Simple simulation of water effect (3A game effect, please bypass)
Effect: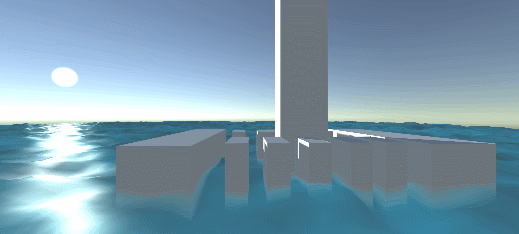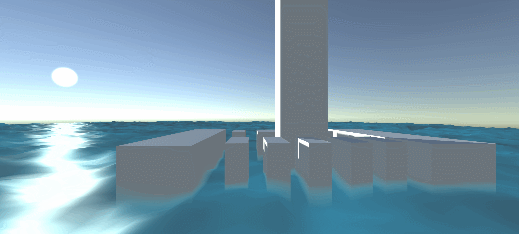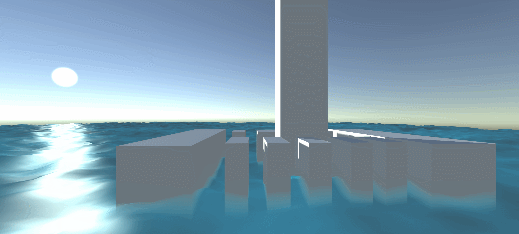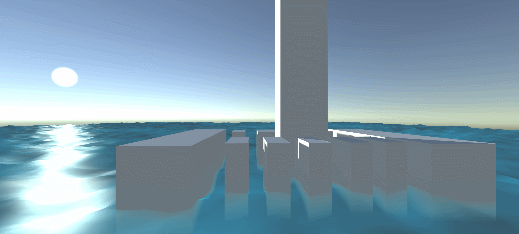
Production steps
- Prepare the water grid (generated by the grid script, refer to: Unity Shader - Noise noise map - simple mountain)
- Disturbed water grid vertex (Reference: Unity Shader - use Noise noise Noise map to generate simple mountains (use tex2Dlod to control vertex height))
- Add water mesh hue, texture
- Place marine outposts (some random cubes)
- Add water depth perspective effect
- Add water light effect
- Reconstruct the water vertex normal (Reference: Unity Shader - simple mountain - vertex shader to reconstruct normal)
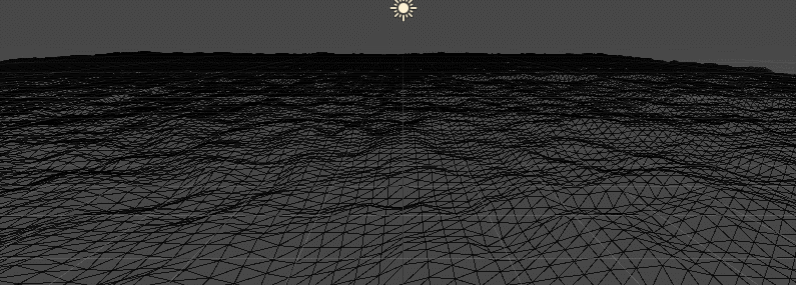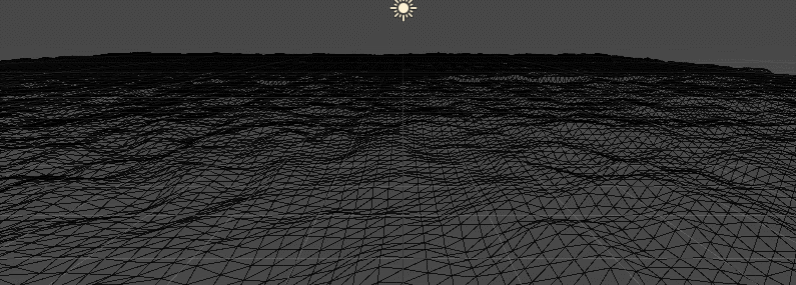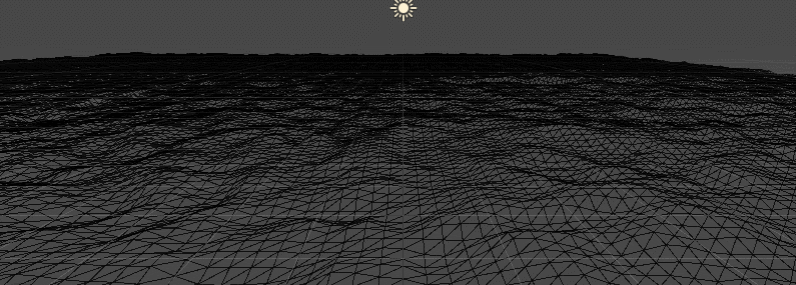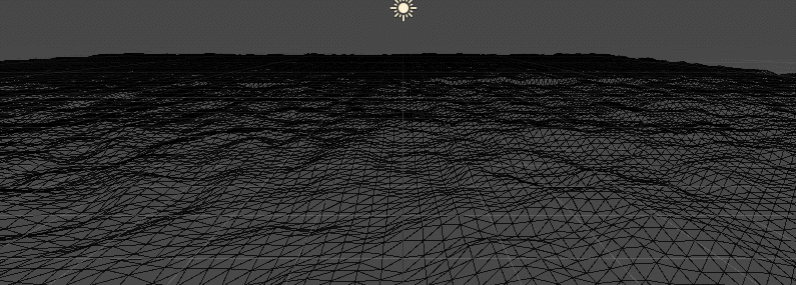
