preface
Some interfaces in the project will be slow when calling the third party, and repeated requests will occur in a short time
There are also users who submit data many times in a short time
There will be concurrency conflicts, which can be intercepted at the front end
At present, I have summarized two methods:
The first scheme: add loading waiting on the submit confirmation button
The second scheme: repeat submission and interception in the axios request for a unified interface
The following describes how to use the two cases
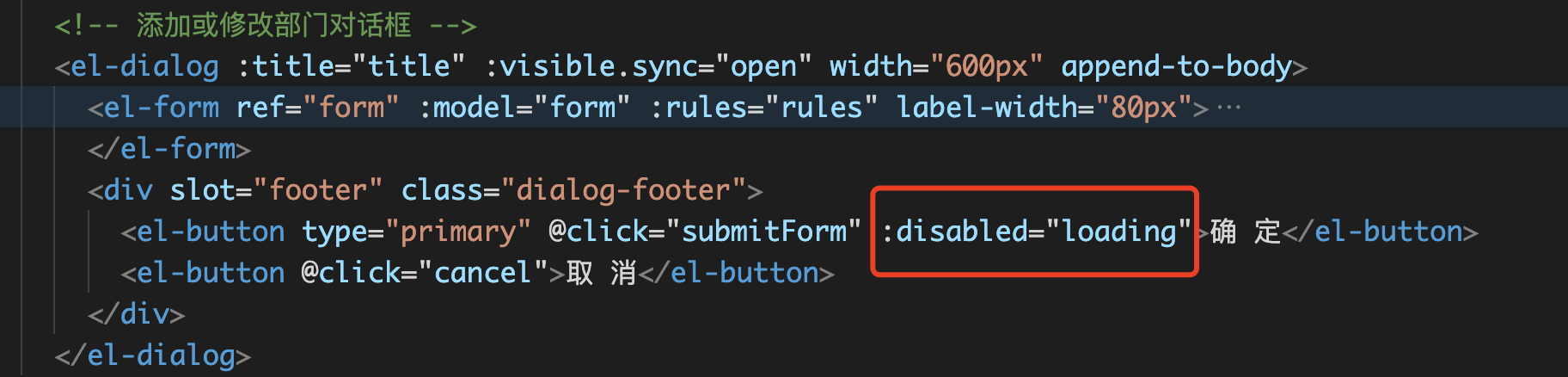
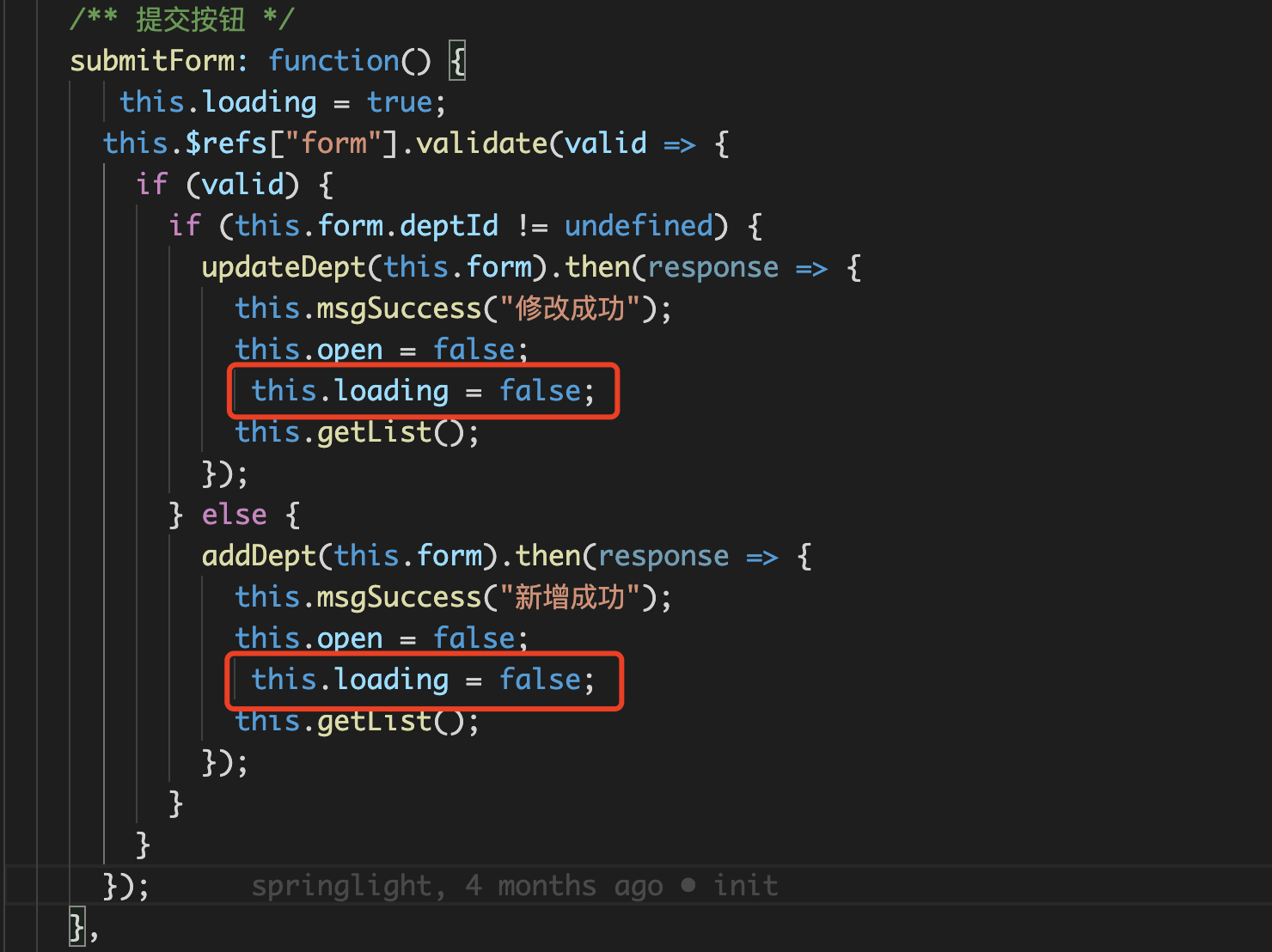
Add loading wait on the submit confirmation button
This method is relatively simple. It mainly refers to the usual coding habits When a vue page requests an interface, it adds loading:true before the request. After the interface call is successful, it will load: false. This is also a relatively simple and rough solution. It can be described as a white cat and a black cat. Catching a mouse is a good cat

Practical application in the project:
axios requests to add unified interception
There are many cases of concurrency in the project. When our project achieves a certain degree, it is obviously not the best solution to solve the concurrency problem by adding loading above
Every request of the interface will be concurrent. If axios in our project is uniformly encapsulated for the second time, we can add request interception at the place of unified request and automatically process repeated requests, which also greatly optimizes our business code
