This article is forwarded from: blog.csdn.net/KH_FC/article/detail...
When it comes to Web pages, you may first think of HTML, CSS or JavaScript.
This little F will introduce you how to make a data visualization web page in Python, using the Streamlit library.
Easily convert an Excel data file into a Web page for everyone to view online.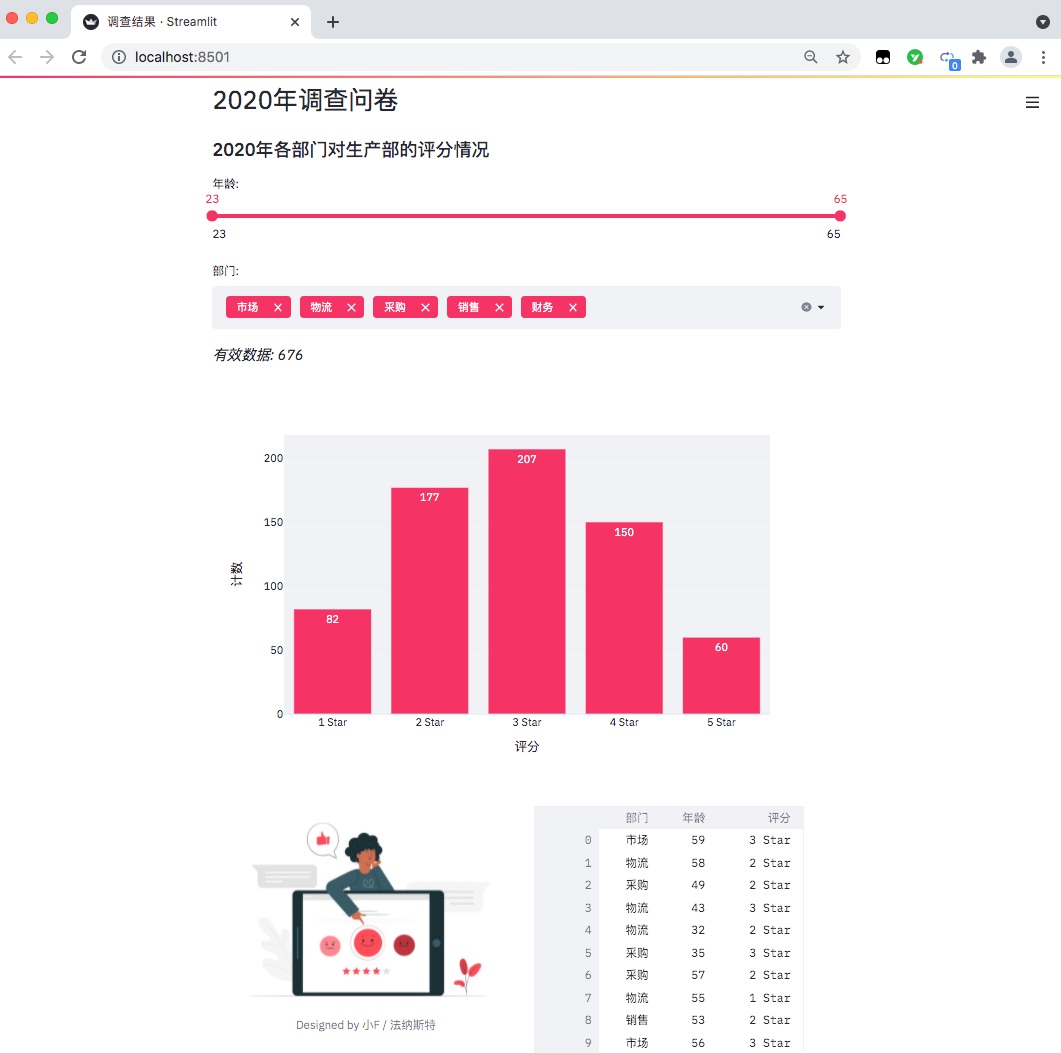
Whenever you save changes to Excel files, Web pages can be updated in real time. It's really good.
Streamlit's documentation and tutorials are addressed below.
docs.streamlit.io/en/stable/
streamlit.io/gallery
The relevant API usage can be viewed in the documentation, which has detailed explanations.
There are three files in the project: program, picture and Excel data.