Prepare water grid
Generated by grid script, refer to: Unity Shader - Noise noise map - simple mountain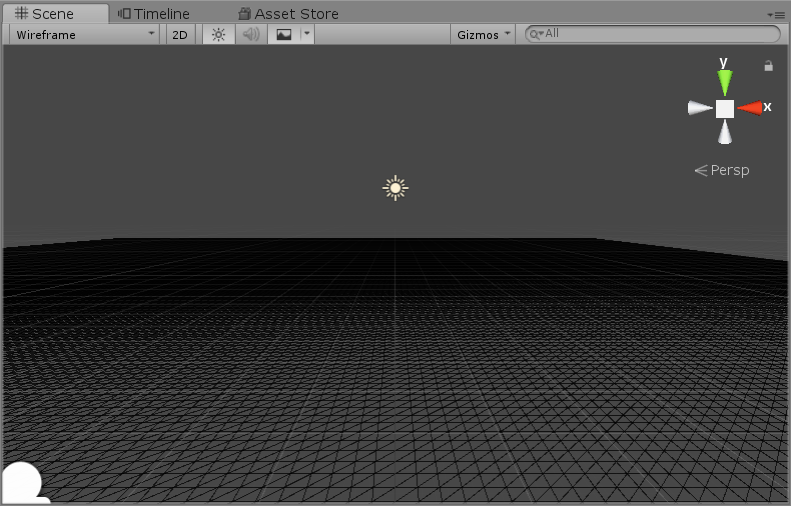
Disturbed water grid
Reference resources: Unity Shader - use Noise noise Noise map to generate simple mountains (use tex2Dlod to control vertex height)
I used: the superposition of big waves and small waves
float centerH = sin(_Time.y * _BigWaveLen + v.uv.x + v.uv.y) * _BigWaveAmplitude; centerH += tex2Dlod(_MainTex, float4(v.uv + float2(_Time.x * _SmallWaveSpeedX, _Time.x * _SmallWaveSpeedY), 0, 0)).r * _SmallWaveAmplitude; v.vertex.y = centerH;
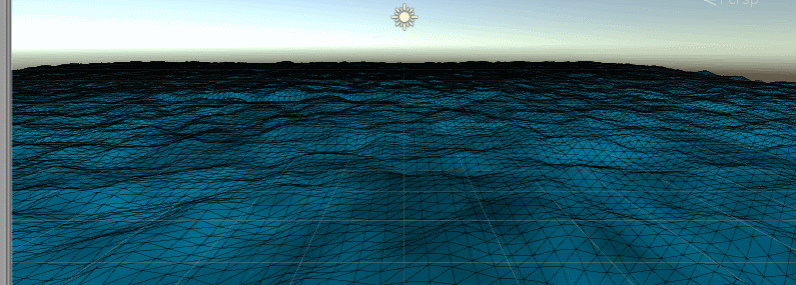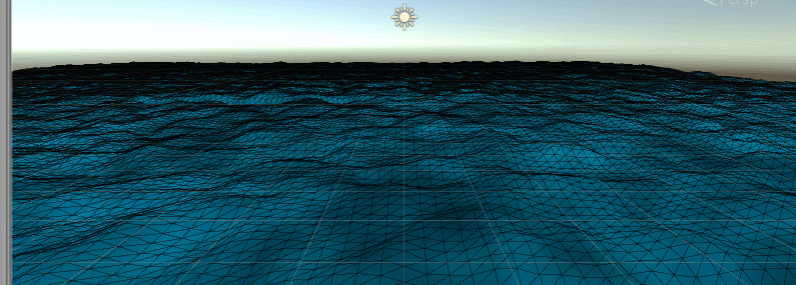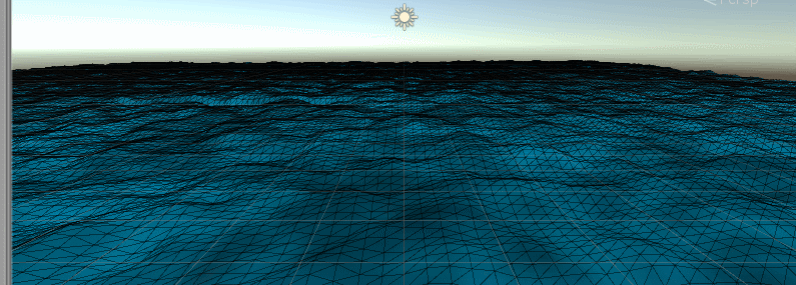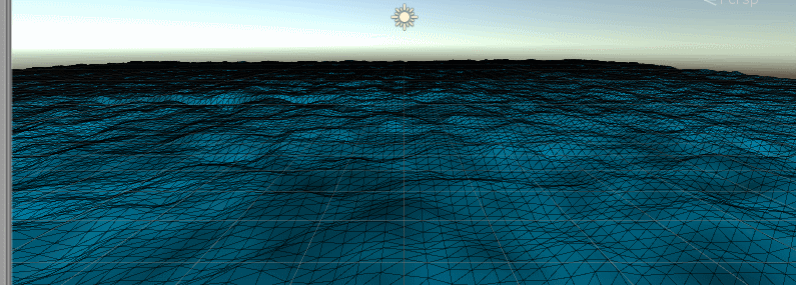
Add water mesh hue, texture
Got a tone and scrolled through the uv animation
