1, C language code block
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
int ftrl(int n)
{
if (n == 1) {
// ne1
return 1; // ne2
} // ne3
int pre = ftrl(n - 1); // ne4
return pre * n; // ne5
}
void main()
{
int a = 3, b; // ne1
b = ftrl(a); // ne2
printf("b: %d\n", b); // ne3
}
2, Process
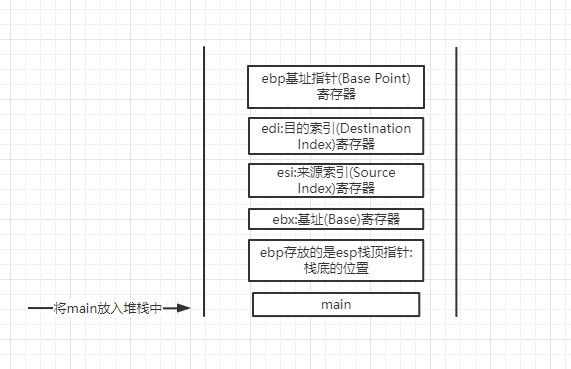
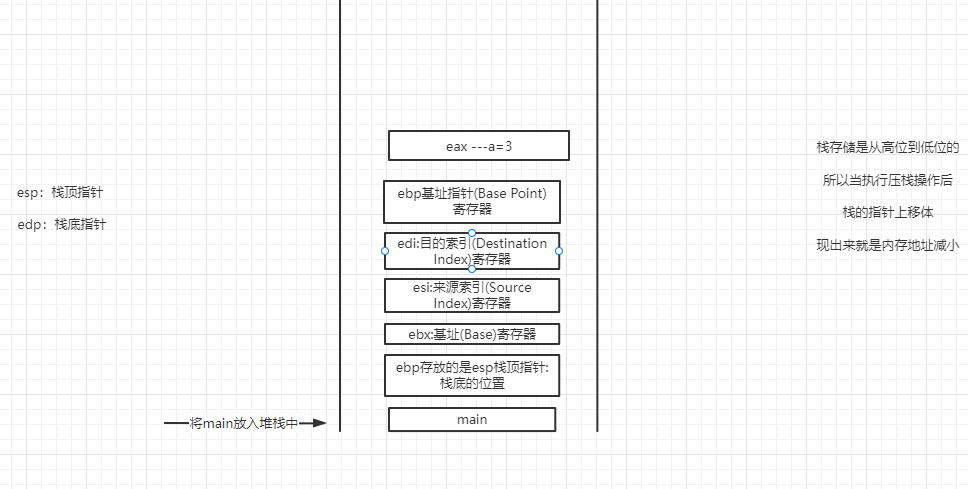
2.1 put main on the stack
push: stack pressing pop: stack out esp: stack top pointer edp: stack bottom pointer
sub: minus add: plus mov: assignment
- Stack storage is from high to low, so when the stack is pressed, the pointer of the stack moves up, which is reflected in the decrease of memory address
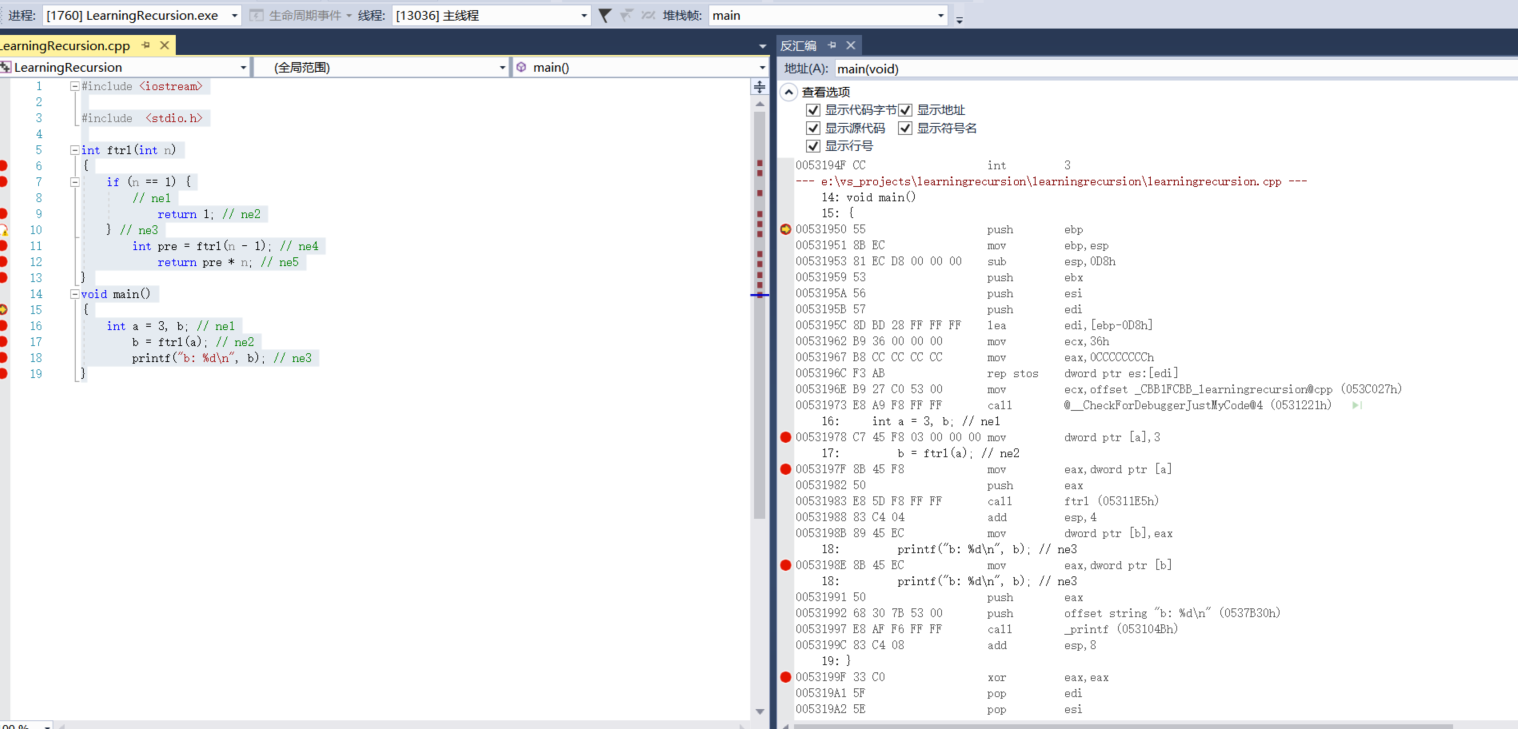
address command operation ebp:Base address pointer(Base Point)register 00531950 push ebp -----> 1.hold ebp Push into stack esp:Stack pointer(Stack Point)register 00531951 mov ebp,esp -----> 2.hold esp Put ebp 00531953 sub esp,0D8h -----> 3.In this way, the original position at the bottom of the stack