When axios sends http requests, the official has two core API s for intercepting requests:
1.interceptors
n. Interceptor ship, [aviation] [military] interceptor; Interceptor; Interceptor (plural of interceptor)
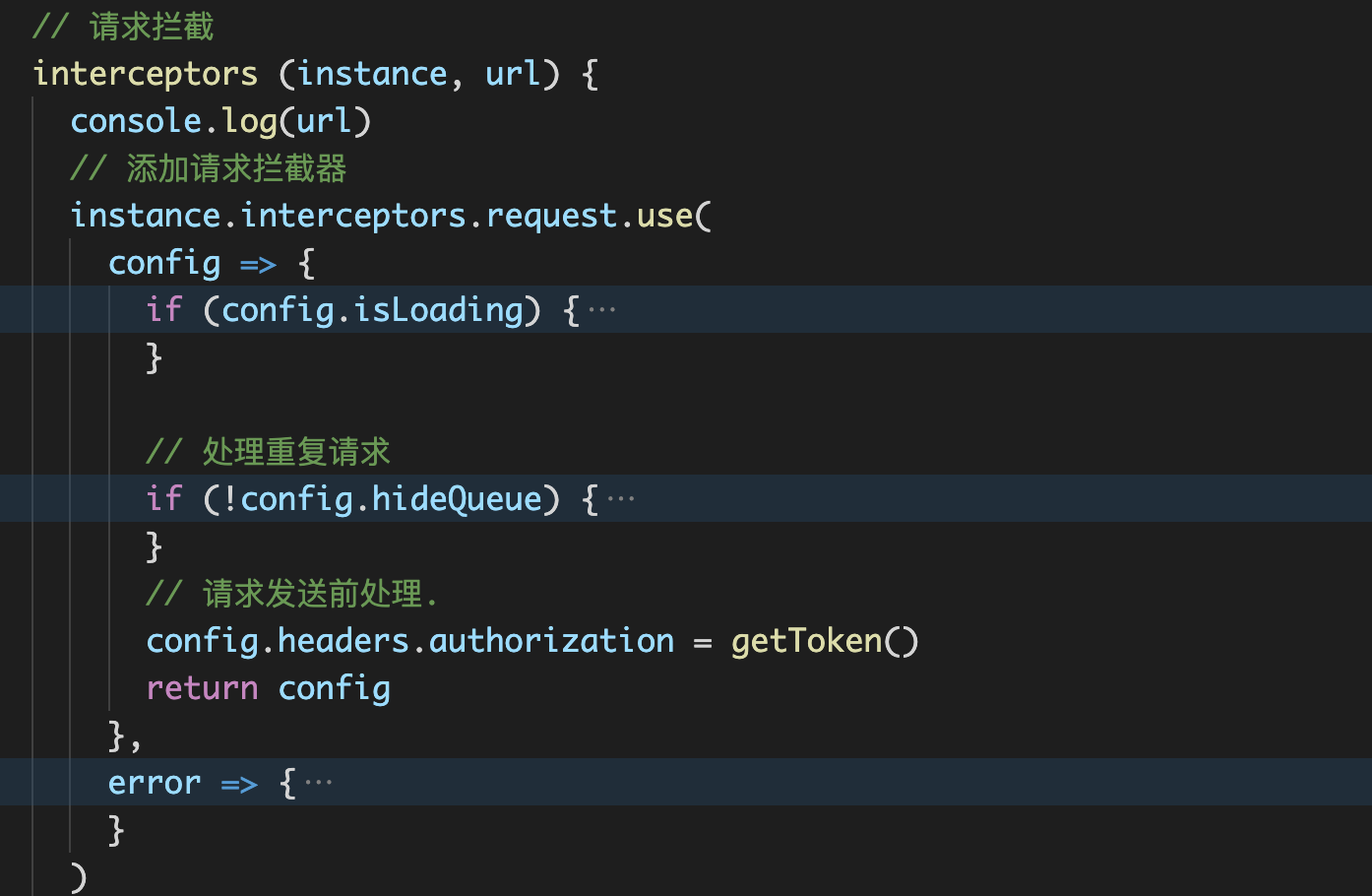
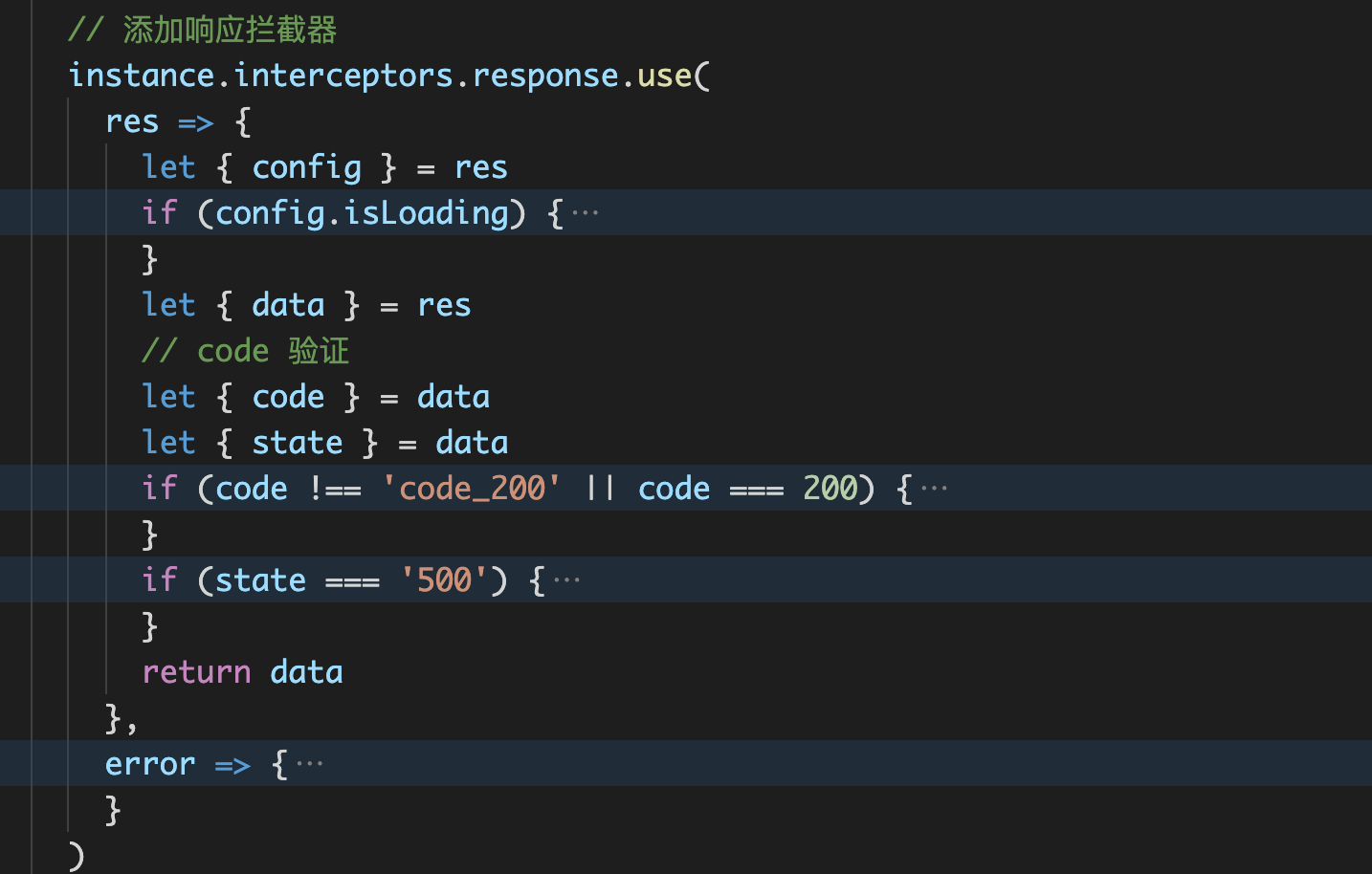
There are two kinds of interceptors (request interception and corresponding interception). We can handle them in these two places
Practical application in the project:
2.cancel token:
Call the cancel token API to cancel the request. The official website provides two ways to build a # cancel token. We use this method: create a # cancel token by passing a # executor # function to the constructor of # CancelToken, so that duplicate requests can be detected in the above request interceptor and executed immediately:
let cancel
config.cancelToken = new axios.CancelToken(function (c) {
cancel = c
})All codes of the request
import axios from 'axios'
import { getToken } from '_utils/token'
export default class httpRequest {
constructor (baseUrl = '') {
this.baseUrl = baseUrl
// Storage request queue
this.queue = []
}
getInsideConfig () {
const config = {
baseURL: this.baseUrl,
// Request timeout
timeout: 10 * 1000,
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json; charset=utf-8',
'X-URL-PATH': location.pathname
},
}
return config
}
// Make configuration modification for special configuration requirements - you can add configuration for special interfaces
changeConfig (options) {
let tempOptions = options
return tempOptions
}
// Destroy request instance
destroy (config) {