fixed4 col = tex2D(_MainTex, i.uv + float2(_Time.y * _BigWaveLen * _UVSpeed, 0)); col.rgb *= _MainColor.rgb;
Place marine outposts (some random cubes)
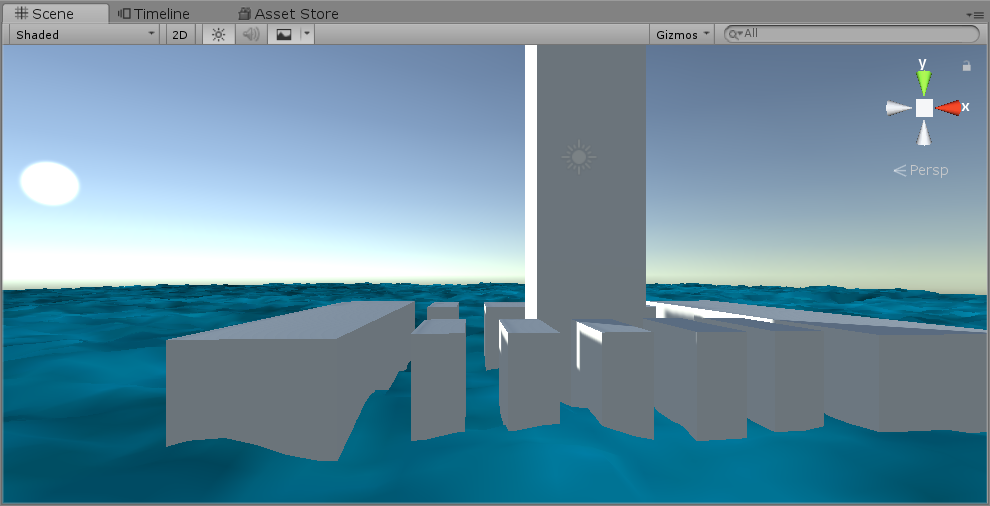
Add water depth perspective effect
This refers to the idea of handling soft particles in unit's built-in shader:
- buffViewZ of view space to get depth texture
- Get fragViewZ of view space of current clip
- The depth of delta = buffViewZ - fragViewZ is interpolated to control the alpha perspective of the water body
// vert #if DEEP_EFF o.projPos = ComputeScreenPos (o.pos); COMPUTE_EYEDEPTH(o.projPos.z); #endif // frag #if DEEP_EFF // Depth effect // Depth effect // Here refer to the built-in shader of unit to realize the soft example: the writing method of Soft particle // When the depth is far away from the background, the alpha is higher, while the alpha near the background is lower // First, get the z value under the view space