The data are as follows: in the questionnaire survey (fictitious data) at the end of the year of a company, the relevant departments scored the work cooperation of the production department.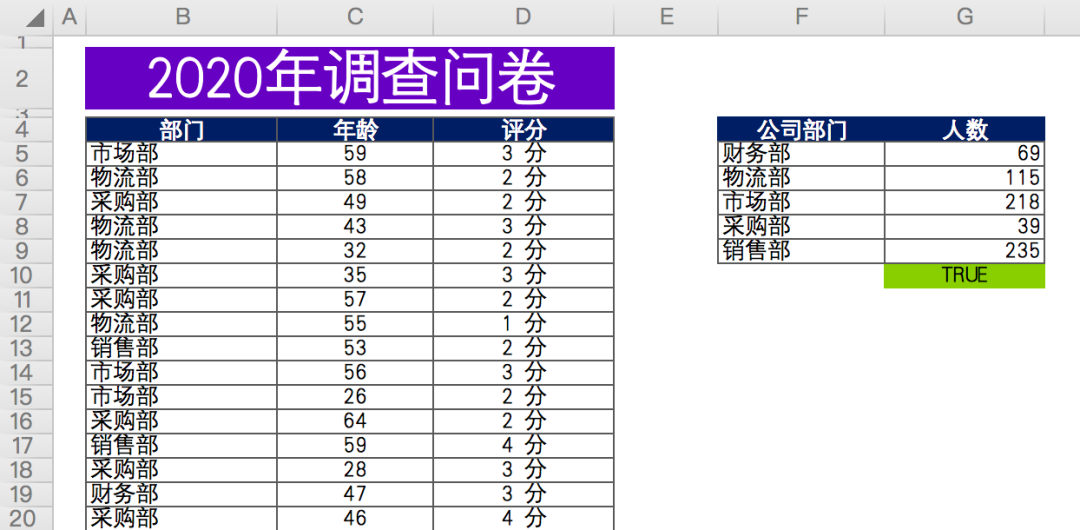
There are about 676 valid data in total, including anonymous questionnaire, including the Department, age and score of the person filling in the questionnaire.
Finally, the number of participants in each department is summarized and counted (data on the right).
First, install the relevant Python library and use Baidu source.
# Installing streamlit pip install streamlit -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple/ # Install plot Express pip install plotly_express==0.4.0 -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple/ # Install xlrd pip install xlrd==1.2.0 -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple/
Because our data file is in xlsx format, the latest version of xlrd only supports xls files.
Therefore, you need to specify the xlrd version as 1.2.0 so that pandas can successfully read the data.
The command line terminal starts the web page.
# The path where the command line terminal opens the file cd Excel_Webapp # Run web page streamlit run app.py
After success, there will be a prompt, and the browser will automatically pop up the web page.
If it does not pop up automatically, you can directly access the address in the figure above.
The results are as follows, a data visualization web page comes out.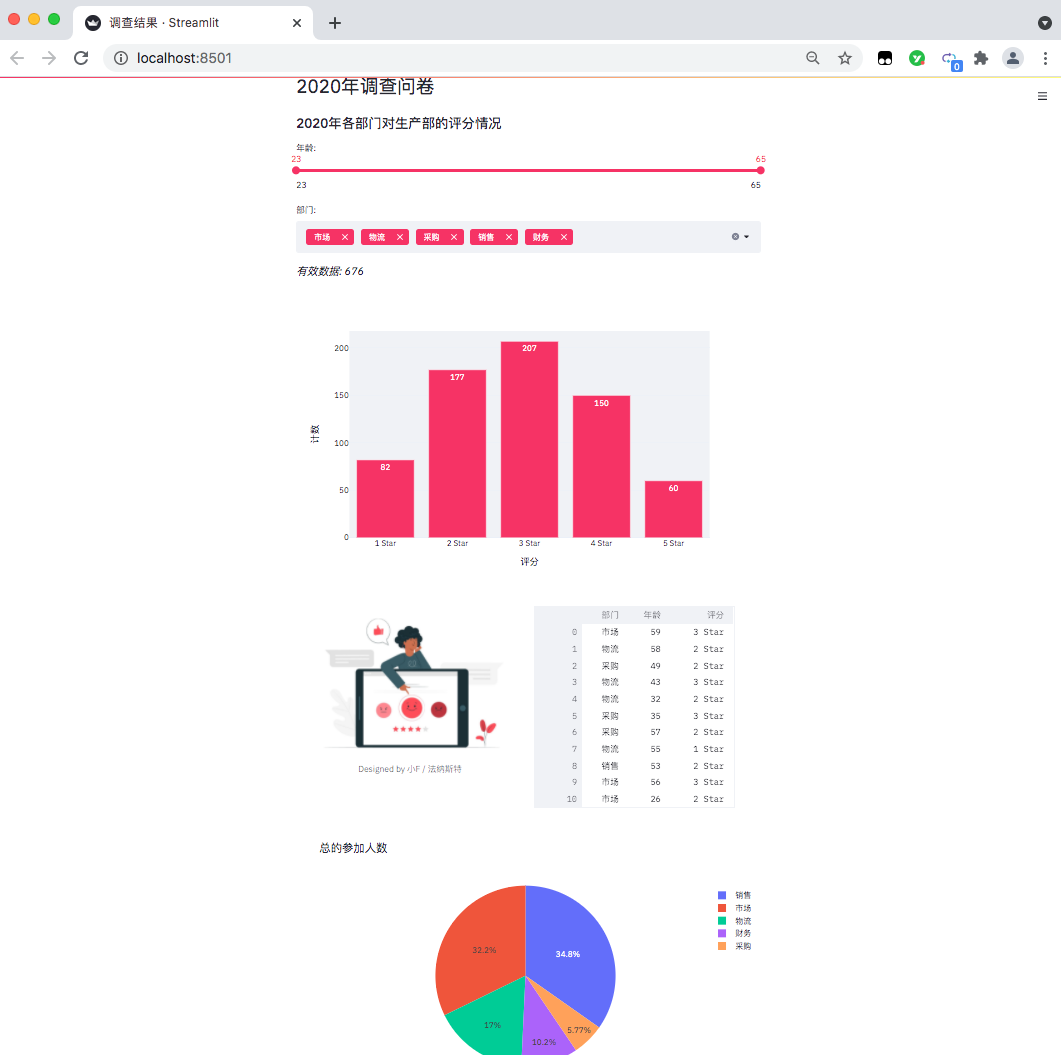