let matchIndex = findMatchIndex(this.queue, config)
if (matchIndex !== -1) {
this.queue.splice(matchIndex, 1) //After the interface request succeeds, it is deleted from the array of the request queue
}
LoadingBar.finish()
store.dict.state.loading = false
}
// Intercept request
interceptors (instance, url, method) {
// Add request interceptor
instance.interceptors.request.use(
config => {
if (config.isLoading) {
// Here you can add global loading You can add the state of the interface to the store for global use
}
// Process duplicate requests
let cancel
config.cancelToken = new axios.CancelToken(function (c) {
cancel = c
})
let matchIndex = findMatchIndex(this.queue, config)
if (matchIndex !== -1) {
Notice.error({
title: 'Tips',
desc: 'Please do not submit again'
})
cancel('Request interrupt')
} else {
//When it is judged that the interface does not have repeated requests, the interface is added to the request queue
this.queue.push({
url: config.url,
method: config.method,
params: config.params
})
}
// Processing before sending a request
config.headers.authorization = getToken()
return config
},
error => {
// Request error handling
return Promise.reject(error)
}
)
// Add response interceptor
instance.interceptors.response.use(
res => {
let { config } = res
if (config.isLoading) {
// Destroy request instance after request response
this.destroy(config)
}
let { data } = res
// code verification
let { code } = data
let { state } = data
if (code === 200) {
// No permission
if (code === 'code_400') {
return Promise.reject(data)
}
// Error 401 invalid token delete token return to authentication center (login page)