of the depth map: buffViewZ float buffViewZ = LinearEyeD,epth (SAMPLE_DEPTH_TEXTURE_PROJ(_CameraDepthTexture, UNITY_PROJ_COORD(i.projPos))); // Then get the z value of the view space of the fragment: fragViewZ float fragViewZ = i.projPos.z; // Then go to the distance between them and control the alpha, and change the color lerp float fade = saturate ((buffViewZ-fragViewZ) * _DeepFactor); combined.rgb = lerp(combined.rgb + _ShallowColor.rgb * (_ShallowColor.a * 2), combined.rgb, fade); combined.a *= fade; #endif
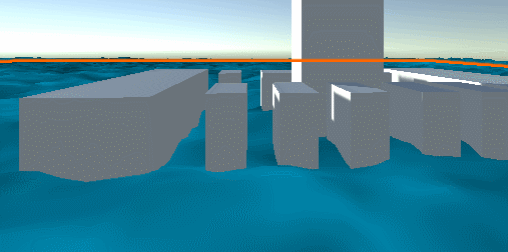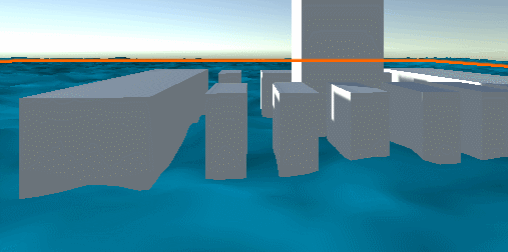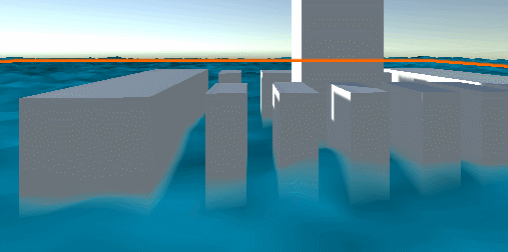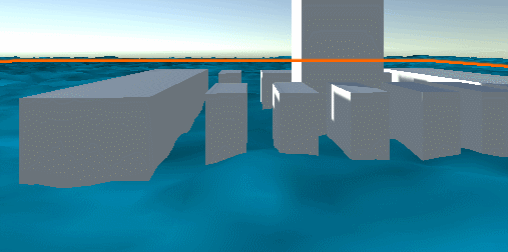
Add water light effect
This is the traditional empirical lighting model: ambient + diffuse (half Lambert) + special (Blinn Phong)