At present, it can only be accessed locally. If you want to put it on the Internet, you can deploy it through the server. You need to study it yourself
Let's take a look at the specific code.
import pandas as pd
import streamlit as st
import plotly.express as px
from PIL import Image
# Set page name
st.set_page_config(page_title='Findings')
# Set page title
st.header('2020 Annual questionnaire')
# Set page subtitle
st.subheader('2020 Evaluation of production department by each department in')Import relevant Python packages, pandas process data, and streamlit is used to generate web pages, plot Express generates charts and PIL reads pictures.
Set the page name, as well as the title and subtitle in the page.
# Read data
excel_file = 'Scoring of production department by each department.xlsx'
sheet_name = 'DATA'
df = pd.read_excel(excel_file,
sheet_name=sheet_name,
usecols='B:D',
header=3)
# Here is the number of people participating in the questionnaire survey of each department
df_participants = pd.read_excel(excel_file,
sheet_name=sheet_name,
usecols='F:G',
header=3)
df_participants.dropna(inplace=True)
# Multiple selection of streamlit (option data)
department = df['department'].unique().tolist()
# Slide bar for streamlit (age data)
ages = df['Age'].unique().tolist()Read the Excel data, and get the age distribution and departments. There are five departments in total.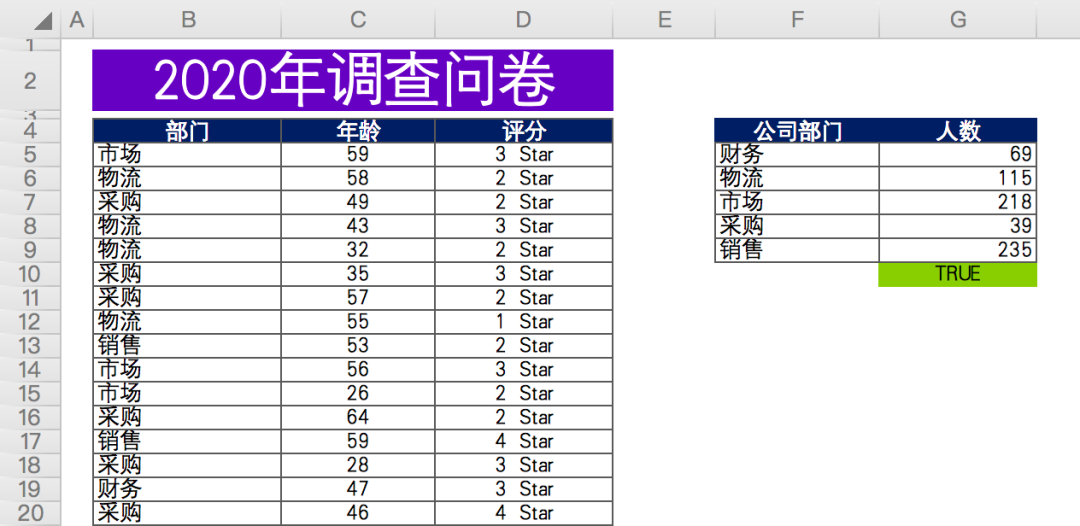
Add data options for sliders and multiple selections.