if (code === 401) {
logoff()
// Other error handling
}
if (code === 'code_500') {
return Promise.reject(data)
}
if (code === 'code_406') { //Incorrect request parameters!
return Promise.reject(data)
}
}
if (state === '500') { //Server error
}
return data
},
error => {
LoadingBar.error()
// Response error handling
return Promise.reject(error)
}
)
}
request (options) {
const instance = axios.create()
// Merge options
options = this.changeConfig(Object.assign(this.getInsideConfig(), options))
// Register interceptor
this.interceptors(instance, options.url, options.method)
// Return instance
return instance(options)
}
}
function findMatchIndex (map, config) {
return map.findIndex(item => {
if (
config.url.includes(item.url) &&
item.method === config.method &&
diff(item.params, config.params)
) {
}
return (
config.url.includes(item.url) &&
item.method === config.method &&
diff(item.params, config.params)
)
})
}
function diff (obj1, obj2) {
if (Object.keys(obj1).length !== Object.keys(obj2).length) {
return false
}
let obj1Keys = Object.keys(obj1)
for (let i = 0; i < obj1Keys.length; i++) {
if (obj1[obj1Keys[i]] !== obj2[obj1Keys[i]]) {
return false
}
}
return true
}
summary
Concurrent requests are quite common. Interface requests are processed uniformly. However, in a specific business, the interface that takes a long time to request an interface still needs to control the button when submitting data through the global loading state. Loading or disabling is added to the button, which is treated according to its own business