// frag #if LIGHTING_ON // Illumination effect // ambient fixed3 ambient = UNITY_LIGHTMODEL_AMBIENT.rgb; // diffuse half3 L = normalize(_WorldSpaceLightPos0.xyz); half3 N = normalize(i.normal); half LdotN = dot(L, N) * 0.5 + 0.5; fixed3 diffuse = col.rgb * LdotN; // specular half3 specular = 0; half3 V = normalize(_WorldSpaceCameraPos.xyz - i.wPos); half3 H = normalize(L + V); half HdotN = max(0, dot(H, N)); // blinn-phone specular = _LightColor0.rgb * pow(HdotN, _SpecularGlossy * 100) * _SpecularIntensity; // combined color fixed4 combined = fixed4(ambient + diffuse + specular, col.a); #else // LIGHTING_OFF fixed4 combined = col; #endif
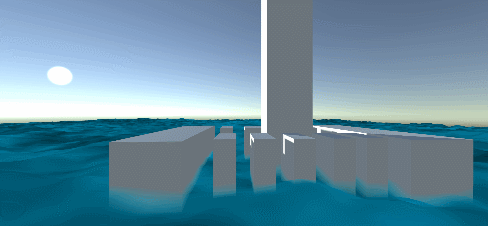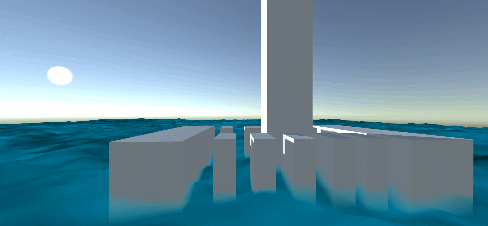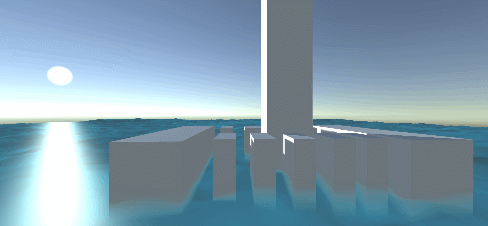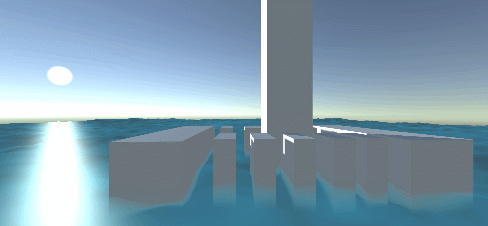
Reconstruction of water vertex normal
Reference resources: Unity Shader - simple mountain - vertex shader to reconstruct normal I won't say it here. The reference article is very clear.