is recorded, and the original position can be returned only after the function call is completed. here sub esp,0D8h Subtract 0 from the pointer address at the top of the stack D8h,Because the stack is stored from high to low, it is equivalent to moving the pointer at the top of the stack upward. ebx:Base address(Base)register 00531959 push ebx -----> 4.hold ebx Push into stack esi:Source index(Source Index)register 0053195A push esi -----> 5.hold esi Push into stack edi:Destination index(Destination Index)register 0053195B push edi -----> 6.hold edi Push into stack 0053195C lea edi,[ebp+FFFFFF28h] -----> 7. lea Destination address transfer instruction.LEA Load valid address. example: LEA DX,string ;Save offset address to DX. 00531962 mov ecx,36h -----> 8 00531967 mov eax,0CCCCCCCCh -----> 9 initialization eax 0053196C rep stos dword ptr es:[edi] -----> 10 Here are four(7---10)This instruction is actually doing one thing: initialization: just 3 sub esp,0D8h Minus 36 h*4 The contents of bytes become 0 xcc. ecx: Counter(Counter)register 0053196E mov ecx,53C027h -----> 11 00531973 call 00531221-----> 12 CALL Procedure call procedure
ebp base point register


2.2 initializing variables and calling functions
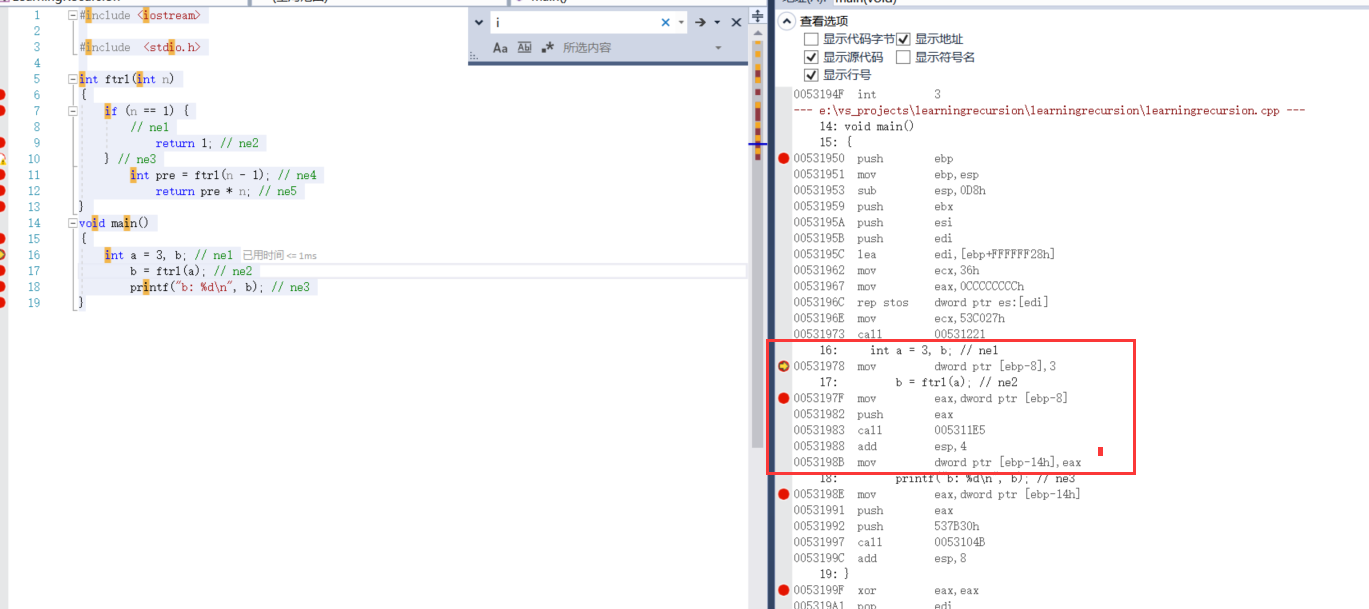
16: int a = 3, b; // ne1 00531978 mov dword ptr [ebp-8],3
dword doubleword is four bytes
ptr pointer abbreviation is pointer
The data in [] is an address value, which points to a double font data
For example, mov eax, dword ptr [12345678] assigns double font (32-bit) data in memory address 12345678 to eax
17: b = ftrl(a); // ne2 0053197F mov eax,dword ptr [ebp-8] 00531982 push eax
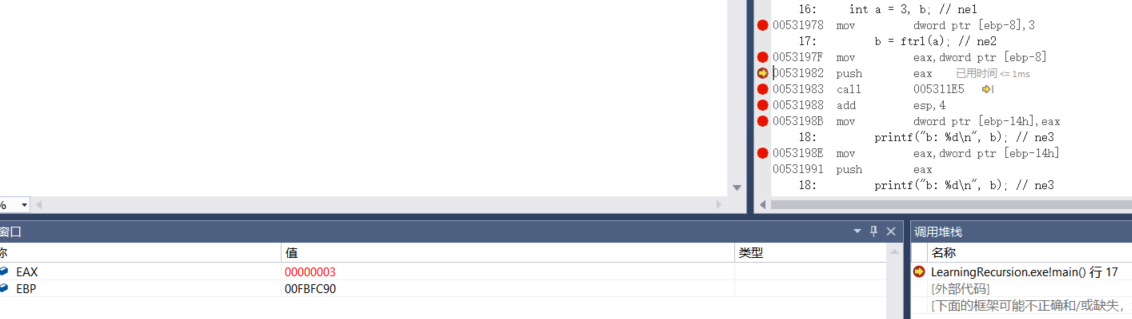
00531983 call 005311E5 ---->Call function int ftrl(int n) 00531988 add esp,4 0053198B mov dword ptr [ebp-14h],eax

The CALL instruction calls a procedure and instructs the processor to execute from a new memory address. The procedure uses the RET (return from procedure) instruction to turn the processor back to the program point where the procedure is called.