# Slider, Max, min, range
age_selection = st.slider('Age:',
min_value=min(ages),
max_value=max(ages),
value=(min(ages), max(ages)))
# Multiple selection, select all by default
department_selection = st.multiselect('department:',
department,
default=department)The results are as follows.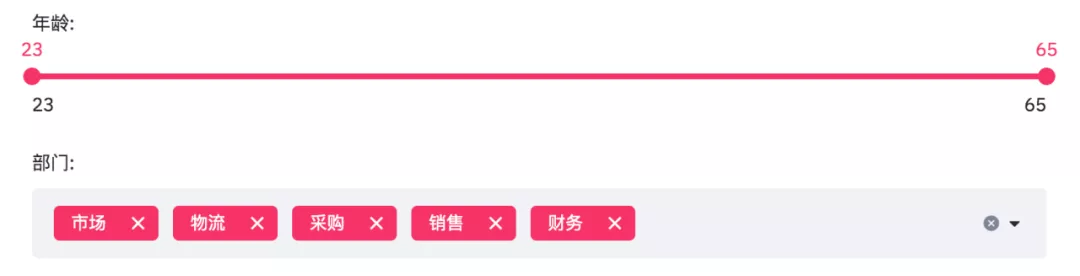
The age is from 23 to 65, and the departments are marketing, logistics, procurement, sales and finance.
Since the slider and multiple selections are variable, the final data needs to be obtained according to the filtering conditions.
# Filter data according to selection
mask = (df['Age'].between(*age_selection)) & (df['department'].isin(department_selection))
number_of_result = df[mask].shape[0]
# Get valid data according to the screening conditions
st.markdown(f'*Valid data: {number_of_result}*')
# Group data according to selection
df_grouped = df[mask].groupby(by=['score']).count()[['Age']]
df_grouped = df_grouped.rename(columns={'Age': 'count'})
df_grouped = df_grouped.reset_index()When you get the data, you can draw a histogram.