#if REBUILD_NORMAL // Refactoring normal, reference: https://blog.csdn.net/linjf520/article/details/104859710 // reconstruct normals // This 4x4 data can also be passed in externally, which can save the computation of the vertex shader ALU and L1 caches. const float4x4 offset_xz = { {+1,+0, /* gap **/ +1,-1}, // lower right {+0,-1, /* gap **/ -1,-1}, // Left lower {-1,+0, /* gap **/ -1,+1}, // Left upper {+0,+1, /* gap **/ +1,+1} // Right upper }; // The default vector can also be passed in externally, because the default normal above can be adjusted // Now I'll say that the default normals are initialized to: up float3 sumNormal = float3(0, 1, 0); float4 uv4 = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { // Get offset data float4 uvs_offset = offset_xz[i]; // Get the height of offset data half h1 = sin(_Time.y * _BigWaveLen + v.uv.x + uvs_offset.x * _MainTex_TexelSize.x + v.uv.y + uvs_offset.y * _MainTex_TexelSize.y) * _BigWaveAmplitude; uv4 = float4(v.uv + uvs_offset.xy * _MainTex_TexelSize.xy + float2(_Time.x * _SmallWaveSpeedX, _Time.x * _SmallWaveSpeedY), 0, 0); h1 += tex2Dlod(_MainTex, uv4).r * _SmallWaveAmplitude; half h2 = sin(_Time.y * _BigWaveLen + v.uv.x + uvs_offset.z * _MainTex_TexelSize.x + v.uv.y + uvs_offset.w * _MainTex_TexelSize.y) * _BigWaveAmplitude; uv4 = float4(v.uv + uvs_offset.zw * _MainTex_TexelSize.xy + float2(_Time.x * _SmallWaveSpeedX, _Time.x * _SmallWaveSpeedY), 0, 0); h2 += tex2Dlod(_MainTex, uv4).r * _SmallWaveAmplitude; // According to the offset direction, the two vectors of height from the current vertex to the nearby offset point are reconstructed float3 dir1 = float3(uvs_offset.x * _GridGap, h1 - centerH, uvs_offset.y * _GridGap); float3 dir2 = float3(uvs_offset.z * _GridGap, h2 - centerH, uvs_offset.w * _GridGap); // According to two vectors of the plane (two vectors can determine a plane, such as two tangent vectors of TB in TBN) // The normal vector of a plane is obtained by cross multiplication float3 newNormal = (cross(dir1, dir2)); // Add to blend vector sumNormal += newNormal; } // Mean mixing sumNormal /= 5; o.normal = UnityObjectToWorldNormal(sumNormal); #else // REBUILD_NORMAL off o.normal = UnityObjectToWorldNormal(v.normal); #endif
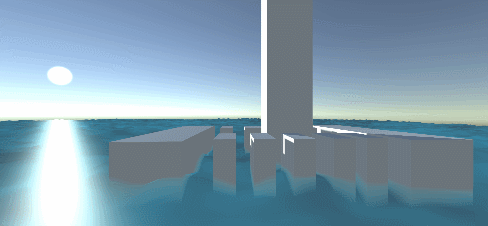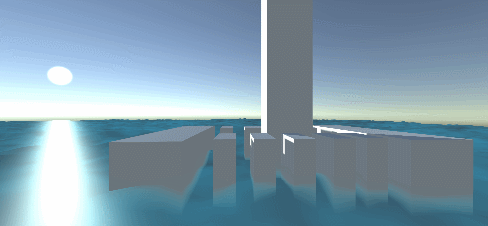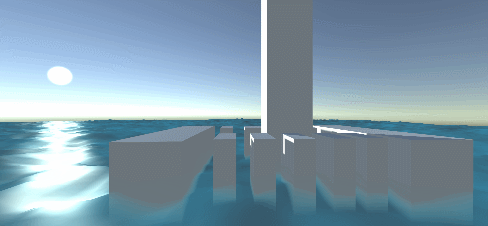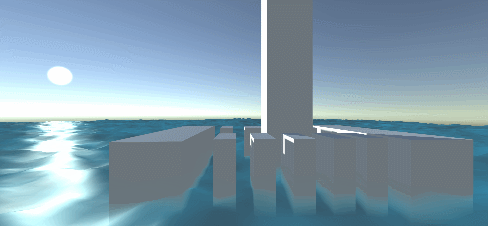
Project
backup : UnityShader_SimpleWater_ShallowToDeepEffect_2018.3.0f2
References
- Simple Water Shader in Unity
- Generated by grid script, refer to: Unity Shader - Noise noise map - simple mountain.
- Disturbed water grid vertex, reference: Unity Shader - use Noise noise Noise map to generate simple mountains (use tex2Dlod to control vertex height).
- Reconstruction of water vertex normal, refer to: Unity Shader - simple mountain - vertex shader to reconstruct normal.