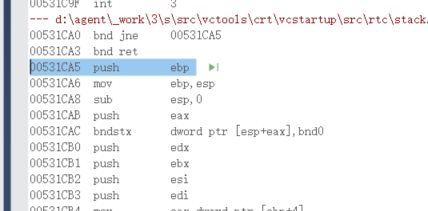
2.3 first entry function
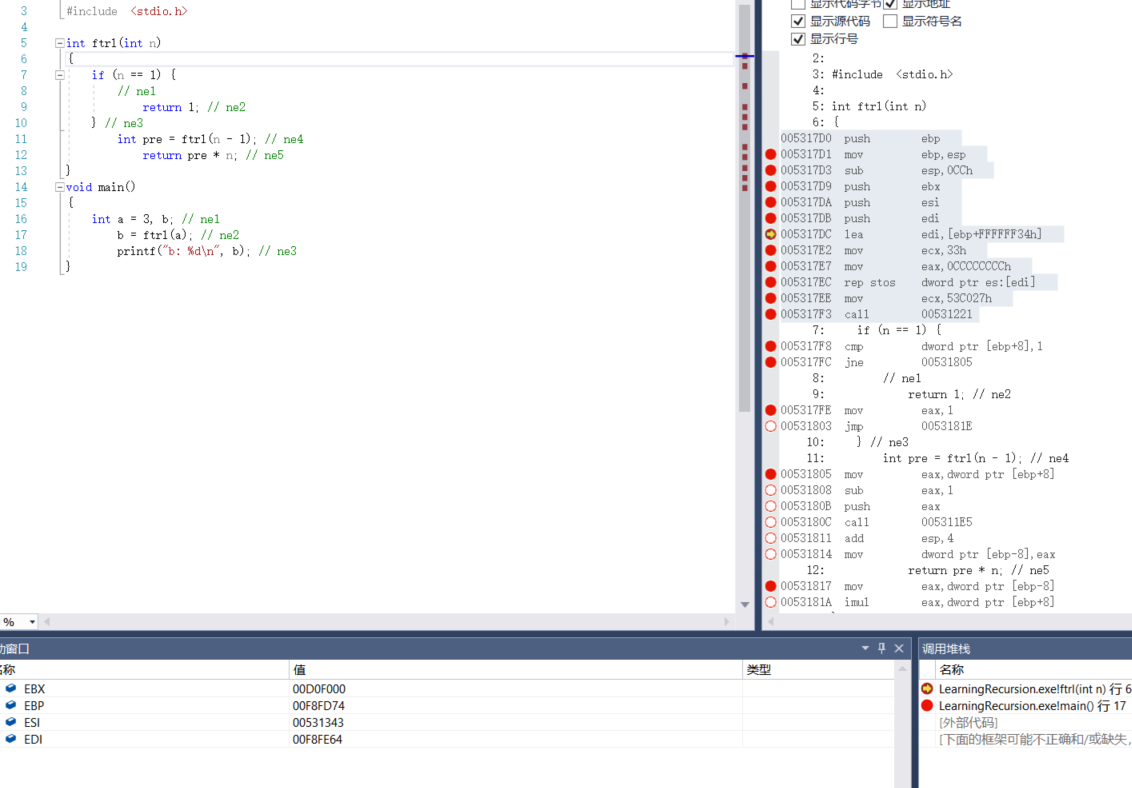
003617D0 55 push ebp // The first step is to push the EBP (base point) register onto the stack 003617D1 8B EC mov ebp,esp //Step 2: stack pointer ESP is placed in ebp 003617D3 81 EC CC 00 00 00 sub esp,0CCh //Step 3 initialization: the initial value of a local variable that is not initialized at the time of definition is the same as "0xCCH" 003617D9 53 push ebx // Base register 003617DA 56 push esi //Source index register 003617DB 57 push edi //Destination index register 003617DC 8D BD 34 FF FF FF lea edi,[ebp+FFFFFF34h] //LEA destination address transfer instruction LEA loads valid addresses Example: LEA DX,string; Save the offset address to DX 003617E2 B9 33 00 00 00 mov ecx,33h 003617E7 B8 CC CC CC CC mov eax,0CCCCCCCCh //Initialize eax 003617EC F3 AB rep stos dword ptr es:[edi] //There are four instructions here, which are actually doing one thing: change the 33h*4 bytes added in the third step sub ESP, 0cch into 0xcc.
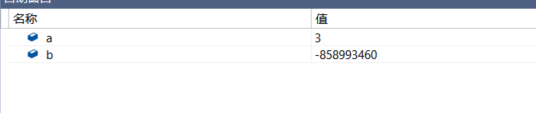
In the function, when "{" is encountered, the local space is allocated and initialized with the value "0xCCH". The initial value of a local variable that is not initialized at the time of definition is related to "0xCCH". Therefore, since the int type variable occupies four bytes, its initial value is - 858993460 (0xCCCCC-CCCH); two consecutive 0xcchs correspond to the Chinese character "hot"
lea (load effective address): this instruction transfers the address of the source operand to the destination operand. The source operand here is ebp-0cch.
rep: this instruction means that the immediately following instruction is ecx times. ecx puts the number of cycles in advance, here is 33h.
stos: put the contents of eax into the address specified by the destination operand.