# Draw histogram and configure relevant parameters
bar_chart = px.bar(df_grouped,
x='score',
y='count',
text='count',
color_discrete_sequence=['#F63366']*len(df_grouped),
template='plotly_white')
st.plotly_chart(bar_chart)Plot the histogram using plot.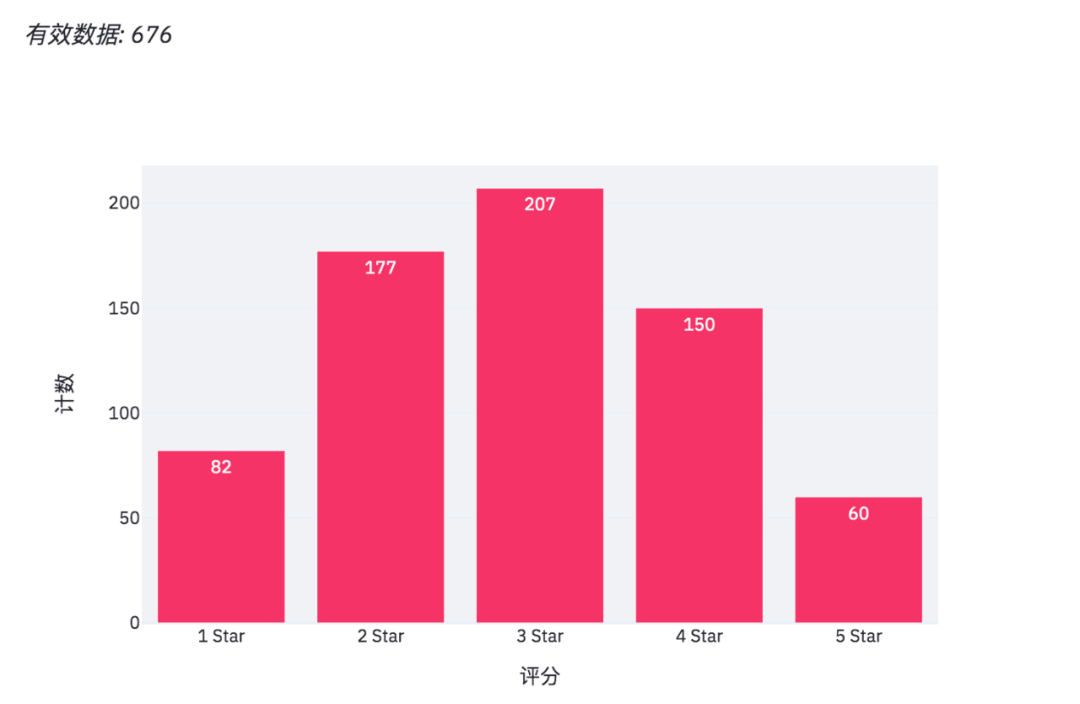
When we adjust the options on the web page, the effective data and histogram will also change.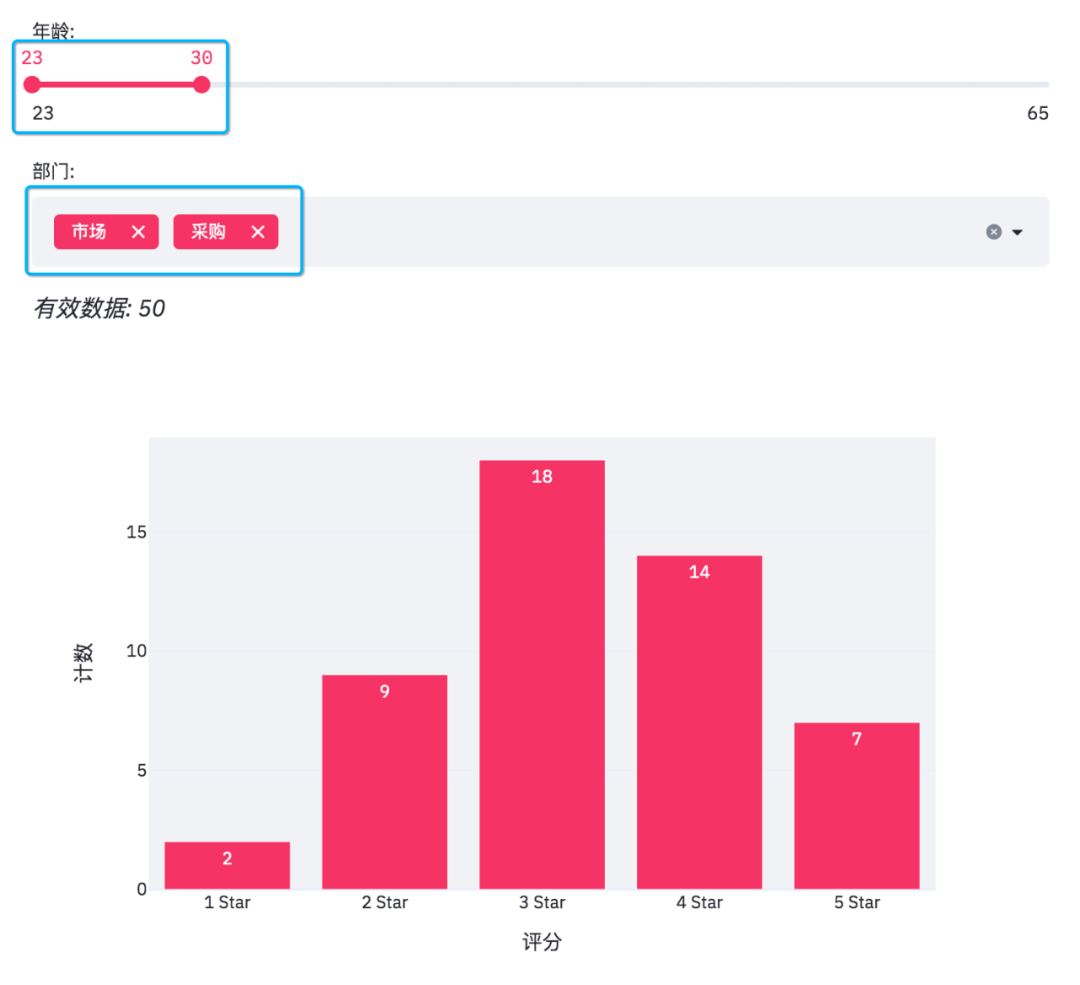
In addition, streamlit can add pictures and interactive tables to web pages.
