = u2.connect_usb(serial=serial)
self.size = self.get_windowsize()
self.handle_watcher()
def handle_watcher(self):
"""Define a monitor"""
# The monitor will start a separate thread
# User privacy agreement
self.d.watcher.when('//*[@resource-id="com.tal.kaoyan:id/tip_commit"]').click()
# advertisement
self.d.watcher.when('//*[@resource-id="com.tal.kaoyan:id/tv_skip"]').click()
# After the monitor is written, start it through the start method
self.d.watcher.start()
def get_windowsize(self):
"""Get the size of the phone screen"""
return self.d.window_size()
def close_app(self):
# Monitor off
self.d.watcher.stop()
# Stop the postgraduate entrance examination help app
self.d.app_stop("com.tal.kaoyan")
# Clean cache
self.d.app_clear("com.tal.kaoyan")
def handle_kaoyanbang_app(self):
"""Start the postgraduate entrance examination group app,And realize automatic operation"""
# aapt this tool
# Via webitor
self.d.app_start(package_name="com.tal.kaoyan")
# Before clicking, you need to judge whether there is this control
self.d(text="Password login").click_exists(timeout=10)
# After finding the relevant control, the text control, set_text this method to enter text
self.d(resourceId="com.tal.kaoyan:id/login_email_edittext").set_text("450120127@163.com")
# Input password
self.d(resourceId="com.tal.kaoyan:id/login_password_edittext").set_text("abcd1234")
# self.d(resourceId="com.tal.kaoyan:id/login_login_btn").click()
self.d(text="Sign in").click()
# In 10 seconds, if this interface starts
if self.d.wait_activity("com.tal.kaoyan.ui.activity.HomeTabActivity", timeout=10):
self.d(text="Inquiry").click_exists(timeout=10)
# Get the center point of the screen, x-axis
# After obtaining the distant point of y-axis, obtain the near point of y-axis
x1 = int(self.size[0] * 0.5)
y1 = int(self.size[1] * 0.9)
y2 = int(self.size[1] * 0.15)
while True:
# get toast is an information prompt operation of Android system
if self.d.toast.get_message(0) == "The content has been fully loaded":
self.close_app()
return
# Start sliding inquiry
self.d.swipe(x1, y1, x1, y2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
k = HandleKaoyanbang()
k.handle_kaoyanbang_app()