2.3.1 first judgment
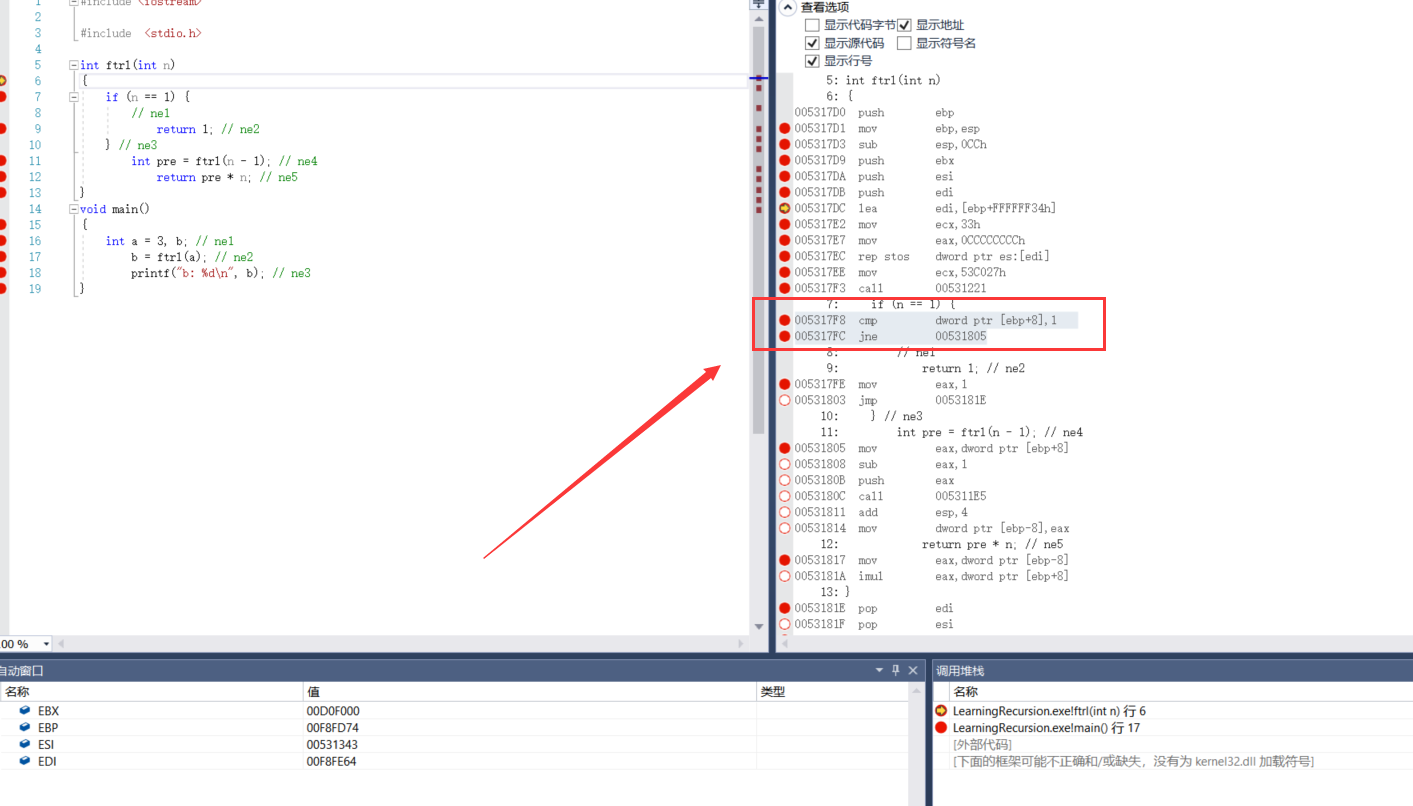
005317F8 cmp dword ptr [ebp+8],1 005317FC jne 00531805
These two steps are judgment
cmp
jne is a conditional transfer instruction. When ZF=0, go to the label and execute
2.3.2 prepare for next recursion
int pre = ftrl(n - 1); // ne4
00531805 mov eax,dword ptr [ebp+8] 00531808 sub eax,1 0053180B push eax 0053180C call 005311E5
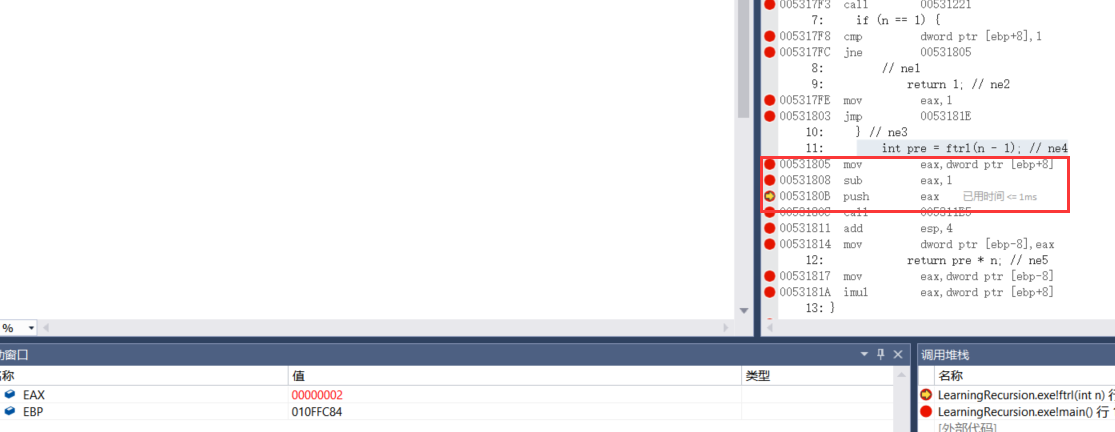
2.4 second entry function
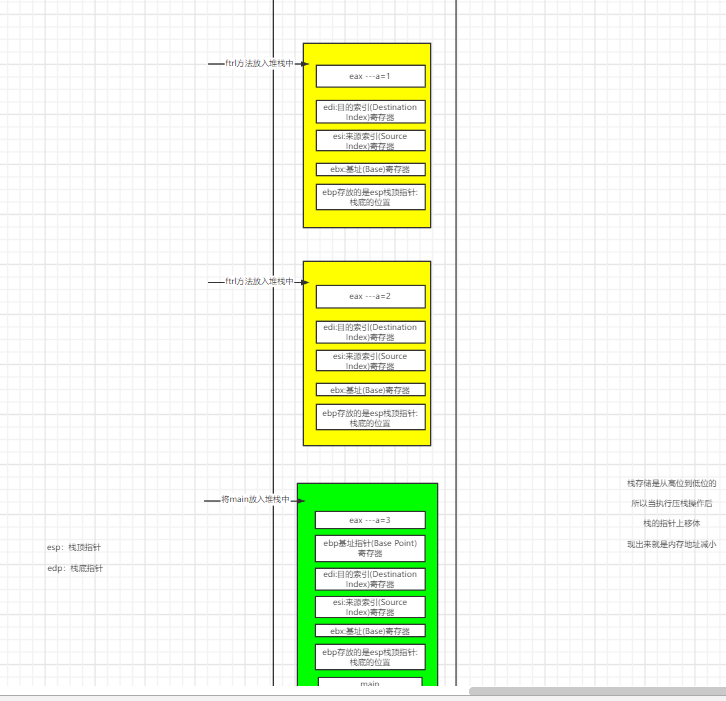
ditto
2.5 third entry function