# Add pictures and interactive tables
col1, col2 = st.beta_columns(2)
image = Image.open('survey.jpg')
col1.image(image,
caption='Designed by Small F / Farnast',
use_column_width=True)
col2.dataframe(df[mask], width=300)The results are as follows.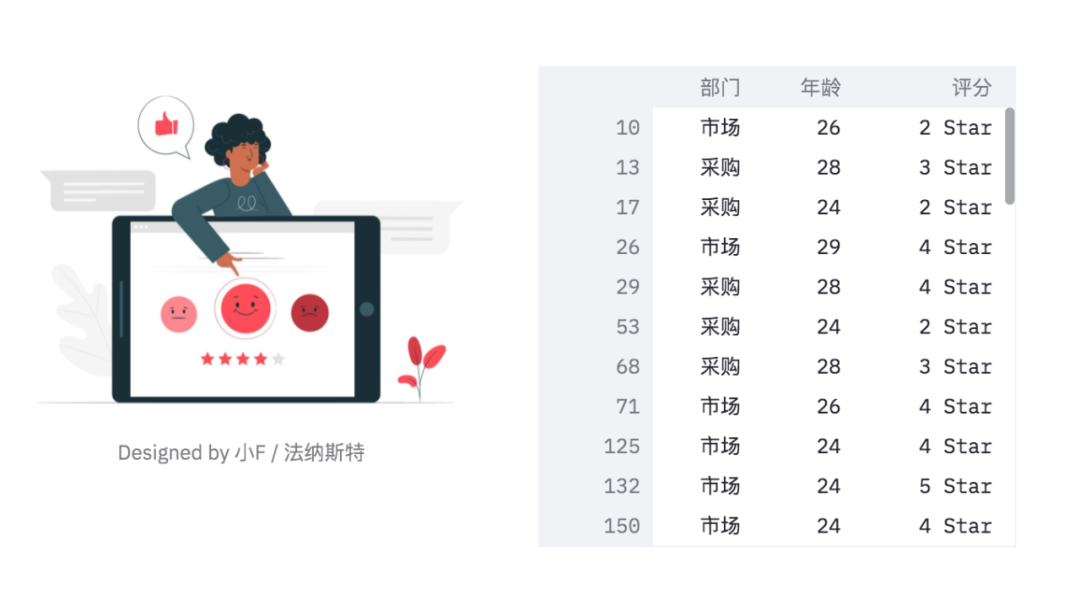
You can see that the table has a sliding bar, which can be viewed by scrolling with the mouse wheel.
Finally, draw a pie chart!