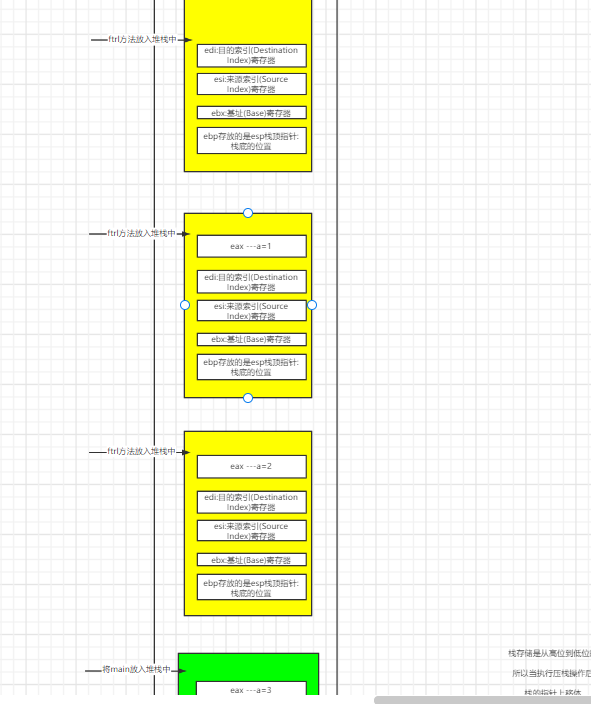
2.5.1 make the third judgment
005317F8 cmp dword ptr [ebp+8],1 005317FC jne 00531805
jne condition judgment is correct and jump is not performed
2.5.2 recursion ends and returns for the first time
005317FE mov eax,1 00531803 jmp 0053181E
Return value through eax
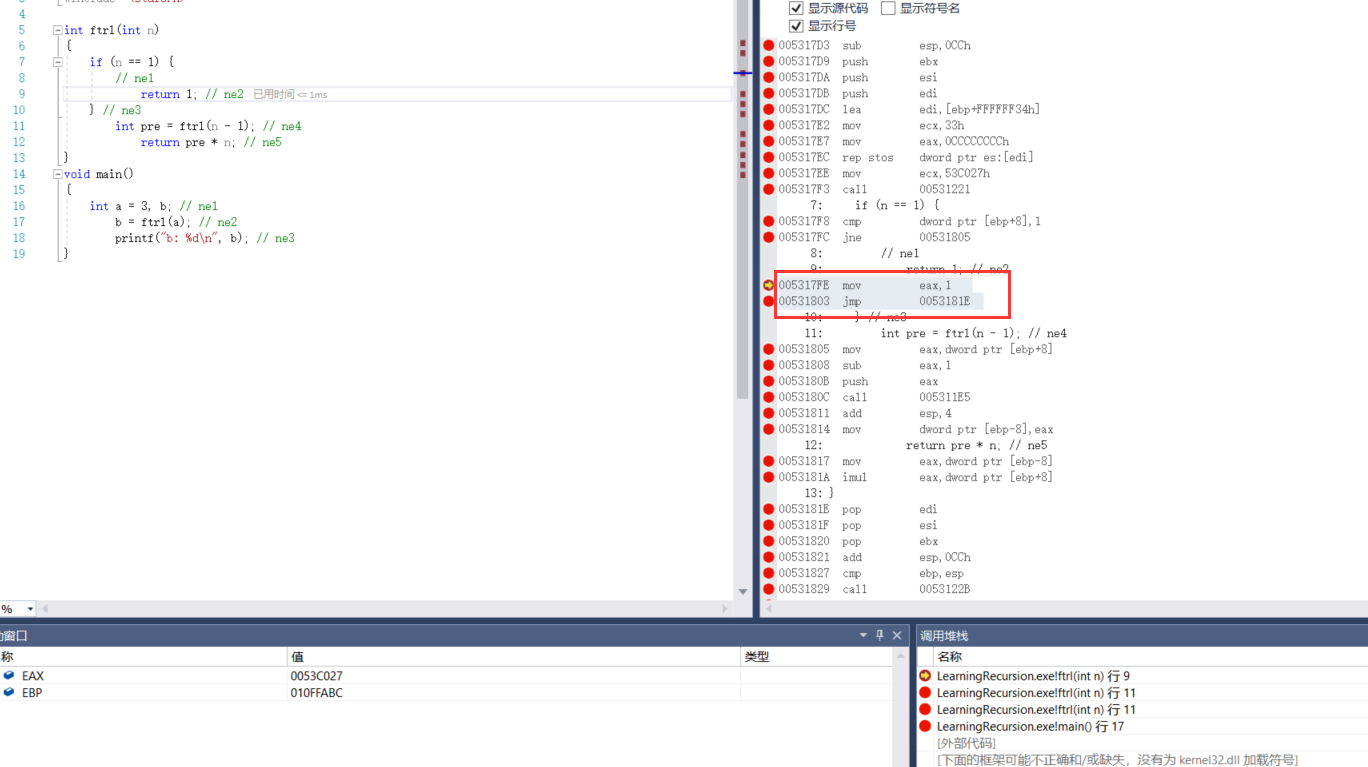
eject
0053181E pop edi 0053181F pop esi 00531820 pop ebx
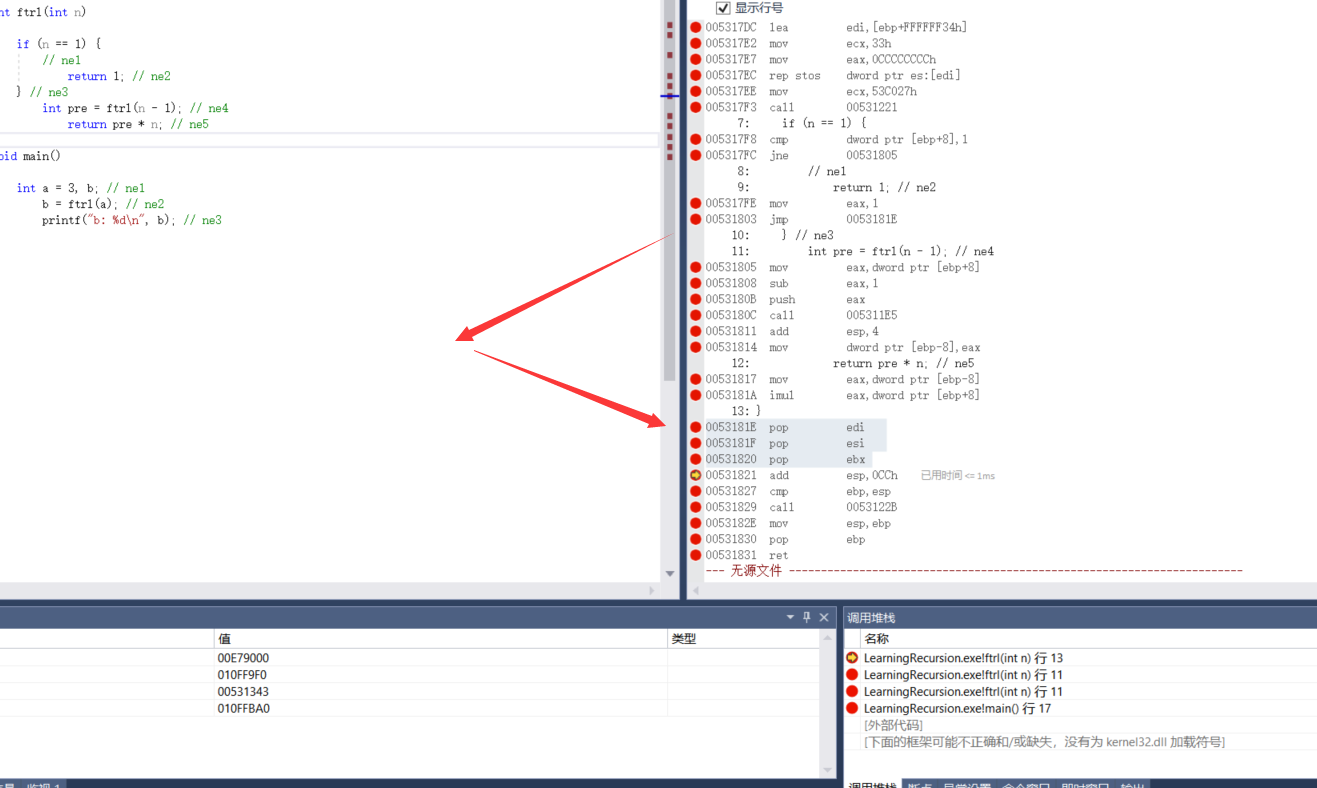

ret and retf
ret instruction uses the data in the stack to modify the content of IP, so as to realize near transfer;
retf instruction uses the data in the stack to modify the contents of CS and IP, so as to realize remote transfer.
When the CPU executes the ret instruction, perform the following two steps:
(1)(IP) = ((ss)*16 +(sp))
(2)(sp) = (sp)+2
When the CPU executes the retf instruction, perform the following four steps:
(1)(IP) = ((ss)*16) + (sp)
(2)(sp) = (sp) + 2
(3)(CS) = ((ss)*16) + (sp)
(4)(sp) = (sp) + 2
Based on 8086 CPU When programming, you can use a piece of memory as a stack.
Stack segment register SS,Storage section address, SP The register stores the offset address at any time, SS:SP Point to stack top element
8086CPU When entering the stack, the top of the stack increases from high address to low address.
push ax Indicates that the register will be ax The data in is sent to the stack in two steps.
1,SP=SP-2,SS:SP Point to the cell in front of the current stack top, and take the cell in front of the current stack top as the new stack top;
2,take ax Content in SS:SP At the memory unit pointed to, SS:SP This points to the top of the new stack