# Draw pie chart
pie_chart = px.pie(df_participants,
title='Total number of participants',
values='Number of people',
names='Company Department')
st.plotly_chart(pie_chart)The results are as follows.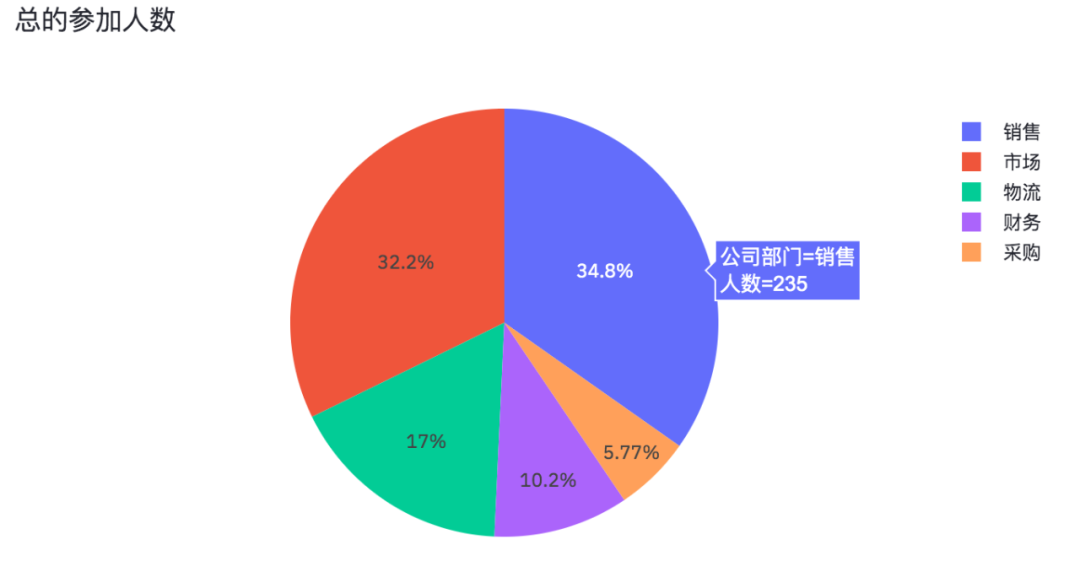
The number of people in each department participating in the questionnaire survey is also an interactive chart.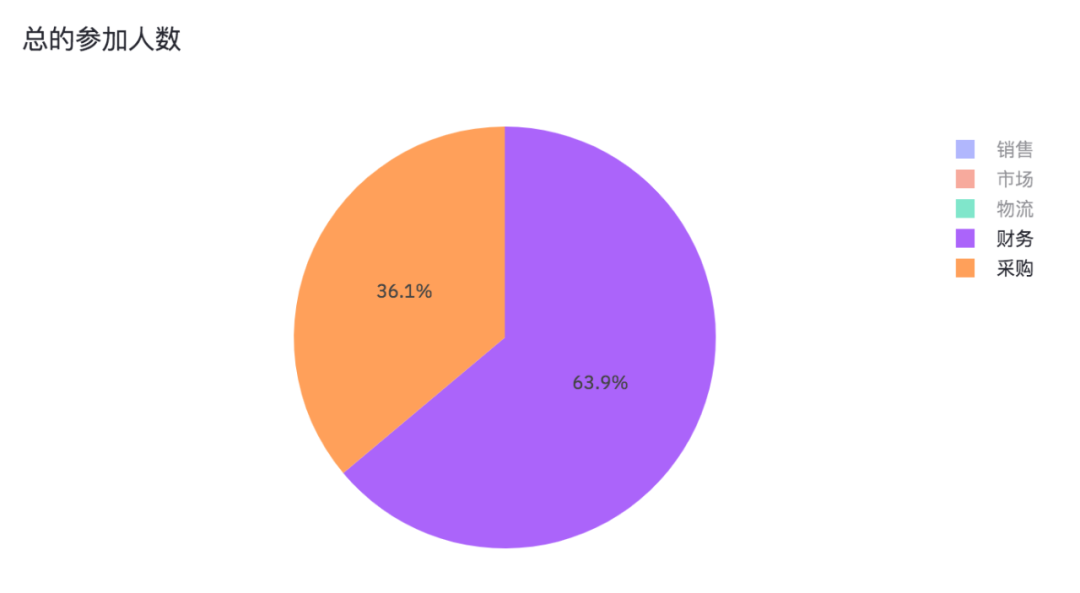
By canceling sales, marketing and logistics, we can see the proportion of financial and procurement participants in the questionnaire survey.
Well, the sharing of this issue is over. Interested partners can practice and learn by themselves.